Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chapter 8
Hochgeladen von
Dimple ArriesgadoCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 8
Hochgeladen von
Dimple ArriesgadoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
8/2/16
Animal Tissues and
Organ Systems
Stem Cell Research
Stem cells remarkable potential
internal repair system
Important for the maintenance and
repair of bodily tissues and organs.
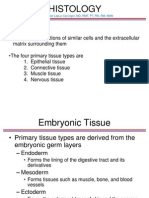
Tissues to Organs
Tissue - interacting cells
- extracellular
- one or more specialized tasks.
Four types of tissues:
Epithelial Tissues
Connective Tissues
Muscle Tissues
Nervous Tissues
Tissues to Organs
Organs - structural unit of two or more tissues
- specific organization
- specialized functions
Organ systems two or more organs
physical and chemical
interaction
8/2/16
Cell Junctions
Epithelial Tissues
Epithelial tissues covers outer body surfaces
- lining of the internal cavity
Classified according to SHAPE:
1.Squamous
2.Cuboidal
3.Columnar
Classified according to NUMBER OF LAYERS:
1.Simple epithelium
2.Stratified epithelium
Epithelial Tissues
Glandular Epithelium
Glands only present in epithelial tissues
- produce and secrete substances onto the skin,
into a body cavity or interstitial fluid
Two types:
1.Exocrine glands
2.Endocrine glands
8/2/16
Connective Tissues
Connective Tissues
Connective tissues connects body parts
- structural and functional support
- extracellular matrix ( own secretions)
Classified by cell type and extracellular matrix composition.
Two types of soft connective tissues:
1.Loose
2.Dense
Loose Connective Tissues
Dense Regular Connective Tissues
Collagen fibers
Fibroblast nuclei
Fibroblast nuclei
Collagen fibers
Elastic fibers
8/2/16
Dense Irregular Connective Tissues
Fibroblast nuclei
Collagen fibers
Specialized Connective Tissues
Types of specialized connective tissues:
1. Cartilage tissues
2. Adipose tissues
3. Bone tissues
4. Blood tissues
Cartilage
Adipose
Perichondrium
Hyaline matrix
Adipocytes
Nucleus of
adipose
cells
Chondrocytes
8/2/16
Bone
Blood
Haversian
canal
osteocytes
Canaliculus
Muscle Tissues
Types of Muscle Tissues
Muscle tissues made of cells that can contract.
Three types of muscle tissues:
1.Skeletal muscle
2.Cardiac muscle
3.Smooth muscle
8/2/16
Vertebrates
Humans is a member of the Phylum Chordata (called
chordates).
All chordates have a structure called a notochord.
A notochord is a flexible, rod-shaped structure found
in the embryos of all chordates.
Vertebrates
All vertebrates have an internal skeleton for
support, protection, and a place for
muscles to be attached.
The bones and muscles of vertebrates work
together to provide a structural framework
for movement.
Vertebrates
All vertebrates have a
backbone and a skull.
The backbone is a
segmented column of
interlocking bones called
vertebrae.
Vertebrates
All vertebrates have a
body cavity that holds the
organ systems.
Thoracic cavity
Abdominal cavity
8/2/16
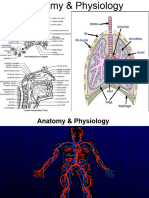
Vertebrate Organ Systems
Vertebrate Organ Systems
Nervous Tissues receives and transmits impulses
- consist of neuron (signalling cells)
Add nervous tissue picture
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksVon EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Cells Powerpoint CarpenterDokument37 SeitenCells Powerpoint CarpenterJervin EleydoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master File - ChronicDokument671 SeitenMaster File - ChronicsubhojitnayekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell DiversityDokument3 SeitenCell DiversityMrGilmartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Physiology: Ethem Gelir, M.D., Assoc. Prof. of PhysiologyDokument26 SeitenIntroduction To Physiology: Ethem Gelir, M.D., Assoc. Prof. of PhysiologyMohmed El King100% (1)
- Module 4-Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDokument55 SeitenModule 4-Tissues, Glands, and MembranesGlory MuedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Physiology 1Dokument53 SeitenIntro To Physiology 1Lemma Deme ResearcherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen. Bio ReviewerDokument4 SeitenGen. Bio ReviewerXyrish TripulcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Animal Body and Principles of RegulationDokument39 SeitenThe Animal Body and Principles of RegulationSweet EmmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- LSM1301 Animal Form and FunctionDokument13 SeitenLSM1301 Animal Form and FunctionantheaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Anatomy, Chapter 1: Outline of Class Notes Objectives: After Studying This Chapter You Should Be Able ToDokument13 SeitenIntroduction To Anatomy, Chapter 1: Outline of Class Notes Objectives: After Studying This Chapter You Should Be Able ToAesthethic finds100% (1)
- Grade 8 Science Unit 4: "Cells, Tissues, Organs & Systems"Dokument27 SeitenGrade 8 Science Unit 4: "Cells, Tissues, Organs & Systems"Wilson ZhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Lecture PPTDokument46 Seiten04 Lecture PPTSam Tagarda100% (1)
