Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Diode Rectifier Circuits Experiment
Hochgeladen von
Sam0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
179 Ansichten5 SeitenThis document describes an experiment to analyze and understand diode applications as rectifiers. It discusses three types of rectifiers: half-wave, full-wave center-tapped, and full-wave bridge. The experiment uses a Livewire software to simulate circuits of each rectifier. Students will observe the output waveforms on an oscilloscope and draw their conclusions in tables to understand how diodes allow current to flow in only one direction, converting AC to DC.
Originalbeschreibung:
Electronic System Sem 2 Question PMM
Originaltitel
EXPERIMENT 1_Diode as Rectifier
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document describes an experiment to analyze and understand diode applications as rectifiers. It discusses three types of rectifiers: half-wave, full-wave center-tapped, and full-wave bridge. The experiment uses a Livewire software to simulate circuits of each rectifier. Students will observe the output waveforms on an oscilloscope and draw their conclusions in tables to understand how diodes allow current to flow in only one direction, converting AC to DC.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
179 Ansichten5 SeitenDiode Rectifier Circuits Experiment
Hochgeladen von
SamThis document describes an experiment to analyze and understand diode applications as rectifiers. It discusses three types of rectifiers: half-wave, full-wave center-tapped, and full-wave bridge. The experiment uses a Livewire software to simulate circuits of each rectifier. Students will observe the output waveforms on an oscilloscope and draw their conclusions in tables to understand how diodes allow current to flow in only one direction, converting AC to DC.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 5
ELECTRONIC SYSTEM
EXPERIMENT 1: DIODE AS A RECTIFIER
(PLO4; CLO2)
1.0 AIM
1. To analyze and understand diode applications as rectifier
2.0 OUTCOMES
At the end of the session the students will be able to:1. Determine output waveform of half-wave, full-wave center-tapped and fullwave bridge rectifier
3.0 EQUIPMENTS/MATERIALS NEEDED
1. Livewire software
4.0 THEORY
The function of rectifier is to change an alternating current (AC) to a direct
current (DC). There are several types of rectifiers such as half wave rectifier, full
wave centre-tapped rectifier and full wave bridge rectifier.
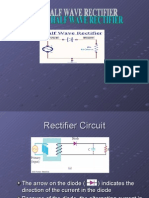
1.0 HALF-WAVE RECTIFIER
The simplest type of rectifier circuit is a half-wave rectifier. It only allows one
half of a positive cycle of an AC waveform to pass through the load as in
Figure 1(a).
Figure 1(a): Half Wave Rectifier
2.0 FULL-WAVE CENTER-TAPPED RECTIFIER
Experiment 1: Diode As A Rectifier
ELECTRONIC SYSTEM
As shown in Figure 1(b), full wave rectifier is created by using only two
diodes. Its requiring a center tapped transformer to establish the input signal
across each section of the transformer secondary side.
During a positive half-cycle of the input voltage, a power is supplied to the
load through diode D1. During the negative cycle, diode D2 conducts with
maintaining the same polarity for the voltage across the load. The net effect
is the same output as that full wave bridge rectifier with the same dc levels.
Figure 1(b): Full-Wave Center-Tapped Rectifier
3.0 FULL-WAVE BRIDGE RECTIFIER
Figure 1(c) is the circuit diagram of full-wave bridge rectifier. During the
positive half-cycle, shown in red, the top end of the transformer winding is
positive with respect to the bottom half. Therefore, the transformer pushes
electrons from its bottom end, through D3 which is forward biased, and
through the load resistor in the direction shown by the red arrows. Electrons
then continue through the forward-biased D2, and from there to the top of
the transformer winding. This forms a complete circuit, so current can indeed
flow. At the same time, D1 and D4 are reverse biased, so they do not conduct
any current.
During the negative half-cycle, the top end of the transformer winding is
negative. Now, D1 and D4 are forward biased, and D2 and D3 are reverse
biased. Therefore, electrons move through D1, the resistor, and D4 in the
direction shown by the blue arrows. As with the positive half-cycle,
electrons move through the resistor from left to right.
In this manner, the diodes keep switching the transformer connections to
the resistor so that current always flows in only one direction through the
resistor.
Experiment 1: Diode As A Rectifier
ELECTRONIC SYSTEM
Figure 1(c): Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier
5.0 EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
5.1 HALF-WAVE RECTIFIER
1. By using livewire software, connect a circuit as shown in figure 1(d).
Figure 1(d): Half Wave Rectifier
2. Set AC voltage source value to 5V, 1Hz.
3. Then, insert the graph to display the oscilloscope waveform.
4. Draw output waveform in Table 1.0.
Table 1.0: Half Wave Rectifier waveform
5.2 FULL-WAVE CENTER-TAPPED RECTIFIER
1. By using livewire software, connect a circuit as shown in figure 1(e).
Experiment 1: Diode As A Rectifier
ELECTRONIC SYSTEM
Figure 1(e): Full-Wave Center-Tapped Rectifier
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Set AC voltage source value to 100V, 1Hz.
