Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
10th Grade Geometry
Hochgeladen von
api-325896611Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
10th Grade Geometry
Hochgeladen von
api-325896611Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
1-2 Skills Practice
Order of Operations
Evaluate each expression.
4. 33
3.
2.
1.
5. (5 + 4) 7
6. (9 2) 3
7. 4 + 6 3
8. 12 + 2 2
9. (3 + 5) 5 + 1
10. 9 + 4(3 + 1)
11. 30 5 4 + 2
12. 10 + 2 6 + 4
13. 14 7 5 32
14. 4[30 (10 2) 3]
15. 5 + [30 (6 1)2]
16. 2[12 +
(5 2)2 ]
Evaluate each expression if x = 6, y = 8, and z = 3.
17. xy + z
18. yz x
19. 2x + 3y z
20. 2(x + z) y
21. 5z + (y x)
22. 5x (y + 2z)
23.
x2 +
25.
y + xz
2
Chapter 2
y 2 10z
z3 + (
24.
26.
y 2 4x)
3 y + x2
z
23
Glencoe Algebra 1
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
1-4 Study Guide and Intervention
The Distributive Property
Evaluate Expressions The Distributive Property can be used to help evaluate expressions.
For any numbers a, b, and c, a(b + c) = ab + ac and (b + c)a = ba + ca and a(b c) = ab
ac and (b c)a = ba ca.
Distributive Property
Example 1: Use the Distributive Property to rewrite 6(8 + 10). Then evaluate.
6(8 + 10) = 6 8 + 6 10
Distributive Property
= 48 + 60
Multiply.
= 108
Add.
Example 2: Use the Distributive Property to rewrite 2(3 x 2 + 5x + 1). Then simplify.
2(3 x 2
+ 5x + 1) = 2(3 x 2 ) + (2)(5x) + (2)(1)
= 6 x 2
= 6 x
Distributive Property
+ (10x) + (2)
Multiply.
10x 2
Simplify.
Exercises
Use the Distributive Property to rewrite each expression. Then evaluate.
1
2
1. 20(31)
2. 12 4
4. 5(4x 9)
5. 3(8 2x)
7. 12
(2+ 12 x)
10. 2(3x + 2y z)
13.
1
(16x 12y + 4z)
4
Chapter 2
8.
3. 5(311)
6. 12
1
(12 4t)
4
9. 3(2x y)
11. (x 2)y
14. (2 3x +
(6 12 x)
12. 2(3a 2b + c)
x 2 )3
23
15. 2(2 x 2
+ 3x + 1)
Glencoe Algebra 1
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
1-4 Study Guide and Intervention
(continued)
The Distributive Property
Simplify Expressions A term is a number, a variable, or a product or quotient of numbers and variables. Like terms
are terms that contain the same variables, with corresponding variables having the same powers. The Distributive Property
and properties of equalities can be used to simplify expressions. An expression is in simplest form if it is replaced by an
equivalent expression with no like terms or parentheses.
Example : Simplify 4( a2 + 3ab) ab.
4( a2
+ 3ab) ab = 4( a2
+ 3ab) 1ab
+ 12ab 1ab
=4 a
+ (12 1)ab
= 4 a2
+ 11ab
=4 a
Multiplicative Identity
Distributive Property
Distributive Property
Substitution
Exercises
Simplify each expression. If not possible, write simplified.
1. 12a a
2. 3x + 6x
4. 20a + 12a 8
5. 3 x 2
7. 2p +
10. 4x +
1
q
2
1
(16x 20y)
4
3. 3x 1
+ 2 x2
6. 6x + 3 x 2 + 10 x 2
8. 10xy 4(xy + xy)
11. 2 1 6x +
9. 21a + 18a + 31b 3b
x2
12. 4 x 2 + 3 x 2
+ 2x
Write an algebraic expression for each verbal expression. Then simplify, indicating the properties used.
13. six times the difference of 2a and b, increased by 4b
14. two times the sum of x squared and y squared, increased by three times the sum of x squared and y squared
Chapter 2
23
Glencoe Algebra 1
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
2-6 Skills Practice
Ratios and Proportions
Determine whether each pair of ratios are equivalent ratios. Write yes or no.