- Tissue: The Living Fabric: Chapter 4 - Part ADokument6 SeitenTissue: The Living Fabric: Chapter 4 - Part AJonathan HigginbothamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell To Organism NoteDokument3 SeitenCell To Organism NoteIshani Anushika JayakodyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 - Bio SyllabusDokument13 SeitenModule 2 - Bio SyllabusChamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Animal TissuesDokument53 Seiten1.1 Animal TissuesEva NatashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnaPhy 3 TissuesDokument42 SeitenAnaPhy 3 TissuesFeah DaydayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDokument11 SeitenChapter 4 Tissues, Glands, and MembranesMaria Angela Del Gallego100% (2)
- Lecture VII. General Principles of Tissue Organization. EpitheliumDokument4 SeitenLecture VII. General Principles of Tissue Organization. EpitheliumExton JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diff Types of Animal TissueDokument31 SeitenDiff Types of Animal TissueJames Patrick Milan100% (1)
- Cell Structure.Dokument9 SeitenCell Structure.Feranmi AkinboboyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Module 2 Study NotesDokument41 SeitenBiology Module 2 Study NotesKatie BellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Morphology and Physiology: CellsDokument57 SeitenMorphology and Physiology: CellsDiana Mae Caigas SimbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.animal TissuesDokument50 Seiten2.animal TissuesAhmed OrabyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal TissueDokument28 SeitenAnimal TissueArjunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Architectural Pattern of An AnimalDokument47 SeitenArchitectural Pattern of An AnimalRacky SabidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- M2 NQ 8 F1 U LUt P@pho T0 ERx Z6 VVQ ZTTS28 QTF SNGD 9 e 68!Dokument3 SeitenM2 NQ 8 F1 U LUt P@pho T0 ERx Z6 VVQ ZTTS28 QTF SNGD 9 e 68!deep.deepkNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Dokument33 SeitenThe Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Maira Garcia C.100% (2)
- Final Term - ZoologyDokument21 SeitenFinal Term - ZoologyJustin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell OrganisationDokument32 SeitenCell OrganisationAtifah ZulaikhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Levels of OrganizationDokument2 SeitenLevels of OrganizationDonalyn Veruela AbonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology I - Lecture Notes - IntroductionDokument51 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology I - Lecture Notes - IntroductionNgoc TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form1 Integrated Science "Cells, Tissues, Organs & Systems"Dokument14 SeitenForm1 Integrated Science "Cells, Tissues, Organs & Systems"Victoria RampersadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 - Revision NotesDokument32 SeitenClass 11 Biology Chapter 7 - Revision Notesshusa harsha100% (1)
- Tissue Structure & FunctionDokument74 SeitenTissue Structure & FunctionTaufiqurrahman Sidqi100% (1)
- The Human BodyDokument35 SeitenThe Human BodyDon Chiaw ManongdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epithelial HighlightedDokument33 SeitenEpithelial HighlightedharizgaleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family: Other Images Provided by Science: A Closer Look (Maryland), Pages 28 and 30 (Macmillan/Mcgraw-Hill, 2008)Dokument49 SeitenFamily: Other Images Provided by Science: A Closer Look (Maryland), Pages 28 and 30 (Macmillan/Mcgraw-Hill, 2008)Zay SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Systems: OrganizationDokument23 SeitenAnimal Systems: OrganizationEugine QuirozNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 1 Intoduction To Human Body 2022Dokument54 SeitenCHAPTER 1 Intoduction To Human Body 2022Adlyn Shaheera100% (1)
- Animal TissueDokument47 SeitenAnimal TissueJoshua Verzosa PalconitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Animal Tissues: Dr. AarifDokument60 SeitenStudy of Animal Tissues: Dr. AarifEntirety 4uNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Levels of Organization 2024 (Lecture)Dokument26 SeitenFinal Levels of Organization 2024 (Lecture)rk4876001Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Animal's Specialized StructuresDokument58 Seiten1.1 Animal's Specialized StructuresNathaliabee100% (1)
- Updated-Pbl Content Invesitgation Bodies and SystemsDokument5 SeitenUpdated-Pbl Content Invesitgation Bodies and Systemsapi-535089620Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Notes Week3Dokument18 SeitenAnatomy Notes Week3Zainab Ali100% (1)
