Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Biologyaplus - Smskb.edu - My - WP Content - Uploads - 2011 - 11 - 2 2mark Scheme P2 FRM 4 SBP 2011 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Ismaliza IshakOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Biologyaplus - Smskb.edu - My - WP Content - Uploads - 2011 - 11 - 2 2mark Scheme P2 FRM 4 SBP 2011 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Ismaliza IshakCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
2
SULIT
Question 1
No
Mark scheme
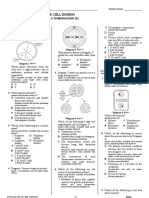
1(a)(i) Able to name structure labeled O and Q.
4551/2
Sub
Mark
1+1
Answer :
R : Mitocondria
Q : Golgi apparatus / body
(a)(ii)
Total
Mark
Able to state the function of structure R and P.
1+1
Sample answer :
R : to generate/ produce/ release energy
(b)(i)
Reject: provide
P : to trap sunlight // to carry out photosynthesis
Reject: absorb
Able to state the main component of M.
1
Answer :
Cellulose
(ii)
Able to explain one characteristic of M.
Sample answer
F1 : Permeable
E1 : has tiny pores
E2 : to allow substances to move freely into and out of the
cell
F2: Rigid/though/
E3: give shape to plant cell
E4: to provide mechanical support to plant cell
E5: to protect the plant cell from rupturing
1+1
F with any correspond E
(c)(i)
Able to explain the condition of the structure N in distilled
water.
Sample answer
F : Vacuole expand / swell up.
1+1+1+1
E1 : Distilled water is hypotonic to the cell (sap) // Cell
(sap) is hypertonic to distilled water // the
concentration of solute in distilled water is lower than
concentration of solute in the cell (sap)
E2 : Water (molecules) diffuse into the cell
E3: by osmosis
3
Any three
4551/2 2011 Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama Penuh
Peraturan pemarkahan
SULIT
4551/2
No
Mark scheme
(ii)
Able to draw a labeled diagram of the condition of vacuole
Sub
Mark
1+1
Total
Mark
Sample answer
D- The shape of the cell rectangular.
The cell wall is drawn with double line
The vacuole must be large/enlarge
L - Label vacuole // cell wall
Cell wall
Accept any correct shape of plant cell
TOTAL
4551/2 2011 Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama Penuh
2
12
Peraturan pemarkahan
SULIT
4551/2
Question 2
No
Mark scheme
Sub
Mark
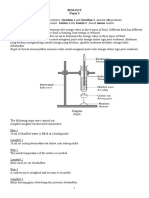
2(a)(i) Able to name respiratory system shown in Diagram 2.1
Answer:
Tracheal System
(ii)
Total
Mark
Able to state a difference between the respiratory system
of organism X and organism Y.
Sample answer :
Organism X
Organisma X
Organism Y
Organisma Y
Oxygen diffuses directly
into the body tissue
oxygen diffuses directly
into the blood capillaries
Gaseous exchange directly
into tissues
gaseous exchange occur
at specific organ/ lung
Any one
(b)(i)
Able to name structure P and Q.
1+1
Sample answer
P : trachea
Q : bronchus
2
(b)(ii)
Able to state the common characteristic
Sample answer :
Both have (tracheal) ring/ any explanation
b(iii)
Able to explain why the characteristic is important
1+1
Sample answer :
F : To prevent deflation/ air passage collapsing
E 1: atmospheric pressure is higher than the pressure
inside the trachea
E2: both ring is to strengthen air tube.
Any two
4551/2 2011 Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama Penuh
2
Peraturan pemarkahan
SULIT
No
(c)(i)
4551/2
Mark scheme
Sub
Mark
Able to state one characteristics that they have in common
to increase the efficiency of gases exchange.
Total
Mark
Sample answer :
P1 : Has large surface area/ higher TSA
P2: One cell thick
P3 : Moist ( surface)
Any one
(c)(ii)
Able to explain the importance of gas exchange in both
organisms.
1+1
Sample answer :
P1: To supply oxygen for cellular respiration
P2 : oxidized glucose to produce energy
P3 :To excrete carbon dioxide produced by cells
Any two
(d)
Able to explain how smoking habit affect the intake of
oxygen intake of oxygen efficiency in human.
2
1+1
Sample answer :
F1 : less oxygen combine with haemoglobin.
E1: Carbon monoxide can bind with haemoglobin
E2 : to form carboxyhaemoglobin
F2 : reduce diffusion of oxygen
E3 : tobacco tar will be deposited/ logged/ accumulated
(inside the lungs) // thick // explanation
F3 : Oxygen cannot be dissolved
E4 : Heat from the smoke
E5 : Dry the surface of the alveoli
Any F with correspond E
TOTAL
4551/2 2011 Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama Penuh
12
Peraturan pemarkahan
SULIT
4551/2
Question 3
No
(a)
Mark scheme
Sub
Mark
1+1+1
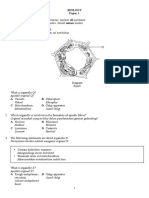
Able to name the organelles X, Y and Z.
Answer :
X : Golgi apparatus
Y : rough endoplasmic reticulum
Z : secretory vesicle
(b)
Able to state two types of nucleic acid inside the nucleus that
provide the information to synthesize the protein.
1+1
Answer:
1. DNA //deoxyribonucleic acid
2. RNA // ribonucleic acid
(c)(i)
Able to state the type of structure shown.
Answer :
Quarternary (structure)
(ii)
Able to name one example of the structure.
Sample answer :
Heamoglobin
(iii)
Able to describe the structure of molecule P
1+1
Sample answer :
P1 : complex (protein) molecule
P2 : combination of two /more tertiary structure (of polypeptide
chain)
P3 : form large protein molecule
Any two
(d)
Total
Mark
Reject
RER
Able to explain how damage to the chromosome structure by
radioactive rays can disrupt the synthesis of the extracellular
enzyme
2
1+ 1 +
1
Sample answer:
F : mutation occur
E1 : genetic code/ information / gene of DNA
E2 : destroyed / change /
E3 : cannot synthesise the enzyme / amylase / lipase / protease /
any suitable enzyme.
E4 : organism cannot digest food // rate of metabolism become lower
// organism die.
4551/2 2011 Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama Penuh
Peraturan pemarkahan
SULIT
4551/2
Any three
TOTAL
12
Question 4
No
(a)(i)
Mark scheme
Able to state type of cell division in cell P and cell Q.
Sub
Mark
1+1
Answer :
Cell P : mitosis / mitotic
Cell Q : Meiosis
(ii)
Total
Mark
State one importance of the cell division in cell P and cell
1+1
Q.
Sample answer :
Cell p : to increase number of cell // to replace damage /
dead cell // for asexual reproduction / culture tissue / cloning
// to produce new cell // to maintain diploid number of
chromosome.
Cell Q : to produce variation / gametes // to maintain the
chromosomal number of offspring // to ensure haploid
number in gametes.
(b)(i)
Able to state one difference between chromosomal
behavior at the stage in cell P and cell Q .
Sample answer :
Stage in cell P
Chromosome / sister
chromatid align at
metaphase plate / equator
2
1
Stage in cell Q
Homologous chromosome
align at metaphase plate /
equator.
1
(ii)
No
Able to explain one importance of the chromosomal
behaviour in cell P.
Sample answer :
F : to ensure equal distribution of chromosome in daughter
cell.
E : to prevent daughter cell have an abnormal number of
chromosome. // any explanation.
Mark scheme
4551/2 2011 Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama Penuh
1+1
2
Sub
Total
Peraturan pemarkahan
SULIT
(c)(i)
4551/2
Mark
1
Able to Name the organism produced from scientific
technique
Mark
Sample answer :
Transgenic plant / organism
(ii)
Able to describe how the technique is carried out.
1+1+1
Sample answer :
P1: shoot/ root/ leaf
P2: wash/ sterilize with satirizing agent/ bleaching agent/
hydrogen peroxide
P3: tissue/ explants is cultured in sterilize nutrient medium,
with suitable temperature and pH value.
P4: cell divide to form callus,
P5: small pieces of callus than is cultured in nutrient
medium
P6: callus differentiate to form root/ shoot seedling/ clone
Any 3
12
TOTAL
Question 5
No
(a)(i)
Mark scheme
Able to name P reaction and molecule R.