1.
4
,
5
20
25
2.
5
,
9
7
11
3.
6
,
7
24
28
4.
8
,
9
72
81
5.
7
,
16
42
90
6.
13
,
19
26
38
7.
3
,
14
21
98
8.
12
,
17
50
85
Solve each proportion. If necessary, round to the nearest hundredth.
9.
1
a
2
14
10.
5
b
3
9
11.
9
g
15
10
12.
3
a
1
6
13.
6
z
3
5
14.
5
f
35
21
15.
12
7
36
m
16.
6
23
17.
42
56
6
f
18.
7
b
19.
10
14
30
m
20.
11
15
n
60
21.
9
c
22.
5
12
20
g
Chapter 2
27
39
23
y
69
1
9
Glencoe Algebra 1
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
23.
4
21
y
84
22
x
24.
11
30
25. BOATING Hues boat used 5 gallons of gasoline in 4 hours. At this rate, how many gallons of gasoline will the boat
use in 10 hours?
2-2 Skills Practice
Solving One-Step Equations
Solve each equation. Check your solution.
1. y 7 = 8
2. w + 14 = 8
3. p 4 = 6
4. 13 = 5 + x
5. 98 = b + 34
6. y 32 = 1
7. n + (28) = 0
8. y + (10) = 6
9. 1 = t + (19)
10. j (17) = 36
11. 14 = d + (10)
12. u + (5) = 15
13. 11 = 16 + y
14. c (3) = 100
15. 47 = w (8)
16. x (74) = 22
17. 4 (h) = 68
18. 56 = 20 (j)
19. 12z = 108
20. 7t = 49
21. 18f = 216
22. 22 = 11v
23. 6d = 42
24. 96 = 24a
25.
c
4
27. 84 =
Chapter 2
= 16
d
3
26.
a
16
=9
28.
23
d
7
= 13
Glencoe Algebra 1
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
29.
t
4
= 13
2
z
3
31. 6 =
33.
30. 31 =
32.
5
p = 10
9
1
n
6
2
q = 4
7
34.
a
10
2
5
2-4 Study Guide and Intervention
Solving Equations with the Variable on Each Side
Variables on Each Side To solve an equation with the same variable on each side, first use the Addition or the
Subtraction Property of Equality to write an equivalent equation that has the variable on just one side of the equation.
Then solve the equation.
Example 2: Solve 11 3y = 8y + 1.
Example 1: Solve 5y 8 = 3y + 12.
5y 8 = 3y + 12
11 3y = 8y + 1
5y 8 3y = 3y + 12 3y
11 3y + 3y = 8y + 1 + 3y
2y 8 = 12
11 = 11y + 1
2y 8 + 8 = 12 + 8
11 1 = 11y + 1 1
12 = 11y
2y = 20
2y
2
12
11 y
=
11
11
1
1
=y
11
1
The solution is 1
11
20
2
y = 10
The solution is 10.
Chapter 2
23
Glencoe Algebra 1
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
Exercises
Solve each equation. Check your solution.
1. 6 b = 5b + 30
2. 5y 2y = 3y + 2
3. 5x + 2 = 2x 10
4. 4n 8 = 3n + 2
5. 1.2x + 4.3 = 2.1 x
6. 4.4m + 6.2 = 8.8m 1.8
7.
1
2
1
8
b+4=
b + 88
8.
3
4
k5=
1
4
k1
9. 8 5p = 4p 1
10. 4b 8 = 10 2b
11. 0.2x 8 = 2 x
12. 3y 1.8 = 3y 1.8
13. 4 3x = 7x 6
14. 8 + 4k = 10 + k
15. 20 a = 10a 2
16.
2
3
1
2
n+8=
n+2
19. 4 3x = 6x 6
17.
2
5
y8=9
3
5
20. 18 4k = 10 4k
18. 4r + 5 = 5 4r
21. 12 + 2y = 10y 12
2-4 Study Guide and Intervention
(continued)
Solving Equations with the Variable on Each Side
Grouping Symbols When solving equations that contain grouping symbols, first use the Distributive Property to
eliminate grouping symbols. Then solve.
