Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Assessing Childbearing Women
Hochgeladen von
Jola OgundiyaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Assessing Childbearing Women
Hochgeladen von
Jola OgundiyaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Assessing Childbearing Women (Ch.
29)
Structure & Function Pregnancy Changes
There are Physiologic & anatomic changes
Most of those changes are influenced by hormone changes related to
pregnancy. Hormone mainly include:
o Estrogen
o Progesterone
Skin, Hair, and Nails
Most changes resolve after pregnancy
Striae Gravidarum are pregnancy stretch marks; They typically never
completely resolve
Hyperpigmentation occurs. Linea Nigra is the dark line from umbilicus
to mons pubis; chloasma is the mask of pregnancy, which is the
darkening of skin on face
Areolae, nipples, axillae, umbilicus, & perineum darken
Vascular changes known as spider veins
Pruritic urticarial is common in the 3rd trimester. It is erythematous
papules, plaques, & urticarial that occurs with intense itching and
resolves few weeks post delivery
Acne may worsen or improve
There is an increased growth in hair & nails during pregnancy
Hirsutism may happen on face, abdomen, back in 2-3rd trimesters due
to androgens
Ears
& Hearing
Hearing may decrease
Sense of fullness in ears
Earache related to increase vascularity of Thematic Membrane &
blockage of eustachian tubes
Mouth-Throat-Sinuses
Women may have Gingival bleeding during brushing
The can have Hypertrophy of gums which increase gum bleeding
Epulis is a small, irritating nodules on gum line
Vocal changes related to edema of larynx
Women have Nasal stuffiness & epistaxis: elated to estrogen induced
edema & vascular congestion of nasal mucosa & sinuses
Thorax & Lungs
Progesterone causes relaxation of joints & ligaments
o Rib cage flare: increase in anteroposterior & transverse
diameters: required as pregnancy progresses
The Respiratory pattern changes, it moves from abdominal to costal
breathing
o Shortness of breath common in pregnant women
Oxygen requirements increase related to additional cellular growth of
body & fetus
Breasts
The breast enlarge related to the estrogen & progesterone surge
Mammary gland changes:
o Tingling sensation & tenderness in breast
o Enlargement of breast & nipple
o Hyperpigmentation of areola & nipple
o Enlargement of Montgomery tubercles
o Prominence of superficial veins
o Striae development
o Expression of colostrum 2nd & 3rd trimesters
Heart
Increased cardiac output & maternal blood
volume. Goes up 4050% during pregnancy
Heart size increases due to increase of blood volume being pumped
Position rotated up & left approximately 1-1.5 cm
Heart rate: increases 10-15 bpm
Murmur may be heard
Peripheral Vascular System
Physiologic anemia (pseudoanemia) because of disproportionate
increase in blood volume compared to increase in RBC production.
Plasma volume increases by 40-50%, RBC volume increase by 18-30%
Progesterone acts on vessels causing relaxation & dilation. This results
in dizziness, lightheadedness. Peaks at 32-34 weeks
Dependent edema & varicosities are common and happen usually later
in day
It is related to the expanding uterus pressure on femoral venous area,
resulting in stagnation of the lower extremity blood return
Varicose veins common in childbearing women
Thrombophlebitis is a vein inflammation & blood clot
Abdomen
Abdominal muscles stretch to accommodate uterus
Diastasis recti abdominis is permanent separation of abdominal
muscles that can occur in pregnancy
4 Paired ligaments: broad, uterosacral, cardinal, & round help support
uterus & position in pelvis
Women report pressure on bladder, kidney, ureters. This increases risk
of UTI
Urinary frequency common
Small intestine: in the increase pressure from the fetus and the uterus
help to decrease gastric motility & heartburn
Ptyalism is increase salivation; pica: crave non-nutritional items
Glucose may also increase. As glucose use increases, it may decrease
maternal glucose levels
Later in pregnancy the opposite occur. May have an increase risk to
hyperglycemia & hyperinsulinemia
Genitalia
The Uterus dramatic increase in size & volume capacity
Growth size of uterus by week
McDonalds rule: fundal height in cm times 8/7 = fundal height
