Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
E&M Sheet
Hochgeladen von
timvrghsOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
E&M Sheet
Hochgeladen von
timvrghsCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT
Coding and Documentation Reference Guide
CPT codes, descriptions, and other data only are copyright 2008 American Medical
Association. All rights reserved. Applicable FARS/DFARS clauses apply.
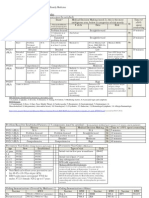
HISTORY
HPI (History of Present Illness): Characterize HPI by considering either the Status of chronic conditions or
the number of elements recorded.
1 condition
2 conditions
3 conditions
OR
Location
Severity
Timing
Modifying factors
Quality
Duration
Context
Associated signs and symptoms
ROS (Review of Systems):
Constitutional
Ears, nose,
(wt loss, etc.)
mouth, throat
Eyes
Card/vasc
GI
GU
Musculo
Resp
Integumentary
(skin, breast)
Neuro
Psych
Endo
Hem/lymph
All/immuno
Status of
3 chronic
conditions
Status of
3 chronic
conditions
Brief (13)
Extended
(4 or more)
Extended
(4 or more)
N/A
PFSH (Past, Family, Social History):
Past history (the patients past experiences with illnesses, operations, injuries and treatments)
Family history (a review of medical events in the patients family, including diseases that may be hereditary or
place the patient at risk)
Social history (an age-appropriate review of past and current activities)
*Complete PFSH:
Status of
Status of
12 chronic 12 chronic
conditions conditions
Pertinent to
Extended
problem (Pert and others)
(1 system) (29 systems)
N/A
2 history areas: a) established patients office (outpatient) care, domiciliary care, home care;
b) emergency department; c) subsequent nursing facility care; and, d) subsequent hospital
care.
N/A
EXP.
PROBLEMPROBLEMFOCUSED
FOCUSED
3 history areas: a) new patients office (outpatient) care, domiciliary care, home care;
b) consultations; c) initial hospital care; d) hospital observation; and, e) initial nursing facility
care.
Brief (13)
Complete
(Pert and all
others)
(10 systems)
Pertinent
(1 history area)
*Complete
(2 or 3 history
areas)
DETAILED
COMPREHENSIVE
Final History requires all 3 components
above met or exceeded
EXAMINATION
CPT Exam Description
95 Guideline Requirements
97 Guideline Requirements
One body area or organ system
15 bulleted elements
PROBLEM-FOCUSED EXAM
Affected body area or organ system and other symptomatic or
related organ systems
27 body areas and/or organ
systems
611 bulleted elements
EXPANDED
PROBLEM-FOCUSED EXAM
Extended exam of affected body area or organ system and
other symptomatic or related organ systems
27 body areas and/or organ
systems
1217 bulleted elements for
2 or more systems
DETAILED EXAM
General multi-system
8 or more body areas and/or
organ systems
18 or more bulleted elements for
9 or more systems
Not defined
See requirements for individual
single system exams
Limited to affected body area or organ system
Complete single organ system exam
CPT Type of Exam
COMPREHENSIVE EXAM
MEDICAL DECISION-MAKING
Instructions for Using TrailBlazers MDM Coding Method
Coding Medical Decision-Making (MDM) begins with separately coding the three distinct components of MDM. Two of the three components determine the final level of MDM
complexity documented in a record of Evaluation and Management (E/M) service. These components are:
1.
Number of diagnoses and/or management options.
2.
Amount and/or complexity of data reviewed or ordered.
3.
Risk of complication and/or mortality.
The TrailBlazer MDM coding method corresponds directly to the components above as follows:
Section A corresponds to number of diagnoses and/or management options.
Section B corresponds to amount and/or complexity of data reviewed or ordered.
Section C corresponds to risk of complication and/or mortality.
Code each component separately using respective Tables AC, then compare results from Tables AC to requirements in Table D to determine the overall MDM level.
Section A
Coding Number of Diagnoses or Management Options Use the Tables A.1 and A.2 on page 2 to determine the numbers of diagnoses or management options.
