Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Set 719e8be6
Hochgeladen von
davidvpnOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Set 719e8be6
Hochgeladen von
davidvpnCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
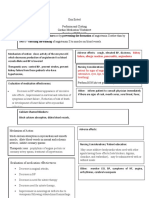
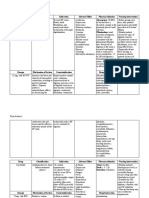
Cardiac Pharm Drugs
Study online at quizlet.com/_ikf3l
Abciximab,
Eptifibatide,
Tirofiban
Platelet Receptor Glycoprotein Inhibitors
Prevents platelet aggregation by competing with
fibrinogen for glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptors on
platelet surface
Indications - Adjunct to PCI for UA/NSTEMI.
Contraindications - Active internal bleeding,
GI/GU bleeding or recent stroke, coagulation
disorders, platelet count < 100k, INR >1.2
2.
ACE
Inhibitors
Lisinopril (Zestril)
3.
ACS Drugs
Clopidogrel
Dipyridamole
Aspirin
Abciximab
Eptifibatide
Tirofiban
Heparin
Lovenox
Fondaparinux
Bivalirudin
Desiruden
Warfarin
Dabigatran
Rivaroxaban
Alteplase
Reteplase
Tenecteplase
Urokinase
Streptokinase
1.
4.
Adenosine
Antiarrhythmic Agent
Slows AV node conduction time, interrupting AV
node re-entry pathways.
Indications - PSVT
Contraindications - 2nd or 3rd degree AVB w/o
pacer, sinus brady, bronchospasm disorders.
Adverse Effects - Flushing, dyspnea, chest
pressure, lightheadedness, bradycardia,
complete AVB.
5.
Adenosine
Other
6 second half-life.
6.
Adenosine
Trade Name
Adenocard
7.
Alpha2
Agonists
Methyldopa
Clonidine
8.
Alpha
Blockers
Prazosin
Doxizosin
Terazosin
9.
Alteplase
ACS Drug - Fibrinolytic Agent
Binds to fibrin and converts tissue plasminogen
to plasmin, promoting fibrinolysis.
Indications - STEMI, acute thrombotic CVA with
symptoms 3 hours or less, acute PE.
Contraindications - Many, see thrombolytic
protocol.
Adverse Effects - Bleeding, intracranial
hemorrhage, reperfusion arrhythmias.
10.
Alteplase Trade
Name
Activase
11.
Amiodarone
Antiarrhythmic Agent - Class III
Prolongs action potential phase 3,
prolonging repolarization/refractoriness.
NO effect on conduction velocity or
automaticity.
Indications - Life threatening ventricular
arrhythmias.
Contraindications - 2nd or 3rd degree
AVB, Long QT, Pregnancy or
breastfeeding.
Adverse Effects - Corneal deposits,
pulmonary toxicity or peripheral
neuropathy with prolonged use.
12.
Amiodarone
Other
BLACK BOX WARNING
Hospitalize to administer loading dose or
dose changes. Restrict use to life
threatening arrhythmias only due to drug
associated toxicity.
13.
Amiodarone
Trade Name
Cordarone
14.
Amlodapine
Dihydropyridine CCB
Inhibits calcium influx into vascular
smooth muscle and myocardium primarily
reducing peripheral vascular resistance.
Indications - HTN, Angina.
Contraindications - Hypersensitivity
Adverse Effects - Peripheral edema,
fatigue, palpitations, may exacerbate
angina.
15.
Amlodipine Trade
Name
Norvasc
16.
Angiotensin
Receptor Blocker
Losartan (Cozaar)
17.
Antihypertensives
Furosemide
Chlorthalidone
Hydrochlorothiazide
Triamterene
18.
Aspirin
Antiplatelet Agent
Blocks thromboxane synthesis and
inhibits platelet activation and aggregation
for the lifetime of the platelet (5-7 days).
Indications - Anything requiring platelet
aggregation inhibition (ACS, etc.)
Contraindications - ASA or NSAID induced
asthma or urticaria, uncontrolled HTN, GI
bleeding, ASA triad.
Adverse Effects - N/V/D/C other GI
issues, rash, tinnitus.
19.
Atenolol
Beta Blocker
Selectively antagonizes beta-1 adrenergic
receptors in the heart, reducing rate and
contractility.
Indications - Acute MI, HTN, Angina
Contraindications - Uncompensated HF,
cardiogenic shock, bradycardia.
Adverse Effects - Bradycardia, hypotension,
bronchospasm, fatigue, depression,
impotence, loss of libido.
26.
Clonidine
Alpha 2 Agonist
Stimulates alpha 2 adrenergic receptors
(centrally acting antihypertensive), reducing
sympathetic outflow from vasomotor centers in
the brain.