Example: Solve 4(2a 1) = 10(a 5).
4(2a 1) = 10(a 5)
8a 4 = 10a + 50
8a 4 + 10a = 10a + 50 + 10a
18a 4 = 50
Add 10a to each side.
Add 4 to each side.
18a = 54
a=3
Distributive Property
Simplify.
18a 4 + 4 = 50 + 4
18 a
18
Original equation
Simplify.
54
18
Divide each side by 18.
Simplify.
The solution is 3.
Exercises
Chapter 5
Glencoe Algebra 1
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
Solve each equation. Check your solution.
1. 3(x + 5) = 3(x 1)
2. 2(7 + 3t) = t
3. 3(a + 1) 5 = 3a 2
4. 75 9g = 5(4 + 2g)
5. 5(f + 2) = 2(3 f )
6. 4(p + 3) = 36
7. 18 = 3(2t + 2)
8. 3(d 8) = 3d
9. 5(p + 3) + 9 = 3( p 2) + 6
11. 1.2(x 2) = 2 x
12.
10. 4(b 2) = 2(5 b)
13.
a8
12
2 a+5
3
3+ y
4
14. 2(4 + 2k) + 10 = k
y
8
15. 2(w 1) + 4 = 4(w + 1)
16. 6(n 1) = 2(2n + 4)
17. 2[2 + 3( y 1)] = 22
18. 4(r + 2) = 4(2 4r)
19. 3(x 8) = 24
20. 4(4 4k) = 10 16k
21. 6(2 2y) = 5(2y 2)
5-1 Study Guide and Intervention
Solving Inequalities by Addition and Subtraction
Solve Inequalities by Addition Addition can be used to solve inequalities. If any number is added to each side of a
true inequality, the resulting inequality is also true.
Addition Property of Inequalities
For all numbers a, b, and c, if a > b, then a + c > b + c, and if a < b,
then a + c < b + c
The property is also true when > and < are replaced with and .
Example 1: Solve x 8 6. Then graph the solution.
x 8 6
x 8 + 8 6 + 8
x2
Original inequality
Add 8 to each side.
Example 2: Solve 4 2a > a. Then graph the solution.
Simplify.
4 2a > a
4 2a + 2a > a + 2a
The solution in set-builder notation is {x | x 2}.
Number line graph:
Chapter 5
Original inequality
Add 2a to each side.
4>a
Simplify.
a<4
4 > a is the same as a < 4.
Glencoe Algebra 1
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
The solution in set-builder notation is {a | a < 4}.
Number line graph:
Chapter 5
Glencoe Algebra 1
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
Exercises
Solve each inequality. Check your solution, and then graph it on a number line.
1. t 12 16
2. n 12 < 6
3. 6 g 3
4. n 8 < 13
5. 12 > 12 + y
6. 6 > m 8
Solve each inequality. Check your solution.
7. 3x 8 4x
10. y 10 > 15 2y
8. 0.6n 12 0.4n
11. z
1
3
4
3
9. 8k 12 < 9k
12. 2b > 4 3b
Define a variable, write an inequality, and solve each problem. Check your solution.
13. A number decreased by 4 is less than 14.
14. The difference of two numbers is more than 12, and one of the numbers is 3.
15. Forty is no greater than the difference of a number and 2.
5-1 Study Guide and Intervention
(continued)
Solving Inequalities by Addition and Subtraction
Solve Inequalities by Subtraction Subtraction can be used to solve inequalities. If any number is subtracted from
each side of a true inequality, the resulting inequality is also true.
Subtraction Property of Inequalities
For all numbers a, b, and c, if a > b, then a c > b c, and if a < b,
then a c < b c.
The property is also true when > and < are replaced with and .
Example: Solve 3a + 5 > 4 + 2a. Then graph it on a number line.
3a + 5 > 4 + 2a
3a + 5 2a > 4 + 2a 2a
a+5>4
a+55>45
a > 1
Original inequality
Subtract 2a from each side.
Simplify.
Subtract 5 from each side.
Simplify.
The solution is {a a > 1}.