(approximately 1 cm per week of pregnancy)
As the Uterine wall thins closer to delivery, easy palpation of fetal
areas occurs
Cervix, vagina, & vulva also change. May see Goodells sign which is
the cervical softening, Chadwicks sign which is a bluish discoloration
or hypertrophy of cervical canal glands cause an increase in vaginal
discharge
Anus & Rectum
Constipation is common because of decreased gastric motility. There is
more time for absorption of nutrients
Iron supplements also related to constipation
Hemorrhoids are the varicose veins of rectum related to vascular
congestion, pressure on venous structures, & straining to have BM
Musculoskeletal
Uterine growth pulls pelvis forward resulting in curvature of spine
leading to lordosis
Shoulders droop R/T enlarging breasts
Progesterone & relaxin cause relaxation of pelvic joints & ligaments
Symphysis pubis, sacroiliac, & sacrococcygeal joints relax, increasing
flexibility and allowing pelvic outlet to increase for delivery usually
remains larger (doesnt go back to pre pregnancy size
Relaxin is a chemical produced in the body that also changes gait
during pregnancy which may lead to change in center of gravity, &
weight gain causing backaches which are common
Neurologic
Pain or thigh tingling due to pressure on lateral femoral cutaneous
nerve
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome where there is pressure on median nerve in
wrist
Leg cramps are common related to inadequate calcium intake
Dizziness & lightheadedness is related to BP changes, vasodilation,
decreased vascular resistance; later pregnancy, uterus compression on
vena cava & aorta worse when supine leading to supine hypotensive
syndrome
Collecting Subjective Data
History of present concern: Pre-pregnancy weight,
fever or
illness since Last Menstrual Period, nasal congestion, epistaxis, cough
or throat issues, N/V frequency, thirst level, bowel habits, bloody
stool, pain/burning on urination, vaginal bleeding-leakingdischarge, appetite, sleeping, breast pain-lumps-leakage, any other
concerns
Health history: include pt.'s age (older women have increased risk
complications), prenatal care, number of pregnancies & births,
previous pregnancy complications or issues, STI, vaginal infections,
blood type, medical conditions, medications, allergies, immunizations
Subjective Data Continues
Family History: any inherited birth defects, blood disorders, ethnic or
racial group, rheumatic fever or cardiac issues before age 50, lung
problems, chronic illnesses, cancer
Lifestyle: tobacco intake, alcohol intake, street drug use, food intake
amount & type, vitamins, exercise, ADLs, fatigue, exposure to
chemicals, radiation, or environmental risks, cat or cat liter exposure
(increases risk of toxoplasmosis), occupation, feeling about pregnancy,
support person, violence concern, any other children at home
Collecting Objective Data
Key points for examination
Accurate & complete prenatal history
Understand & recognize pregnancy Cardiovascular changes
Note skin changes
Identify common pregnancy complaints & the cause
Measure uterus growth
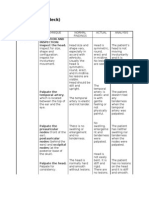
Demonstrate 4 Leopold maneuvers & significance
Collecting Objective Data
General Survey: ht, wt, temperature, P, BP, behavior
Skin, Hair, Nails: looking for hyperpigmentation, vascular markings,
inspect hair & nails
Head & Neck: looking for cervical lymph change, thyroid
Eyes: cornea, lens, iris, pupil, fundus
Ears: looking at Tympanic Membrane (TM). Women may have
decreased hearing due to increase vascularity of the TM
Mouth, Throat, Nose: teeth, gums, throat, nose
Lungs & Thorax: inspect, palpate, percuss,
auscultate: identify
abnormal respiratory sounds & any distress
Collecting Objective Data
Breasts: noting symmetry, color, inversion, pain, redness, tenderness,
warmth, discharge
Heart: rate, rhythm, regularity, murmurs, extra sounds
Peripheral Vascular: color, edema, reflexes
Abdomen: Inspection: notice striae, scars, size, shape;
Palpation: organs, masses, fetal movement, contractions (timing,
relaxation between); Measure fundal height; note Fetal position (using
Leopold); Fetal heart rate next slide
Collecting Objective Data, Look at:
External & Internal Genitalia
Anus & Rectum
Musculoskeletal
These will not be demonstrated or examined during your clinical lab &
