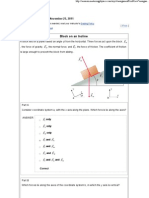
Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
GATE Syllabus
Hochgeladen von
Manohar Vemparala0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
16 Ansichten3 Seitenchemical engineering gate syllabus for the year 2017
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenchemical engineering gate syllabus for the year 2017
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
16 Ansichten3 SeitenGATE Syllabus
Hochgeladen von
Manohar Vemparalachemical engineering gate syllabus for the year 2017
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
Section 1: Engineering Mathematics
Linear Algebra: Matrix algebra, Systems of linear equations, Eigen values
and
eigenvectors.
Calculus: Functions of single variable, Limit, continuity and differentiability,
Taylor
series, Mean value theorems, Evaluation of definite and improper integrals,
Partial
derivatives, Total derivative, Maxima and minima, Gradient, Divergence and
Curl,
Vector identities, Directional derivatives, Line, Surface and Volume integrals,
Stokes,
Gauss and Greens theorems.
Differential equations: First order equations (linear and nonlinear), Higher
order linear
differential equations with constant coefficients, Cauchys and Eulers
equations,
Initial and boundary value problems, Laplace transforms, Solutions of one
dimensional heat and wave equations and Laplace equation.
Complex variables: Complex number, polar form of complex number,
triangle
inequality.
Probability and Statistics: Definitions of probability and sampling
theorems,
Conditional probability, Mean, median, mode and standard deviation,
Random
variables, Poisson, Normal and Binomial distributions, Linear regression
analysis.
Numerical Methods: Numerical solutions of linear and non-linear algebraic
equations. Integration by trapezoidal and Simpsons rule. Single and multistep
methods for numerical solution of differential equations.
Section 2: Process Calculations and Thermodynamics
Steady and unsteady state mass and energy balances including multiphase,
multicomponent,
reacting and non-reacting systems. Use of tie components; recycle,
bypass and purge calculations; Gibbs phase rule and degree of freedom
analysis.
First and Second laws of thermodynamics. Applications of first law to close
and
open systems. Second law and Entropy. Thermodynamic properties of pure
substances: Equation of State and residual properties, properties of mixtures:
partial
molar properties, fugacity, excess properties and activity coefficients; phase
equilibria: predicting VLE of systems; chemical reaction equilibrium.
Section 3: Fluid Mechanics and Mechanical Operations
Fluid statics, Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids, shell-balances including
differential form of Bernoulli equation and energy balance, Macroscopic
friction
factors, dimensional analysis and similitude, flow through pipeline systems,
flow
meters, pumps and compressors, elementary boundary layer theory, flow
past
immersed bodies including packed and fluidized beds, Turbulent flow:
fluctuating
velocity, universal velocity profile and pressure drop.
Particle size and shape, particle size distribution, size reduction and
classification of
solid particles; free and hindered settling; centrifuge and cyclones;
thickening and
classification, filtration, agitation and mixing; conveying of solids.
13 of 72
Section 4: Heat Transfer
Steady and unsteady heat conduction, convection and radiation, thermal
boundary layer and heat transfer coefficients, boiling, condensation and
evaporation; types of heat exchangers and evaporators and their process
calculations. Design of double pipe, shell and tube heat exchangers, and
single
and multiple effect evaporators.
Section 5: Mass Transfer
Ficks laws, molecular diffusion in fluids, mass transfer coefficients, film,
penetration
and surface renewal theories; momentum, heat and mass transfer analogies;
stage-wise and continuous contacting and stage efficiencies; HTU & NTU
concepts;
design and operation of equipment for distillation, absorption, leaching,
liquid-liquid
extraction, drying, humidification, dehumidification and adsorption.
Section 6: Chemical Reaction Engineering
Theories of reaction rates; kinetics of homogeneous reactions, interpretation
of
kinetic data, single and multiple reactions in ideal reactors, non-ideal
reactors;
residence time distribution, single parameter model; non-isothermal
reactors;
kinetics of heterogeneous catalytic reactions; diffusion effects in catalysis.
Section 7: Instrumentation and Process Control
Measurement of process variables; sensors, transducers and their dynamics,
process
modeling and linearization, transfer functions and dynamic responses of
various
systems, systems with inverse response, process reaction curve, controller
modes (P,
PI, and PID); control valves; analysis of closed loop systems including
stability,
frequency response, controller tuning, cascade and feed forward control.