Number line graph:
Chapter 5
11
Glencoe Algebra 1
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
Exercises
Solve each inequality. Check your solution, and then graph it on a number line
1. t + 12 8
2. n + 12 > 12
3. 16 h + 9
4. y + 4 > 2
5. 3r + 6 > 4r
6.
3
q5
2
1
q
2
Solve each inequality. Check your solution.
7. 4p 3p + 0.7
1
4
8. r +
10. 1.2 > 2.4 + y
>
3
8
9. 9k + 12 > 8k
11. 4y < 5y+ 14
12. 3n + 17 < 4n
Define a variable, write an inequality, and solve each problem. Check your solution.
13. The sum of a number and 8 is less than 12.
14. The sum of two numbers is at most 6, and one of the numbers is 2.
15. The sum of a number and 6 is greater than or equal to 4.
5-2 Study Guide and Intervention
Solving Inequalities by Multiplication and Division
Solve Inequalities by Multiplication If each side of an inequality is multiplied by the same positive number, the
resulting inequality is also true. However, if each side of an inequality is multiplied by the same negative number, the
direction of the inequality must be reversed for the resulting inequality to be true.
For all numbers a, b, and c, with c 0,
Multiplication Property of Inequalities
1. if c is positive and a > b, then ac > bc;
if c is positive and a < b, then ac < bc;
2. if c is negative and a > b, then ac < bc;
if c is negative and a < b, then ac > bc.
The property is also true when > and < are replaced with and .
Example 1: solve
(8)
y
8
( y8 )
Chapter 5
12
y
8
y 96
12
Simplify.
Original inequality
(8)12 Multiply each side by 8;change to .
11
Glencoe Algebra 1
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
The solution is { y| y 96}.Example 2: solve
3
4
k<
15
3
4
Chapter 5
( 43 )
3
4
k < 20
k < 15
Original inequality
k<
( 43 )
15
Multiply each side by
4
3
Simplify.
The solution is {kk < 20}.
11
Glencoe Algebra 1
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
Exercises
Solve each inequality. Check your solution.
1.
y
2
6
2.
n
50
5.
1
n 10
4
6.
2
b
3
9.
g
5
10.
3
4
3.
3
h 3
5
1
3
7.
3m
5
<
9 p
5
11.
n
10
5.4
> 22
<
>
4.
3
20
p
6
< 6
8. 2.51
12.
2a
7
2 h
4
Define a variable, write an inequality, and solve each problem. Check your solution.
13. Half of a number is at least 14.
14. The opposite of one-third a number is greater than 9.
15. One fifth of a number is at most 30.
Chapter 8
37
Glencoe Algebra 1
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
5-2 Study Guide and Intervention
(continued)
Solving Inequalities by Multiplication and Division
Solve Inequalities by Division If each side of a true inequality is divided by the same positive number, the resulting
inequality is also true. However, if each side of an inequality is divided by the same negative number, the direction of the
inequality symbol must be reversed for the resulting inequality to be true.
For all numbers a, b, and c with c 0,
1. if c is positive and a > b, then
a
c
Division Property of Inequalities
<
>
>
b
; if c is positive and a < b, then
c
b
;
c
2. if c is negative and a > b, then
a
c
a
c
a
c
<
b
; if c is negative and a < b, then
c
b
.
c
The property is also true when > and < are replaced with and .
Example : Solve 12y 48.
12y 48
12 y
12
Original inequality
48
12
y 4
Divide each side by 12 and change to .
Simplify.
The solution is { yy 4}.
Exercises
Solve each inequality. Check your solution.
1. 25g 100
5. 6k <
1
5
9. 25 2m
13. 40 > 10h
2. 2x 9
3. 5c > 2
4. 8m < 64
6. 18 < 3b
7. 30 < 3n
8. 0.24 < 0.6w
10. 30 > 5p
11. 2n 6.2
14.
2
3n
15. 3 <
p
4
12. 35 < 0.05h
16. 4 >
x
2
Define a variable, write an inequality, and solve each problem. Then check your solution.