Indications - HTN
Contraindications - abrupt discontinuation
(causes rebound HTN)
Adverse Effects - xerostomia, drowsiness,
hypotension, bradycardia.
20.
Atrovastatin
Trade Name
Lipitor
27.
Clonidine
Trade Name
Catapres
21.
Beta Blockers
Atenolol
Metoprolol
Propranalol
28.
Clopidogrel
22.
Bile Acid
Binding Resins
Cholestyramine
Colestipol
Colesevelam
23.
Bivaliruden
ACS Drug - Direct Thrombin Inhibitor
Directly and reversibly inhibits circulating
thrombin.
Indications - Anticoagulation in patients
undergoing PCI.
Contraindications - IM administration, active
bleeding.
Adverse Effects - Injection site reaction,
hemorrhage.
Anitplatelet Agent
Irriversibly inhibits ADP receptors on the
surface of platelets, reducing platelet
aggregation: augments cGMP production,
dilating coronary arteries.
Indications - Thromboembolism prophylaxis,
NSTEMI, STEMI.
Contraindications - Active bleeding
Adverse Effects - Bleeding and bruising,
pruritis.
29.
Clopidogrel
Other Info.
A prodrug- must be metabolized by CYP2C19 to
become active. Proton Pump Inhibitors,
particularly omeprazole, inhibits activation. It is
important to identify poor metabolizers with
ACS.
30.
Clopidogrel
Trade Name
Plavix
31.
Colestipol
and
Colesevelam
Bile Acid Binding Resins
Bind bile acids and bile salts in the small
intestines, inhibiting their reuptake by the
enterohepatic system. This triggers
hepatocytes to increase conversion of
cholesterol to bile acids to replenish the lost
supply, requireing increased hepatic uptake of
LDL particles form the blood, lowering blood
LDL concentrations.
Indications - Elevated LDL
32.
Dabigatran
ACS Drug - Oral Anticoagulant
Direct thrombin inhibitor that directly and
reversibly inhibits circulating thrombin.
Indications - Thromboembolism and stroke
prophylaxis.
Contraindications - Active bleeding, mechanical
heart valve.
Adverse Effects - GI s/s, bleeding and
bruising. Increased risk of MI over Warfarin.
33.
Dabigatran
Trade Name
Pradaxa
34.
Desirudin
ACS Drug - Direct Thrombin Inhibitor
Directly and reversibly inhibits circulating
thrombin.
Indications - DVT prophylaxis
Contraindications - IM administration, active
bleeding.
Adverse Effects - Injection site reaction,
anemia, hemorrhage, anaphylaxis.
24.
25.
Chlorthalidone
and HCTZ
Cholestyramine
Thiazide Diuretic
Inhibits distal convoluted tubule sodium and
chloride resorption.
Used for HTN and edema.
Contraindications/adverse effects - anuria,
hypokalemia, hyperuricemia, hyperglycemia,
lowered electrolytes and photosensitivity.
Bile Acid Binding Resin
Bind bile acids and bile salts in the small
intestines, inhibiting their reuptake by the
enterohepatic system. This triggers
hepatocytes to increase conversion of
cholesterol to bile acids to replenish the lost
supply, requireing increased hepatic uptake
of LDL particles form the blood, lowering
blood LDL concentrations.
Indications - Elevated LDL, BBW:
cholestasis-associated pruritis and diarrhea
pruritis.
Contraindications - biliary obstruction
Adverse Effects - Abdominal pain, cramps,
distention, constipation, fecal impaction,
may reduce absorption of other drugs, may
lower plasma folate levels.
35.
Digoxin
Antiarrhythmic Agent
Prolongs the effective refractory period and
diminishes conduction velocity in the AV node.
Indications - Rate control of chronic Afib in
systolic heart failure.
Contraindications - Vfib, myocarditis, Acute MI,
IHSS, WPW.
Adverse Effects - NVD, anorexia, bradycardia,
haloes around lights.
36.
Digoxin
Trade Name
Lenoxin
37.
Diltiazem
CCB
Non-dihydropyridine CCB, inhibits calcium ion
influx into vascular smooth muscle and
myocardium, primarily reducing heart rate and
contractility.
Indications - HTN, Angina, SVT, Afib, Aflutter.
Contraindications - 2nd and 3rd degree AV
blocks, cardiogenic Shock, hypotension,
afib/flutter with accessory bypass tract, CHF,
sick sinus syndrome.
Adverse Effects - MC constipation and
peripheral edema. Headache, bradycardia, AV
block.
38.
Diltiazem AA
Antiarrhythmic Agent - Class IV
Non-dihydropyridine CCB - inhibits calcium
channel influx into vascular smooth muscle
and myocardium, primarily reducing heart rate
and contractility by prolonging AV nodal
refractoriness.