Note: In all cases, the information in the clinical record (history and physical) must clearly support diagnostic impressions. Diagnostic impressions listed but not supported
elsewhere in the clinical record must not be included in the problem list for coding purposes.
Revised September 2009
Page 1
Continued
MEDICAL DECISION-MAKING (continued)
Determine total points for each diagnosis or problem and associated management options using Tables A.1 and A.2. Use the larger of the two Totals for Section D. Final
Assignment of Medical Decision Making Type.
Table A.2 Management Options
Table A.1 Number of Diagnoses
A problem is defined as definitive diagnosis or,
for undiagnosed problems, a related group of
presenting symptoms and/or clinical findings.
Each new or established problem for which the
diagnosis and/or treatment plan is evident with or
without diagnostic confirmation
2 plausible differential
diagnoses, comorbidities or
complications (not counted
as separate problems)
clearly stated and supported
by information in record:
requiring diagnostic
evaluation or confirmation
Each new or
established
problem for which
the diagnosis
and/or treatment
plan is not evident
3 plausible differential
diagnoses, comorbidities or
complications (not counted
as separate problems)
clearly stated and supported
by information in record:
requiring diagnostic
evaluation or confirmation
4 or more plausible
differential diagnoses,
comorbidities or
complications (not counted
as separate problems)
clearly stated and supported
by information in record:
requiring diagnostic
evaluation or confirmation
Total Points
Important Note:
Points
These tables are not all inclusive. The entries are examples
of commonly prescribed treatments and the point values are
illustrative of their intended quantifications. Many other
treatments exist and should be counted when documented.
Points
Do not count as treatment options notations such as: Continue same therapy or
no change in therapy (including drug management) if specified therapy is not described
(record does not document what the current therapy is nor that the physician reviewed
it).
Drug management, per problem. Includes same therapy
or no change in therapy if specified therapy is described
(i.e., record documents what the current therapy is and
that the physician reviewed it). Dose changes for current
medications are not required; however, the record must
reflect conscious decision-making to make no dose
changes in order to count for coding purposes.
<3 new or current
medications per problem
>3 new or current
medications per problem
Open or percutaneous therapeutic cardiac, surgical or radiological procedure; minor or
major
Physical, occupational or speech therapy or other manipulation
Closed treatment for fracture or dislocation
IV fluid or fluid component replacement, or establish IV access when record is clear that
such involved physician decision-making and was not standard facility protocol
Complex insulin prescription (SC or combo of SC/IV), hyperalimentation, insulin drip or
other complex IV admix prescription
Conservative measures such as rest, ice/heat, specific diet, etc.
Radiation therapy
Joint, body cavity, soft tissue, etc injection/aspiration
Patient education regarding self or home care
Decision to admit to hospital
Discuss case with other physician
Other
1
Total Points
Section B
Coding Amount and/or Complexity of Data Reviewed or Ordered Determine total points for amount and/or complexity of data reviewed or ordered using Table B. Use the Total
Points for Section D. Final assignment of Medical Decision Making Type.
Table B Data Reviewed or Ordered
Point Value
Order and/or review medically reasonable and necessary clinical laboratory procedures.
Note: Count laboratory panels as one procedure.
Order and/or review medically reasonable and necessary diagnostic imaging studies in Radiology section of CPT.
Order and/or review medically reasonable and necessary diagnostic procedures in Medical section of CPT.
13 procedures
>4 procedures
13 procedures
>4 procedures
13 procedures
>4 procedures
Discuss test results with performing physician.
Discuss case with other physician(s) involved in patients care or consult another physician (i.e., true consultation meaning seeking opinion or advice of another
physician regarding the patients care). This does not include referring patient to another physician for future care.
Order/review
Order and/or review old records. Record type and source must be noted. Review of old records must be reasonable and necessary based on the
without
nature of the patients condition. Practice- or facility protocol-driven record ordering does not require physician work thus should not be considered
summary
when coding E/M services. Perfunctory notation of old record ordering/review solely for coding purposes is inappropriate and counting such is not
Order/review
permitted.
and summarize
Independent visualization and interpretation of an image, EKG or laboratory specimen not reported for separate payment.
Note: Each visualization and interpretation is allowed one point.
Review of significant physiologic monitoring or testing data not reported for separate payment (e.g., prolonged or serial cardiac monitoring data not
qualifying for payment as rhythm electrocardiograms).
Total Points
Revised September 2009
Page 2
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
1
1
2
1
1
Continued
MEDICAL DECISION-MAKING (continued)
Section C
Use Table C.1 to determine the highest level or risk associated with each of the following: presenting problems, diagnostic procedure(s) ordered/performed, management options(s)
chosen. Then use Table C.2 to determine the final risk, which is the highest of the three risks from Table C.1. The final risk from Table C.2 is used for Section D. Final Assignment
of Medical Decision Making Type.
Table C.1 Risk of Complications and/or Morbidity or Mortality
Level of Risk
Presenting Problem(s)
One self-limited or minor problem, e.g., cold,
insect bite, tinea corporis
Minimal
Two or more self-limited or minor problems
One stable chronic illness, e.g., wellcontrolled hypertension or non-insulin
dependent diabetes, cataract, BPH
Acute uncomplicated illness or injury, e.g.,
cystitis, allergic rhinitis, simple sprain
Low
One or more chronic illnesses with mild
exacerbation, progression or side effects of
treatment
Two or more stable chronic illnesses
Undiagnosed new problem with uncertain
prognosis, e.g., lump in breast
Acute illness with systemic symptoms, e.g.,
pyelonephritis, pneumonitis, colitis
Acute complicated injury, e.g., head injury
with brief loss of consciousness
One or more chronic illnesses with severe
exacerbation, progression or side effects of
treatment
Acute or chronic illnesses or injuries that
may pose a threat to life or bodily function,
e.g., multiple trauma, acute MI, pulmonary
embolus, severe respiratory distress,
progressive severe rheumatoid arthritis,
psychiatric illness with potential threat to self
or others, peritonitis, acute renal failure
An abrupt change in neurologic status, e.g.,
seizure, TIA, weakness or sensory loss
Moderate
High
Diagnostic Procedure(s) Ordered
Laboratory tests requiring venipuncture
Chest X-rays
EKG/EEG
Urinalysis
Ultrasound, e.g., echo
KOH prep
Physiologic tests not under stress, e.g.,
pulmonary function tests
Non-cardiovascular imaging studies with
contrast, e.g., barium enema
Superficial needle biopsies
Clinical laboratory tests requiring arterial
puncture
Skin biopsies
Physiologic tests under stress, e.g., cardiac
stress test, fetal contraction stress test
Diagnostic endoscopies with no identified risk
factors
Dee needle or incisional biopsy
Cardiovascular imaging studies with contrast
and no identified risk factors, e.g., arteriogram
cardiac cath
Obtain fluid from body cavity, e.g., lumbar
procedure, thoracentesis, culdocentesis
Cardiovascular imaging studies with contrast
with identified risk factors
Cardiac electrophysiological tests
Diagnostic endoscopies with identified risk
factors
Discography
Management Options Selected
Rest
Gargles
Elastic bandages
Superficial dressings
Over-the-counter drugs
Minor surgery with no identified risk factors
Physical therapy
Occupational therapy
IV fluids without additives
Minor surgery with identified risk factors
Elective major surgery (open, percutaneous or
endoscopic) with no identified risk factors
Prescription drug management
Therapeutic nuclear medicine
IV fluids with additives
Closed treatment of fracture or dislocation
without manipulation
Elective major surgery (open, percutaneous or
endoscopic with identified risk factors)
Emergency major surgery (open,
percutaneous or endoscopic)
Parenteral controlled substances
Drug therapy requiring intensive monitoring for
toxicity
Decision not to resuscitate or to de-escalate
care because of poor prognosis.
