Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Dynamic Cone Penetration Test
Hochgeladen von
Bibhuti B. BhardwajCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Dynamic Cone Penetration Test
Hochgeladen von
Bibhuti B. BhardwajCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Transportation Engineering Laboratory, IITG
EXPERIMENT NO.
NAME OF THE EXPERIMENT: DYNAMIC CONE PENETRATION TEST
AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT: To determine the in situ CBR value of
undisturbed soil using dynamic cone penetrometer.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
In this test the Dynamic Cone Penetrometer tip is driven in to the
undisturbed soil or compacted material by using the sliding hammer. The
total penetration for a given number of blows is measured and recorded in
mm/blow which is then used to find in- situ CBR strength. It is typically used
to assess material properties of soil down to a depth of 1000 mm.
The correlation of penetration per blow (DCP) is derived from the following
equation recommended by the US Army Corps of EngineersCBR value=
292
( DCP)1.12
for DCP in mm / blows
APPARATUS USED:
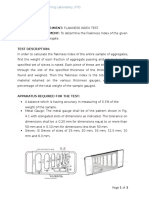
1) Handle: The handle is located at the top of the device and is used to
hold the DCP shafts plumb and to limit the upward movement of the
hammer.
2) Hammer: The hammer is generally of 8 kg weight with a freefall of 575
mm and is used to transfer energy to the cone tip.
3) Upper shaft: It is a 16 mm diameter steel shaft on which the hammer
moves.
4) Anvil: It serves as the lower stopping mechanism for the hammer and
5)
6)
7)
8)
connects the upper and lower shafts.
Lower shaft: It is a 16 mm diameter steel shaft and 1000 mm long.
Cone: The cone measures 20 mm in diameter with 600 apex angle.
A vertical graduated scale capable of reading increments of 1mm
An optional sliding attachment for use with a separate scale
Page 1 of 3
Transportation Engineering Laboratory, IITG
9) A rotary hammer drill or coring apparatus capable of drilling a
minimum diameter hole of 25 mm
10)
Thread locking compound
Fig.1 DCPT
sketch
Fig.2 The
Dynamic Cone Penetrometer
RELEVANT CODES:
ASTM D6951/D6951M-09: Standard Test Method for Use of the Dynamic Cone Penetrometer in
Shallow Pavement Applications, American Society for Testing and Materials
PROCEDURE:
Checking of the equipment: Before the test begins, the DCP device is
inspected for damaged parts especially the coupler, the handle, the drive rod
and replaceable point tip. All the joints should be securely tightened.
Basic operation: The operator holds the device by the handle in a vertical
and lifts and releases the hammer from the standard drop height. The
recorder measures and records the total penetration for a given number of
blows or the penetration per blow.
Page 2 of 3
Transportation Engineering Laboratory, IITG
Initial Reading: The DCP is held vertically and the tip seated such that the
top of the widest part of the tip is ush with the surface of the material to be
tested. An initial reading is obtained from the graduated drive rod or a
separate vertical scale/measuring rod. When testing materials underlying a
bound layer, a coring apparatus is used to provide an access hole to the
layer to be tested.
Testing Sequence:
i.
Dropping the Hammer: The DCP device is held in a vertical or plumb
position. The operator raises the hammer until it makes only light
contact with the handle. The hammer shall not impact the handle when
being raised. The hammer is then allowed to free-fall and impact the
anvil coupler assembly. The number of blows and corresponding
ii.
penetrations are recorded.
Depth of Penetration: It will vary with application. A penetration less
than 900 mm will generally be adequate for typical highway
iii.
applications.
Refusal: If after 5 blows, the device has not advanced more than 2 mm
or the handle has deected more than 75 mm from the vertical
position, the test shall be stopped, and the device moved to another
test location.