Indications - HTN, Angina, Afib, Aflutter.
Contraindications - 2nd or 3rd degree AVB,
cardiogenic shock, hypotension, Afib/Aflutter
with bypass tract.
Adverse Effects - MC is constipation and
peripheral edema. HA and dizziness,
bradycardia, AV block.
39.
Diltiazem
Trade Name
Cardizem
40.
Dipyridamole
Antiplatelet Agent
Inhibits platelet uptake of adenosine and
blocks ADP-induced platelet aggregation;
augments cGMP production, dilating coronary
arteries.
Indications - Thromboembolism prophylaxis.
Contraindications - Hypersensitivity
Adverse Effects - Severe HA and diarrhea,
resolves with continued use.
41.
Dipyridamole
Trade Name
Persantine
42.
Direct
Vasodilators
Hydralazine
Minoxidil
Sodium Nitroprusside
43.
Drug
Contraindication
Pearl
All drugs are contraindicated if the patient
is hypersensitive or has had a previous
reaction to any class or component of the
drug, unless otherwise explained.
44.
Esmolol
Antiarrhythmic Agent - Class II
Selectively antagonizes beta-1 adrenergic
receptors.
Indications - PSVT, Hypertensive
emergency.
Contraindications - 2nd or 3rd degree AVB
w/o pacer, sinus brady, cardiogenic shock,
uncompensated heart failure.
Adverse Effects - Hypotension, bradycadia,
heart block, bronchospasms.
45.
Ezetimibe
Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitor
Selectively inhibits absorption of dietary
and biliary cholesterol at the small intestinal
brush border, causing the liver to have to
use increased amounts of cholesterol from
the blood.
Indications - Hyperlipidemia
Contraindications - Hypersensitivity
Adverse Effects - Diarrhea, URI s/s
46.
Ezetimibe Trade
Name
Zetia
47.
Fibric Acid
Derivative
Other Info.
May lower LDL, but when decreasing
elevated trigs, LDL-C may increase.
Particularly indicated in patients with
hypertriglyceridemia severe enough to be at
risk for pancreatitis and those who have
hypertriglycerideamia with low LDL-C.
48.
Fish Oil
Supplement
Contains eicosapentaenoic acid and
docosahexaenoic acid - which somehow
lower triglycerides.
Indications - Hypertriglyceridemia
Contraindications - Known allergy or
hypersensitivity to fish, fish oil, or omega-3
fatty acid products derived from fish.
Adverse Effects - Nausea and Diarrhea are
MC.
49.
Flecainide
Antiarrhythmic Agent - Class 1c
Stabilizes membranes, depresses action
potential phase 0. Strongly reduces
conduction velocity, decreases
automaticity, has NO effect on
repolarization/refractoriness.
Indications - Prevention of paroxysmal atrial
flutter/fib. Life threatening ventricular
arrhythmias.
Contraindications - 2nd or 3rd degree AVB
w/o pacer, bifascicular block w/o pacer
Adverse Effects - Arrhythmias, QT
prolongation, Torsades.
50.
Flecainide
Other
BLACK BOX WARNING
Increased mortality in asymptomatic non-life
threatening ventricular arrhythmias w/ MI 6
days - 2 years prior. Restrict use to lifethreatening arrhythmias only.
51.
Fondaparinux
ACS Drug - Parenteral Anticoagulant
Synthetic selective factor Xa inhibitor that
selectively binds to antithrombin III,
potentiating factor Xa neutralization and
inhibition of thrombin formation.
Indications - ACS, DVT prophylaxis
Contraindications - Severe thrombocytopenia,
active bleeding, epidural or spinal anesthesia.
Adverse Effects - Injection site reaction,
anemia, hemorrhage, HIT.
52.
53.
54.
55.
56.
Fondaparinux
Other
Furosemide
As effective and safe as UFH and LMWH for
prophylaxis and Tx of VTE, but much less
likely to cause heparin-induced
thrombocytopenia.
Black Box Warning - Spinal/Epidural
hematomas may occur with spinal or epidural
puncture in anticoagulated patients.
Loop Diuretic
Inhibits Loop of Henle and proximal and distal
confoluted tubule sodium and chloride
resorption.
Used for HTN and edema.
Contraindications - anuria, hepatic coma and
electrolyte imbalances or depletion.
Most potent of the antihypertensives
Furosemide
Trade Name
Lasix
Gemfibrozil
and
Fenofibrate
Fibric Acid Derivative
Inhibits peripheral lipolysis, decreases hepatic
free fatty acid extraction, inhibits synthesis
and incrases clearance of VLDL carrier
apolipoprotein B (APOB), mechanism of
increased HDL unknown.
