Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Domain 1
Hochgeladen von
api-3254139610 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
38 Ansichten1 SeiteOriginaltitel
domain 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
38 Ansichten1 SeiteDomain 1
Hochgeladen von
api-325413961Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
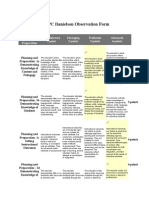
Domain 1: Planning & Preparation
UNSATISFACTORY
BASIC
1a:
Demonstrating
Knowledge of
Content and
Pedagogy
Teacher displays little understanding of
the subject or structure of the discipline,
or of content-related pedagogy.
Teachers content and pedagogical
knowledge represents basic understanding
but does not extend to connections with other
disciplines or to possible student
misconceptions.
Teacher demonstrates solid understanding of
the content and its prerequisite relationships
and connections with other disciplines.
Teachers instructional practices reflect
current pedagogical knowledge.
PROFICIENT
Teachers knowledge of the content and
pedagogy are extensive, showing evidence
of a continuing search for improved practice.
Teacher actively builds on knowledge of
prerequisites and misconceptions when
describing instruction or seeking causes for
student misunderstanding.
DISTINGUISHED
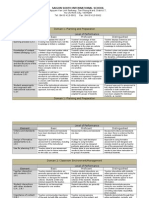
1b:
Demonstrating
Knowledge of
Students
Teacher makes little or no attempt to
acquire knowledge of students
backgrounds, skills, or interests, and
does not use such information in
planning.
Teacher demonstrates partial knowledge of
students backgrounds, skills, and interests,
and attempts to use this knowledge in
planning for the class as a whole.
Teacher demonstrates thorough knowledge of
students backgrounds, skills, and interests,
and uses this knowledge to plan for groups of
students.
Teacher demonstrates thorough knowledge
of students backgrounds, skills, and
interests, and uses this knowledge to plan for
individual student learning.
1c:
Selecting
Instructional Goals
Teachers goals represent trivial
learning, are unsuitable for students, or
are stated only as instructional activities,
and they do not permit viable methods
of assessment.
Teachers goals are of moderate value, or
suitability for students in the class, consisting
of a combination of goals and activities, some
of which permit viable methods of
assessment.
Teachers goals represent valuable learning
and are suitable for most students in the class;
they reflect opportunities for integration and
permit viable methods of assessment.
Teachers goals reflect high-level learning
relating to curriculum frameworks and
standards; they are adapted, where necessary,
to the needs of individual students, and
permit viable methods of assessment.
1d:
Demonstrating
Knowledge of
Resources
Teacher is unaware of school or district
resources available either for teaching or
for students who need them.
Teacher displays limited knowledge of school
or district resources available either for
teaching or for students who need them.
Teacher is fully aware of school and district
resources and knows how to gain access to
school and district resources for students who
need them.
Teacher seeks out resources for teaching in
professional organizations and in the
community, and is aware of resources
available for students who need them, in the
school, the district, and the larger
community.
1e:
Designing Coherent
Instruction
The various elements of the instructional
design do not support the stated
instructional goals or engage students in
meaningful learning, and the lesson or
unit has no defined structure.
Some of the elements of the instructional
design support the stated instructional goals
and engage students in meaningful learning,
while others do not. Teachers lesson or unit
has a recognizable structure.
Most of the elements of the instructional
design support the stated instructional goals
and engage students in meaningful learning,
and the lesson or unit has a clearly defined
structure.
All of the elements of the instructional
design support the stated instructional goals,
engage students in meaningful learning, and
show evidence of student input. Teachers
lesson or unit is highly coherent and has a
clear structure.
1f:
Assessing Student
Learning
Teachers approach to assessing student
learning contains no clear criteria or
standards, and lacks congruence with the
instructional goals. Teacher has no plans
to use assessment results in designing
future instruction.
Teachers plan for student assessment is
partially aligned with the instructional goals
and includes criteria and standards that are
not entirely clear or understood by students.
Teacher uses the assessment to plan for future
instruction for the class as a whole.
Teachers plan for student assessment is
aligned with the instructional goals at least
nominally, with clear assessment criteria and
standards that have been communicated to
students. Teacher uses the assessment to plan
for groups of students of individuals.