Table C.2 Risk of Complication and/or Mortality (see Table C.1)
Nature of the presenting illness
Minimal
Low
Moderate
High
Risk conferred by diagnostic options
Minimal
Low
Moderate
High
Minimal
Low
Moderate
High
Risk conferred by therapeutic options
Final Risk determined by highest of 3 components above
Section D
Final Assignment of Medical Decision Making Type
1. Line A Use Total Diagnosis Points or the Total Management Option Points from Section A (Tables A.1 and A.2).
2. Line B Use Total Points from Section B (Table B).
3. Line C Use highest level of risk from Section C (Table C.2).
4. Choose final Type of Medical Decision Making. Final Type Requires 2 of the 3 MDM Components below be met or exceeded.
Table D Final Assignment of Medical Decision Making Type
A. Number of diagnoses or management options
B. Amount and complexity of data reviewed/ordered
C. Risk
Type of medical decision-making
1 Point Minimal
2 Points Limited
3 Points Multiple
>4 Points Extensive
<1 Point None/Minimal
2 Points Limited
3 Points Multiple
>4 Points Extensive
Minimal
Low
Moderate
High
Straightforward
Low Complexity
Moderate Complexity
High Complexity
Final Medical Decision-Making requires 2 of 3 components above met or exceeded
Revised September 2009
Page 3
Continued
LEVEL OF SERVICE
OUTPATIENT, CONSULTS (OUTPATIENT AND INPATIENT) AND ER
History
Examination
Complexity of
Medical Decision
Average Time
(minutes)
(ER has no
average time)
Level
New Office/Consults/ER
Established Office
Requires 3 components within shaded area
Requires 2 components within shaded area
PF
ER: PF
PF
ER: PF
EPF
ER: EPF
EPF
ER: EPF
D
ER: EPF
D
ER: EPF
C
ER: D
C
ER: D
C
ER: C
C
ER: C
SF
ER: SF
SF
ER: L
L
ER: M
M
ER: M
H
ER: H
10 New (99201)
15 Outpt cons (99241)
20 Inpat cons (99251)
ER (99281)
20 New (99202)
30 Outpt cons (99242)
40 Inpat cons (99252)
ER (99282)
30 New (99203)
40 Outpt cons (99243)
55 Inpat cons (99253)
ER (99283)
II
45 New (99204)
60 Outpt cons (99244)
80 Inpat cons (99254)
ER (99284)
III
Minimal
problem
that may
not require
presence
of
physician
60 New (99205)
80 Outpt cons (99245)
100 Inpat cons (99255)
ER (99285)
IV
PF
EPF
PF
EPF
SF
5
(99211)
10
(99212)
15
(99213)
25
(99214)
40
(99215)
II
III
IV
INPATIENT
Initial Hospital/Observation
Subsequent Inpatient/Follow-up
Requires 3 components within shaded area
History
Examination
Complexity of
Medical Decision
Average Time
(minutes)
(Observation care
has no average
time)
Level
Requires 2 components within shaded area
D or C
D or C
C
C
C
C
PF interval
PF
EPF interval
EPF
D interval
D
SF/L
SF/L
30 Init hosp (99221)
Observ care (99218)
50 Init hosp (99222)
Observ care (99219)
70 init hosp (99223)
Observ care (99220)
15 Subsequent (99231)
25 Subsequent (99232)
35 Subsequent (99233)
II
III
II
III
NURSING FACILITY
Annual Assessment/Admission
Old Plan Review
New Plan
Admission
Subsequent Nursing Facility
Requires 3 components within shaded area
History
Examination
Complexity of
Medical Decision
No Average Time
Established
(Confirmatory
consults and ER
have no average
time)
Level
Requires 2 components within shaded area
D/C
D/C
C
C
C
C
PF interval
PF
EPF interval
EPF
D interval
D
C interval
C
SF
SF
(99304)
(99305)
(99306)
(99307)
(99308)
(99309)
(99310)
II
III
II
III
IV
DOMICILIARY (REST HOME, CUSTODIAL CARE) AND HOME CARE
History
Examination
Complexity of
Medical
Decision
Average Time
(minutes)
Level
New
Established
Requires 3 components within shaded area
Requires 2 components within shaded area
PF
PF
EPF
EPF
D
D
C
C
C
C
PF interval
PF
EPF interval
EPF
D interval
D
C
C
SF
SF
20 Domiciliary
(99324)
20 Home care
(99341)
I
30 Domiciliary
(99325)
30 Home care
(99342)
II
45 Domiciliary
(99326)
45 Home care
(99343)
III
60 Domiciliary
(99327)
60 Home care
(99344)
IV
75 Domiciliary
(99328)
75 Home care
(99345)
V
15 Domiciliary
(99334)
15 Home care
(99347)
I
25 Domiciliary
(99335)
25 Home care
(99348)
II
40 Domiciliary
(99336)
40 Home care
(99349)
III
60 Domiciliary
(99337)
60 Home care
(99350)
IV
PF = Problem focused y EPF = Expanded problem focused y D = Detailed y C = Comprehensive y SF = Straightforward y L = Low y M = Moderate y H = High
Revised September 2009
Page 4