will be presented in depth during your OB course
Textbook Pages 685-688
Summary
Critical to understand changes associated with pregnancy & why they occur
Identify critical information in subjective data placing mother & fetus at risk
Understand how to obtain objective data
Distinguish normal & abnormal findings
Understand significance of abnormal findings & those requiring immediate
attention
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Essential New Born Care ScriptDokument3 SeitenEssential New Born Care ScriptShiela Joy DuquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of The Childbearing WomanDokument122 SeitenAssessment of The Childbearing WomanLaurisse April Necesito100% (1)
- Case Analysis Format by CI SirDokument1 SeiteCase Analysis Format by CI Sirapi-3732260Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2020thoraxlungs Neckheart VesselsDokument171 Seiten2020thoraxlungs Neckheart VesselsFaith madayagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample ROS, PE PDFDokument4 SeitenSample ROS, PE PDFKASIA SyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compilation of Reviewer For Fundamentals of Nursing PDF FreeDokument49 SeitenCompilation of Reviewer For Fundamentals of Nursing PDF FreeTyler VintNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your Hormone Levels (Estrogen and Progesterone) Usually Change Throughout The Menstrual Cycle and Can Cause Menstrual SymptomsDokument14 SeitenYour Hormone Levels (Estrogen and Progesterone) Usually Change Throughout The Menstrual Cycle and Can Cause Menstrual SymptomsBeverly DatuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal and Abnormal Findings of Thorax and LungsDokument3 SeitenNormal and Abnormal Findings of Thorax and LungsOtherin Ojibwa TejanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vital SignDokument40 SeitenVital SignYoelBagusGiarto0% (1)
- Far Eastern University Institute of Nursing Instructional Script With Actual Findings of Assessing MusculoskeletalDokument6 SeitenFar Eastern University Institute of Nursing Instructional Script With Actual Findings of Assessing MusculoskeletalHeinna Alyssa GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing The Nose and SinusesDokument5 SeitenAssessing The Nose and SinusesYudi TrigunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Lymphoid Tissue & Immune System & Histology of Lymph Node & Thymus PDFDokument12 SeitenIntroduction To Lymphoid Tissue & Immune System & Histology of Lymph Node & Thymus PDFhassam qaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Survey and Integumentary I. General Appearance and Mental Status Normal Findings Actual Findings Analysis and InterpretationDokument9 SeitenGeneral Survey and Integumentary I. General Appearance and Mental Status Normal Findings Actual Findings Analysis and InterpretationAllana RayosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care of A Family With A Toddler Child: Christine M. Fiel, RN MN LPT MaedDokument25 SeitenNursing Care of A Family With A Toddler Child: Christine M. Fiel, RN MN LPT MaedJrose CuerpoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychosocial HistoryDokument3 SeitenPsychosocial HistoryMaxinne Allyssa Cancino RoseñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing General Status Vital Signs 1Dokument20 SeitenAssessing General Status Vital Signs 1Geylla FaeldoniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cmca Transes PrelimDokument33 SeitenCmca Transes Prelimangelalorin.balano.cvt100% (1)
- P.A. 1Dokument6 SeitenP.A. 1SamSarah BongolanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Term Growth and Development Both Refers To Dynamic ProcessDokument13 SeitenThe Term Growth and Development Both Refers To Dynamic ProcessMarc LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout 9 Introduction To Fluids and ElectrolytesDokument22 SeitenHandout 9 Introduction To Fluids and ElectrolytesGrape JuiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing As Art-CaringDokument14 SeitenNursing As Art-CaringBasti HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Thorax and LungsDokument8 SeitenAssessment of Thorax and LungsMikkaela FedelisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Concept of Man, Health and IllnessDokument37 Seiten1 - Concept of Man, Health and IllnessMia Grace Garcia100% (1)
