Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lecture 8: Examples: Module 3: Hydrostatic Forces On Submerged Bodies
Hochgeladen von
Vamsee KiranOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lecture 8: Examples: Module 3: Hydrostatic Forces On Submerged Bodies
Hochgeladen von
Vamsee KiranCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Objectives_template
Module 3: Hydrostatic forces on submerged bodies
Lecture 8: Examples
Examples on forces on stationary submerged bodies
file:///D|/Web%20Course/Dr.%20Nishith%20Verma/local%20server/fluid_mechanics/lecture8/8_1.htm[5/9/2012 3:06:06 PM]
Objectives_template
Module 3: Hydrostatic forces on submerged bodies
Lecture 8: Examples
Examples on forces on stationary submerged bodies
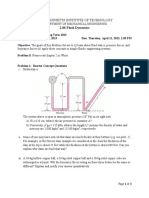
Example1:
See the drawing below. A tank is filled with water. At the bottom of the tank, a gate AB is hinged at
A. To keep the gate in place, a vertical force,
Compute
is applied at the distance of 1m from the hinge.
. Given g =10 m/s2 . The width of the gate is 2 m.
(Fig. 8a)
Weight of water over AB will make the gate open in the clockwise direction. F acting vertically
upward will keep the gate in place (rotational equilibrium). Note that the weight of the water-column
of height 3 m will be acting on the gate and be uniform.
Therefore,
And, this force will act at a distance of 0.75 m from A.
(Moment about A)
(Fig. 8b)
file:///D|/Web%20Course/Dr.%20Nishith%20Verma/local%20server/fluid_mechanics/lecture8/8_2.htm[5/9/2012 3:06:06 PM]
Objectives_template
Module 3: Hydrostatic forces on submerged bodies
Lecture 8: Examples
Example 2:
Consider a vertical water-gate AB of height 2 m hinged at O, the center of the gate. Determine the
horizontal force
required to hold the gate in place. The gate is 1 m wide.
(Fig. 8c)
Consider the section AO (above the hinge). The hydrostatic pressure-force acting horizontally will
make the gate rotate in the clockwise direction, whereas that below the hinge O will make the gate
rotate in the anti-clockwise direction. Take moment about O of these forces and equate to that of F:
(Fig. 8d)
file:///D|/Web%20Course/Dr.%20Nishith%20Verma/local%20server/fluid_mechanics/lecture8/8_3.htm[5/9/2012 3:06:07 PM]
Objectives_template
Module 3: Hydrostatic forces on submerged bodies
Lecture 8: Examples
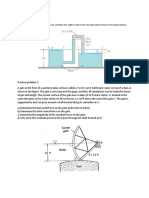
Example 3:
See the figure below. On one-side of the wall, AB, are filled two immiscible liquids, oil and water.
Calculate the horizontal force acting on the wall. Plot pressure-distribution. Assume the width of the
wall = 0.5 m
(Fig. 8e)
Horizontal force acting on AO
file:///D|/Web%20Course/Dr.%20Nishith%20Verma/local%20server/fluid_mechanics/lecture8/8_4.htm[5/9/2012 3:06:07 PM]
Objectives_template
Module 3: Hydrostatic forces on submerged bodies
Lecture 8: Examples
Horizontal force acting on OB
Pressure-distribution is linear
(Fig. 8f)
file:///D|/Web%20Course/Dr.%20Nishith%20Verma/local%20server/fluid_mechanics/lecture8/8_5.htm[5/9/2012 3:06:07 PM]
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisVon EverandThe Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 3 Hydrostatic Forces On Submerged SurfacesDokument5 SeitenSheet 3 Hydrostatic Forces On Submerged SurfacesMohamed EzzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 206 Spring 2013 PDFDokument37 Seiten206 Spring 2013 PDFcombatps133% (3)
- Assignment (3) Fluid Statics (Hydrostatic Force On A Plane Surface)Dokument3 SeitenAssignment (3) Fluid Statics (Hydrostatic Force On A Plane Surface)Mahmoud EmamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group Assignment IDokument5 SeitenGroup Assignment Ilelisagetachew90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mek 307 - HW1Dokument3 SeitenMek 307 - HW1ozan_k_1989Noch keine Bewertungen
- Universiti Tunku Abdul RahmanDokument6 SeitenUniversiti Tunku Abdul RahmanfreeloadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrostatic Force On Curved SurfacesDokument14 SeitenHydrostatic Force On Curved Surfaceseric labordoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Dynamics - MITDokument6 SeitenFluid Dynamics - MITPlatoon Nicart BejerNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEP10L ProbSet 2Dokument4 SeitenCEP10L ProbSet 2Karl MacalindongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Booklet (Printable) PDFDokument8 SeitenBooklet (Printable) PDFMarben Leynes-Cereno Agustin-ViernesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Questions DR YuanDokument5 SeitenPractice Questions DR YuanSteven KuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Finite Element Analysis of in Situ - 2001 - Elsevier Ocean EngineeringDokument11 SeitenChapter 7 Finite Element Analysis of in Situ - 2001 - Elsevier Ocean EngineeringL KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrau 1Dokument3 SeitenHydrau 1Mayya BonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics Lesson 3 PDFDokument5 SeitenFluid Mechanics Lesson 3 PDFALEX CLYDE TUBIANOSANoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics Lesson 3Dokument5 SeitenFluid Mechanics Lesson 3AlejandroGonzaga63% (8)