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Em Coding TablesDokument2 SeitenEm Coding Tablesapi-270179959Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cracking the Code: A quick reference guide to interpreting patient medical notesVon EverandCracking the Code: A quick reference guide to interpreting patient medical notesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 42, Evaluation and Management of Coding and DocumentationVon EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 42, Evaluation and Management of Coding and DocumentationNoch keine Bewertungen
- E - M Pocket Card 07.09.12Dokument3 SeitenE - M Pocket Card 07.09.12adllurikaushik50% (2)
- Billing Basics - Hospitalist Lecture - Ashley BusuttilDokument59 SeitenBilling Basics - Hospitalist Lecture - Ashley BusuttilJacobDMillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- HEDIS Documentation Coding Guide-Adult 2020 - 900-3807A-0819 Approved 9.6rev10.21Dokument10 SeitenHEDIS Documentation Coding Guide-Adult 2020 - 900-3807A-0819 Approved 9.6rev10.21Stephany GrandersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- A few minutes to improve Risk documentation Accuracy even when you know nothing about Medicare Risk AdjustmentVon EverandA few minutes to improve Risk documentation Accuracy even when you know nothing about Medicare Risk AdjustmentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your Healthcare Job Hunt: How Your Digital Presence Can Make or Break Your CareerVon EverandYour Healthcare Job Hunt: How Your Digital Presence Can Make or Break Your CareerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Utilization Review Coordinator: Passbooks Study GuideVon EverandUtilization Review Coordinator: Passbooks Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 38, Audits by Managed-Care Organizations and Regulatory AgenciesVon EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 38, Audits by Managed-Care Organizations and Regulatory AgenciesNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPT Modifier NewDokument10 SeitenCPT Modifier NewSeenuvasanLeeManiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING ADMINISTRATION, ADVANCED: Passbooks Study GuideVon EverandNURSING ADMINISTRATION, ADVANCED: Passbooks Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- HOME HEALTH NURSE: Passbooks Study GuideVon EverandHOME HEALTH NURSE: Passbooks Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 17, Physician Extenders in the Urgent Care CenterVon EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 17, Physician Extenders in the Urgent Care CenterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supervising Registered Nurse: Passbooks Study GuideVon EverandSupervising Registered Nurse: Passbooks Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coding Cheat SheetDokument10 SeitenCoding Cheat SheetLucy AndrianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Based E/M CodingDokument5 SeitenRisk Based E/M CodingSandra WeeksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Downcoding and Bundling ClaimsDokument10 SeitenDowncoding and Bundling ClaimsKarna Palanivelu100% (1)
- Icd Jan1Dokument325 SeitenIcd Jan1Riyan NugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinica Coading PlanDokument13 SeitenClinica Coading PlanNagib OtaybiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demystifying Medical DocumentationDokument37 SeitenDemystifying Medical Documentationadultmedicalconsultants100% (14)
- ModifiersDokument8 SeitenModifiersKarna Palanivelu100% (6)
- Coding ExamplesDokument10 SeitenCoding ExamplesO.r. CadzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Coding SummaryDokument5 SeitenMedical Coding SummaryYhanie De GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPT 2023 Further Refines E - M Coding - AAPC Knowledge CenterDokument5 SeitenCPT 2023 Further Refines E - M Coding - AAPC Knowledge CenterKittu ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ahima Data Quality Management ModelDokument11 SeitenAhima Data Quality Management Modelselinasimpson2301Noch keine Bewertungen
- Icd10 CM Quick CoderDokument2 SeitenIcd10 CM Quick CoderErez Tryaza Himura50% (2)