17. Four times a number is no more than 108.
Chapter 8
37
Glencoe Algebra 1
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
18. The opposite of three times a number is greater than 12.
19. Negative five times a number is at most 100.
8-6 Study Guide and Intervention
Solving x2 + bx + c = 0
Factor
+ bx + c To factor a trinomial of the form
+ bx + c, find two integers, m and p, whose sum is equal
to b and whose product is equal to c.
Factoring
+c
+ bx
+ bx + c = (x + m)(x + p), where m + p = b and mp = c
Example 2 : Factor x 2 + 6x 16.
Example 1: Factor each polynomial.
a. x 2 + 7x + 10
In this trinomial, b = 6 and c = 16. This means m + p is
positive and mp is negative. Make a list of the factors of
16, where one factor of each pair is positive.
In this trinomial, b = 7 and c = 10.
Factors of 10
Sum of Factors
1, 10
11
2, 5
Since 2 + 5 = 7 and 2 _ 5 = 10, let m = 2 and p = 5.
2
x + 7x + 10 = (x + 5)(x + 2)
b. x 2 8x + 7
In this trinomial, b = 8 and c = 7. Notice that m + p is
negative and mp is positive, so m and p are both negative.
Factors of 16
Sum of Factors
1, 16
15
1, 16
15
2, 8
2, 8
Therefore, m = 2 and p = 8.
x 2 + 6x 16 = (x 2)(x + 8)
Since 7 + (1) = 8 and (7)(1) = 7, m = 7 and p = 1.
x 2 8x + 7 = (x 7)(x 1)
Chapter 8
37
Glencoe Algebra 1
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
Exercises
Factor each polynomial.
1.
x 2 + 4x + 3
2.
m2 + 12m + 32
4.
x2 x 6
5.
x 2 4x 21
7.
t 2 4t 12
8.
p2 16p + 64
10.
+ 6x + 5
11.
13.
x 2 2x 3
14.
y 2 + 14y + 13
16.
x 2 + 12x + 20
19.
Chapter 1
+ 2xy +
17.
2
13
r 2 3r + 2
6.
9. 9 10x +
+ 8a 9
a2 14a + 24
20.
3.
4ab + 4 b2
12.
15.
x 2 22x + 121
x2
y
7y 8
m 2 + 9m + 20
18. 18 + 11y +
y2
21.
+ 6xy 7
Glencoe Algebra 1
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
8-6 Study Guide and Intervention (continued)
Solving x2 + bx + c = 0
Solve Equations by Factoring Factoring and the Zero Product Property can be used to solve many equations of the
form x 2 + bx + c = 0.
Example 1: Solve
x
x
x 2 + 6x = 7. Check your solutions.
+ 6x = 7
+ 6x 7 = 0
Original equation
Rewrite equation so that one side equals 0.
(x 1)(x + 7) = 0
Factor.
x 1 = 0 or x + 7 = 0
Zero Product Property
x=1
x = 7
The solution set is {1, 7}. Since
Solve each equation.
2
12 + 6(1) = 7 and ( 7) + 6(7) = 7, the solutions check.
Example 2: ROCKET LAUNCH The formula h = vt 16 t 2 gives the height h of a rocket after t seconds when
the initial velocity v is given in feet per second. If a rocket is fired with initial velocity 2288 feet per second, how
many seconds will it take for the rocket to reach a height of 6720 feet?
h = vt 16 t 2
Formula
6720 = 2288t 16 t 2
0 = 16 t 2
Substitute.
+ 2288t 6720
Rewrite equation so that one side equals 0.
0 = 16(t 143t + 420)
Factor out GCF.
0 = 16(t 3)(t 140)
Factor
t 3 = 0 or t 140 = 0
t=3
Zero Product Property
t = 140
Solve each equation.
The rocket reaches 6720 feet in 3 seconds and again in 140 seconds, or 2 minutes 20 seconds after launch.
Exercises
Solve each equation. Check the solutions.
1.
0
x 2 4x + 3 = 0
4.
0
7.
=x+2
t 2 8 = 7t
2.
y 2 5y + 4 = 0
5.
8.
p2 = 9p 14
10. x 2 + 6 = 5x
+ 15 = 0
13.