Indications - Hyperglyceridemia
Contraindications - Gallbladder disease,
hepatic impairment, unexplained elevation of
LFTs.
Adverse Effects - Increased AST/ALT, GI
complaints, potentially cholelithiasis, hepatitis
and myositis.
Heparin
Other
Shorter half life, more variable anticoagulant
response, more adverse bleeding than LMW
version. Must be monitored with PTT. Must be
given in hospital.
57.
Heparin
(UFH)
ACS Drug - Parenteral Anticoagulant
Increases rate of action of antithrombin III's
effect on inhibiting clotting factor thrombin and
factor Xa by a 1000 fold.
Indications - Thromboembolism prophylaxis and
Tx, PCI, adjunct Tx for STEMI and NSTEMI.
Contraindications - hypersensitivity to pork
products, IM administartion, severe
thrombocyopenia, hx of HIT, hemorrhage or
active bleeding (except if DIC).
Adverse Effects - Bleeding and bruising, HIT
58.
Hydralazine
Direct Vasodilator
Directly dilates arterioles, not veins, reducing
SVR.
Indications - HTN and hypertensive emergency.
Contraindications - Coronary Artery Disease
Adverse Effects - Headache, tachycardia,
angina, palpitations
59.
Lidocaine
Antiarrhythmic Agent - Class 1b
Inhibits Na ion channels, stabilizing neuronal cell
membranes and inhibiting nerve impulse initiation
and conduction. Primarily decreases
automaticity. Mild decrease in conduction
velocity and repolarization/refractoriness.
Indications - Ventricular arrhythmias.
Contraindications - WPW, Stokes-adams
syndrome, AVB w/o pacemaker.
Adverse Effects - Hypotension, seizures,
respiratory arrest.
60.
Lidocaine
Trade Name
Xylocaine
61.
Lisinopril
ACE Inhibitor
Blocks conversion of angiotensin I to
angiotensin II.
Indications - heart failure, HTN, and as a renal
protectent in DM.
Contraindications - hx of angioedema,
pregnancy.
Adverse Effects - angioedema, hypotension,
cough, hyperkalemia.
62.
Lisinopril
Trade Name
Zestril
63.
Lorsartan
Trade Name
Cozaar
64.
Losartan
ARB
Blocks receptors in peripheral vasculature and
adrenals for angiotensin II.
Indications - HTN, T2DM nephropathy.
Contraindications - pregnancy
Adverse Effects - angioedema, hypotension,
URI s/s.
65.
Lovenox
ACS drug - Parenteral Anticoagulant
Accelerates interaction of antithrombin III with
Factor Xa, but not with thrombin.
Indications - ACS, DVT prophylaxis
Contraindications - Hypersensitivity to pork
products or benzyl alcohol, active major
bleeding, thrombocytopenia history.
Adverse Effects - Local injection site reaction,
anemia, hemorrhage, thrombocytopenia.
66.
Lovenox
Other
Longer half life, less variable anticoagulant
response, fewer adverse bleeding than UFH.
Does not need to be monitored with PTT, may
be given in hospital or out.
Black Box Warning - Spinal/Epidural hematomas
may occur with spinal or epidural puncture in
anticoagulated patients.
72.
Niacin
Nicotinic Acid
Inhibits lipolysis at the cellular level. Lipolysis
produces free fatty acids which the liver uses
to make triglycerides, VLDLs and ultimately
LDLs. Also increases HDL levels.
Indications - Hypercholesterolemia (lowers
trigs and raises HDL mostly, also lowers LDL
somewhat)
Contraindications - Active peptic ulcers or
arterial bleeding, active liver disease.
Adverse Effects - Flushing, pruritis, GI
distress, glucose intolerance, hyperuricemia.
73.
Other Lipid
Lowering
Drugs
Cholestyramine
Colestipol
Colesevelam
Niacin
Gemfibrozil
Fenofibrate
Ezetimibe
Fish Oil
Red Yeast Rice
67.
Low
Molecular
Weight
Heparin
Trade Name
Lovenox
68.
Methyldopa
Alpha 2 Agonist
Stimulates alpha 2 adrenergic receptors
(centrally acting antihypertensive), reducing
sympathetic outflow from vasomotor centers in
the brain.
Indications - HTN
Contraindications - Hepatitis or Cirrhosis
Adverse Effects - sedation, headache, black
tongue, orthostatic hypotension.
74.
Prazosin,
Doxazosin,
Terazosin
Alpha Blockers
Blocks alpha 1 adrenergic receptors, causing
relaxation of arteriole and venous smooth
muscles, reducing PVR.
Indications - HTN, BPH
Contraindications - Hypersensitivity
Adverse Effects - Hypotension with the first
few doses. Headache, dizziness, nausea,
palpitations.