- Assg Codingcasestudies 20171109 Ah102 KPDokument1 SeiteAssg Codingcasestudies 20171109 Ah102 KPapi-427618755Noch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Procedural and Diagnostic Billing CodesDokument2 Seiten01 Procedural and Diagnostic Billing CodesbhaskarkolluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coding ZupkoDokument8 SeitenCoding Zupkoashwanirana09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coding Modifiers TableDokument22 SeitenCoding Modifiers TableArindamDuttaChoudhury100% (1)
- Dca CPT CodesDokument1 SeiteDca CPT CodesMonstrozeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Inpatient EM Coding TrainingDokument43 SeitenBasic Inpatient EM Coding Trainingfahhad lashariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation Training To Medical BillingDokument23 SeitenFoundation Training To Medical BillingHarry CanabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coding For Lab SvcsDokument54 SeitenCoding For Lab SvcsTintinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Therapy Requiring Intensive Monitoring For ToxicityDokument1 SeiteDrug Therapy Requiring Intensive Monitoring For ToxicityadllurikaushikNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPT CodesDokument9 SeitenCPT CodesSheree AnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICD, CPT Codes & ModifiersDokument13 SeitenICD, CPT Codes & ModifiersSaeed ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEHP Medi-Cal Members Rights and Responsibilities PDFDokument11 SeitenIEHP Medi-Cal Members Rights and Responsibilities PDFminipower50Noch keine Bewertungen
- Certification/Recertification Examination Content Outline: Cma (Aama)Dokument4 SeitenCertification/Recertification Examination Content Outline: Cma (Aama)pen2trinity3200Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnostic Coding GuidelinesDokument27 SeitenDiagnostic Coding GuidelinesShona ImlahNoch keine Bewertungen
- E/M: Physical Examination CodingDokument29 SeitenE/M: Physical Examination CodingSupercoderNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICD 10QuickRefer508Dokument2 SeitenICD 10QuickRefer508rkllerNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Patient History FormDokument6 SeitenNew Patient History Formعبدالله الكافNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Coding and Billing Basics PDFDokument33 SeitenChapter 6 Coding and Billing Basics PDFamruthkiranbabujiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System 2019 Updates - Shared1Dokument112 SeitenHospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System 2019 Updates - Shared1Nunya BiznesNoch keine Bewertungen
- OIG Compliance Program For Third-Party Medical Billing CompaniesDokument15 SeitenOIG Compliance Program For Third-Party Medical Billing CompaniesaaronborosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Transcription Industry: Prepared byDokument27 SeitenMedical Transcription Industry: Prepared byrohitpatel203100% (1)
- Cardiology Billing ServicesDokument3 SeitenCardiology Billing Servicesnixxe mbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abt Medical TranscriptionDokument10 SeitenAbt Medical TranscriptionprasoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- (AMA) CPT 2021 Professional EditionDokument3.824 Seiten(AMA) CPT 2021 Professional EditionjbmbritoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coding Cheat Sheet For Residents in Outpatient MedicineDokument3 SeitenCoding Cheat Sheet For Residents in Outpatient MedicineRayCTsai86% (21)
- Coding Ahead - List of ModifiersDokument16 SeitenCoding Ahead - List of ModifiersSandeep DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- EM Coding GuidelinesDokument2 SeitenEM Coding Guidelineskar883100% (2)
- Evaluation & Management CodingDokument14 SeitenEvaluation & Management Codingsherrij1025Noch keine Bewertungen
- Flow ChartDokument8 SeitenFlow ChartiEuvilleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Assitant ProjectDokument18 SeitenMedical Assitant Projectapi-378167354100% (1)
