Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Drill & Hydraulics
Hochgeladen von
tomc8053Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Drill & Hydraulics
Hochgeladen von
tomc8053Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
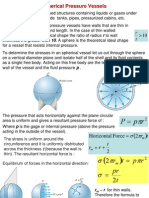
Tension Strength!
Total weight, P, (body immersed in mud) Equation 1:!
P = wt drill pipe in mud + wt drill collar in mud = ((Ldp * Wdp) + (Ldc * Wdc)) * BF!
Buoyancy Factor, BF = (1 - m / s) = (1 - m / s)!
m = specific weight of mud (kN/m3)!
Drill pipe strength expressed in terms of yield strength Eqn. 2:!
Pa = Pt * 0.9!
!
(Pa = max tensile load, Pt = drill pipe yield strength)!
!
Margin of over pull (MOP) = P - P!
!
Safety factor (SF): SF = P / P!
!
a
(Nominal values for MOP are 220-400kN)!
Subbing in Pa & P, rearranging gives;
!
!
!
!
(Equation 3): !
!
!
!
!
(Equation 4): !
Collapse!
Max differential pressure across pipe: p = Y * m* g!
!
Safety factor in collapse, SF = C
!
/ p! !
(distance from surface)!
(CR is collapse resistance)!
Shock loading can happen when slips are set on moving drill pipe, which will create
additional tensile force. Additional tensile force, FS = 9.4 * Wdp!
FS is additional tensile force (kN), Wdp is weight of drill pipe per unit length!
Equation governing elastic torsional behaviour in a
cylinder, Equation 5:!
T = applied torque, J = polar second moment of area of a cylinder, = shear stress!
r = radius at which the stress is measured, = angle through which cylinder rotated,
L = length of the cylinder, = shear modulus, = / L = T / GJ!
First yield will occur at the outer fibres of the cylinder at r = D / 2.
Substituting back into Equation 5 gives the applied torque for
first yield as (Equation 6), 3x10^3 if in mm!
Drill Stem Testing is a test that temporarily brings the well on stream without altering
the wells equipment. Used to collect samples of fluids in the rock and provide an
estimate of flow rate and reservoir pressure.!
Page 1 of 2
In a Newtonian fluid there is a linear relationship between (shear stress) and
(shear strain):! = !
Non-Newtonian fluids do not have a linear relation between and , i.e. the
viscosity varies. Three types of Non-Newtonian Fluid:!
Bingham plastic fluid Deformation takes place after a minimum value of shear
stress (called the Yield Point, YP). Beyond YP, the relationship between stress and
stain is linear with constant viscosity, known as Plastic Viscosity, PV. ! !
Therefore:! = YP + (PV)!
Power-law fluid Shear stress and shear strain are related by the following
expression:!
= !
You need to understand the derivation of the following equations: Bingham &
Power.!
!
!
Pbit = Ppump - ( P1(surface) + P2 + P3 + P4 +P5)
Page 2 of 2
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Solved Problems in Fluid MechanicsDokument19 SeitenSolved Problems in Fluid MechanicsPrincess Janine CatralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orsted Ocean Wind Offshore Wind Farm - COP Volume IDokument169 SeitenOrsted Ocean Wind Offshore Wind Farm - COP Volume Itomc8053Noch keine Bewertungen
- FE Fluids Review - Notes and Problems113pdfDokument25 SeitenFE Fluids Review - Notes and Problems113pdfMahmoud HelmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIPP Pressure Pipe ThicknessDokument42 SeitenCIPP Pressure Pipe ThicknessMike McClernanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure VesselDokument32 SeitenPressure VesselYonjon SubhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Mechanics of Buried Pipes: Anderson, Loren Runar Et Al "RING STABILITY" Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 2000Dokument19 SeitenStructural Mechanics of Buried Pipes: Anderson, Loren Runar Et Al "RING STABILITY" Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 2000obricenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Von EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (5)
- Refinery Sludge DisposalDokument24 SeitenRefinery Sludge Disposaltomc8053Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wellbore Hydraulics, Pressure Drop CalculationsDokument85 SeitenWellbore Hydraulics, Pressure Drop CalculationsNikhil ShahaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Solutions 2009-2010Dokument9 SeitenFinal Exam Solutions 2009-2010engnavaljoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Concepts Overburden Pore FractureDokument44 SeitenPressure Concepts Overburden Pore Fractureamir_hayfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.mud Hydraulics Fundamentals PDFDokument11 Seiten6.mud Hydraulics Fundamentals PDFمعلومات ممتعه mohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rev#2 HDD Jembatan SembayatDokument15 SeitenRev#2 HDD Jembatan Sembayatnizar ivan100% (1)
- Drilling Hydraulics ADokument63 SeitenDrilling Hydraulics Asryn89100% (3)
- Line SizingDokument20 SeitenLine SizingAhmed HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4102 - Chap 9 Creep Notes PDFDokument19 Seiten4102 - Chap 9 Creep Notes PDFjonthemesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.7 Pressure Drop CalculationsDokument29 Seiten1.7 Pressure Drop Calculationsduncmcleod100% (1)
- Drilling Engineering Year 2 Tutorial Questions For ExamDokument55 SeitenDrilling Engineering Year 2 Tutorial Questions For Examshanecarl100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics For DrillingDokument44 SeitenFluid Mechanics For DrillingIsmail IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresVon EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Wellbore Hydraulics, Pressure Drop CalculationsDokument85 SeitenWellbore Hydraulics, Pressure Drop CalculationsDan Morrell100% (1)