= 24 10x
Use the formula h = vt 16 t 2
Chapter 1
4x = 5
11.
14.
3.
m 2 + 10m + 9 =
6.
9. 9 8x +
a2 = 11a 18
18a = 72
12x + 36 =
12.
15.
x2 = 0
y 2 8y
= 10b 16
to solve each problem.
13
Glencoe Algebra 1
NAME ______________________________________________ DATE______________________________ PERIOD ______________
16. FOOTBALL A punter can kick a football with an initial velocity of 48 feet per second. How many seconds will it
take for the ball to first reach a height of 32 feet?
17. ROCKET LAUNCH If a rocket is launched with an initial velocity of 1600 feet per second, when will the rocket be
14,400 feet high?
Chapter 1
13
Glencoe Algebra 1
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 9-4 Skills Practice: Solving Quadratic Equations by FactoringDokument8 Seiten9-4 Skills Practice: Solving Quadratic Equations by FactoringFatima AlmuheiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8-2 Study Guide and Intervention: Multiplying A Polynomial by A MonomialDokument2 Seiten8-2 Study Guide and Intervention: Multiplying A Polynomial by A MonomialDiana SolanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fractional Equations Worksheet - 2Dokument14 SeitenFractional Equations Worksheet - 2Parul AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Multi Step Equations WS3Dokument4 SeitenWorksheet Multi Step Equations WS3Suchaya AngsakulNoch keine Bewertungen
- L1 Maths Algebra WorkBookDokument37 SeitenL1 Maths Algebra WorkBookDeepak SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics - AlgebraDokument27 SeitenMathematics - AlgebraJericho EncarnacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6kuya AlvsDokument15 SeitenChapter 6kuya Alvsapi-239044897Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8-5 Skills PracticeDokument1 Seite8-5 Skills PracticeQuinn SewardNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEBEP Bridging Algebra 2Dokument8 SeitenCEBEP Bridging Algebra 2cebep math pilipinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- slws2 Oxford Answers Chapter 2 Ib Diploma SLDokument10 Seitenslws2 Oxford Answers Chapter 2 Ib Diploma SLbibabibebuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factoring quadratic expressionsDokument5 SeitenFactoring quadratic expressionsAbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiplication Properties of Exponents 2Dokument3 SeitenMultiplication Properties of Exponents 2api-307558170Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solving Equations 1: Solve Each EquationDokument18 SeitenSolving Equations 1: Solve Each EquationRuizhi WangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solving linear equations from Sekolah Dato' Abdul RazakDokument2 SeitenSolving linear equations from Sekolah Dato' Abdul RazakYusriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key in MathDokument16 SeitenAnswer Key in MathArmilyn Macasero Lubuguin100% (1)
- I.G.C.S.E. Algebra 01 Index & QuestionsDokument13 SeitenI.G.C.S.E. Algebra 01 Index & Questionsdeyaa1000000Noch keine Bewertungen
- OCR FSMQ Worked Solutions 4thDokument113 SeitenOCR FSMQ Worked Solutions 4thafaflotfi_155696459Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solving complex equationsDokument7 SeitenSolving complex equationsRuizhi WangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 8 Activity Sheet 1ST Quarter SY 2021 2022Dokument12 SeitenMath 8 Activity Sheet 1ST Quarter SY 2021 2022Angel CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math G8 Act. 1Dokument1 SeiteMath G8 Act. 1Hanna Grace SalorsanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACCUPLACER College Level Math Study GuideDokument22 SeitenACCUPLACER College Level Math Study GuideDodit FabrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Diploma Programe Standard Level Course Companion Worked Solution Chapter 1Dokument13 SeitenIB Diploma Programe Standard Level Course Companion Worked Solution Chapter 1DeeganasNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW Chapter 2Dokument15 SeitenHW Chapter 2crampingpaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra IAnswer KeyDokument7 SeitenAlgebra IAnswer KeyJalil badnasebNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATHEMATICS IN THE MODERM WORLD Module 1Dokument6 SeitenMATHEMATICS IN THE MODERM WORLD Module 1Jerusa May CabinganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Algebraaic ExpressionsDokument33 SeitenChapter 7 Algebraaic ExpressionsCik Yana100% (3)