- CPT® 2015: Watch For Changes in Vertebral Fracture AssessmentDokument3 SeitenCPT® 2015: Watch For Changes in Vertebral Fracture AssessmenttimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bariatric SurgeryDokument5 SeitenBariatric SurgerytimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPT © 2014 American Medical Association. All Rights ReservedDokument2 SeitenCPT © 2014 American Medical Association. All Rights ReservedtimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple) ) - If The Intraoperative Biopsy Reveals Malignancy, The Ob-Gyn May Convert To An Open Procedure To RemoveDokument2 SeitenMultiple) ) - If The Intraoperative Biopsy Reveals Malignancy, The Ob-Gyn May Convert To An Open Procedure To RemovetimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- (E.g., Hips, Pelvis, Spine) ) With V82.81 (Special Screening For Osteoporosis)Dokument2 Seiten(E.g., Hips, Pelvis, Spine) ) With V82.81 (Special Screening For Osteoporosis)timvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allergen ImmunotherapyDokument3 SeitenAllergen ImmunotherapytimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Anesthesia: Plus: Migraine Revisions Focus On Punctuation Addition, Not Descriptor ChangeDokument2 SeitenChapter 1: Anesthesia: Plus: Migraine Revisions Focus On Punctuation Addition, Not Descriptor ChangetimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPT © 2014 American Medical Association. All Rights ReservedDokument2 SeitenCPT © 2014 American Medical Association. All Rights ReservedtimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPT © 2014 American Medical Association. All Rights ReservedDokument2 SeitenCPT © 2014 American Medical Association. All Rights ReservedtimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infanrix Hexa (Preservative Free) CMI PDF Clean PDFDokument5 SeitenInfanrix Hexa (Preservative Free) CMI PDF Clean PDFtimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abortion Diagnosis CodingDokument3 SeitenAbortion Diagnosis CodingtimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Website - EX Rate - 02 - Sep - 2016 PDFDokument1 SeiteWebsite - EX Rate - 02 - Sep - 2016 PDFtimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Of Intestinal Adhesion) (Separate Procedure) ) Because The Correct Coding Initiative (CCI) Permanently Bundles 44005Dokument2 SeitenOf Intestinal Adhesion) (Separate Procedure) ) Because The Correct Coding Initiative (CCI) Permanently Bundles 44005timvrghs100% (1)
- Abdomen X RayDokument4 SeitenAbdomen X RaytimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Coding Updates92Dokument14 Seiten2015 Coding Updates92timvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Coding UpdatesDokument4 Seiten2015 Coding UpdatestimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pen TaximDokument5 SeitenPen TaximtimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotate QDokument13 SeitenRotate QtimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aap 2011 Vaccine Coding ChangesDokument9 SeitenAap 2011 Vaccine Coding ChangestimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canine Fossa.: CPT © 2015 American Medical Association. All Rights ReservedDokument6 SeitenCanine Fossa.: CPT © 2015 American Medical Association. All Rights ReservedtimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treasury Department: Currency Code BUY SellDokument1 SeiteTreasury Department: Currency Code BUY SelltimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paediatrics Case History Format by S.P.Kamthankar PDFDokument10 SeitenPaediatrics Case History Format by S.P.Kamthankar PDFManisha PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Commission On Human Rights National Inquiry ReportDokument38 SeitenPhilippine Commission On Human Rights National Inquiry ReportHumanRights_PhNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANNEX 9 Project Work Plan and Budget MatrixDokument2 SeitenANNEX 9 Project Work Plan and Budget MatrixSharifa Aynee JamsuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pernyataan Persetujuan Pemberian Informasi Medis Release of Medical Information Consent FormDokument1 SeitePernyataan Persetujuan Pemberian Informasi Medis Release of Medical Information Consent FormInta SugiartoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notice: GR Modifier UseDokument2 SeitenNotice: GR Modifier UseJustia.