Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Unusual Cause of Multiple Cranial Nerve Palsy: Md. Shahriar Mahbub
Hochgeladen von
Nicolas SaputraOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Unusual Cause of Multiple Cranial Nerve Palsy: Md. Shahriar Mahbub
Hochgeladen von
Nicolas SaputraCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
J MEDICINE 2011; 12 : 96
Unusual Cause of Multiple Cranial Nerve Palsy
MD. SHAHRIAR MAHBUB,1 ABDULLAH AL FARUQ,1 MOHAMMAD ASHIK IMRAN KHAN,2 HAM NAZMUL AHASAN3
B
A
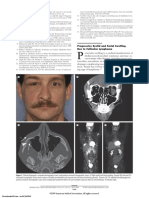
Fig. 1 MRI T1 axial (A) & coronal (B) section of brain showing lesion extending into left para-sellar area, left sphenoidal
sinus, left orbit and pharyngeal space. Left middle ear and mastoid region showing inflammatory changes
(20%), extremities (20%), trunk (10%), and other (10%).1 RMS
in the region of head and neck involves orbit, paranasal
sinuses, nasopharynx, nasal cavity, middle ear and soft
tissues of the neck. Involvement of these parameningeal
regions leads to multiple cranial nerve palsy. It arises from
skeletal muscle as well as mastoid air cells and paranasal
sinuses.2 Local invasion, local recurrence, hematogenous
and lymphatic metastasis are common in RMS. Treatment
options of RMS include combination of chemotherapy,
radiotherapy and surgery depending on the primary tumor
site, pathologic findings, and the clinical stage of the tumor.
A 55 year old male presented with 2 months history of
difficulty in deglutition, dimness of vision in his left eye,
headache associated with nausea. On examination, a swelling
was noted on the hard palate and left posterior cervical lymph
nodes were palpable. Cranial nerve examination revealed the
left II, III, IV, V, VI, IX, X, XII nerves were affected. Fundoscopy
showed left primary optic atrophy.
MRI of brain showed hypointense on T1 and hyperintense
lesion on T2 involving the pharyngeal space, extending into
left para-sellar, left sphenoidal sinus, left orbit causing mild
proptosis (Figure 1). Gadolinium contrast imaging showed
lesion in masticator space with irregular rim enhancement.
The clinical and imaging features were suggestive of
rhabdomyosarcoma. Differentials were nasopharyngeal
carcinoma, lymphoma, poorly differentiated carcinoma,
metastatic tumor and melanoma. The patient refused further
investigation and sought discharge against medical advice.
Conflict of Interest: None
References:
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is very uncommon in adult
population, being more common in children. The primary
sites of RMS are: head and neck (40%), genitourinary system
1.
Moon HS, Kwon SW, Lee JH. A case of alveolar
rhabdomyosarcoma of the ethmoid sinus invading the orbit
in an adult. Korean J Ophthalmol 2006;20:70-75
2.
Koenigsberg RA, Noah R, Turtz A, et al. Rhabdomyosarcoma
of the paranasal sinuses in an adult. Clinical Imaging
1995;19:234-236
1. FCPS (Medicine) course student, Department of Medicine, Dhaka Medical College
2. Post-graduate trainee, Department of Medicine, Dhaka Medical College
3. Professor, Department of Medicine, Dhaka Medical College
Correspondence: Dr. Md. Shahriar Mahbub, Department of Medicine, Dhaka Medical College, Dhaka, Bangladesh. E-mail:
shahriar04@yahoo.com
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Neurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IIVon EverandNeurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IIBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- CA Sinonasal PDFDokument2 SeitenCA Sinonasal PDFGek DewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 26Dokument8 SeitenChapter 26Saurabh SatheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Tympanomastoid Region - A Rare and Often Misdiagnosed EntityDokument4 SeitenSquamous Cell Carcinoma of Tympanomastoid Region - A Rare and Often Misdiagnosed EntitymawarmelatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ajol File Journals - 449 - Articles - 116044 - Submission - Proof - 116044 5329 322635 1 10 20150421Dokument6 SeitenAjol File Journals - 449 - Articles - 116044 - Submission - Proof - 116044 5329 322635 1 10 20150421valeria navarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Rare Case of Space Occupying Lesion of Brainstem in An Elderly Male PatientDokument3 SeitenA Rare Case of Space Occupying Lesion of Brainstem in An Elderly Male PatientInternational Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Research (IJCBR)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stroke Differential Diagnosis and Mimics: Part 2Dokument9 SeitenStroke Differential Diagnosis and Mimics: Part 2Natalia E PenagosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinonasal Cavernous Haemangioma: A