PRECAUTIONS:
All the while the shaft should be kept vertical
Wear safety shoes
Care should be taken while handling with the hammer
Page 3 of 3
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- PDFDokument16 SeitenPDFBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConsolidationDokument13 SeitenConsolidationthuaiyaalhinaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Penetration TestDokument4 SeitenStandard Penetration TestbusyspiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shallow Foundations: Discussions and Problem SolvingVon EverandShallow Foundations: Discussions and Problem SolvingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Consolidation TestDokument16 SeitenConsolidation Test1man1bookNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS-1377part9-90 InSitu Test PDFDokument63 SeitenBS-1377part9-90 InSitu Test PDFpeiyin_88100% (8)
- Reciprocating Compressor Foundation Design With Driven Steel PilesDokument27 SeitenReciprocating Compressor Foundation Design With Driven Steel Pileskaty parraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBR (California Bearing Ratio) Test: 1. ObjectiveDokument7 SeitenCBR (California Bearing Ratio) Test: 1. Objectivesdfsdf100% (1)
- Astm D1196Dokument10 SeitenAstm D1196emreakinay100% (3)
- Standard Practice For Preserving and Transporting Soil Samples D 4220Dokument10 SeitenStandard Practice For Preserving and Transporting Soil Samples D 4220Akkshay ChadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCP TestDokument10 SeitenDCP TestRicardo Alfaro100% (1)
- Dynamic Cone Penetration TestDokument109 SeitenDynamic Cone Penetration TestEndra Nugroho100% (1)
- Falling Head Permeability TestDokument8 SeitenFalling Head Permeability Testdwivediashish2100% (2)
- Hannigan Et Al 2006 V1 V2Dokument1.399 SeitenHannigan Et Al 2006 V1 V2Irina Perepelitsa100% (1)
- BS 1377-5Dokument40 SeitenBS 1377-5selcukxNoch keine Bewertungen
- 00016341Dokument12 Seiten00016341Ridip DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm D2937 PDFDokument5 SeitenAstm D2937 PDFZeeshan Mirza100% (1)
- D6951 Ver03Dokument7 SeitenD6951 Ver03Abdul Malek100% (2)
- Geotechnical Laboratory Manual-IIDokument124 SeitenGeotechnical Laboratory Manual-IIMir100% (6)
- Sand ReplacementDokument14 SeitenSand ReplacementMuniey Aziz75% (8)
- Ufc 3 220 01Dokument35 SeitenUfc 3 220 01M Refaat FathNoch keine Bewertungen
- HMA Mix Design Report-2Dokument11 SeitenHMA Mix Design Report-2yustinokwingwa100% (1)
- CBR ReportDokument18 SeitenCBR ReportMaitrayee Aditya20% (5)
- Plate Load Test For Safe Bearing Capacity and SettlementDokument10 SeitenPlate Load Test For Safe Bearing Capacity and SettlementFOZCANNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM Permeability Falling Head LabDokument5 SeitenASTM Permeability Falling Head LabMelissa SammyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stripping Test of AggregatesDokument2 SeitenStripping Test of AggregatesBibhuti B. Bhardwaj100% (2)
- California Bearing Ratio TestDokument7 SeitenCalifornia Bearing Ratio TestBhaskara Rao KatragaddaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elongation Index TestDokument2 SeitenElongation Index TestBibhuti B. Bhardwaj60% (5)
- In-Situ Tests (SPT) PDFDokument28 SeitenIn-Situ Tests (SPT) PDFnikhilarora1988Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stress in Subsoil and Methods of Final Settlement CalculationVon EverandStress in Subsoil and Methods of Final Settlement CalculationNoch keine Bewertungen
- 00024098Dokument20 Seiten00024098Ridip DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consolidation Test of Soil (Complete Report)Dokument10 SeitenConsolidation Test of Soil (Complete Report)Bshfirnaudz89% (38)
- PDFDokument12 SeitenPDFBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Bituminous MixDokument75 SeitenReport On Bituminous MixBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plate Bearing TestDokument11 SeitenPlate Bearing TestKelvin Lau100% (1)
- Vibroflotation VFDokument4 SeitenVibroflotation VFimanacoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prefabricated Vertical Drains For: Soil ConsolidationDokument14 SeitenPrefabricated Vertical Drains For: Soil ConsolidationFerry Yudha Mangiwa100% (1)
- CBR Test.Dokument9 SeitenCBR Test.Dilanka S GunasinghaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faculty of Engineering Bellville Campus Laboratory Report (Oedometer)Dokument10 SeitenFaculty of Engineering Bellville Campus Laboratory Report (Oedometer)Makaveli08k100% (1)
- Flakiness Index TestDokument3 SeitenFlakiness Index TestBibhuti B. Bhardwaj0% (1)
- Dyanmic Cone Penetrometer (DCP) Test MS WORDDokument5 SeitenDyanmic Cone Penetrometer (DCP) Test MS WORDAvinash LalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressuremeter Testing: Methods and InterpretationVon EverandPressuremeter Testing: Methods and InterpretationBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Direct Shear Test Lab ManualDokument6 SeitenDirect Shear Test Lab Manualmm0% (1)