Sub
Mark
1+1
Sample answer :
P reaction : dark reaction
Molecule R : Starch
(ii)
Able to name two raw materials for photosynthesis
2
1+1
Sample answer :
1. Carbon dioxide
2. water
(b)(i)
Able to explain the importance of sunlight energy
during light reaction.
Total
Mark
2
1+ 1
Sample answer :
F1 : photolysis (of water)
E1 : split water into hydrogen ion and hydroxyl ion
F2 : to excite electron from chlorophyll
4551/2 2011 Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama Penuh
Peraturan pemarkahan
SULIT
4551/2
Reject : Chloroplast
(ii)
E2 : to produce ATP
E3: electron combine with hydrogen ion to produce
atom Q / hydrogen atom
Any F with correspond E
Able to describe how oxygen and water are produced
1+1
during photosynthesis.
Sample answer :
P1 : hydroxyl ion loses an electron
P2 : to form hydroxyl group
P3 : electron is received by chloropyll
P4 : the hydroxyl group combine each other to form
water and oxygen
Any two
(c)
Able to explain the role of atom Q during P reaction.
2
1+1
Sample answer :
F : atom Q is hydrogen atom
E1 : fix / reduce carbon dioxide
E2 : to form (CHO)n / basic unit of glucose/ 6 carbon
molecule.
Any two
(d)
Explain how air pollution have an effect on rate of
photosynthesis .
Sample answer :
F : rate of photosynthesis decreases / low
E1 : pollutant / dust / particle / any suitable example
cover the surface of the leaf.
E2 : reduce light intensity (received by chloroplast)
E3 : lodge / cover the stoma/ reduce gases
exchange/ carbon dioxide
Any two
TOTAL
4551/2 2011 Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama Penuh
2
1+1
12
Peraturan pemarkahan
10
SULIT
4551/2
Question 6
No
(a)
Mark scheme
Sub
Mark
Able to explain the process shown in Diagram 6.1
Total
Mark
Max 4
Sample answer :
P1 : the process is diffusion.
P2 : molecule of sugar move randomly
P3 : against concentration gradient // from higher
concentration region towards lower concentration
region.
P4 : concentration of sugar is higher at the bottom of
the beaker
P5 : (diffusion process continues until) the sugar
molecule are evenly dispersed
P6 : reach a dynamic equilibrium (at the end of the
experiment.)
Any four
(b)
Able to explain the similarities and differences between
the movement of molecule across plasma membrane
in type 1 and type 2.
4
Max 2
Sample answer :
Similarities
S1 : Both need protein
E1 : Both transport specific molecules only
E2 : Both processes occur in living cell
Any two
Differences :
Type 2
Facilitated diffusion
D1 Down the
concentration gradient
E1
Molecule moves from
higher concentration
region to lower
concentration region
D2 Molecules move in
both direction across
the plasma membrane
2
Max 4
Type 1
Active transport
Against the
concentration gradient
Molecule moves from
lower concentration
region to higher
concentration region
Molecules move in
one direction across
the plasma membrane
4551/2 2011 Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama Penuh
Peraturan pemarkahan
11
SULIT
E2
Molecule move
through pore proteins
4551/2
Molecule can move
through carrier
proteins
D3 No energy used
Energy is used
E3
Energy is needed for
binding / bind with
active site
Molecule can move
through (pore) protein
without binding
D4 Molecule need pore
protein to help the
movement
Need carrier protein
only to help the
movement
D5 Could achieve
equilibrium
Results in
accumulation /
elimination
D6 Not affected by
inhibitors
Inhibited by inhibitor
E6
Depended on cellular
respiration
Not depended on
cellular respiration
Any 4
(c)
Able to explain what happens to the cell in each
diagram.