Teachers plan for student assessment is fully
aligned with the instructional goals,
containing clear assessment criteria and
standards that are not only understood by
students but also show evidence of student
participation in their development. Teachers
students monitor their own progress in
achieving the goals.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- SDLC Instructional Performance Rating Rubric Fy13Dokument9 SeitenSDLC Instructional Performance Rating Rubric Fy13api-184947815Noch keine Bewertungen
- Framework For EvaluationDokument7 SeitenFramework For Evaluationapi-236831571Noch keine Bewertungen
- Domain 1 Teacher Self-ReflectionDokument3 SeitenDomain 1 Teacher Self-ReflectionleezenarosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Standards Performance Criteria Rubric - Adapted From Charlotte DanielsonDokument5 SeitenTeaching Standards Performance Criteria Rubric - Adapted From Charlotte Danielsonapi-250421371Noch keine Bewertungen
- Joel ObservationDokument8 SeitenJoel Observationapi-258404762Noch keine Bewertungen
- Otes Rubric and MapDokument5 SeitenOtes Rubric and Mapapi-237658564Noch keine Bewertungen
- OTES Rubric 2016-17 Accomplished Only Cheat SheetDokument8 SeitenOTES Rubric 2016-17 Accomplished Only Cheat SheetsaxbillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ohio Teacher Evaluation System RubricDokument10 SeitenOhio Teacher Evaluation System Rubricapi-222581550Noch keine Bewertungen
- Idaho Core Teacher Standards PresentationDokument28 SeitenIdaho Core Teacher Standards Presentationapi-356705303Noch keine Bewertungen
- Formal Observation Summary: PowerDokument11 SeitenFormal Observation Summary: Powerapi-137669263100% (1)
- Observation Rating Hs 10Dokument7 SeitenObservation Rating Hs 10api-353224250Noch keine Bewertungen
- SPS Danielson FrameworkDokument15 SeitenSPS Danielson FrameworkJulian A.100% (1)
- Ohio Teacher Evaluation System Rubric July2013Dokument10 SeitenOhio Teacher Evaluation System Rubric July2013Asiff MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self AssessmentDokument9 SeitenSelf Assessmentapi-284405851Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8601 Assignmnt 1Dokument24 Seiten8601 Assignmnt 1saimasheikh869Noch keine Bewertungen
- Teacher Self Assessment 1Dokument9 SeitenTeacher Self Assessment 1api-253664586Noch keine Bewertungen
- L Holly 2014-15 Formal EvaluationDokument10 SeitenL Holly 2014-15 Formal Evaluationapi-248723658Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 Nov. 14Dokument4 SeitenModule 3 Nov. 14Asliah CawasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teacher Self-Appraisal RubricsDokument7 SeitenTeacher Self-Appraisal Rubricsgjohnston9077Noch keine Bewertungen
- 506 Learning Plan RubricDokument2 Seiten506 Learning Plan Rubricapi-253792172100% (1)
- M Star Teacher Self AssessmentDokument22 SeitenM Star Teacher Self AssessmentPowhatan Vanhugh BeltonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abstract of Framework - Linda DanielsonDokument6 SeitenAbstract of Framework - Linda DanielsonClaudia Javier MendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 Observation 2Dokument5 Seiten2014 Observation 2api-285996086Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lisa EvalDokument5 SeitenLisa Evalapi-203365948Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 Observation 3Dokument5 Seiten2014 Observation 3api-285996086Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jeffrey Beloso Bas BSED - Fil 3-B Subject: PROF ED 9 Instructor: Mrs. Bernardita ManaloDokument3 SeitenJeffrey Beloso Bas BSED - Fil 3-B Subject: PROF ED 9 Instructor: Mrs. Bernardita ManaloJeff Beloso BasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monika Obs 1Dokument9 SeitenMonika Obs 1api-311130965Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kentuckyteacherstandards 2Dokument11 SeitenKentuckyteacherstandards 2api-320207927Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment #2Dokument2 SeitenAssignment #2Snappy CookiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Year - Summative Evaluation - April 2016Dokument16 SeitenFirst Year - Summative Evaluation - April 2016api-264963856Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Planning For The Implementation of LDM 2 For Teachers Individual/Lac Group Presentation For Mts and HtsDokument6 Seiten2-Planning For The Implementation of LDM 2 For Teachers Individual/Lac Group Presentation For Mts and HtsMarlon LumangNoch keine Bewertungen