- CBR Test PDFDokument37 SeitenCBR Test PDFPoru ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement of Drawbar Pull of Earth-Moving Machinery: Method ForDokument14 SeitenMeasurement of Drawbar Pull of Earth-Moving Machinery: Method ForBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Manual - Triaxial CD TestDokument3 SeitenLaboratory Manual - Triaxial CD TestMarcos Morrison50% (2)
- Marshall StabilityDokument10 SeitenMarshall StabilityOhmae BaranskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unbound Aggregates in RoadsVon EverandUnbound Aggregates in RoadsR.H. JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Impact Energy Dynamic CompactionDokument10 SeitenHigh Impact Energy Dynamic CompactionsezaitanyoluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 567 Marshall Mix Design MethodDokument20 SeitenExp 567 Marshall Mix Design Methodali100% (1)
- D1557 PDFDokument8 SeitenD1557 PDFgadNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument14 SeitenPDFBibhuti B. Bhardwaj100% (1)
- Piezocone and Cone Penetration Test (CPTu and CPT) Applications in Foundation EngineeringVon EverandPiezocone and Cone Penetration Test (CPTu and CPT) Applications in Foundation EngineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm D6236-11Dokument7 SeitenAstm D6236-11LydiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Swell IndexDokument3 SeitenFree Swell IndexGanesh ÇkmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bs 1377 Part 2 Methods of Test For Soils For Civil En80cpdfDokument68 SeitenBs 1377 Part 2 Methods of Test For Soils For Civil En80cpdfsamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm D698Dokument13 SeitenAstm D698Jorge CarrascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan Penyelidikan Geoteknik Cirebon PDFDokument213 SeitenLaporan Penyelidikan Geoteknik Cirebon PDFHendra SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5) UCS TestDokument5 Seiten5) UCS TestPn EkanayakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Developments in Geotechnical EngineeringVon EverandDevelopments in Geotechnical EngineeringBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- DCA Europe HDD GuidelinesDokument66 SeitenDCA Europe HDD Guidelines仲达Noch keine Bewertungen
- NP P94-117-2 PDFDokument3 SeitenNP P94-117-2 PDFJay ParkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marshall Stability and Flow TestDokument5 SeitenMarshall Stability and Flow TestBhaskar Pratim Das75% (4)
- 34) Extraction of Bitumen From Paving MixturesDokument6 Seiten34) Extraction of Bitumen From Paving MixturesPn EkanayakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Sampling and Testing of ConcreteDokument4 SeitenCore Sampling and Testing of Concretevigneshwarimahamuni100% (2)
- In-Situ CBR TestDokument1 SeiteIn-Situ CBR TestMichael Tan33% (3)
- 03 Determination of Differential Free Swell IndexDokument3 Seiten03 Determination of Differential Free Swell IndexAbhijit Haval100% (2)
- En 14490 After CEN Enquiry (Soil Nailing)Dokument59 SeitenEn 14490 After CEN Enquiry (Soil Nailing)Abraham FIgueroa ARevaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flakiness & Elongation IndexDokument3 SeitenFlakiness & Elongation Indexramzimusthafa100% (8)
- IS - Free Swell IndexDokument2 SeitenIS - Free Swell IndexDr Wong Kim YuenNoch keine Bewertungen
- IS 9103 - 1999 - Concrete Admixtures SpecificationDokument18 SeitenIS 9103 - 1999 - Concrete Admixtures Specificationm.shahbaghiNoch keine Bewertungen
- As 1141.23-2009 Methods For Sampling and Testing Aggregates Los Angeles ValueDokument2 SeitenAs 1141.23-2009 Methods For Sampling and Testing Aggregates Los Angeles ValueSAI Global - APACNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No. Name of The Experiment: Dynamic Cone Penetration Test AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT: To Determine The in Situ CBR Value ofDokument3 SeitenExperiment No. Name of The Experiment: Dynamic Cone Penetration Test AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT: To Determine The in Situ CBR Value ofMuhammad IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Information NoteDokument8 SeitenTechnical Information Noteabdikarim_omarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MerlinDokument4 SeitenMerlinBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specific Gravity of Coarse and Fine AggregateDokument5 SeitenSpecific Gravity of Coarse and Fine AggregateBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sieve AnalysisDokument3 SeitenSieve AnalysisBibhuti B. Bhardwaj100% (1)