Section 8: Plant Design and Economics
Principles of process economics and cost estimation including depreciation
and
total annualized cost, cost indices, rate of return, payback period, discounted
cash
flow, optimization in process design and sizing of chemical engineering
equipments
such as compressors, heat exchangers, multistage contactors.
Section 9: Chemical Technology
Inorganic chemical industries (sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, chlor-alkali
industry),
fertilizers (Ammonia, Urea, SSP and TSP); natural products industries (Pulp
and Paper,
Sugar, Oil, and Fats); petroleum refining and petrochemicals; polymerization
industries (polyethylene, polypropylene, PVC and polyester synthetic fibers).
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- MathsDokument7 SeitenMathsHiiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LOGARITHMSDokument23 SeitenLOGARITHMSAERGATLA LAXMINoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10 - Maths - Quadratic Equations SolutionsDokument30 SeitenClass 10 - Maths - Quadratic Equations Solutionsanirahul jtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guptasarma 1997Dokument18 SeitenGuptasarma 1997MatiasAedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airfoil Inverse DesignDokument12 SeitenAirfoil Inverse DesignFilip StojkovskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- r05012101 Numerical MethodsDokument8 Seitenr05012101 Numerical MethodsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution of Algebraic and Transcendental Equation Using Bisection MethodDokument7 SeitenSolution of Algebraic and Transcendental Equation Using Bisection MethodSubhranil SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 2 - Tangents/Normals: y X X 1 Dy DX y (X +1) (2 X) A (0,2), P (2,0) QDokument3 SeitenExercise 2 - Tangents/Normals: y X X 1 Dy DX y (X +1) (2 X) A (0,2), P (2,0) QTimothy ImiereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson PlanDokument7 SeitenLesson Planapi-311729077Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.formative Assement Manual For X MathsDokument186 Seiten1.formative Assement Manual For X MathsManya ElhanceNoch keine Bewertungen
- MECH 374 Numerical Methods in EngineeringDokument8 SeitenMECH 374 Numerical Methods in Engineeringrodi10100% (8)
- Philosophy and Science in Islamic Golden AgeDokument63 SeitenPhilosophy and Science in Islamic Golden AgeMuhammad HareesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comm, MathDokument3 SeitenComm, MathTahajan M. HadjirulNoch keine Bewertungen
- (A K Ray S K Gupta) Mathematical Methods in ChemiDokument28 Seiten(A K Ray S K Gupta) Mathematical Methods in ChemiKapilSahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Theory of Fractional Differential EquationsDokument6 SeitenBasic Theory of Fractional Differential EquationsMehboob AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Glance at Numerical RelationshipsDokument14 SeitenA Glance at Numerical RelationshipsreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mastering Physics - Mek2 - Assignment 1Dokument11 SeitenMastering Physics - Mek2 - Assignment 1rexc483% (6)
- Review of AlgebraDokument47 SeitenReview of AlgebraJohnfer AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enseee Maths IBVPs 1 PDFDokument26 SeitenEnseee Maths IBVPs 1 PDFJihad HasanainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch01 Linear FunctionsDokument42 SeitenCh01 Linear FunctionsLinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Lesson Midterms Polynomial InterpolationDokument77 Seiten3 Lesson Midterms Polynomial InterpolationAizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths PDFDokument3 SeitenMaths PDFSubrata PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forces and Moments in CFD AnalysisDokument11 SeitenForces and Moments in CFD Analysisjuan carlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM 950 SP Math (M) (9.3.12)Dokument54 SeitenSTPM 950 SP Math (M) (9.3.12)abnu98Noch keine Bewertungen
- C 03 Quadratic RelationshipsDokument68 SeitenC 03 Quadratic Relationshipsmilk shakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise PDFDokument1 SeiteExercise PDFAniruddha PhalakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan in EliminationDokument7 SeitenLesson Plan in EliminationCathy Jane FloridaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMU Advanced Engineering MATHEMATICS III-1 PDFDokument149 SeitenAMU Advanced Engineering MATHEMATICS III-1 PDFISRAEL HAILUNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE (Advanced) 2015 - A Detailed Analysis by Resonance Expert Team - Reso BlogDokument9 SeitenJEE (Advanced) 2015 - A Detailed Analysis by Resonance Expert Team - Reso BlogGaurav YadavNoch keine Bewertungen