- PED12 Lesson Proper For Week 1Dokument6 SeitenPED12 Lesson Proper For Week 1Joel B. SemañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Va Teacher Standards Look Fors CombinedDokument28 SeitenVa Teacher Standards Look Fors CombinedMary McDonnell100% (1)
- Understanding the NCBTS FrameworkDokument23 SeitenUnderstanding the NCBTS FrameworkMark Lester Tulo100% (1)
- Lesson Plan 2Dokument6 SeitenLesson Plan 2api-299978111Noch keine Bewertungen
- PED-10 21st Century and New Literacies and Curriculum ProcessDokument26 SeitenPED-10 21st Century and New Literacies and Curriculum ProcessBTLED-1202 Aggabao ErwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives of Remedial InstructionDokument4 SeitenObjectives of Remedial InstructionCatherine Garcia100% (1)
- Student Teaching Midterm EvaluationDokument4 SeitenStudent Teaching Midterm EvaluationtentingerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 5&6 BuildingDokument7 SeitenWeek 5&6 BuildingMaybe Calunsag - AbucayNoch keine Bewertungen
- T-Tess Six Educator StandardsDokument1 SeiteT-Tess Six Educator Standardsapi-351054075100% (1)
- Criteria Curriculum AssessmentDokument58 SeitenCriteria Curriculum AssessmentJosephine Nomolas100% (2)
- Assignment 8601Dokument24 SeitenAssignment 8601arifiqra246100% (1)
- Summative Evauation April 2016Dokument16 SeitenSummative Evauation April 2016api-252092263Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Evaluation - Janet WellmanDokument13 SeitenFinal Evaluation - Janet Wellmanapi-384686461Noch keine Bewertungen
- CrosswalkfinalDokument5 SeitenCrosswalkfinalapi-258834665Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edad 310Dokument4 SeitenEdad 310Lubeth Cabatu0% (1)
- Educ 313 - Curriculum Development: Topic: Chapter 3 Curriculum ImplementationDokument4 SeitenEduc 313 - Curriculum Development: Topic: Chapter 3 Curriculum ImplementationRyan Delos ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kelompok 9 InggrisDokument18 SeitenKelompok 9 InggrisErna Pasimbong RumpaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standards Table-2Dokument5 SeitenStandards Table-2api-252851226Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Evaluation AdeliDokument13 SeitenFinal Evaluation Adeliapi-301715328Noch keine Bewertungen
- Teacher Final Evaluation 2023 - 2024Dokument7 SeitenTeacher Final Evaluation 2023 - 2024Ayman Bou KarroumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 1. Rocel NavajaDokument3 SeitenActivity 1. Rocel NavajaRocel NavajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRINCIPLES OF TEACHING NotesDokument24 SeitenPRINCIPLES OF TEACHING NotesHOLLY MARIE PALANGAN100% (2)
- Mku Bem 2209 Cat1 - 2Dokument5 SeitenMku Bem 2209 Cat1 - 2Elija ChesainaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Planning in TeachingDokument10 SeitenLesson Planning in TeachingTaskeen ZafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Problem and Its SettingDokument27 SeitenThe Problem and Its Settingchristian capunongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weaknesses in Writing A Lesson PlanDokument2 SeitenWeaknesses in Writing A Lesson PlanJOHN CARMELO SAULON100% (2)
- TPESDokument12 SeitenTPESStudy BuddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Structured Method of Pedagogy: Effective Teaching in the Era of the New Mission for Public Education in the United StatesVon EverandThe Structured Method of Pedagogy: Effective Teaching in the Era of the New Mission for Public Education in the United StatesNoch keine Bewertungen
- GROUP BEHAVIOUR AND DYNAMICS EXPLAINEDDokument41 SeitenGROUP BEHAVIOUR AND DYNAMICS EXPLAINEDPriya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dueling LoopsDokument209 SeitenDueling Loopsinstantkaffee100% (1)