69.
Methyldopa
Trade Name
Aldomet
75.
Procainamide
70.
Metoprolol
Beta Blocker
Selectively antagonizes beta-1 adrenergic
receptors in the heart, reducing rate and
contractility.
Indications - Acute MI, HTN, Angina, Heart
Failure.
Contraindications - Uncompensated HF,
cardiogenic shock, bradycardia.
Adverse Effects - Bradycardia, hypotension,
bronchospasm, fatigue, depression, impotence,
loss of libido.
Antiarrhythmic Agent - Class 1a
Stabilizes membranes, depresses action
potential phase 0. Decreases conductions
velocity, increases repol./refractoriness, and
decreases automaticity.
Indications - Ventricular arrhythmias.
Contraindications - SLE, 2nd and 3rd degree
AV blocks, Torsades, Long QT syndrome,
uncorrected electrolyte abnormalities.
Adverse Effects - hypotension, bradycardia,
QT prolongation, SLE
76.
Propranolol
Beta Blocker
Non-selective. Antagonized Beta-1 and Beta-2
adrenergic receptors (heart and lungs).
Indications - HTN, Angina, SVT, Migraine
prophylaxis.
Contraindications - Uncompensated HF,
cardiogenic shock, bradycardia.
Adverse Effects - Bradycardia, hypotension,
bronchospasm, fatigue, depression,
impotence, loss of libido.
71.
Minoxidil
Direct Vasodilator
Directly dilates arterioles, not veins, reducing
SVR.
Indications - Refractory HTN
Contraindications - hypersensitivity
Adverse Effects - CHF, SJS
77.
Red Yeast
Rice
Supplement
Contains several compounds collectively
known as monacolins, substances known to
inhibit cholesterol synthesis. One of which has
the same chemical structure as lovastatin and
mevinolin, potent HMG-CoA reductase
inhibitors.
Indications - hyperlipidemia
Contraindications - pregnancy and/or breast
feeding.
Adverse Effects - HA, GI complaints.
78.
Reteplase
and
Tenecteplase
ACS Drug - Fibrinolytic Agent
Binds to fibrin and converts tissue
plasminogen to plasmin, promoting fibrinolysis.
Indications - STEMI
Contraindications - Many, see thrombolytic
protocol
Adverse Effects - Bleeding, intracranial
hemorrhage, reperfusion arrhythmias.
79.
Reteplase
Trade Name
Retavase
80.
Rivaroxaban
ACS Drug - Oral Anticoagulant
Direct thrombin inhibitor that directly and
reversibly inhibits circulating thrombin.
Indications - Thromboembolism and stroke
prophylaxis, DVT prophylaxis and Tx.
Contraindications - Acvtive bleeding, Hepatic
impairment.
Adverse Effects - Bleeding, Elevated LFTs,
Thrombocytopenia.
81.
Rivaroxaban
Trade Name
Xerelto
82.
Rosuvastatin,
Atorvastatin,
Simvastatin,
Pravastatin,
Lovastatin
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor
Inhibits HMG-CoA reductase, the enzyme that
converts HMG-CoA to de novo cholesterol in
cells, which leads to cells increasing the
number of cell-surface LDL receptors that can
bind to circulating LDLs, lowering blood LDL
levels.
Indications - Hyperlipidemia
83.
Rosuvastatin
Trade Name
Crestor
84.
Simvastatin
Trade Name
Zocor
85.
Sodium
Nitroprusside
Direct Vasodilator
Powerful parenteral vasodilator - dilates both
arterioles and venules, reducing both PVR and
venous return.
Indications - Hypertensive emergency
Contraindications - Hypersensitivity (among
many others).
Adverse Effects - Hypotension, cyanide
toxicity, metahemaglobinemia. Can cause
precipitous decrease in BP. Cyanide levels
reach toxic amounts with prolonged use or
high infusion rates.
86.
Sotalol
Antiarrhythmic Agent - Class III
Non-selectively antagonizes beta 1 and beta
2 adrenergic receptors, prolonging action
potential phase 3.
Indications - Ventricular arrhythmias,
symptomatic afib/aflutter.
Contraindications - 2nd or 3rd degree AVB,
sinus brady, cardiogenic shock,
uncompensated heart failure.
Adverse Effects - Hypotension, bradycardia,
heart block, bronchospasms, QT
prolongation, torsades.
87.
Sotalol Other
BLACK BOX WARNING
Administer in facility with EKG until stable
maintenance does x3 days in found.
88.
Sotalol Trade
Name
Betapace
89.
Statin Drugs
(Lipid
Lowering
Drugs)
Lovastatin
Atorvastatin
Rosuvastatin
Simvastatin
Pravastatin
90.
Streptokinase
ACS Drug - Fibrinolytic Agent
Binds to fibrin and converts tissue
plasminogen to plasmin, promoting
fibrinolysis.
Indications - STEMI, PE, and occluded IV
catheters.
Contraindications - Hypersensitivity.
Adverse Effects - Bleeding.
91.
Tenecteplase
Trade name
TNKase
92.
Thriamterene
Potassium-sparing diuretic.
Inhibits sodium reabsorption at the DCT,
decreasing water resorption and increasing
potassium retention.
Indications - HTN and edema.
Contraindications - severe renal disease,
anuria.
Adverse Effects - Fatigue, hyperkalemia.
93.
Urokinase
ACS Drug - Fibrinolytic Agent
Binds to fibrin and converts tissue
plasminogen to plasmin, promoting
fibrinolysis.
Indications - PE and occluded IV catheters.
Contraindications - Hypersensitivity
Adverse Effects - Bleeding
94.
Verapamil
CCB
Non-dihydropyridine CCB, inhibits calcium ion influx into vascular smooth muscle and myocardium, primarily reducing
heart rate and contractility.
Indications - HTN, Angina, SVT, Afib, Aflutter, Migraine prophylaxis
Contraindications - 2nd and 3rd degree AV blocks, cardiogenic Shock, hypotension, afib/flutter with accessory bypass
tract, CHF, sick sinus syndrome.
Adverse Effects - MC constipation and peripheral edema. Headache, bradycardia, AV block.
95.
Warfarin
ACS drug - Oral Anticoagulant
Inhibits vitamin K-dependent coagulation factor synthesis (II, VII, IX, X, protein C and S).
Indications - Anticoagulation in patients for DVT prophylaxis. Thromboembolic complications of Afib. Thromboembolic
prophylaxis with bio synthetic and mechanical heart valves.
Contraindications - Bleeding, malignant HTN, Many more.
Adverse Effects - Bleeding and bruising, abdominal cramps, purple toes syndrome.
96.
Warfarin
Other
Must monitor effectiveness with PT/INR.
Black Box Warning - Major or Fatal Bleeding Risk
97.
Warfarin
Trade Name
Coumadin
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 19BCPDokument64 Seiten19BCPNinna Isabel VictorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument7 SeitenDrug StudyAnn Therese C. GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Guide For Final Pharmacology HypertensionDokument39 SeitenStudy Guide For Final Pharmacology HypertensionAlejandro Daniel Landa MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardio Lab MedsDokument11 SeitenCardio Lab MedsDianne Erika MeguinesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiotonic DrugsDokument67 SeitenCardiotonic DrugsLady Mae Ramos100% (1)
- 17 Cardiac DrugsDokument6 Seiten17 Cardiac DrugshiwaralelataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency Drugs KathDokument29 SeitenEmergency Drugs Kathmajin655Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Medications TemplateDokument5 SeitenCardiac Medications TemplateErinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug CardsDokument38 SeitenDrug CardsJason D Wilkins92% (25)
- Pertemuan 7 LiyanaDokument36 SeitenPertemuan 7 LiyanaLiyana SafitriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congestive Heart Failure: CardiacDokument36 SeitenCongestive Heart Failure: CardiacHUZAIFA YAMAANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rug Therapy For Heart Failure: Dr. Santhosh RamakrishnaDokument40 SeitenRug Therapy For Heart Failure: Dr. Santhosh RamakrishnaNiteesh Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument6 SeitenDrug StudyMaurence John Feliciano LuluquisenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study CARDIODokument17 SeitenDrug Study CARDIODiannetotz Morales100% (1)
- Heart Talk (Ii) in Pandemic Of: COVID-19Dokument27 SeitenHeart Talk (Ii) in Pandemic Of: COVID-19Alles FirmansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class: Statin (PCKS9 Inhibitors) o High Intensity: Atorvastatin (Lipitor), Rosuvastatin (Crestor)Dokument15 SeitenClass: Statin (PCKS9 Inhibitors) o High Intensity: Atorvastatin (Lipitor), Rosuvastatin (Crestor)LionelWrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug ReviseDokument6 SeitenDrug ReviseNikko DioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anticoagulant/Thrombolytic 1. Anticoagulant: Parenteral AnticoagulantsDokument4 SeitenAnticoagulant/Thrombolytic 1. Anticoagulant: Parenteral AnticoagulantsHannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiology Review: HTN: Julia Akaah M.DDokument40 SeitenCardiology Review: HTN: Julia Akaah M.DJose LunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacotherapy of Hypertension: Dr. R. Jamuna Rani MD, Professor & HOD, Department of PharmacologyDokument24 SeitenPharmacotherapy of Hypertension: Dr. R. Jamuna Rani MD, Professor & HOD, Department of PharmacologyshyamkattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti Hypertensive 20191211Dokument35 SeitenAnti Hypertensive 20191211helloitsmenadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study For TetanusDokument10 SeitenDrug Study For TetanusMei PayumoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study GuideDokument9 SeitenDrug Study GuideSh3meeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11A Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemDokument85 Seiten11A Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemJaps De la CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument23 