Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
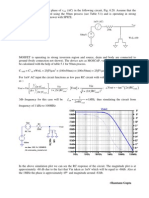
Characteristics
Hochgeladen von
Divya Shettigar0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
4 Ansichten2 SeitenDiode Voltages
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenDiode Voltages
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
4 Ansichten2 SeitenCharacteristics
Hochgeladen von
Divya ShettigarDiode Voltages
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
Characteristics
Threshold
Voltage
Ideal Diode
Coventional Diode
Conventional diodes do have a threshold voltage.
This is the voltage which must be supplied to the
diode for it to conduct any considerable forward
current. For silicon diodes, the threshold voltage is
approximately 0.7V. For germanium diodes, it is
approximately 0.3V. This voltage is needed
Ideal diodes do not have a
so that the electrons of the n junction can have
threshold voltage. Once any
enough push to break the barrier in between and
forward voltage is applied
cross over into the p junction. This is how current
across the diode, it will
flows in a diode. Any voltage below the threshold
conduct current instantly
voltage will not be sufficient to push the electrons
across its junctions.
through from one barrier to the next. You can see
this marked on the diode characteristics curve.
Before the threshold point, very little current flows
across the diode. However,
after the diode receives a voltage above this, it
produces considerable current flow.
Ideal diodes have infinite
forward current when any
forward voltage is applied
across their terminals. This is
because in the ideal
condition, the internal
resistance of the diode would
Forward Current
be 0. The diode would have
no internal resistance at all.
Since current, I=V/R, an
infinite amount of current
would be conducted and
supplied to a circuit with an
ideal diode.
Conventional diodes conduct a large current when
forward voltage above its threshold voltage is
supplied to the diode, but it is still a finite amount of
current. Conventional diodes, even though small,
still have internal resistance. It is impossible to
create any physical component that does not have
some internal resistance. The resistance ensures
that the current will be finite in nature and cannot be
infinite.
Breakdown
Voltage
Ideal diodes do not have a
breakdown voltage. This is
because ideal diodes have
infinite resistance to reverse
voltage. It will not conduct
any current at all when
voltage is applied in reverse,
no matter how great the
voltage is.
Conventional diodes do have a breakdown voltage.
This is the reverse voltage that when applied to the
diode will cause the diode junctions to break down
and conduct a large amount of current, even though
the voltage is applied with incorrect polarity. A diode
should not conduct current when voltage is applied
the wrong way. However, after a certain point,
called the breakdown point, it will give way and
conduct.
Reverse
(leakage)
Current
Since an ideal diode does
A conventional diode will conduct some leakage
not have a breakdown point, current even when reverse voltage is applied, even
it never conducts any
when the reverse voltage hasn't reach the
reverse current, called
leakage current. It is a
perfect insulator when
voltage is applied in reverse.
breakdown point. After the breakdown voltage is
reached, it will conduct a large amount of current,
called avalanche current, in reverse. This is
because a conventional diode can never be a
perfect insulator and will give way if enough reverse
voltage is supplied to it.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- 10n65a 10n65afDokument6 Seiten10n65a 10n65afYeo LeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Fabrication of A 2-Bit ComparatorDokument23 SeitenDesign and Fabrication of A 2-Bit ComparatorKendra KruegerNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGBT Behavior Under Short Igbt ShortoffDokument3 SeitenIGBT Behavior Under Short Igbt ShortoffAndré OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar Power Charge Controller Seminar PresentationDokument16 SeitenSolar Power Charge Controller Seminar PresentationPravat SatpathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Si7615adn MosfetDokument13 SeitenSi7615adn MosfetahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Microelectronics Solutions Chapter 5 PDFDokument3 SeitenFundamentals of Microelectronics Solutions Chapter 5 PDFHARIKA REDDY0% (1)
- NandhiniDokument11 SeitenNandhiniSravan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logic Families and Programmable Logic DevicesDokument3 SeitenLogic Families and Programmable Logic DevicesDei PehNoch keine Bewertungen
- FET - Inverter12v - IRF740Dokument9 SeitenFET - Inverter12v - IRF740Macuco CamNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDC Lesson Plan NewDokument26 SeitenPDC Lesson Plan NewVenky VenkateshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improving BEOL For Sub 10nm Nodes PDFDokument39 SeitenImproving BEOL For Sub 10nm Nodes PDFGabriel DonovanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo Led CompletoDokument20 SeitenCatalogo Led CompletoketocNoch keine Bewertungen
- BC548 Transistor Pinout, Equivalent, Working As Amplifier-Switch & DatasheetDokument12 SeitenBC548 Transistor Pinout, Equivalent, Working As Amplifier-Switch & DatasheetAderinla OkeowoNoch keine Bewertungen
- VLSI Companies PDFDokument4 SeitenVLSI Companies PDFm.sreenivasulu yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finfet: Soi and The Non-Planar Finfet DeviceDokument34 SeitenFinfet: Soi and The Non-Planar Finfet Devicesandeeppareek926100% (1)
- VLSI Interview QuestionsDokument19 SeitenVLSI Interview QuestionssamNoch keine Bewertungen
- BJT Fabrication 2018Dokument13 SeitenBJT Fabrication 2018عہۣۗثہۣۗمہۣۗان الہۣۗضہۣۗاحہۣۗيNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Report Cover SheetDokument6 SeitenLaboratory Report Cover SheetPre DatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Description Features: LTC485 Low Power RS485 Interface TransceiverDokument14 SeitenDescription Features: LTC485 Low Power RS485 Interface Transceivergreemax100% (1)
- Types of DiodeDokument30 SeitenTypes of DiodeJozueuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transistor CookbookDokument6 SeitenTransistor CookbookShahid SiddiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- APM4953 Dual P-Channel Enhancement Mode Mosfet: FeaturesDokument7 SeitenAPM4953 Dual P-Channel Enhancement Mode Mosfet: FeaturesАндрей ПоляковNoch keine Bewertungen
- 66thECTC Panel KimSKHynix PDFDokument11 Seiten66thECTC Panel KimSKHynix PDF黃冠旗Noch keine Bewertungen
- PS2239 Flash Support List - 2009.08.27-1Dokument10 SeitenPS2239 Flash Support List - 2009.08.27-1Davod AmirajamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cmos Sequential CircuitsDokument33 SeitenCmos Sequential Circuitslachuns123Noch keine Bewertungen
- BSIM3v3.1 Model Parameters Extraction and OptimizationDokument18 SeitenBSIM3v3.1 Model Parameters Extraction and OptimizationMohsen RadfarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article Detail RoutingDokument2 SeitenArticle Detail RoutingmanojkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solns 6Dokument11 SeitenSolns 6ramprakash_rampelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3: Bipolar Junction TransistorDokument85 SeitenChapter 3: Bipolar Junction TransistorAnonymous m4MF1g100% (2)
- Introduction To Cmos Vlsi Design: Unit 1Dokument37 SeitenIntroduction To Cmos Vlsi Design: Unit 1raghava06Noch keine Bewertungen