Sample answer :
(in Diagram 6.3)
Max 3
F : cell under normal condition / protoplasm in normal
shape
P1 : solution is isotonic to the (plant) cell (sap)
P2 : there is a balanced diffusion of water molecules in
and out // water molecules entering the cell is
equivalent to water molecule leaving the cell
P3 : by osmosis
Any three
( in solution Y)
Max 4
F : Cell plasmolyses / undergoes plasmolysis //
becomes flaccid
P1 : because solution Y is hypertonic to (sap) cell
P2 : water molecule diffuse out from the cell
4551/2 2011 Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama Penuh
Peraturan pemarkahan
12
SULIT
4551/2
P3 : by osmosis
P4: cytoplasm shrinks // cell membrane moves away
from the cell wall.
Any four
( in solution X)
Max 3
F : cell become turgid
P1 : solution Y is hypotonic to the (sap) cell
P2 : water molecule diffuse into plant cell
P3 : by osmosis.
Any three
TOTAL
20
Question 7
No
(a)(i)
Mark scheme
Able to describe the succession process in zone 1 and
zone 2
Sub
Mark
Max 4
Total
Mark
Sample answer :
P1 : Pneumatophore of pioneer sp / Avicennia sp /
Sonneratia sp traps/ collect muds / organic
substances/ sediments
P2 : Increase the thickness of the soil / land become
higher
P3 : (As time pass by )the soil becomes more dense/
compact / firm / drier
P4 : The condition favours the growth of Rhizophora
sp.
P5 : The Rhizophora sp. replaces the pioneer species.
Any four
(ii)
Able to explain the problems faced by mangrove trees
and how they overcome these problems.
4
Max 6
Sample answer :
(P) Problem faced by
mangrove
Soft muddy soil, the
P1 plant collapse
How to overcome//
adaptation
have long /
E1 branched cable /
prop roots to
support / anchor
the plants to the
4551/2 2011 Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama Penuh
Peraturan pemarkahan
13
SULIT
4551/2
muddy soil.
P2
P3
P4
P5
Waterlogged
conditions of the soil
decrease the
amount of oxygen
has breathing
E2 roots /
pneumatophores
to absorb oxygen
from atmosphere
//
pneumatophores
have pores /
lenticels exchange
gases takes placed
Direct exposure to
the sun leads to a
high rate of
transpiration
A thick layer of
E3 cuticle covers the
leaves to reduce
(rate of )
transpiration
//
The leaves are
thick and succulent
to store water.
The cell sap of the
E4 roots cells has a
higher osmotic
pressure than the
soil water that
surrounds them to
ensure that the
roots do not lose
water by osmosis.
//
Have pores on the
leaves /
hydathodes to
excrete the excess
salt in the
hypertonic water of
the soil which
enters the roots.
The surrounding
water in the soil
hypertonic as
compared to the cell
sap of the root cells
Seeds which fall
onto the ground die
because they are
submerged within
the soft and
waterlogged soil.
Seeds have
E5 vivipary
characteristic.
//
the seed are able
to germinate while
still attached to the
parent plant.
4551/2 2011 Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama Penuh
Peraturan pemarkahan
14
SULIT
4551/2
Any six
6
(b)
Able to explain the importance of microorganisms in
farming.
Max 10
Sample answer :
P1: Nitrogen fixing bacteria carries out fixation of
nitrogen
P2 : Rhizobium in root nodules of leguminous plants//
Free-living bacteria/ Azotobacter/ Nostoc
P3: Use nitrogen in the air to make nitrates/
ammonium compound
P4: Nitrates produced by the bacteria are absorbed by
plants to make protein
P5 : to make protein
P6: When animals eat plants the protein is transferred
to animals
P7: Excretory nitrogenous substances/ urea/ waste
material/ faeces from animal
P8 : and when plants/ animals die,
P9 : are decomposed/ decayed by decaying bacteria/
saprophytic bacteria/ fungi
P10 : Breaks them down to ammonia/ ammonium
compounds
P11: Nitrifying bacteria/ Nitrosomonas converts
ammonium compounds/ ammonia to nitrites
P12: Nitrifying bacteria/ Nitrobacter converts nitrites to
nitrates
P13 : Mineral ions /nitrates be released/ returned to
the soil
P14 : Soil becomes fertile/ more nutrient in the soil
P15 : Plants will grow/ photosynthesis take place /
crop yield increase
Any 10
TOTAL
4551/2 2011 Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama Penuh
10
20
Peraturan pemarkahan
15
SULIT
4551/2
Question 8
No
Mark scheme
(a)
Able to explain how the production of these products can
endanger ecosystem
Sub
Mark
Max
5
Sample answer :
F : Ozone depletion
E 1 : Leaf cells and chlorophyll are damaged by
ultraviolet rays
E2 : lower the rate of photosynthesis
E3 : reduce crop yield
E4 : Ultraviolet rays kill microorganisms/ phytoplankton//
destroy
E5 : disrupt the marine food chain
E6 : Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation lead to
skin cancer/ melanoma/ cataract/ weakened the immune
system
E7 : Greenhouse effect/ global warming
E8 : damage the eggs of certain amphibians// wind
patterns change// climatic changes
Any 6
Total
Mark
Able to suggest measures to be taken to reduce this
problem.