- Choked Gas Flow - Milton BeychokDokument8 SeitenChoked Gas Flow - Milton BeychokSteve WanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Julia Bryant LIFE IN A FLUIDDokument31 SeitenDR Julia Bryant LIFE IN A FLUIDguru_maheshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analyzing DST Using Homer PlotDokument18 SeitenAnalyzing DST Using Homer Plotalirezagholami79.putNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oana Tatiana Nedelcu, Victor Moagar-PoladianDokument4 SeitenOana Tatiana Nedelcu, Victor Moagar-PoladianChandra SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIE3150 2017 Case Study Beam V 03-2Dokument19 SeitenCIE3150 2017 Case Study Beam V 03-2FerdiVKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data MaterialsDokument40 SeitenData Materialsjeff_56Noch keine Bewertungen
- FMM Ques Bank With AnsDokument3 SeitenFMM Ques Bank With AnsAmal MechanicNoch keine Bewertungen
- FE Fluids Review 2013Dokument31 SeitenFE Fluids Review 2013Mahmoud HelmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics 4-29Dokument44 SeitenFluid Mechanics 4-29Hakan_KURU100% (5)
- Calculations Involved in Hydraulic Fracturing Design: Fracture GeometryDokument8 SeitenCalculations Involved in Hydraulic Fracturing Design: Fracture GeometryAbdullah IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch.E. Applications in Fluid Statics: Intended Learning OutcomesDokument8 SeitenCh.E. Applications in Fluid Statics: Intended Learning Outcomescarlette11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit6-Elasticity Shrinkage and Creep PDFDokument20 SeitenUnit6-Elasticity Shrinkage and Creep PDFscribd2106Noch keine Bewertungen
- L12 - Thin Shells (Compatibility Mode)Dokument30 SeitenL12 - Thin Shells (Compatibility Mode)Raja ShekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Syphon JetDokument50 SeitenTheory of Syphon JetLLNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 6510lec 3Dokument36 SeitenCE 6510lec 3Shashika Anuradha KoswaththaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Unit Operations Laboratory-2) : Name: Siraj Ali Aldeeb ID: 3214118Dokument9 Seiten(Unit Operations Laboratory-2) : Name: Siraj Ali Aldeeb ID: 3214118Siraj AL sharifNoch keine Bewertungen
- NOZZELDokument21 SeitenNOZZELokeke ekeneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thin Walled Pressure Vessel Apparatus Chandigarh (1) 2Dokument8 SeitenThin Walled Pressure Vessel Apparatus Chandigarh (1) 2Komborerai MuvhiringiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3: APSC 253 Fluid MechanicsDokument7 SeitenAssignment 3: APSC 253 Fluid MechanicsDusty QueefNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 FluidDynamicsDokument39 Seiten10 FluidDynamicsSyed Raheel AdeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two Phase Flow, Rheology and Powder Flow: Chapters 6, 9 & 10 in FundamentalsDokument44 SeitenTwo Phase Flow, Rheology and Powder Flow: Chapters 6, 9 & 10 in FundamentalsUmesh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- III I Civ CT Unit ViDokument18 SeitenIII I Civ CT Unit ViShriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp6 Air Flow Velocity and Pressure Coefficient Around The 90o Rectangular DuctDokument7 SeitenExp6 Air Flow Velocity and Pressure Coefficient Around The 90o Rectangular DuctKawar Abid100% (1)
- Piping Thrust RestraintDokument4 SeitenPiping Thrust RestraintMohamad ArrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bahan Kuliah Fluida (2016) PDFDokument86 SeitenBahan Kuliah Fluida (2016) PDFReinhard Tetap SemangatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2395 CH 15Dokument19 Seiten2395 CH 15abdülkadir cebeciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iahr 2006 2 PDFDokument15 SeitenIahr 2006 2 PDFRabei RomulusNoch keine Bewertungen
- IAHR2006 Paper234 Final PDFDokument15 SeitenIAHR2006 Paper234 Final PDFFolpoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single PhaseDokument15 SeitenSingle PhaseDhafin RizqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pore Pressure & HydraulicsDokument16 SeitenPore Pressure & Hydraulicskarla quintanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light Globes 2000-33Dokument8 SeitenLight Globes 2000-33Sandro GhiottoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch1 Chap1v2pres mj3mDokument146 Seitench1 Chap1v2pres mj3mDanOtahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions Manual To Accompany Introduction To Flight 8 Edition by John D. Anderson, JRDokument9 SeitenSolutions Manual To Accompany Introduction To Flight 8 Edition by John D. Anderson, JR754097Noch keine Bewertungen
- SPE 130823 Numerical Simulation of Subsea Wellhead Stability For Deepwater DrillingDokument11 SeitenSPE 130823 Numerical Simulation of Subsea Wellhead Stability For Deepwater DrillingAbraham RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsVon EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- RINA FLOW CertificationDokument115 SeitenRINA FLOW Certificationtomc8053Noch keine Bewertungen
- Certification Report Site Conditions HKW DNV GLDokument37 SeitenCertification Report Site Conditions HKW DNV GLtomc8053Noch keine Bewertungen
- FOW - Concrete Barge - Thomas - ChoisnetDokument5 SeitenFOW - Concrete Barge - Thomas - Choisnettomc8053Noch keine Bewertungen
- How Hydrogen Empowers The Energy TransitionDokument28 SeitenHow Hydrogen Empowers The Energy Transitiontomc8053Noch keine Bewertungen
- Leading Global Engineering ConsultancyDokument12 SeitenLeading Global Engineering Consultancytomc80530% (1)
- Outlook For 2016Dokument10 SeitenOutlook For 2016tomc8053Noch keine Bewertungen