Case ReportDokument2 SeitenSinonasal Cavernous Haemangioma: A Case Reportcity22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mandibular Ameloblastic Carcinoma in A Young Patient: A S E E P O R TDokument5 SeitenMandibular Ameloblastic Carcinoma in A Young Patient: A S E E P O R TYasmin Salwa LestariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Posterior Fossa Metastases: Are There Pathognomonic MRI Features?Dokument2 SeitenPosterior Fossa Metastases: Are There Pathognomonic MRI Features?Ira TadikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seizure, Headaches, and Right Hemiparesis: R M. B Iii, MDDokument2 SeitenSeizure, Headaches, and Right Hemiparesis: R M. B Iii, MDcazecageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epulis KongenitalDokument3 SeitenEpulis KongenitalFriadi NataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adult Orbital Rhabdomyosarcoma Case ReportDokument3 SeitenAdult Orbital Rhabdomyosarcoma Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parry Romberg Syndrome: 7 Cases and Literature Review: Head & NeckDokument7 SeitenParry Romberg Syndrome: 7 Cases and Literature Review: Head & NeckCuiting FengNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case of Maxillary Sinus CarcinomaDokument3 SeitenA Case of Maxillary Sinus CarcinomajasmniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pararapharyngeal Schwannoma Arising From Lingual Nerve: (A Rare Case Report) AbstractDokument4 SeitenPararapharyngeal Schwannoma Arising From Lingual Nerve: (A Rare Case Report) AbstractDivyanisaAvantikaRahayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CT and MR Findings of Michel Anomaly: Inner Ear Aplasia: Case ReportDokument4 SeitenCT and MR Findings of Michel Anomaly: Inner Ear Aplasia: Case ReportEBE THTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemifacial Microsomia (HFM) and Treacher Collins Syndrome: Manikandhan RamanathanDokument44 SeitenHemifacial Microsomia (HFM) and Treacher Collins Syndrome: Manikandhan RamanathanÁngel Marcelo BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Braca 05Dokument3 SeitenBraca 05moiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Orbital Rhabdomyosarcoma: About 2 Cases and Literature ReviewDokument7 SeitenManagement of Orbital Rhabdomyosarcoma: About 2 Cases and Literature ReviewIJAR JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Medicine, and PathologyDokument7 SeitenJournal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Medicine, and PathologyOMFS FKG UnimusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Progressive Eyelid and Facial Swelling Due To Follicular LymphomaDokument3 SeitenProgressive Eyelid and Facial Swelling Due To Follicular Lymphomajack rainagleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuro 1995Dokument55 SeitenNeuro 1995mic_ron100% (2)
- MeningiomaDokument19 SeitenMeningiomaRavanno Fanizza HarahapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Juvenile Nasopharyngeal AngiofibromaDokument6 SeitenJuvenile Nasopharyngeal AngiofibromaSivaneasan KandiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extracranial Metastases of Anaplastic Meningioma: Case ReportDokument6 SeitenExtracranial Metastases of Anaplastic Meningioma: Case ReportRizky AdriansahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recurrent Desmoplastic Ameloblastoma of The Maxilla: A Case ReportDokument5 SeitenRecurrent Desmoplastic Ameloblastoma of The Maxilla: A Case ReportKharismaNisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skull Base Tumors PDFDokument20 SeitenSkull Base Tumors PDFhimadriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salivary Glands Neoplasms: Artigo de RevisãoDokument10 SeitenSalivary Glands Neoplasms: Artigo de RevisãoCeriaindriasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Osteosarcoma of The Nasal Fossa: An Exceptional PresentationDokument5 SeitenPrimary Osteosarcoma of The Nasal Fossa: An Exceptional PresentationRian HasniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 SMDokument4 Seiten1 SMLasauva YardhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dent05 p0340Dokument4 SeitenDent05 p0340Nabila RizkikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain MassesDokument22 SeitenBrain MassesRaj PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orbital Rhabdomyosarcomas: A Review: Ocular Oncology UpdateDokument9 SeitenOrbital Rhabdomyosarcomas: A Review: Ocular Oncology UpdateHermawan LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cerebellopontine Angle TumoursDokument11 SeitenCerebellopontine Angle TumoursIsmail Sholeh Bahrun MakkaratteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal BM Dok JulDokument7 SeitenJurnal BM Dok JulFajar RamadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solomon 1969Dokument3 SeitenSolomon 1969putu risyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vol06 b2 32-33strDokument2 SeitenVol06 b2 32-33strAyuAnggayantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Report: Primary Oral Malignant Melanoma: Two Case Reports and Review of LiteratureDokument6 SeitenCase Report: Primary Oral Malignant Melanoma: Two Case Reports and Review of LiteratureSoumya AnandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Challenging Neurological Manifestations in Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Lcnec A Case Study of Extensive Intracranial and Intradural MetastasesDokument3 SeitenChallenging Neurological Manifestations in Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Lcnec A Case Study of Extensive Intracranial and Intradural MetastasesHerald Scholarly Open AccessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Follow UpDokument6 SeitenFollow UpWinda HaeriyokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TMP BCFFDokument3 SeitenTMP BCFFFrontiersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonnie Vorasubin, MD Arthur Wu, MD Chi Lai, MD Elliot Abemayor, MD, PHDDokument1 SeiteBonnie Vorasubin, MD Arthur Wu, MD Chi Lai, MD Elliot Abemayor, MD, PHDmandible removerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vol11No2 Pg68-69Dokument2 SeitenVol11No2 Pg68-69ikawyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiologia Espacio Masticador 2020Dokument11 SeitenRadiologia Espacio Masticador 2020Marcela GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicine: Leiomyosarcoma in The MandibleDokument4 SeitenMedicine: Leiomyosarcoma in The MandibleDaniel LesmanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Tonsil Limfoma Non HodgkinDokument5 SeitenJurnal Tonsil Limfoma Non HodgkinAhmad RamadhanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical Neurology International: Unusual Growth Pattern of A MeningiomaDokument3 SeitenSurgical Neurology International: Unusual Growth Pattern of A MeningiomaJamie NicholsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foster KennedyDokument3 SeitenFoster KennedyIsaac TellezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Associations of High Hypermetropia in Childhood JE Marr Et AlDokument2 SeitenAssociations of High Hypermetropia in Childhood JE Marr Et AlArisa RosyadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canine Choroid Plexus Tumor With Intracranial Dissemination Presenting As Multiple Cystic LesionsDokument5 SeitenCanine Choroid Plexus Tumor With Intracranial Dissemination Presenting As Multiple Cystic LesionsMihai SavescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- J Joms 2014 08 040Dokument7 SeitenJ Joms 2014 08 040Gisela LalitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Report Primary Rosai-Dorfman Disease of Bone - A Report of Two CasesDokument7 SeitenCase Report Primary Rosai-Dorfman Disease of Bone - A Report of Two CasesrexaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Abses SerebelumDokument6 Seiten1 Abses SerebelumseruniallisaaslimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Desmoid Fibromatosis of TheDokument4 SeitenPediatric Desmoid Fibromatosis of ThevatankhahpooyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arch Ophthalmol 2011 YehDokument4 SeitenArch Ophthalmol 2011 YehremotmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imagerie Des TumeursDokument14 SeitenImagerie Des TumeursOuma TaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laryngeal Plasmacytoma in Kahlers Disease: A Case ReportDokument6 SeitenLaryngeal Plasmacytoma in Kahlers Disease: A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- EJHM - Volume 72 - Issue 5 - Pages 4572-4575Dokument4 SeitenEJHM - Volume 72 - Issue 5 - Pages 4572-4575Khumaira SantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Appendicitis: Review and UpdateDokument15 SeitenAcute Appendicitis: Review and UpdateNicolas SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Study ProtocolDokument9 SeitenInternational Study ProtocolNicolas SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fibrosing Inflammatory Pseudotumors Involving The Skull Base: MR and CT Manifestations With Histopathologic ComparisonDokument7 SeitenFibrosing Inflammatory Pseudotumors Involving The Skull Base: MR and CT Manifestations With Histopathologic ComparisonNicolas SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastric Bypass DietDokument9 SeitenGastric Bypass DietNicolas SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case of A Patient With Both Chorea and Restless Legs SyndromeDokument4 SeitenA Case of A Patient With Both Chorea and Restless Legs