Set the centre tap transformer turn ratio to 10:1.
Determine output at resistance R1 10K ohm with oscilloscope.
Insert the graph to display the oscilloscope waveform.
Draw output waveform in Table 1.1.
Table 1.1: Full-Wave Center-Tapped Rectifier waveform
5.3 FULL-WAVE BRIDGE RECTIFIER
1. By using livewire software, connect a circuit as shown in figure 1(f).
Experiment 1: Diode As A Rectifier
ELECTRONIC SYSTEM
Figure 1(f): Full-Wave Center-Tapped Rectifier
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Set AC voltage source value to 50V, 1Hz.
Set the centre tap transformer turn ratio to 10:1.
Determine output at resistance R1 10K ohm with oscilloscope.
Insert the graph to display the oscilloscope waveform.
Draw output waveform in Table 1.2.
Table 1.2: Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier waveform
Experiment 1: Diode As A Rectifier
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- HALO CHORDS (Ver 2) by Beyoncé @Dokument5 SeitenHALO CHORDS (Ver 2) by Beyoncé @Miss_AccountantNoch keine Bewertungen
- 387141-Blue Moon - With WALKING BASS and ImprovisationDokument2 Seiten387141-Blue Moon - With WALKING BASS and ImprovisationBeluga ProjectNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esquema Eletrico KS 532319Dokument17 SeitenEsquema Eletrico KS 532319Vagner Silva0% (1)
- Power Systems Protection Course: Al-Balqa Applied UniversityDokument36 SeitenPower Systems Protection Course: Al-Balqa Applied UniversityAayush PatidarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alan YuDokument70 SeitenAlan YubingwazzupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No.02 To Observe The Characteristics of A Half Wave RectifierDokument4 SeitenExperiment No.02 To Observe The Characteristics of A Half Wave RectifierWaqas MughalNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Modified SEPIC Converter For High Power Factor Rectifier and Universal Input Voltage ApplicationsDokument12 SeitenA Modified SEPIC Converter For High Power Factor Rectifier and Universal Input Voltage ApplicationsBritto TigerNoch keine Bewertungen
- NAT EXAM 2022-2023 MOCK TEST CPARDokument7 SeitenNAT EXAM 2022-2023 MOCK TEST CPARArnel LomocsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modal Verbs 1 - AbilityDokument3 SeitenModal Verbs 1 - AbilityperdidalmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01-HSDPA Principle and ConfigurationDokument78 Seiten01-HSDPA Principle and ConfigurationSameer IbraimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complexity Scales and Licensing in Phonology (2010)Dokument324 SeitenComplexity Scales and Licensing in Phonology (2010)Chochomz N de PandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report Solayman Ewu - CompressDokument12 SeitenLab Report Solayman Ewu - CompressVic100% (1)
- Buck ReportDokument9 SeitenBuck ReportNaeem GulNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Power Supply Circuit ExperimentDokument6 SeitenDC Power Supply Circuit ExperimentSam67% (3)
- Full Wave Rectifier Guide: Circuit, Theory & UsesDokument7 SeitenFull Wave Rectifier Guide: Circuit, Theory & UsesArun PratapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 24: The Potentiometer: PurposeDokument6 SeitenExperiment 24: The Potentiometer: PurposekirtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 325 Lab 8 ReportDokument10 Seiten325 Lab 8 Reportapi-241454978Noch keine Bewertungen
- ch11 PDFDokument43 Seitench11 PDFmri_leon100% (1)
- Electronic Devices Experiment 4Dokument13 SeitenElectronic Devices Experiment 4ArvinALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 4 Half Wave and Full WaveDokument8 SeitenLab 4 Half Wave and Full WaveRashid Rind Rashid Rind100% (1)
- Exp 8 Buck ConverterDokument7 SeitenExp 8 Buck Converterusmpowerlab50% (2)
- Photodiode vs Phototransistor: Key Differences (39Dokument5 SeitenPhotodiode vs Phototransistor: Key Differences (39CladyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 5 Diode As Rectifier BBN 10205 (Done)Dokument10 SeitenLab 5 Diode As Rectifier BBN 10205 (Done)Zhamir ZhakwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- (ACTA Universitatis Cibiniensis) Testing The Performance of A Single-Phase Autotransformer On MATLABSimulinkDokument6 Seiten(ACTA Universitatis Cibiniensis) Testing The Performance of A Single-Phase Autotransformer On MATLABSimulinkbeimanalfredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cpe08 Midterm Exam Part 1and 2Dokument4 SeitenCpe08 Midterm Exam Part 1and 2Elle ElleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bridge Rectifier - Definition, Construction and WorkingDokument14 SeitenBridge Rectifier - Definition, Construction and WorkingRamKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signals and SystemsDokument17 SeitenSignals and SystemsSanthosh Vegeta Goku GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee460 Lab Manual 2006Dokument80 SeitenEe460 Lab Manual 2006F0x123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sourcemeter Smu Instruments: Selector Guide Series 2600BDokument56 SeitenSourcemeter Smu Instruments: Selector Guide Series 2600BSatian Anantapanyakul100% (1)
- CUK Converter Using LM2611 PDFDokument65 SeitenCUK Converter Using LM2611 PDFrijilpoothadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Biomechanics AssignmentDokument1 SeiteAdvanced Biomechanics AssignmentsmalldotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ReportDokument15 SeitenLab Reportaeoliano0% (1)
- EEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Report4 - BJT BiasingDokument4 SeitenEEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Report4 - BJT Biasingdonatello84Noch keine Bewertungen
- RL Series Circuit ReportDokument11 SeitenRL Series Circuit Reportfedley sikolia100% (1)
- Power Electronics Half-Wave Rectifier CalculationsDokument3 SeitenPower Electronics Half-Wave Rectifier CalculationsMohab SamehNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEC Tutorial 3Dokument3 SeitenPEC Tutorial 3harsh chaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torque - Slip Characteristic of A Three - Phase Induction MachineDokument28 SeitenTorque - Slip Characteristic of A Three - Phase Induction MachineAli AltahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multistage Transistor AmplifierDokument23 SeitenMultistage Transistor AmplifierHemant SaraswatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 12-Resonance Lab ReportDokument8 SeitenExperiment 12-Resonance Lab ReportShahzad JameelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment # 1: P-N Junction Diode: TheoryDokument9 SeitenExperiment # 1: P-N Junction Diode: Theorypoonginithi040% (1)
- BJT DC CHARACTERISTICS LABDokument5 SeitenBJT DC CHARACTERISTICS LABKrishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of A Bi-Directional DC To A DC Converter?Dokument14 SeitenWhat Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of A Bi-Directional DC To A DC Converter?BALAJINoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report: Submitted ToDokument7 SeitenLab Report: Submitted ToMd. Al Amin 201-15-34790% (1)
- ET Tut2 Ans AUT2016-17Dokument6 SeitenET Tut2 Ans AUT2016-17Tirumala Rao Yalla100% (1)
- Introduction To Circuit LabDokument8 SeitenIntroduction To Circuit LabDaudKhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding of Harmonics in Power Distribution System: Instructor: Dr. Adel. M. SharafDokument29 SeitenUnderstanding of Harmonics in Power Distribution System: Instructor: Dr. Adel. M. SharafkgskgmNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE309 Notes 07 PDFDokument4 SeitenEE309 Notes 07 PDFbals123456100% (1)
- Electrical and Electronic MeasurementsDokument47 SeitenElectrical and Electronic MeasurementsAkashGauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Seamless Mode Transfer Maximum Power Point Tracking Controller For Thermoelectric Generator ApplicationsDokument10 SeitenA Seamless Mode Transfer Maximum Power Point Tracking Controller For Thermoelectric Generator Applicationssumiths32Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transient Response of RC CircuitDokument5 SeitenTransient Response of RC CircuitJayesh Ruikar100% (1)
- DC Link CurrentDokument8 SeitenDC Link CurrentsubbannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 3.1 Finding The Performance Parameters of A Full-Wave Rectifier With A Center-Tapped TransformerDokument4 SeitenExample 3.1 Finding The Performance Parameters of A Full-Wave Rectifier With A Center-Tapped TransformersoberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Half Wave RectifierDokument15 SeitenHalf Wave RectifierYash Mangal40% (5)
- SEPIC ConverterDokument16 SeitenSEPIC ConverterDina GaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE328 Power Electronics: Course BooksDokument36 SeitenEE328 Power Electronics: Course Booksconcurso5 eletricaufmsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No.2 Ferranti Effect: Objective: ApparatusDokument6 SeitenExperiment No.2 Ferranti Effect: Objective: ApparatusMian TauseefNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Network Theorem Dual to Miller's TheoremDokument5 SeitenA Network Theorem Dual to Miller's TheoremSiddhant Jain0% (1)
- Protective Relaying QuizDokument3 SeitenProtective Relaying QuizCattleya Tabor PeñalosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08-Com101 AMDokument11 Seiten08-Com101 AMHồng HoanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic CircuitsDokument5 SeitenElectronic CircuitsSage MaphikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEET2274 Online Laboratory 3 2021Dokument9 SeitenEEET2274 Online Laboratory 3 2021waqasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 2 EST OLIVA PDFDokument13 SeitenExperiment 2 EST OLIVA PDFMark joseph BayletNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Devices Lab - Exp 2 - Mid Term - Fall 22-23 - ACSDokument19 SeitenElectronics Devices Lab - Exp 2 - Mid Term - Fall 22-23 - ACSdark lionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apl Lab 12aDokument8 SeitenApl Lab 12amanavlund5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exp5 RectifierDokument3 SeitenExp5 RectifiertarunkumarcladNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rectifiers and FiltersDokument13 SeitenRectifiers and FiltersAko si GianNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE 301 Electronics 1: A. Half-Wave RectificationDokument24 SeitenECE 301 Electronics 1: A. Half-Wave RectificationVince Hugo GutibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rectifier Types and Operation GuideDokument18 SeitenRectifier Types and Operation GuideYacine KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- يجوملا موقملا RectifierDokument18 Seitenيجوملا موقملا RectifierYacine KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study: PN Norakmar Binti JamalDokument13 SeitenCase Study: PN Norakmar Binti JamalSamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Pneumatic 2bDokument4 SeitenLab Pneumatic 2bSamNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB 2: PNEUMATIC DIRECT CONTROLDokument4 SeitenLAB 2: PNEUMATIC DIRECT CONTROLSam100% (1)
- Experiment 3 AmplifierDokument3 SeitenExperiment 3 AmplifierSamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiq Eo 1Dokument7 SeitenFiq Eo 1SamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eoc 1 e System AnsweredDokument4 SeitenEoc 1 e System AnsweredSamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eoc 2 - Linear DC Power Supply - Q - Jun 2016Dokument2 SeitenEoc 2 - Linear DC Power Supply - Q - Jun 2016SamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welding ReportDokument15 SeitenWelding ReportSamNoch keine Bewertungen
- FULL REPORT Design ProjectDokument31 SeitenFULL REPORT Design ProjectNurulAnisAhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrosion and Protection of Transmission Steel Structure TowerDokument5 SeitenCorrosion and Protection of Transmission Steel Structure Towerabhi120783Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6683 Intelligent Network Services Migration More Value The VoiceDokument11 Seiten6683 Intelligent Network Services Migration More Value The VoiceAlexandra NeacsuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 500 Greatest Songs of All Time - Rolling Stone356-285Dokument39 Seiten500 Greatest Songs of All Time - Rolling Stone356-285BETRENoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical InterviewDokument3 SeitenTechnical InterviewGerard Paul NaidasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CommblksDokument583 SeitenCommblksgvirbila1298Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eslprintables 2010517032571020834787Dokument1 SeiteEslprintables 2010517032571020834787madalinaaaa1979Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aip EbciDokument50 SeitenAip Ebcigiuseppe751Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reasons Bless The LordDokument2 SeitenReasons Bless The Lorddacs6417100% (1)
- Beyond The SeaDokument2 SeitenBeyond The SeaEnrique DelgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 William Shakespeare'S Sonnets: 3.0 ObjectivesDokument10 SeitenUnit 3 William Shakespeare'S Sonnets: 3.0 ObjectivesChetu Arsha KriyanshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Review 1Dokument1 SeiteCritical Review 1api-286904025Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summative Test 2ND in Mapeh 9Dokument5 SeitenSummative Test 2ND in Mapeh 9Vhannie AcquiatanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philips LED Technology Backgrounder: 2009Dokument13 SeitenPhilips LED Technology Backgrounder: 2009Deutsch FcmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formatting and Baseband ModulationDokument16 SeitenFormatting and Baseband Modulationlongyeuhuong50% (2)
- Friends Pilot Episode RecapDokument7 SeitenFriends Pilot Episode RecapLuana AlvesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13 Energy-Efficient WSN SlidesDokument31 SeitenChapter 13 Energy-Efficient WSN Slidesrizi007Noch keine Bewertungen
- 932789Dokument38 Seiten932789Ivana Kupola MišićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Display Frame Unit: Product Features ESSENTIAL ACCESSORIES (Not Included)Dokument3 SeitenDisplay Frame Unit: Product Features ESSENTIAL ACCESSORIES (Not Included)Vishal SuryawaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete dialogue with greetingsDokument1 SeiteComplete dialogue with greetingsRodrigo BurNoch keine Bewertungen
- WiFi Technology GuideDokument40 SeitenWiFi Technology GuideSowjanya Sowji100% (1)
- JJ 2020 ShapDokument4 SeitenJJ 2020 Shapjagan royalNoch keine Bewertungen