SeitenDrug StudyJoyce Anne SupnetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument28 SeitenDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 22 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE - 2Dokument22 SeitenLec 22 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE - 2Abdul MananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Chapter 42 p-3Dokument19 SeitenPharmacology Chapter 42 p-3sho bartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy: Sutomo Tanzil Dept - of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Sriwijaya UniversityDokument44 SeitenCardiovascular Pharmacotherapy: Sutomo Tanzil Dept - of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Sriwijaya UniversitydeviamufidazaharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pages From First Aid For The USMLE Step 1 2015, 25 Edition-2Dokument7 SeitenPages From First Aid For The USMLE Step 1 2015, 25 Edition-2Mahmoud MohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart DrugsDokument10 SeitenHeart DrugsVanessa FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs Class I Sodium Channel Blockers: Disopyramide (Norpace)Dokument5 SeitenAntiarrhythmic Drugs Class I Sodium Channel Blockers: Disopyramide (Norpace)HannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationDokument5 SeitenSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ishac M2 Cardio Antihypertensives 2010Dokument16 SeitenIshac M2 Cardio Antihypertensives 2010Franchesca LugoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneDokument28 SeitenAntihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneLopez JoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATI Flash Cards 06, Medications Affecting The Cardiovascular SystemDokument48 SeitenATI Flash Cards 06, Medications Affecting The Cardiovascular SystemWiilka QarnigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug ClassDokument13 SeitenDrug ClassEdfren Salazar Colon100% (1)
- Pharmacotherapy of Hypertention TerbaruDokument45 SeitenPharmacotherapy of Hypertention TerbarulisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiplatelet Drugs: Thomas Eipe Pharm D InternDokument12 SeitenAntiplatelet Drugs: Thomas Eipe Pharm D InternThomas EipeNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrugsDokument113 SeitenDrugsCARE CATH LABNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacological Management of Ischaemic Heart Disease and Acute Myocardial InfarctionDokument50 SeitenPharmacological Management of Ischaemic Heart Disease and Acute Myocardial InfarctionMuh Akbar BaharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curs Studenti Clase Terapeutice - 2015Dokument84 SeitenCurs Studenti Clase Terapeutice - 2015Teodor NeaguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular PharmacologyDokument61 SeitenCardiovascular PharmacologyTeeOne920% (1)
- 13 Drug StudyDokument6 Seiten13 Drug StudyRachel Yvonne Cabacungan100% (1)
- Pharmacology NoteDokument53 SeitenPharmacology NotefirstrikerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antihypertensives 2Dokument6 SeitenAntihypertensives 2Manyal Kutin KoakNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 and 11 Treatment of Hypertension and AnginaDokument10 Seiten10 and 11 Treatment of Hypertension and AnginaBrandon AviciiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency MedsDokument24 SeitenEmergency MedsNursyNurse100% (1)
- Drugs For Hypertension 2023Dokument19 SeitenDrugs For Hypertension 2023aguilarjanicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Emergency DrugsDokument4 Seiten10 Emergency DrugsmusicwizardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Used in Cardio Vascular SystemDokument138 SeitenDrugs Used in Cardio Vascular SystemSagun lohalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10-11 Treatment of HypertensionDokument11 Seiten10-11 Treatment of HypertensionHanif GandohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antihypertensive Drugs: Dr/Azza Baraka Prof of Clinical Pharmacology Faculty of Medicine Alexandria UniversityDokument71 SeitenAntihypertensive Drugs: Dr/Azza Baraka Prof of Clinical Pharmacology Faculty of Medicine Alexandria UniversityMoonAIRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fu Rose MideDokument3 SeitenFu Rose MideWahyuni SetiawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTN JmiDokument39 SeitenHTN Jmink999999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Curs Studenti Clase Terapeutice - 2015Dokument88 SeitenCurs Studenti Clase Terapeutice - 2015Elie FlorrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 3 Study Guide PharmacologyDokument23 SeitenExam 3 Study Guide PharmacologymmonsonfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeVon EverandCardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set Ea505092Dokument3 SeitenSet Ea505092davidvpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set 4c16c8b0Dokument4 SeitenSet 4c16c8b0davidvpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set 4afee412Dokument1 SeiteSet 4afee412davidvpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Block 2 Lab QuizDokument1 SeiteBlock 2 Lab QuizdavidvpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Assessment Exam 1 - RlblackmoreDokument2 SeitenHealth Assessment Exam 1 - RlblackmoredavidvpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set 64522153Dokument1 SeiteSet 64522153davidvpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1 NUR 151Dokument3 SeitenTest 1 NUR 151davidvpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCLEX True or False QuestionsDokument2 SeitenNCLEX True or False Questionsdavidvpn100% (2)