SyndromeNicolas SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huntington Chorea: April 21, 2006 Articles Images CME Advanced Search Consumer Health Link To This SiteDokument8 SeitenHuntington Chorea: April 21, 2006 Articles Images CME Advanced Search Consumer Health Link To This SiteNicolas SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sleep, Neurobehavioral Functioning, and Behavior Problems in School-Age ChildrenDokument13 SeitenSleep, Neurobehavioral Functioning, and Behavior Problems in School-Age ChildrenNicolas SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Management OF Breast CancerDokument46 SeitenCurrent Management OF Breast CancerNicolas SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis 97Dokument109 SeitenThesis 97shahzadanjum333100% (1)
- Buzzwords For ExamsDokument16 SeitenBuzzwords For ExamsU Rock BhalraamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensory Stimulation Treatments For Oropharyngeal Dysphagia. Alvarez Berdugo, D. - Clavé, P.Dokument17 SeitenSensory Stimulation Treatments For Oropharyngeal Dysphagia. Alvarez Berdugo, D. - Clavé, P.Anonymous xvlg4m5xLXNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal Neurological ExaminationDokument10 SeitenNeonatal Neurological ExaminationNancy Montes ArteagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (PEDIA) 2.04 Pediatric Neurologic Exam - Dr. Rivera PDFDokument15 Seiten(PEDIA) 2.04 Pediatric Neurologic Exam - Dr. Rivera PDFJudith Dianne IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Handbook (Sick Calls Book 2009)Dokument287 SeitenMedical Handbook (Sick Calls Book 2009)Luc Mouws100% (1)
- The Neurological ExaminationDokument28 SeitenThe Neurological ExaminationpremaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arteries, Veins and NervesDokument8 SeitenArteries, Veins and NervesMuhammad Usman FastNUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerve Test & Testing KitsDokument1 SeiteCranial Nerve Test & Testing Kitsmamun31100% (1)
- 7 Bates Assessment ToolDokument10 Seiten7 Bates Assessment ToolNur Fatima Sanaani0% (1)
- Final - Exam - 6512N - EXAM 1Dokument13 SeitenFinal - Exam - 6512N - EXAM 1erick kanyi100% (1)
- Case Study: Diabetic KetoacidosisDokument29 SeitenCase Study: Diabetic KetoacidosisJuhina AlkalbaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 Quarter 3 Lym ADokument4 SeitenGrade 10 Quarter 3 Lym ALymberth BenallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerves LesionsDokument43 SeitenCranial Nerves LesionsAdilah RadziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kdigo Aki GuidelineDokument187 SeitenKdigo Aki GuidelineGoghuladheeiwy ChandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuro Exam Checklist 2008Dokument2 SeitenNeuro Exam Checklist 2008sara ashari100% (2)
- Cns Case Proforma-1Dokument12 SeitenCns Case Proforma-1Radha Madhav Alapati100% (2)
- Maders Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology 8th Edition Susannah Nelson Longenbaker Test Bank DownloadDokument75 SeitenMaders Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology 8th Edition Susannah Nelson Longenbaker Test Bank Downloadjordangonzaleswqigpzmcst100% (22)
- Abubakr Muhammad Ibn Zakaria Razi, Rhazes (865-925) : Child S Nervous System December 2007Dokument3 SeitenAbubakr Muhammad Ibn Zakaria Razi, Rhazes (865-925) : Child S Nervous System December 2007Nirav PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- SnorlaaaxDokument15 SeitenSnorlaaaxPinklet Arleena CubianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 1 Doc GonsalvesDokument7 SeitenCase 1 Doc GonsalvesMonique Angela Turingan GanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument94 SeitenNervous Systemmr pcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Mnemonics Head Neck PDFDokument2 SeitenAnatomy Mnemonics Head Neck PDFong_marieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Pius Troy Macapaz Section: BSN-III N32: Neurologic Assessment QuizDokument3 SeitenName: Pius Troy Macapaz Section: BSN-III N32: Neurologic Assessment QuizYamete KudasaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerve AssessmentDokument2 SeitenCranial Nerve AssessmentTina RyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Cranial Nerve 5, 6,7Dokument44 Seiten1 - Cranial Nerve 5, 6,7ewijayapalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing Lockjaw Disorders in Dogs: TrismusDokument14 SeitenManaging Lockjaw Disorders in Dogs: TrismusmiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study - Brain Tumor FINALDokument41 SeitenCase Study - Brain Tumor FINALJaneeh Miranda67% (6)
- Neuro Ophtha DR MarianoDokument6 SeitenNeuro Ophtha DR MarianoMarvinson Hermogino AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen