Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
7.5B-7.6 Handout
Hochgeladen von
AshwiniSelvakumaranCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
7.5B-7.6 Handout
Hochgeladen von
AshwiniSelvakumaranCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MPM 2DA Unit 7 & 8
Similar Triangles & Trigonometry
Lesson 3 - Page 1 of 3
Sections 7.5B & 7.6
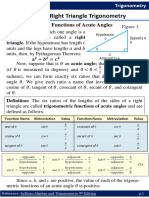
7.5/7.6 SOLVING RIGHT TRIANGLE PROBLEMS
If a problem involving the calculation of a length or an angle can be represented with a right
triangle, then it can be solved using primary trigonometric ratios! Trigonometry helps us to
indirectly measure distances and heights. For example, a surveyor can measure width of a river
or any other distance on a plane:
Solving Triangles: solving for ALL unknown sides and angles in a triangle.
Tools we have to solve a RIGHT triangle
Primary Trigonometric Ratios (SOH CAH TOA) Sine, Cosine, Tangent
Pythagorean Theorem 2 = 2 + 2
Sum of Interior Angles of a Triangle = 180o
Angle of Elevation:
Angle of Depression:
The angle between the horizontal and the
line of sight looking up.
The angle between the horizontal and the
line of sight looking down.
If you stand outside to observe a hot air
balloon, and you are looking up, the
angle that your line of sight makes with
the horizontal is known as the angle of
elevation:
If you are in the hot air balloon looking
down on a bag of money on the ground,
the angle that your line of sight makes
with the horizontal is known as the angle
of depression:
The horizontals are always parallel to each other.
Angle of elevation = Angle of
depression due to Alternate Angles.
Z Pattern
MPM 2DA Unit 7 & 8
Similar Triangles & Trigonometry
Lesson 3 - Page 2 of 3
Sections 7.5B & 7.6
Example 1:
From a point on the ground, 258 m from the base of the CN Tower, the angle of elevation to the
top of the tower is 65o. Find the height of the CN Tower, to the nearest metre.
Example 2:
Ernest is standing on top of a bridge that is 10m off the ground. Ernest is 1.7m tall. He looks
down and sees a duck in the water. The angle of depression is 40 o. How far away is the duck
from the bridge?
Example 3:
A communications tower 62 m tall has to be supported with cables running from the top of the
tower to anchors in the ground on both sides of the tower. The cables must form an angle of 50 o
with the ground. How far from the base of the tower should the anchors be placed?
MPM 2DA Unit 7 & 8
Similar Triangles & Trigonometry
Lesson 3 - Page 3 of 3
Sections 7.5B & 7.6
Example 4:
A ladder leaning against a wall at certain angles can be unstable. Some repair manuals
recommend that the angle the ladder makes with the ground should be no more than 75 0 and no
less than 60o. If the base of an 8 m ladder is placed 1.5 m from the wall, is the ladder safe?
Explain and justify your answer. Determine the minimum and maximum distances the base of
the ladder can be placed from the wall safely to meet the safety guidelines.
Example 5:
Isabel is looking out the top of a 100m building. If she looks up at 35 o she can see the top of the
next building. If she looks down at 42o, she can see the bottom of the next building.
a) How far apart are the two buildings?
b) How tall is the next building?
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CHAPTER 2.1, Trigonometry in Right Angled TriangleDokument10 SeitenCHAPTER 2.1, Trigonometry in Right Angled TriangleaungminsfuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry MidtermDokument1 SeiteTrigonometry MidtermKoleen Lhyte T. UYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 TrigonometryDokument52 SeitenChapter 9 TrigonometryJojobaby51714100% (3)
- Math 100 Module 2Dokument2 SeitenMath 100 Module 2Francis DurayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.28 Trig ApplicationsDokument19 Seiten2.28 Trig Applicationshazel_enaNoch keine Bewertungen
- T-ENGM110 Final 2021 (2)Dokument2 SeitenT-ENGM110 Final 2021 (2)Sanjoe Angelo ManaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of TrigoDokument3 SeitenApplication of Trigohackerboy99356Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plane & Spherical TrigonometryDokument29 SeitenPlane & Spherical TrigonometryLumiere Silvamillion CloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCR3U Applications of Right Angle Trigonometry AssignmentDokument1 SeiteMCR3U Applications of Right Angle Trigonometry Assignmentapi-22661649Noch keine Bewertungen
- MathDokument3 SeitenMathMELCRIS VICHONoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Trig Functions: EQ: How Do I Use Trigonometry in Real-Life Application Problems?Dokument20 SeitenApplications of Trig Functions: EQ: How Do I Use Trigonometry in Real-Life Application Problems?Dipak KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 9 Quarter 4 Week 4Dokument16 SeitenMathematics 9 Quarter 4 Week 4DENISE MAREE ROMASANTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 CH 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry Session 1Dokument48 SeitenGrade 10 CH 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry Session 1Swapnil YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quarter 4 Week 4Dokument10 SeitenQuarter 4 Week 4Josiah hernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry Word ProblemsDokument5 SeitenTrigonometry Word ProblemsVincent GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Trig Functions: EQ: How Do I Use Trigonometry in Real-Life Application Problems?Dokument19 SeitenApplications of Trig Functions: EQ: How Do I Use Trigonometry in Real-Life Application Problems?Charry DawnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Josiah T. Hernandez QUARTER 4 WEEK 4Dokument10 SeitenJosiah T. Hernandez QUARTER 4 WEEK 4Josiah hernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrigonometryDokument37 SeitenTrigonometryTushar Gawande67% (3)
- 10 CH 9 ExamplesDokument24 Seiten10 CH 9 ExamplesSwapnil YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW Chapter 6Dokument12 SeitenHW Chapter 6crampingpaul100% (1)
- Midterm Exam Trigonometry Math Ii GENERAL DIRECTION: Solve Each of The Following Problems. Write Your Solution/s On TheDokument1 SeiteMidterm Exam Trigonometry Math Ii GENERAL DIRECTION: Solve Each of The Following Problems. Write Your Solution/s On TheNico SoredaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics: (Chapter - 9) (Some Applications of Trigonometry)Dokument19 SeitenMathematics: (Chapter - 9) (Some Applications of Trigonometry)HappyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 8 QTR 4 Week 1Dokument12 SeitenMath 8 QTR 4 Week 1Sancho ManlangitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Trigonometry FilesDokument4 SeitenSample Trigonometry FilesAmelita TupazNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1692343286521.QP - CB - X - Math - CH - 9. Some Applications of Trigonometry - MCQDokument3 Seiten1692343286521.QP - CB - X - Math - CH - 9. Some Applications of Trigonometry - MCQNEEL PAREKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ttrignometric Ratios Real World Sohcahtoa Worksheet Ans EtzDokument6 SeitenTtrignometric Ratios Real World Sohcahtoa Worksheet Ans EtzsarikaagrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH9 Q4 WEEK 3 To 5 HYBRID VERSION1Dokument14 SeitenMATH9 Q4 WEEK 3 To 5 HYBRID VERSION1Mystic AungNoch keine Bewertungen