- CBR TestDokument5 SeitenCBR TestBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument16 SeitenPDFBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No. Name of The Experiment: Aggregate Impact Test AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT: To Determine The Aggregate Impact Value ofDokument4 SeitenExperiment No. Name of The Experiment: Aggregate Impact Test AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT: To Determine The Aggregate Impact Value ofBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preservation and Storage of Earth-Moving Machinery: Methods ForDokument10 SeitenPreservation and Storage of Earth-Moving Machinery: Methods ForBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 00016614Dokument12 Seiten00016614Ridip DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agularity Number TestDokument3 SeitenAgularity Number TestBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument8 SeitenPDFBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument8 SeitenPDFBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument8 SeitenPDFBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument12 SeitenPDFBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument10 SeitenPDFBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument12 SeitenPDFBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument10 SeitenPDFBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 00021826Dokument8 Seiten00021826Ridip DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MillingDokument24 SeitenMillingBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- File 1120201401025350 PDFDokument197 SeitenFile 1120201401025350 PDFBibhuti B. BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liquefaction and Cyclic Softening Potential of Soils - A Unified Piezocone Penetration Testing-Based ApproachDokument6 SeitenLiquefaction and Cyclic Softening Potential of Soils - A Unified Piezocone Penetration Testing-Based ApproachBárbara RodríguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce 483 Subsoil Exploration 38-39 IDokument108 SeitenCe 483 Subsoil Exploration 38-39 IAman Raj MajhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS - en 1997-2 DK Na - 2011 eDokument9 SeitenDS - en 1997-2 DK Na - 2011 ep_meulendijks108Noch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Exploration PDFDokument36 SeitenSoil Exploration PDFp.v.n. lakshmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bu Mat MOI IIIDokument84 SeitenBu Mat MOI IIILarry Wayne Sumpter, JrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sabp Q 014Dokument14 SeitenSabp Q 014siddiq alviNoch keine Bewertungen
- In Situ Testing in GeomechanicsDokument1 SeiteIn Situ Testing in GeomechanicsPonco SujarmikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- APILE 2014 Users ManualDokument227 SeitenAPILE 2014 Users Manualcepi herdiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.0 Soil InvestigationDokument17 Seiten2.0 Soil InvestigationHikmat AyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.1 Cone Penetrometer Test - GeneralDokument43 Seiten5.1 Cone Penetrometer Test - GeneralJAVIER ADRIANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Cone Penetration Test - Pavement InteractiveDokument2 SeitenDynamic Cone Penetration Test - Pavement InteractiveHoracio Martin Basualdo FioreNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Electro Vibrocone For EvaluationDokument10 SeitenAn Electro Vibrocone For EvaluationImmanuel LumbantobingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dobry and Abdoun 2011 PDFDokument34 SeitenDobry and Abdoun 2011 PDFR.a. Niar Nauri NingsihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fugro: Cone Penetration TestsDokument4 SeitenFugro: Cone Penetration TestsVetriselvan ArumugamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piezocone Profiling of Clays For Maritime Site InvDokument19 SeitenPiezocone Profiling of Clays For Maritime Site Invran2315570Noch keine Bewertungen
- GEOLOGYDokument8 SeitenGEOLOGYbihonmiki061Noch keine Bewertungen
- Interpretation of Cone Penetration Tests - Part IDokument17 SeitenInterpretation of Cone Penetration Tests - Part IwabiyeomunguyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cone Penetration TestDokument34 SeitenCone Penetration TestAnwar Hossain PolasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seismic CPT Whitepaper - Final - May2020Dokument9 SeitenSeismic CPT Whitepaper - Final - May2020Lei QiNoch keine Bewertungen
- In-Situ and Laboratory Testing of Soft Clays: Australian Geomechanics Journal September 2013Dokument16 SeitenIn-Situ and Laboratory Testing of Soft Clays: Australian Geomechanics Journal September 2013AshishBastolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHD Thesis - LATC (401106)Dokument278 SeitenPHD Thesis - LATC (401106)Debdeep SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotechnical Engineering Journal of TheDokument15 SeitenGeotechnical Engineering Journal of TheJulian SandovalNoch keine Bewertungen
- S-AAA-CIV-OHL (Rev.0-2015)Dokument28 SeitenS-AAA-CIV-OHL (Rev.0-2015)Swathish SivaprasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Construction Materials: and TestingDokument145 SeitenIntroduction To Construction Materials: and TestingMuy SamulaNoch keine Bewertungen