- Exam 1 (NUR-152)Dokument5 SeitenExam 1 (NUR-152)davidvpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 1: Who Is Florence Nightingale? Principles of Nightingales TheoryDokument1 SeiteExam 1: Who Is Florence Nightingale? Principles of Nightingales TheorydavidvpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMCC Block One Nursing - Exam 1 Study GuideDokument2 SeitenEMCC Block One Nursing - Exam 1 Study GuidedavidvpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Block One Nursing ProcessDokument2 SeitenBlock One Nursing ProcessdavidvpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vocabulary Skin Hair NailsDokument2 SeitenVocabulary Skin Hair NailsdavidvpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Skills Check-Off 2 NUR307L (1) - RevisedDokument1 SeiteSkills Check-Off 2 NUR307L (1) - ReviseddavidvpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1a EVOLVE-CARE PLAN CONSTRUCTOR TUTORIALDokument4 Seiten1a EVOLVE-CARE PLAN CONSTRUCTOR TUTORIALdavidvpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antianginal Student222Dokument69 SeitenAntianginal Student222MoonAIRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Assignment 3Dokument31 SeitenPharmacology Assignment 3Tujiyye kooNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACLS Drug TherapyDokument8 SeitenACLS Drug TherapySahrensNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antianginal Agents - PharmacologyDokument3 SeitenAntianginal Agents - PharmacologyChona FontanillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medication Options For Stage 1 High Blood PressureDokument2 SeitenMedication Options For Stage 1 High Blood PressureRoking KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions PharmaDokument176 SeitenQuestions Pharmaminakshi boss100% (3)
- What Is Treatment of Hypertension?Dokument11 SeitenWhat Is Treatment of Hypertension?health usefulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paramedic Drugs in EMSDokument12 SeitenParamedic Drugs in EMSJim Hoffman100% (4)
- New Drugs 2018 TableDokument12 SeitenNew Drugs 2018 TablePremangshu GhoshalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.a.antianginal DrugsDokument19 Seiten6.a.antianginal DrugswinnirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calcium Channel BlockersDokument2 SeitenCalcium Channel BlockersBrittany RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study On DOPAMINEDokument5 SeitenDrug Study On DOPAMINEshadow gonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care Intravenous Medications ChartDokument2 SeitenCritical Care Intravenous Medications ChartMichelle Danielle MolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q& A PharmacologyDokument17 SeitenQ& A PharmacologyFilipino Nurses CentralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materi Hipertensi Dr. Irma W, SP - PDDokument56 SeitenMateri Hipertensi Dr. Irma W, SP - PDFina Syahrotul AdzimahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complications of Thoracic SurgeryDokument45 SeitenComplications of Thoracic SurgeryAlin ToaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUG INDEX CompiledDokument24 SeitenDRUG INDEX Compiledahmad aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acls AtpDokument44 SeitenAcls AtpDeborah Anasthasia PakpahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACLS Drugs (2010)Dokument16 SeitenACLS Drugs (2010)RN333100% (2)
- Anti HypertensivesDokument23 SeitenAnti HypertensivesLeena AlateeqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 47 - Antidysrhythmic DrugsDokument10 SeitenChapter 47 - Antidysrhythmic Drugsdlneisha61100% (1)
- Nclex Medication ListDokument32 SeitenNclex Medication ListMikhaila RutherfordNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Pharma) Cardio QuestionnaireDokument38 Seiten(Pharma) Cardio QuestionnaireMarqxczNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertension Topic DiscussionDokument13 SeitenHypertension Topic Discussionapi-665372449Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug AnalysisDokument8 SeitenDrug AnalysisJonie Vince SañosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of Emergency MedicineDokument298 SeitenHandbook of Emergency MedicineJazlan Mohamad100% (15)
- Diltiazem Hydrochloride 2 CreamDokument3 SeitenDiltiazem Hydrochloride 2 CreamOmair FarooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calcium Channel Blockers - AMBOSS PDFDokument5 SeitenCalcium Channel Blockers - AMBOSS PDFOpio IsaacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care Pearls-Basics For Critical Patient Care and Board Review (July 28, 2015) - (9780991056705)Dokument489 SeitenCritical Care Pearls-Basics For Critical Patient Care and Board Review (July 28, 2015) - (9780991056705)taher100% (6)