- Fluid Mechanics Lesson 3 PDF FreeDokument5 SeitenFluid Mechanics Lesson 3 PDF FreeKristelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 Fluids and Hydraulics Problem 1Dokument5 SeitenModule 3 Fluids and Hydraulics Problem 1cjrate gamboaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics Lesson 3 PDF FreeDokument5 SeitenFluid Mechanics Lesson 3 PDF FreeKristelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universiti Tunku Abdul RahmanDokument15 SeitenUniversiti Tunku Abdul RahmanfreeloadNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC222 - 5 Fluid Mechanics QP - Amrita UniversityDokument4 SeitenMEC222 - 5 Fluid Mechanics QP - Amrita UniversityAkshay RajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave Loads On Exposed Jetties: Description of Large Scale Experiments and Preliminary ResultsDokument12 SeitenWave Loads On Exposed Jetties: Description of Large Scale Experiments and Preliminary ResultsSwamy ManiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1Dokument4 SeitenTutorial 1nurulzamrinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics ProblemsDokument3 SeitenFluid Mechanics ProblemsTaker BloodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Statics ExerciseDokument5 SeitenFluid Statics ExercisechitooNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 2-AnalysisofgravitydamDokument12 Seiten2 2-AnalysisofgravitydammorganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics July 2013Dokument0 SeitenFluid Mechanics July 2013Prasad C MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment I SKPU1123 1213 2Dokument4 SeitenAssignment I SKPU1123 1213 2Rajab AliNoch keine Bewertungen
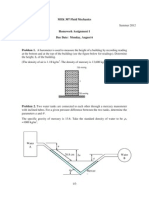
- MM204 Assn3 2017Dokument5 SeitenMM204 Assn3 2017jayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Force On A BendDokument6 SeitenFluid Force On A Bendwild2west919670Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 - CE2040Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 1 - CE2040AshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ece 2203 Assign Ii-2011Dokument2 SeitenEce 2203 Assign Ii-2011Benson Mwathi MungaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- FlowMaster Course - Assignments - 10Qs - 2023 PDFDokument3 SeitenFlowMaster Course - Assignments - 10Qs - 2023 PDFRamil EnsarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech280final 2013Dokument14 SeitenMech280final 2013manrabrarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Book/Notes: First Page of Your Submission and Sign It ThereDokument5 SeitenOpen Book/Notes: First Page of Your Submission and Sign It ThereRobert BuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGR 312-Laboratory 8 Force On A Sluice Gate: ObjectiveDokument4 SeitenENGR 312-Laboratory 8 Force On A Sluice Gate: ObjectiveMuhammad Ali HafeezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids-Chapter 3-Tutorial-1Dokument11 SeitenFluids-Chapter 3-Tutorial-1phizygNoch keine Bewertungen
- BW Version Ecw211 4 Hydrostatic ForcesDokument26 SeitenBW Version Ecw211 4 Hydrostatic ForcesdlraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce371 Home ExercisesDokument11 SeitenCe371 Home ExercisesEnes YavuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mecánica de Fluidos. Taller N 2 (2019-1)Dokument4 SeitenMecánica de Fluidos. Taller N 2 (2019-1)Juan ClavijoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz No 1 Dams, Gates, and Outlet Works (Hydraulics)Dokument3 SeitenQuiz No 1 Dams, Gates, and Outlet Works (Hydraulics)Erwin Jed RachoNoch keine Bewertungen
- (3 Marks) : CIVE2010 Introduction To Water EngineeringDokument7 Seiten(3 Marks) : CIVE2010 Introduction To Water EngineeringtoshugoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM 10CV35 Question PapersDokument11 SeitenFM 10CV35 Question PapersShesha Prakash M NNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALA 1 Chapter 9 - Fluid DynamicsDokument9 SeitenALA 1 Chapter 9 - Fluid Dynamicsphoenix eastwoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cve 240-Assignment 3 - Chapter 3Dokument2 SeitenCve 240-Assignment 3 - Chapter 3Ehab WilsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- #3 Fluid MechanicsDokument9 Seiten#3 Fluid MechanicsRom PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- FMDokument13 SeitenFMSaurabh TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Behaviour of Monopile and Suction Bucket Foundation Systems For Offshore Wind Energy PlantsDokument10 SeitenBehaviour of Monopile and Suction Bucket Foundation Systems For Offshore Wind Energy PlantsDang Quang MinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbstractDokument9 SeitenAbstractEssam Ahmed Abd MeguidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics Problems For Students Ch1-2Dokument19 SeitenFluid Mechanics Problems For Students Ch1-2Adulayasak SeangklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce2202 - Mechanics of FluidsDokument3 SeitenCe2202 - Mechanics of FluidsPrashant GaradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instructions: Analyze and Answer Each of The Following Problems. Show Your Complete Solutions WithDokument8 SeitenInstructions: Analyze and Answer Each of The Following Problems. Show Your Complete Solutions WithMarben Leynes-Cereno Agustin-ViernesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marine Hydrodynamics 1: Sheets BookletDokument13 SeitenMarine Hydrodynamics 1: Sheets BookletKhalid BaragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sloshing Article Final VersionDokument7 SeitenSloshing Article Final VersionDanielGuimarãesCostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homeworks 1-10 PDFDokument95 SeitenHomeworks 1-10 PDFWendy LinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thapar University, Patiala Department of Chemical EngineeringDokument2 SeitenThapar University, Patiala Department of Chemical EngineeringsahibjotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech280final 2012Dokument14 SeitenMech280final 2012manrabrarNoch keine Bewertungen
- WAE Assignment 2018 - UpdatedDokument4 SeitenWAE Assignment 2018 - UpdatedCarl MigaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- U B y B y U: 057:20 TEST # 1 October 2Dokument1 SeiteU B y B y U: 057:20 TEST # 1 October 2Akram AlgerianooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compilation of Solved ProblemsDokument7 SeitenCompilation of Solved ProblemsyslovillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen