Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Isye 3232 Stochastic Manufacturing and Service Models Fall 2015 Z. She, Yl. Chang
Hochgeladen von
David Lee0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten2 SeitenOriginaltitel
HW12Solutions.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten2 SeitenIsye 3232 Stochastic Manufacturing and Service Models Fall 2015 Z. She, Yl. Chang
Hochgeladen von
David LeeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
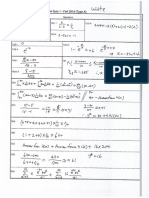
ISyE 3232
Z. She , YL. Chang
Stochastic Manufacturing and Service Models
Fall 2015
Solutions to Homework 12
1. (a) This process can be modeled as follows: here our state space is S = {(0, 0), (1, 0), (0, 1), (1, 1)}
where a state (i, j) means i customers in server 1 and j customers in server 2.
The generator is as follows (the rate transition diagram can be drawn immediately after
knowledge of the generator) :
(0, 0) (1, 0) (1, 1) (0, 1)
(0, 0) 10
10
0
0
6
16
10
0
G = (1, 0)
.
(1, 1)
0
4
10
6
(0, 1)
4
0
10
14
(b) To find the stationary distribution, we need to again solve the system of balance and
normalizing equations. From the generator, we see that
1000
610 + 401
1610
1000 + 411
1011
1010 + 1001
1401
611
00 + 10 + 11 + 01
Solving this, we that 00 = 18/88, 10 = 20/88, 11 = 35/88 and 01 = 15/88.
(c) The long-run fraction of time that server 1 is busy is 10 + 11 = 55/88. The long-run
fraction of time that server 2 is busy is 11 + 01 = 50/88.
2. For all the sub-problem below, the state space will always be {0, 1, 2, 3}.
(a) The transition diagram is as the following
2
3
1
Solve the stationary distribution using the cut method, we get
= (1/15, 2/15, 4/15, 8/15)
So the throughput is ef f = 2(1 3 ) = 14/15. To find the long-run average waiting
time, we use Littles law. Note that L = 12 + 23 = 20/15, so
W =
L
= 10/7.
ef f
(b) The transition diagram is as the following
2
1+1
3
1+1
Solve the stationary distribution using the cut method, we get
= (1/7, 2/7, 2/7, 2/7)
So the throughput is ef f = 2(1 3 ) = 10/7. To find the long-run average waiting time,
we use Littles law. Note that L = 13 = 2/7, so
W =
L
= 1/5.
ef f
(c) The transition diagram is as the following
2
2
1+1
3
1+1+1
Solve the stationary distribution using the cut method, we get
= (3/19, 6/19, 6/19, 4/19)
So the throughput is ef f = 2(1 3 ) = 30/19. To find the long-run average waiting
time, we use Littles law. Note that L = 0, so
W =
L
= 0.
ef f
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Unit 3 SolvedDokument13 SeitenUnit 3 SolvedSHAHUL HAMEED.SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Systems Compensator DESIGN Via Root Locus PDFDokument34 SeitenControl Systems Compensator DESIGN Via Root Locus PDFm_umair72001100% (2)
- BentleyDokument8 SeitenBentleymanaj_mohapatra204180% (5)
- Solutions To Selected Problems in Chapter 5: 1 Problem 5.1Dokument13 SeitenSolutions To Selected Problems in Chapter 5: 1 Problem 5.10721673895Noch keine Bewertungen
- Slow-Scale Bifurcation Behavior of Parallel-Connected Boost Converters Via Averaged ModelsDokument18 SeitenSlow-Scale Bifurcation Behavior of Parallel-Connected Boost Converters Via Averaged ModelselsaordunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gate Mock TestDokument15 SeitenGate Mock TestTuhinansu PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control System MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) - JavatpointDokument51 SeitenControl System MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) - Javatpointم/ياسـر يحيـى الحمـزيNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODELING LINEAR SYSTEMSDokument39 SeitenMODELING LINEAR SYSTEMSFreyley LeyvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- State Variable FilterDokument9 SeitenState Variable FilterSimadri BadatyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 MBRC Simulation RT ControlDokument10 Seiten2014 MBRC Simulation RT ControlMinhaj NaimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital State-Variable Filters: 1 Normalized Second-Order Continuous-Time Lowpass FilterDokument9 SeitenDigital State-Variable Filters: 1 Normalized Second-Order Continuous-Time Lowpass FilterJennifer WilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS MCQSDokument73 SeitenCS MCQSFarhan SafdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSC-session2 - Lola y Laura PDFDokument12 SeitenSSC-session2 - Lola y Laura PDFMARIA BERMUDEZ LOPEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- State Errors - Steady: Eman Ahmad KhalafDokument28 SeitenState Errors - Steady: Eman Ahmad KhalafAhmed Mohammed khalfNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Motivation: Isye 3232C Stochastic Manufacturing and Service Systems Fall 2015 Yl. ChangDokument23 Seiten1 Motivation: Isye 3232C Stochastic Manufacturing and Service Systems Fall 2015 Yl. ChangDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Sufficient Condition For Entrainment of A Van-der-Pol Oscillator Resistively Coupled To A Fixed Voltage InputDokument8 SeitenA Sufficient Condition