Sample answer :
P1 : Reduce/ stop/ ban the use of Chlorofluorocarbon/
CFC
P2 : Replace CFC with HCFC
P3 : Firing ozone missile
P4 : the world comply with the Montreal Protocol to
reduce the use of CFCs (to cut the use of CFCs in half
by the year 1997)
P5 : Reduce the usage of Styrofoam / polystyrene
container
Any 4
(b)
Able to explain the occurrence of these phenomenons
Max
8
Sample answer :
F1 : phenomenon : Green house effect / global warming
F2 : burning of fuel from transports / factories / forest /
excessive deforestation
4551/2 2011 Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama Penuh
Peraturan pemarkahan
SULIT
16
4551/2
F3 : increase carbon dioxide content in the atmosphere
P1 CO trap /absorb more heat in the atmosphere
P2 The layer of green house gases / CO acts as an
insulator / barrier
P3 To prevent the heat from being transmitted to space
P4 Causes a rise in temperature of the atmosphere /
leads to global warming
P5 Thermal expansion of sea water // melting of glaciers
/ ice sheet
P6 Cause sea level to rise / flood / sinking of island
P7 Causes changes in wind direction / sea current
P8 Cause climatic changes / thyphoon
P9 High atmosphere temperature reduces the rate of
photosynthesis
P10 Productivity of crops / livestock decrease
P11 Destruction / disruption of food chains / food webs
P12 Cause extinction of species // biodiversity decreases
8
Able to measures to be taken to reduce this problem.
Sample answer :
P1 : replacing energy of fossil / Energy generated from
wind / water
P2. Limit open burning
P3. Limit deforestation
P4. Replanting after deforestation
P5. Promotes green word.
Any two
TOTAL
4551/2 2011 Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama Penuh
Max
2
20
Peraturan pemarkahan
17
SULIT
4551/2
Question 9
No
(a)
Mark scheme
Sub
Mark
Able to explain the necessity for food processing.
Total
Mark
Max 8
Sample answer :
F1 : prevent food spoilage
E1 : (food spoilage) causes by the action of
microorganism
E2 : decomposing bacteria/fungi on carbohydrate/protein
E3 : produced carbon dioxide / water / ammonia
hydrogen
E4 : make food become toxic
F2 : prevent Oxidation of food when cut/expose to air
E1 : oxygen react with enzymes/chemicals released by
cell
Oily food becomes rancid / smells / taste different
F3 : To increase it commercial value
E1 : food additives is added in preserving the freshness
of
food
E2 : Improve the taste/appearance/texture
F4 : to diversify the uses of food
E1 : increased the variety of products
E2 : more attractive / palatable
F5 : to last longer
E1 : can withstand long periods of transportation /
storage
Any 8
(b)
Able to describe how the method can preserve food for
along period of time.
Max 8
Sample answer :
(Pasteurisation)
P1 : milk is treated to 63oC for 30 minutes // 72oC for 15
seconds
P2 : followed by rapid cooling to below 10oC
P3 : destroy bacterias but not the spores
P4 : retains the natural 17lavor of milk //
nutrients//vitamin B
P5 : retains the nutrients // vitamin B
4551/2 2011 Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama Penuh
Peraturan pemarkahan
SULIT
18
4551/2
P6 : must refrigerated to avoid the germination of
microbe`s spore
Any 3
(Canning)
P1 : use heat sterilisation
P2 : kill microorganisms and spores
P3 : steamed at high temperature / pressure to drive out
air
P4 : sealed while the food is being cooled
P5 : vacuum in the can prevent growth of microorganism
Any 3
(Refrigeration)
P1 : stored at temperature below 0oC
P2 : prevent the growth of microorganisms / the
germination of spores
P3 : remain fresh
Any 2
(c)
Able to describe the aeroponics method to improve the
quality and quantity of food production.