- PUTERIDokument7 SeitenPUTERITurcu ElenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sia3e SSM 07Dokument133 SeitenSia3e SSM 07brianNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4ACh01Quadratic Equations in One UnknownDokument32 Seiten4ACh01Quadratic Equations in One UnknownPrecious GaJaNoch keine Bewertungen
- M M M M P P P P: No. Solution and Mark Scheme Sub Mark Total MarksDokument8 SeitenM M M M P P P P: No. Solution and Mark Scheme Sub Mark Total Marksjonbryan80Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exponents AND Exponential FunctionsDokument22 SeitenExponents AND Exponential FunctionsinamullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTH 100 Review Key 01Dokument24 SeitenMTH 100 Review Key 01AB876Noch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 1 Linear & Quadratic Equations GR 9GCSEDokument3 SeitenWorksheet 1 Linear & Quadratic Equations GR 9GCSEFATIMA SHARHABIL MERGHANI AHMEDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4.1 I Algebraic Expressions EnhanceDokument17 SeitenChapter 4.1 I Algebraic Expressions EnhanceMark YoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge Algebra AnswersDokument6 SeitenCambridge Algebra AnswersDinesCidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Panpac Additional Math: Worked Solutions Chapter 2 Surds, Indices and LogarithmsDokument31 SeitenPanpac Additional Math: Worked Solutions Chapter 2 Surds, Indices and LogarithmsInez SheenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Evolution of Calculus: AnswersDokument11 SeitenThe Evolution of Calculus: AnswersAtharva DesaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8-4 Study Guide and Intervention: Special ProductsDokument3 Seiten8-4 Study Guide and Intervention: Special ProductsDiana SolanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra II Review Packet EssentialsDokument9 SeitenAlgebra II Review Packet EssentialsIsrael ParraNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE-MAIN 2013: Leader & Enthusiast CourseDokument4 SeitenJEE-MAIN 2013: Leader & Enthusiast Coursesanskarid94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Past Paper Questions - SolutionsDokument28 SeitenCredit Past Paper Questions - SolutionsknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra 1 Skill BuildersDokument62 SeitenAlgebra 1 Skill Buildersfreetriala100% (1)
- 2018 MTAP Grade 8Dokument4 Seiten2018 MTAP Grade 8ginalyn100% (1)
- Solving quadratic equations using different methodsDokument31 SeitenSolving quadratic equations using different methodsKelli FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH-9-WORKSHEETDokument16 SeitenMATH-9-WORKSHEETAnie BrabangcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 10 - Algebra Expressions Test With ANSDokument14 SeitenYear 10 - Algebra Expressions Test With ANSJoseph ChengNoch keine Bewertungen
- and Give Your Answer in Its Lowest FormDokument3 Seitenand Give Your Answer in Its Lowest FormWan Nur Aida AkhmalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 8 polynomials expressionsDokument11 SeitenMath 8 polynomials expressionsElton John Santos CapiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 8 WorksheetDokument3 SeitenMathematics 8 WorksheetLabli MercadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACP Algebra 2 Final Exam Review 2023Dokument7 SeitenACP Algebra 2 Final Exam Review 2023middletown njNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 Test Study Guide: Find The Vertex and Use It To Help Sketch The Graph of Each Function. Identify The SolutionsDokument3 SeitenChapter 9 Test Study Guide: Find The Vertex and Use It To Help Sketch The Graph of Each Function. Identify The SolutionsMarissa WalczakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Binomial Theorem: New Progress in Senior Mathematics Module 2 Book 1 (Extended Part) Solution GuideDokument12 SeitenBinomial Theorem: New Progress in Senior Mathematics Module 2 Book 1 (Extended Part) Solution GuideIVANCHAN123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Factoring Practice Packet 2017-2018Dokument30 SeitenFactoring Practice Packet 2017-2018918goody0% (2)