- Chap 11 TQM & Quality ToolsDokument23 SeitenChap 11 TQM & Quality Toolsrogean gullemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supervisor Peer Review FormDokument1 SeiteSupervisor Peer Review FormPow LeanilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gabriel Catren - "A Throw of The Quantum Dice Will Never Overturn The Copernican Revolution"Dokument25 SeitenGabriel Catren - "A Throw of The Quantum Dice Will Never Overturn The Copernican Revolution"Evan Garris100% (2)
- 1b Assignment 1 ExcerptDokument10 Seiten1b Assignment 1 Excerptapi-408544443Noch keine Bewertungen
- How To Improve Communications On Your ProjectDokument3 SeitenHow To Improve Communications On Your ProjectRomneil Cruzabra100% (2)
- Project Proposal in Community Tree PlantingDokument2 SeitenProject Proposal in Community Tree Plantingbam glovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Values DevelopmentDokument26 SeitenValues DevelopmentAudrey GuimteNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Quarter Achievement Rates for 15 SchoolsDokument18 SeitenFirst Quarter Achievement Rates for 15 SchoolsRommel Urbano YabisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Storyboard: Video Script and Storyboard On Evaluating Functions LessonDokument2 SeitenStoryboard: Video Script and Storyboard On Evaluating Functions LessonIvanhoe BalaroteNoch keine Bewertungen
- LANGUAGE FLUENCY AND READING COMPREHENSIONDokument42 SeitenLANGUAGE FLUENCY AND READING COMPREHENSIONMonica Charlotte CallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Planning 1 - 10 GradersDokument4 SeitenLesson Planning 1 - 10 GradersViviana Salgado RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Theory of Mind As Pure Act-Giovanni Gentile - (Actual Idealism)Dokument330 SeitenThe Theory of Mind As Pure Act-Giovanni Gentile - (Actual Idealism)Valentin IonutNoch keine Bewertungen
- University AdvancementDokument47 SeitenUniversity AdvancementqalatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergent Curriculum Instructional Design ModelDokument11 SeitenEmergent Curriculum Instructional Design Modelapi-307926958Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hebb Neural Network: Learning and ApplicationsDokument12 SeitenHebb Neural Network: Learning and ApplicationsVighnesh MNoch keine Bewertungen
- VE021-PPT-Week 10 - Personal Goal Setting - Part 2Dokument16 SeitenVE021-PPT-Week 10 - Personal Goal Setting - Part 2Yorino LoasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Engineer CV Pritam BiswasDokument2 SeitenMechanical Engineer CV Pritam BiswasVIRUS devil GAMING YTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teacher Teaching Styles Effect Student MotivationDokument6 SeitenTeacher Teaching Styles Effect Student Motivationbenita valdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improving Reading Comprehension Through Mind MappingDokument156 SeitenImproving Reading Comprehension Through Mind MappingMori Yohana SimamoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Write A Statement of The ProblemDokument13 SeitenHow To Write A Statement of The ProblemTrixie Pearl TompongNoch keine Bewertungen
- AECT The Definition of Educational TechnDokument10 SeitenAECT The Definition of Educational TechnKreativitas YMPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full TextDokument21 SeitenFull TextKartini AmbomaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self-Esteem and Branded Apparel: An Evaluation of One's Behavioral StateDokument8 SeitenSelf-Esteem and Branded Apparel: An Evaluation of One's Behavioral StateGABRIELLE SOPHIA BAUTISTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Spanish SyllabusDokument7 SeitenSpanish SyllabusKelsey LoontjerNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAMPLE 4as DETAILED LPDokument2 SeitenSAMPLE 4as DETAILED LPVan Redondo VillamorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Project On Action ResearchDokument3 SeitenExperimental Project On Action Researchddum292Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7 An Interactive Life High Flyer IntermediateDokument5 Seiten7 An Interactive Life High Flyer IntermediateIoana-Maria StelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laterricaedwards Teacher ResumeDokument3 SeitenLaterricaedwards Teacher Resumeapi-627213926Noch keine Bewertungen