For Entrainment of A Van-der-Pol Oscillator Resistively Coupled To A Fixed Voltage InputmalaysiatotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Open Loop AnalysisDokument11 Seiten1 Open Loop AnalysisEngr Faisal Saleem JanjuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- N-R BasicsDokument46 SeitenN-R BasicsHossain 'Soroosh' MohammadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lead-Lag Design ExpressionsDokument2 SeitenLead-Lag Design ExpressionsAronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Behavior of More General SystemsDokument32 SeitenDynamic Behavior of More General Systemsjasonbkyle9108Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ee 5307 HomeworksDokument15 SeitenEe 5307 HomeworksManoj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Very Good Bode Plot TutorialDokument5 SeitenVery Good Bode Plot TutorialsukusportyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 (From Seborg Et Al.)Dokument26 SeitenChapter 4 (From Seborg Et Al.)Jamel CayabyabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explicit Method For Solving Parabolic PDE: T L X Where X U C T UDokument9 SeitenExplicit Method For Solving Parabolic PDE: T L X Where X U C T UAshokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laplace Transforms for ODE SolutionsDokument20 SeitenLaplace Transforms for ODE SolutionsJamel CayabyabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Deadbeat Controller Limited OutputDokument4 SeitenDesign Deadbeat Controller Limited OutputmailmadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Convolution and Circuit ResponseDokument6 SeitenConvolution and Circuit ResponseZy AnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control McqsDokument35 SeitenControl McqsNuman Khan100% (1)
- Solving Differential Equations Using MATLABDokument8 SeitenSolving Differential Equations Using MATLABAnonymous DHJ8C3oNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Tuning of A Dead-Time Compensator For Stable, Integrative and Unstable ProcessesDokument6 SeitenAutomatic Tuning of A Dead-Time Compensator For Stable, Integrative and Unstable ProcessesRené PereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIMO ArticleDokument11 SeitenMIMO ArticleCesar GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- F44128640 Homework LCS DING JoelDokument19 SeitenF44128640 Homework LCS DING JoelNotnowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Continuous Systems Diffebential and Vabiational FobmulationsDokument18 SeitenAnalysis of Continuous Systems Diffebential and Vabiational FobmulationsDanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Couette Flow Analytical and Numerical SolutionDokument5 SeitenCouette Flow Analytical and Numerical SolutionRasikh TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0267 Dut 70Dokument10 Seiten0267 Dut 70Ardyas Wisnu BaskoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling of A Three-Phase Step Up/Down Ac/Dc Converter: Jeng-Yue Chen, Ching-Tsai Pan and Yi-Shuo HuangDokument8 SeitenModeling of A Three-Phase Step Up/Down Ac/Dc Converter: Jeng-Yue Chen, Ching-Tsai Pan and Yi-Shuo HuangAhmed JanadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab#1 Sampling and Quantization Objectives:: Communication II Lab (EELE 4170)Dokument6 SeitenLab#1 Sampling and Quantization Objectives:: Communication II Lab (EELE 4170)MarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pid 2Dokument5 SeitenPid 2Sanyaolu AdebodunNoch keine Bewertungen
- The SABR ModelDokument9 SeitenThe SABR Modelabhishek210585Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To The 2011 AP Calculus BC, Form B, Free Response QuestionsDokument6 SeitenSolutions To The 2011 AP Calculus BC, Form B, Free Response Questionsscribdacct123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Control Systems 2Dokument18 SeitenControl Systems 2Sengottu VelusamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Solution of Initial Value ProblemsDokument17 SeitenNumerical Solution of Initial Value ProblemslambdaStudent_eplNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout E.15 - Examples On Transient Response of First and Second Order Systems, System Damping and Natural FrequencyDokument14 SeitenHandout E.15 - Examples On Transient Response of First and Second Order Systems, System Damping and Natural FrequencyRishikesh BhavsarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stability 3: Understanding Unstable Responses and the Equal-Area CriterionDokument15 SeitenStability 3: Understanding Unstable Responses and the Equal-Area CriterionFengxing ZhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transfer Function Modeling For The Buck Converter: Sanda Lefteriu Cécile LabarreDokument4 SeitenTransfer Function Modeling For The Buck Converter: Sanda Lefteriu Cécile Labarre1balamanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control SystemsDokument18 SeitenControl SystemsSengottu VelusamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1999 On A Convex Acceleration of Newton's MethodDokument17 Seiten1999 On A Convex Acceleration of Newton's MethodAldair De Jesus Hoyos TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ioannou Web Ch7Dokument63 SeitenIoannou Web Ch7Yasemin BarutcuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial III Root Locus DesignDokument25 SeitenTutorial III Root Locus Designapi-3856083100% (3)