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsVon EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Mindful Maths 1: Use Your Algebra to Solve These Puzzling PicturesVon EverandMindful Maths 1: Use Your Algebra to Solve These Puzzling PicturesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageVon EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsVon EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesVon EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finished Assignment About SetsDokument8 SeitenFinished Assignment About SetsLeodigardo BerañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 250Dokument216 SeitenMath 250omisheikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hsslive Xii Maths Ch1 Relations and FunctionsDokument4 SeitenHsslive Xii Maths Ch1 Relations and Functionsअहलावत एजुकेशन पैराडाइसNoch keine Bewertungen
- More On The Cauchy-Riemann Equations: Ryan C. DailedaDokument15 SeitenMore On The Cauchy-Riemann Equations: Ryan C. DailedaKay Chan SothearaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frenkel Introduction To Langlands ProgramDokument46 SeitenFrenkel Introduction To Langlands ProgramFernando Conde-Pumpido VelascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orthogonality-Bessel Functions-2Dokument3 SeitenOrthogonality-Bessel Functions-2mfarahat7923Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths 2007Dokument22 SeitenMaths 2007draj1875977Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vectors and MatricesDokument9 SeitenVectors and MatricesAlfaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- M 1.2 RMDokument16 SeitenM 1.2 RMk thejeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Numbers Questions With SolutionsDokument10 SeitenComplex Numbers Questions With SolutionsSankalp ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stokes' TheoremDokument8 SeitenStokes' TheoremSuyog KulkarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 (Rules of Algebraic Linear Equations)Dokument12 SeitenLesson 1 (Rules of Algebraic Linear Equations)Alvin SoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rational Numbers Class 8 WorksheetDokument5 SeitenRational Numbers Class 8 WorksheetAanya Parihar100% (1)
- Linear Algebra Cheat SheetDokument3 SeitenLinear Algebra Cheat SheetMiriam Quan100% (1)
- WewDokument11 SeitenWewSenthil AnnaunivNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 OMT 115 PDFDokument9 SeitenLecture 5 OMT 115 PDFShaboy De MarionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Set Theory PDFDokument28 SeitenMath Set Theory PDFSuryakumar GubbalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam problems with step-by-step solutionsDokument5 SeitenExam problems with step-by-step solutionssapanaNoch keine Bewertungen
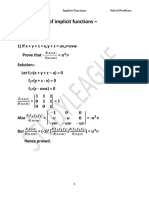
- 3.jacobians of Implicit FunctionsDokument10 Seiten3.jacobians of Implicit FunctionsShubham100% (5)
- Practice Test: Chapter 7: Counting PrinciplesDokument8 SeitenPractice Test: Chapter 7: Counting PrinciplesDoctor ViddaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Divided Difference Formula ExplainedDokument3 SeitenNewton's Divided Difference Formula ExplainedAnik AhamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yusuf Khan - INFINITE SERIES 2019-05-28-1Dokument9 SeitenYusuf Khan - INFINITE SERIES 2019-05-28-1Ritoprovo RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMT-002 2012Dokument5 SeitenMMT-002 2012arocalistus6367Noch keine Bewertungen
- Woking Days TimetableDokument5 SeitenWoking Days TimetableebiadaikalarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Budget of Lesson in Gen - Mathematics 11Dokument6 SeitenBudget of Lesson in Gen - Mathematics 11Eric ManotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handouts General MathematicsDokument70 SeitenHandouts General Mathematicskhalid4vuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feedback and Control Systems Laboratory: ECEA107L/E02/2Q2021Dokument42 SeitenFeedback and Control Systems Laboratory: ECEA107L/E02/2Q2021Kim Andre MacaraegNoch keine Bewertungen
- STD 9th Perfect Mathematics 1 Notes English Medium MH Board PDFDokument26 SeitenSTD 9th Perfect Mathematics 1 Notes English Medium MH Board PDFvitthal sawantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratic Equations - DPP 01 (Of Lec 01) - (Arjuna JEE 2023)Dokument3 SeitenQuadratic Equations - DPP 01 (Of Lec 01) - (Arjuna JEE 2023)sohamrastogi26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Logarithms Formula SheetDokument1 SeiteLogarithms Formula Sheetsethi100% (3)