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: OME Pplications OF RigonometryDokument11 Seiten© Ncert Not To Be Republished: OME Pplications OF RigonometryAkshit MalhotraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3Dokument15 Seiten3api-394983937Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plane TrigonometryDokument76 SeitenPlane TrigonometryjesreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigo Bridging 1 and 2Dokument19 SeitenTrigo Bridging 1 and 2blackmasque100% (1)
- Week 8 Solving Problems SimilarityDokument20 SeitenWeek 8 Solving Problems SimilarityMiriuki Irys Oreo DiolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRIGONOMETRY Workshop Ee 8thDokument7 SeitenTRIGONOMETRY Workshop Ee 8thSonali SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heights and Distances-1Dokument18 SeitenHeights and Distances-1Little BoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrigonometryDokument26 SeitenTrigonometryDwayne TraceyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Questions Trigonometry PDFDokument2 SeitenReview Questions Trigonometry PDFKenneth ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Similarity and Trigonometry - DocDokument19 SeitenSimilarity and Trigonometry - DocJuan Moya Moreno100% (1)
- 2016 Regional Geometry Exam Final PDFDokument15 Seiten2016 Regional Geometry Exam Final PDFPartha SarathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q1 W5 6 Lesson 3 Right Triangle TrigonometryDokument5 SeitenQ1 W5 6 Lesson 3 Right Triangle Trigonometrydelacruz.483586150028Noch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 1 of TrigonometryDokument3 SeitenWorksheet 1 of TrigonometrycandelanibalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lengths and Distances 230602 164642Dokument5 SeitenLengths and Distances 230602 164642JOBIN WilsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP - Hyperlink FilesDokument4 SeitenLP - Hyperlink Filesapi-352439078100% (1)
- Angle of Elevation and Angle of Depression: Pattern in Solving ProblemsDokument8 SeitenAngle of Elevation and Angle of Depression: Pattern in Solving ProblemsCharmaine PamesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 Illustrates Theorems On Triangle InequalitiesDokument51 SeitenLesson 1 Illustrates Theorems On Triangle InequalitiesCianele CambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PP APPLICATIONOFTRIGONOMETRY - D05 Oct 2023Dokument12 SeitenPP APPLICATIONOFTRIGONOMETRY - D05 Oct 2023vyom.jatindpsvNoch keine Bewertungen
- University OF Engineering & Technology., G.T. Road, LahoreDokument5 SeitenUniversity OF Engineering & Technology., G.T. Road, LahoremsbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry WorkbookDokument74 SeitenTrigonometry WorkbookBeatixe CanumayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Quarter 4 - Module 2: Theorems On Triangle InequalitiesDokument10 SeitenMathematics Quarter 4 - Module 2: Theorems On Triangle InequalitiesMcDonz AmbonganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angle of ElevationDokument8 SeitenAngle of ElevationWinna Salve LatigayNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCTG46Dokument8 SeitenLCTG46cri fernadezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 3 G9Dokument24 SeitenMath 3 G9Aiza MaltoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAS - Math-9 4th QuarterDokument32 SeitenLAS - Math-9 4th QuarterRussell Ryder AustriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPLM Trigonometry Part 2Dokument33 SeitenSPLM Trigonometry Part 2Joey TelinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCR 3U Trig IdentitiesDokument2 SeitenMCR 3U Trig IdentitiesFirmino GonçalvesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Application Worksheet 2f4u132Dokument2 Seiten4 Application Worksheet 2f4u132ahmed mahamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Sine, Cosine and TangentDokument6 SeitenApplication of Sine, Cosine and TangentGIDEON PAULNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemoDokument42 SeitenDemoSayrene NaragNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrigonometryDokument43 SeitenTrigonometryAnwar Hossain75% (8)
- Dancing With The DeadDokument2 SeitenDancing With The DeadAshwiniSelvakumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sharpay Likes Troy But Troy Is With Gabriella. Gabriella Is Pregnant Buy Troy Is GayDokument6 SeitenSharpay Likes Troy But Troy Is With Gabriella. Gabriella Is Pregnant Buy Troy Is GayAshwiniSelvakumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.5B-7.6 HandoutDokument3 Seiten7.5B-7.6 HandoutAshwiniSelvakumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Watch Me Change The WorldDokument1 SeiteWatch Me Change The WorldAshwiniSelvakumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/42Dokument20 SeitenCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/42DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math8 - q1 - Mod5b - Adding and Subtracting Similar and Dissimilar Rational Algebraic Expressions - 0809Dokument29 SeitenMath8 - q1 - Mod5b - Adding and Subtracting Similar and Dissimilar Rational Algebraic Expressions - 0809sophia gwynethNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Calculus AB 2013 Summer PacketDokument5 SeitenAP Calculus AB 2013 Summer Packet2013seniorformsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 789 OplDokument70 Seiten789 OplKartikKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Titu Andreescu - 103 TrigonomeDokument229 SeitenTitu Andreescu - 103 Trigonomevictorfpb100% (7)
- Grade 7 Undefined TermsDokument22 SeitenGrade 7 Undefined Termskaren takasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mon Monomial FactoringDokument32 SeitenMon Monomial FactoringLANCE ANTHONY ABALLANoch keine Bewertungen
- Triangle: Obtuse Triangle Has One Angle Greater Than 90°. Each ofDokument7 SeitenTriangle: Obtuse Triangle Has One Angle Greater Than 90°. Each ofAmmar AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 8 HMWRK Lesson 6Dokument3 SeitenModule 8 HMWRK Lesson 6ReekhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Factoring and GCMFDokument16 SeitenIntro To Factoring and GCMFAryne Luzano0% (1)
- Angles and Arcs of Circles PowerPointDokument63 SeitenAngles and Arcs of Circles PowerPointJP Gorospe50% (2)
- Third Dimension Math CalulcationDokument86 SeitenThird Dimension Math Calulcationozzy75Noch keine Bewertungen
- Krishna's Question Bank Analytical GeometryDokument291 SeitenKrishna's Question Bank Analytical Geometryijoky63% (8)
- Descrete Math 2 - 3 Functions CompleteDokument38 SeitenDescrete Math 2 - 3 Functions Completeimmah inayatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Solving Strategies: STRATEGY #1: Use of PatternDokument13 SeitenProblem Solving Strategies: STRATEGY #1: Use of PatternTherese Grace Postrero100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Log: School Grade Level 7 Teacher Learning Area MATHEMATICS Teaching Dates and Time Quarter SECONDDokument12 SeitenDaily Lesson Log: School Grade Level 7 Teacher Learning Area MATHEMATICS Teaching Dates and Time Quarter SECONDVanessa Pangan KellerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 8 - Third Summative Test: Lawaan National High SchoolDokument3 SeitenMathematics 8 - Third Summative Test: Lawaan National High SchoolJohn Mark SandoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Triangles and Its PropertiesDokument26 SeitenTriangles and Its PropertiesBharatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Formula HandbookDokument2 SeitenMathematical Formula HandbookSameer SyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- RMC 2014 PDFDokument104 SeitenRMC 2014 PDFAndrei346Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Test 40 Questions - 75 MinutesDokument13 SeitenPractice Test 40 Questions - 75 MinutesMbadilishaji DuniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHEET No 1 (Section of Solids)Dokument5 SeitenSHEET No 1 (Section of Solids)Ayush Ranjan100% (1)
- Maths AssignmentDokument4 SeitenMaths AssignmentSOHAM CHATTERJEENoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP 2 13thDokument5 SeitenDPP 2 13thsuar90Noch keine Bewertungen
- SEA 2010 Mathematics PDFDokument22 SeitenSEA 2010 Mathematics PDFAnna Del Rey ValtersenNoch keine Bewertungen
- L1 Linear EquationsDokument50 SeitenL1 Linear EquationsjillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Teacher: Date: Score:: Fractions WorksheetsDokument2 SeitenName: Teacher: Date: Score:: Fractions WorksheetsAnnrouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geom12020 ExamDokument28 SeitenGeom12020 ExamHenry LanguisanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MathCanTakeYouPlaces TGDokument496 SeitenMathCanTakeYouPlaces TGJrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 5 288 1620 PDFDokument13 SeitenPaper 5 288 1620 PDFShakerMahmoodNoch keine Bewertungen