Max 4
Sample answer :
P1 : the plants are suspended in a chamber .
P2 : the roots exposed to the air.
P3 : nutrient solutions are sprayed onto the root (at
suitable time
P4 : at suitable time interval // explanation.
P5 : the plant roots absorb more oxygen in between the
periods of spraying.
P6 : light intensity / temperature can be controlled to
ensure the environmental factor are at optimum.
Any 4
TOTAL
20
PERATURAN PERMARKAHAN TAMAT
4551/2 2011 Hak Cipta Sekolah Berasrama Penuh
Peraturan pemarkahan
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Sains Ting 3 Diagnostic Test 2013 (Skema)Dokument8 SeitenSains Ting 3 Diagnostic Test 2013 (Skema)Ismaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 5 (BL)Dokument5 SeitenIT Bio F4 Topical Test 5 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 5 Chapter 4 Reproduction and GrowthDokument81 SeitenForm 5 Chapter 4 Reproduction and Growthbee ling100% (1)
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 8 (BL)Dokument9 SeitenIT Bio F4 Topical Test 8 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 4 (BL)Dokument8 SeitenIT Bio F4 Topical Test 4 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 8 (BL)Dokument9 SeitenIT Bio F4 Topical Test 8 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 3 (BL)Dokument8 SeitenIT Bio F4 Topical Test 3 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topical Test 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation: Ujian Topikal 2: Struktur Sel Dan Organisasi SelDokument5 SeitenTopical Test 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation: Ujian Topikal 2: Struktur Sel Dan Organisasi Selliyanaharuddin100% (1)
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 9 (BL)Dokument8 SeitenIT Bio F4 Topical Test 9 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 7 (BL)Dokument14 SeitenIT Bio F4 Topical Test 7 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 7 (BL)Dokument14 SeitenIT Bio F4 Topical Test 7 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 1 (BL)Dokument4 SeitenIT Bio F4 Topical Test 1 (BL)Elyna Tony MuntingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Past Year 2012Dokument7 SeitenBio Past Year 2012Ismaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 4 (BL)Dokument8 SeitenIT Bio F4 Topical Test 4 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 5 (BL)Dokument5 SeitenIT Bio F4 Topical Test 5 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 2011 JawapanDokument4 SeitenBio 2011 JawapanIsmaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 9 (BL)Dokument8 SeitenIT Bio F4 Topical Test 9 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 1 (BL)Dokument4 SeitenIT Bio F4 Topical Test 1 (BL)Elyna Tony MuntingNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 3 (BL)Dokument8 SeitenIT Bio F4 Topical Test 3 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topical Test 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation: Ujian Topikal 2: Struktur Sel Dan Organisasi SelDokument5 SeitenTopical Test 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation: Ujian Topikal 2: Struktur Sel Dan Organisasi Selliyanaharuddin100% (1)
- Bio Past Year 2011Dokument10 SeitenBio Past Year 2011Ismaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 2012 JawapanDokument4 SeitenBio 2012 JawapanIsmaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 2011 JawapanDokument1 SeiteBio 2011 JawapanIsmaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 2012 JawapanDokument1 SeiteBio 2012 JawapanIsmaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Past Year 2012Dokument17 SeitenBio Past Year 2012Ismaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of cell specialization and homeostasisDokument43 SeitenImportance of cell specialization and homeostasisIsmaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Edu-1.Joshuatly - Com) Trial Perlis SPM 2012 Biology (CB37C9F8)Dokument0 Seiten(Edu-1.Joshuatly - Com) Trial Perlis SPM 2012 Biology (CB37C9F8)Komalesh TheeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Paper 1: This Question Paper Consists of 50 Questions. Answer All QuestionsDokument23 SeitenBiology Paper 1: This Question Paper Consists of 50 Questions. Answer All QuestionsIsmaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology SPMDokument89 SeitenBiology SPMThana SegarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Kepentingan Air kepada Benda HidupDokument12 Seiten5 Kepentingan Air kepada Benda HidupIsmaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Grade 10 Biology Test Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument3 SeitenGrade 10 Biology Test Multiple Choice QuestionsTravis0% (1)