- The Body OrganizationDokument21 SeitenThe Body OrganizationijahsmkutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphysio Orientation 2021 Unit 1Dokument79 SeitenAnaphysio Orientation 2021 Unit 1eizyllebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epithelial TissueDokument10 SeitenEpithelial TissueMichael NyaongoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesDokument11 SeitenCH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesRishabh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology - 4th SemDokument76 SeitenPhysiology - 4th SemSandeep AdapalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDokument6 SeitenStructural Organisation in AnimalsbasheerskNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology Lecture 4Dokument27 SeitenPhysiology Lecture 4Muhammad Khubaib AzeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Physiology?: The Study of Biological FunctionDokument14 SeitenWhat Is Physiology?: The Study of Biological FunctionDamian HamzahNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are The Four Basic Types of Tissues That Make Up The Human Body?Dokument47 SeitenWhat Are The Four Basic Types of Tissues That Make Up The Human Body?SireRyūjinSkylerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin Body Tissues and MembraneDokument50 SeitenSkin Body Tissues and MembraneNaanmatha PuspanathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epithelial TissueDokument26 SeitenEpithelial Tissueaimi BatrisyiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDokument19 SeitenStructural Organisation in AnimalsBiju Mylachal100% (1)
- Review in Science Circulatory System PulmonaryDokument3 SeitenReview in Science Circulatory System PulmonaryElvie Jane P. MolatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Respiratory Obstruction On The Arterial and Venous Circulation in Animals and ManDokument11 SeitenEffect of Respiratory Obstruction On The Arterial and Venous Circulation in Animals and ManlaughAndCry72Noch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment and Activity CellDokument4 SeitenExperiment and Activity CellPang ChixxNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Singh Vol-2Dokument387 SeitenIB Singh Vol-2dannyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy AND Physiology: The Human As An OrganismsDokument26 SeitenAnatomy AND Physiology: The Human As An OrganismsJake Donely C. PaduaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICSE QUESTION PAPER Biology 2010 Class 10 PDFDokument11 SeitenICSE QUESTION PAPER Biology 2010 Class 10 PDFLokesh MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Endoplasmic ReticulumnDokument7 Seiten04 Endoplasmic ReticulumnMian SahibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology in Pregnancy & Coagulation Failure in PregnancyDokument30 SeitenImmunology in Pregnancy & Coagulation Failure in PregnancySrikutty DevuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 TH Science Practical Guide EM PDFDokument15 Seiten10 TH Science Practical Guide EM PDFSRI VISHNUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of The Alimentary System - IDokument27 SeitenDevelopment of The Alimentary System - Iمعاذ القحطانيNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cystotomy 37 LDokument19 SeitenCystotomy 37 LDr Anais AsimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medico Legal CertificateDokument2 SeitenMedico Legal CertificateJoanne besoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Neurologic ExaminationDokument38 SeitenIntroduction To The Neurologic ExaminationYudhistira YuliandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroglossal Duct Cysts: Anatomy, Embryology and TreatmentDokument7 SeitenThyroglossal Duct Cysts: Anatomy, Embryology and TreatmentTasia RozakiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Share Q1 M3-W3 Gen Biology 1Dokument8 SeitenShare Q1 M3-W3 Gen Biology 1Kei VenusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dent I No GenesisDokument14 SeitenDent I No Genesisandre gidion laseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal Delivery Checklist 2020Dokument4 SeitenNormal Delivery Checklist 2020Ever Seneca EscaLeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of Teeth: Khushi Desai III BDS 808Dokument36 SeitenStructure of Teeth: Khushi Desai III BDS 808Khushi DesaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 1Dokument35 SeitenExercise 1Van Labasano67% (3)
- MVW 020Dokument9 SeitenMVW 020SofyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gesc 107Dokument12 SeitenGesc 107Nippu SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HLTAAP002 Student Assessment Task 1 - QuestioningDokument18 SeitenHLTAAP002 Student Assessment Task 1 - QuestioningMuskan Sohal0% (1)
- Histologie Généralité Et Tissu Epithelume PDFDokument2 SeitenHistologie Généralité Et Tissu Epithelume PDFشكوب ستانNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple MyelomaDokument28 SeitenMultiple Myelomamedical notes100% (1)
- Appearances - How To Describe Someone in EnglishDokument26 SeitenAppearances - How To Describe Someone in EnglishNadia Tara DilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Skin: The Morphologic Background of The Normal MammogramDokument10 SeitenThe Skin: The Morphologic Background of The Normal MammogramzixdiddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of Microcirculation: DR AnupamaDokument93 SeitenPhysiology of Microcirculation: DR AnupamaMuskan RastogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rishikesh Seminar Content - SSSOHADokument13 SeitenRishikesh Seminar Content - SSSOHARabindra DhitalNoch keine Bewertungen
- VI 8 Body MovementsDokument16 SeitenVI 8 Body MovementsManisha VarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 8 Digestive System: StructuresDokument18 SeitenCH 8 Digestive System: StructuresBheru LalNoch keine Bewertungen