- Process Systems Steady-State Modeling and DesignDokument12 SeitenProcess Systems Steady-State Modeling and DesignbeichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analyzing stability in multiple loop systemsDokument5 SeitenAnalyzing stability in multiple loop systemsRDVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me Gate-10: y x x x π π π πDokument42 SeitenMe Gate-10: y x x x π π π πudaygwlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ta Proj 1 ReportlDokument12 SeitenTa Proj 1 ReportlshaheerdurraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simpli Ed Derivation of The Heston ModelDokument6 SeitenSimpli Ed Derivation of The Heston Modelmirando93Noch keine Bewertungen
- EE 312 Lecture 4Dokument17 SeitenEE 312 Lecture 4دكتور كونوهاNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finite Automata and Non DeterminismDokument46 SeitenFinite Automata and Non DeterminismElmer PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- State EstimationDokument34 SeitenState EstimationFengxing ZhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Motivation: Isye 3232C Stochastic Manufacturing and Service Systems Fall 2015 Yl. ChangDokument23 Seiten1 Motivation: Isye 3232C Stochastic Manufacturing and Service Systems Fall 2015 Yl. ChangDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motivation Example: Isye 3232C Stochastic Manufacturing and Service Systems Fall 2015 Yl. ChangDokument28 SeitenMotivation Example: Isye 3232C Stochastic Manufacturing and Service Systems Fall 2015 Yl. ChangDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motivation Example: Isye 3232C Stochastic Manufacturing and Service Systems Fall 2015 Yl. ChangDokument28 SeitenMotivation Example: Isye 3232C Stochastic Manufacturing and Service Systems Fall 2015 Yl. ChangDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fall15Midterm1 Sol PDFDokument6 SeitenFall15Midterm1 Sol PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- TeamRegistrationb PDFDokument2 SeitenTeamRegistrationb PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- T1spring2013key PDFDokument2 SeitenT1spring2013key PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- T2fall2014b PDFDokument6 SeitenT2fall2014b PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ztable PDFDokument1 SeiteZtable PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- t1Spring2013A PDFDokument6 Seitent1Spring2013A PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Guide to R SimulationDokument4 SeitenQuick Guide to R SimulationDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- t2Fall2013A PDFDokument7 Seitent2Fall2013A PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- t2Fall2014A PDFDokument4 Seitent2Fall2014A PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- t1Fall2014Keys PDFDokument2 Seitent1Fall2014Keys PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- t1Fall2013A PDFDokument6 Seitent1Fall2013A PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- t1Fall2014A PDFDokument5 Seitent1Fall2014A PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISYE 3232C Quiz 6 Production Line AnalysisDokument2 SeitenISYE 3232C Quiz 6 Production Line AnalysisDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- t1Fall2014Keys PDFDokument2 Seitent1Fall2014Keys PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spring15Midterm1 PDFDokument6 SeitenSpring15Midterm1 PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spring15Midterm1 Sol PDFDokument20 SeitenSpring15Midterm1 Sol PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spring15Midterm2 PDFDokument8 SeitenSpring15Midterm2 PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISYE 3232C Fall 2015 Quiz 9 Honor CodeDokument2 SeitenISYE 3232C Fall 2015 Quiz 9 Honor CodeDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz5Solution PDFDokument2 SeitenQuiz5Solution PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISYE 3232C Fall 2015 Quiz 13Dokument1 SeiteISYE 3232C Fall 2015 Quiz 13David LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz10Solution PDFDokument1 SeiteQuiz10Solution PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISYE 3232C Spring 2015 Quiz 5 - Solutions: Fall 7Dokument3 SeitenISYE 3232C Spring 2015 Quiz 5 - Solutions: Fall 7David LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz11Solution PDFDokument2 SeitenQuiz11Solution PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz3Solution PDFDokument1 SeiteQuiz3Solution PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz2Solution PDFDokument1 SeiteQuiz2Solution PDFDavid LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISYE 3232C Fall 2015 Quiz 2Dokument1 SeiteISYE 3232C Fall 2015 Quiz 2David LeeNoch keine Bewertungen