- Review of Literature on Indoor Plant Growth with Artificial LightingDokument9 SeitenReview of Literature on Indoor Plant Growth with Artificial LightingDylan Francesca G YuloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Complete 5 Model PapersDokument39 SeitenBiology Complete 5 Model PapersQulb- E- AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 12Dokument8 SeitenLab 12Claudia BergeronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebook PDF Understanding Biology 3rd Edition by Kenneth Mason PDFDokument41 SeitenEbook PDF Understanding Biology 3rd Edition by Kenneth Mason PDFrichard.rogers744100% (32)
- Natural Sciences Content Manual Grade 8 Final 2023 Version 1677504822Dokument76 SeitenNatural Sciences Content Manual Grade 8 Final 2023 Version 1677504822SAMANTHA SMITHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapa de Vegetación Cd. Júarez ChihuahuaDokument4 SeitenMapa de Vegetación Cd. Júarez ChihuahuaMi Si HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ati Teas 7 Science Terms and DefinitionsDokument11 SeitenAti Teas 7 Science Terms and DefinitionsSAMUEL WAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument138 SeitenChapter 7Bëar MëNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacteriology 102 - Purple Non-Sulfur Photosynthetic BacteriaDokument6 SeitenBacteriology 102 - Purple Non-Sulfur Photosynthetic BacteriasivabioteckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science MELC PDFDokument114 SeitenScience MELC PDFannebcanciogmail.com100% (23)
- CucumberDokument76 SeitenCucumberБойка Родопска100% (2)
- BIOL 1005 Final Study GuideDokument3 SeitenBIOL 1005 Final Study GuideJjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet: Chapter 5ADokument61 SeitenWorksheet: Chapter 5AMunavi ZamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burger Strontiumintheenvironment ReviewaboutreactionsofplantstowardsstableandradioactivestrontiumisotopesDokument56 SeitenBurger Strontiumintheenvironment ReviewaboutreactionsofplantstowardsstableandradioactivestrontiumisotopesDuo EnergyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raven Biology of Plants 8th Edition Evert Test BankDokument13 SeitenRaven Biology of Plants 8th Edition Evert Test Bankwilliamvanrqg100% (26)
- IGCSE BIology Notes PDFDokument101 SeitenIGCSE BIology Notes PDFTsz Ho Lam100% (2)
- IAL Biology SB2 AnswersDokument77 SeitenIAL Biology SB2 AnswersChryssa Economou100% (7)
- chapter-3-CELL STRUCTURE TAXONOMYDokument54 Seitenchapter-3-CELL STRUCTURE TAXONOMYCza Mae ArsenalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDokument17 SeitenPhotosynthesis in Higher PlantsJK JHA100% (1)
- 2022 Specimen Paper 4 Mark SchemeDokument20 Seiten2022 Specimen Paper 4 Mark Schemeadel hanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacterial PhotosynthesisDokument21 SeitenBacterial PhotosynthesisYuu chanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Csec HSB June 2011 p2Dokument16 SeitenCsec HSB June 2011 p2Sachin Bahadoorsingh100% (1)
- Photosystems I&iiDokument49 SeitenPhotosystems I&iiObiajulu Crystal OnyinyechiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 PDFDokument62 SeitenModule 5 PDFrcherry calaorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monitoreo BiosferaDokument37 SeitenMonitoreo BiosferaHéctor W Moreno QNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Division Of: Teacher Created MaterialsDokument12 SeitenA Division Of: Teacher Created MaterialsRavi KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis: Animations Student WorksheetDokument8 SeitenPhotosynthesis: Animations Student WorksheetChelsea MansuetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOENERGETICSDokument36 SeitenBIOENERGETICSKrizzia BalugoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 9.3 - HomeworkDokument4 SeitenBIO 9.3 - HomeworkalradilaylaNoch keine Bewertungen