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Vitae: Career ObjectiveDokument2 SeitenCurriculum Vitae: Career ObjectiveRajesh Kumar NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Field of SpecialistDokument4 SeitenField of Specialistapi-598083311Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Learning Curve in Revision Cholesteatoma Surgery: Milan StankovicDokument7 SeitenThe Learning Curve in Revision Cholesteatoma Surgery: Milan StankovicLia BirinkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delivering Cloud-Based Solutions For Hospitals, Physicians, Clinics, Patients, and PopulationDokument4 SeitenDelivering Cloud-Based Solutions For Hospitals, Physicians, Clinics, Patients, and PopulationsomyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ismms Gradschool PPT Final 20151019Dokument7 SeitenIsmms Gradschool PPT Final 20151019thedolongsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiopulmonary Physiotherapy in Trauma An Evidence-Based ApproachDokument3 SeitenCardiopulmonary Physiotherapy in Trauma An Evidence-Based ApproachGme RpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hubungan Pelayanan Keperawatan Dengan Kepuasan Pasien Bpjs Rawat Inap Di Rumah Sakit Umum Herna Medan Oleh: Ester Mei Frida, Henti Putri Universitas Darma Agung, MedanDokument8 SeitenHubungan Pelayanan Keperawatan Dengan Kepuasan Pasien Bpjs Rawat Inap Di Rumah Sakit Umum Herna Medan Oleh: Ester Mei Frida, Henti Putri Universitas Darma Agung, Medansepti arumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Please Attach 2x2 Picture: Curriculum VitaeDokument3 SeitenPlease Attach 2x2 Picture: Curriculum Vitaesheree annNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auto Hemoterapia em InglêsDokument5 SeitenAuto Hemoterapia em Inglêsomega_tresNoch keine Bewertungen
- PalDokument5 SeitenPaljfabingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fullerton Health Sustainability Report FY2022Dokument76 SeitenFullerton Health Sustainability Report FY2022Michael YiinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community-Based Health Planning Services: Topic OneDokument28 SeitenCommunity-Based Health Planning Services: Topic OneHigh TechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharma RLE OverviewDokument10 SeitenPharma RLE OverviewNathaniel PulidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIND 24-7 Announces The Opening of Three Express Mental Health Facilities in The Phoenix AreaDokument3 SeitenMIND 24-7 Announces The Opening of Three Express Mental Health Facilities in The Phoenix AreaPR.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graduate Thesis Topics in EconomicsDokument6 SeitenGraduate Thesis Topics in Economicslizbundrenwestminster100% (2)
- Electronic Medical Records: Advantages and DisadvantagesDokument4 SeitenElectronic Medical Records: Advantages and DisadvantagesShelly BadialaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide To Clinical AuditDokument54 SeitenGuide To Clinical Auditzenti78100% (1)
- 1fca PDFDokument13 Seiten1fca PDFHalim SudonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Novartis' BOP Strategy For Healthcare in Rural India: Group: Prachi Dave Anmol Agarwal Dushayanta SawantDokument20 SeitenNovartis' BOP Strategy For Healthcare in Rural India: Group: Prachi Dave Anmol Agarwal Dushayanta SawantJinitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sarin 2014Dokument3 SeitenSarin 2014Vijay JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Occupational Health & Safety ReportDokument18 SeitenOccupational Health & Safety Reportargya nareswaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapeh 10 4TH Quarter Written WorksDokument10 SeitenMapeh 10 4TH Quarter Written Worksadrianlalin5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Orientation On DTP ME With DMOs - November 4 2022Dokument28 SeitenOrientation On DTP ME With DMOs - November 4 2022Arlo Winston De GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balanced Scorecard Template 07Dokument15 SeitenBalanced Scorecard Template 07DiyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burns Protocol PDFDokument18 SeitenBurns Protocol PDFSai MaryNoch keine Bewertungen