- Family Care PlanDokument3 SeitenFamily Care PlanAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathogenesis and Host Defense Mechanism: Instructor: Bertha Escobar-Poni, MDDokument32 SeitenPathogenesis and Host Defense Mechanism: Instructor: Bertha Escobar-Poni, MDGelvia AwaehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 41. Nursing Care of The Child With A Cardiovascular Disorder TermDokument11 SeitenChapter 41. Nursing Care of The Child With A Cardiovascular Disorder TermJœnríčk AzueloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenCues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationKristiene Kyle AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Effectively CommunicateDokument11 SeitenTo Effectively CommunicateChandni KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6B Pregnant and Lactacting WomenDokument3 Seiten6B Pregnant and Lactacting Womenmo'niqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Theory: Florence NightingaleDokument4 SeitenEnvironmental Theory: Florence NightingaleJo Marchianne PigarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical AssessmentDokument4 SeitenPhysical AssessmentLove-lyn Abad CusipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cleansing Bed Bath: General ObjectivesDokument3 SeitenCleansing Bed Bath: General ObjectivesPauline AñesNoch keine Bewertungen
- PART 1 Health Assessment Lec Prelim TransesDokument11 SeitenPART 1 Health Assessment Lec Prelim TransesLoLiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tonsillitis and AdenoiditisDokument12 SeitenTonsillitis and AdenoiditisHannah Angelu CabadingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypomagnesemia: Presented by Shreya JhaDokument44 SeitenHypomagnesemia: Presented by Shreya JhaGregory LitangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure Rationale Remarks: Home VisitDokument3 SeitenProcedure Rationale Remarks: Home VisitBSN CMUNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Study On Pediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia-DDokument58 SeitenA Case Study On Pediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia-DAnonymous A5dkn4N3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thorax and Lungs AssessmentDokument28 SeitenThorax and Lungs AssessmentMiden AlbanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serving and Removing of Bedpan and Urinal EditedDokument30 SeitenServing and Removing of Bedpan and Urinal Editedshannon c. lewisNoch keine Bewertungen
- TFN Reviewer Lecture Notes 1Dokument7 SeitenTFN Reviewer Lecture Notes 1air benderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing As An ArtDokument4 SeitenNursing As An ArtEmjae Colmenares100% (1)
- PRS Ear Instillation - GlovaDokument3 SeitenPRS Ear Instillation - GlovaAndrea Colleen GlovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Initial Database For A Pregnant WomanDokument9 SeitenInitial Database For A Pregnant Womanjulius-ephraim-3374Noch keine Bewertungen
- Patterns of Occurrence and DistributionDokument10 SeitenPatterns of Occurrence and DistributionKrischelle AlimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 107 - Fetal Circulation Final PDFDokument4 SeitenNCM 107 - Fetal Circulation Final PDFAngelica Rose VillegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPPA PresentationDokument28 SeitenIPPA PresentationAsley Austria Alberto RN100% (1)
- Assessing Heart and Central VesselsDokument34 SeitenAssessing Heart and Central VesselsGemmalene Pacleb100% (1)
- Chapter 14Dokument4 SeitenChapter 14Allynne Jane DagasdasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self-Learning Module Unit 3 Physical AssessmentDokument57 SeitenSelf-Learning Module Unit 3 Physical AssessmentMarlon Glorioso IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of The EYEDokument8 SeitenAssessment of The EYENins ArgallonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patricia-Benner-RN-Ph D-F A A N PDFDokument2 SeitenPatricia-Benner-RN-Ph D-F A A N PDFBea Trisha ArietaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 102 ReviewerDokument6 SeitenNCM 102 ReviewerAimeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Agents and Its ImpactsDokument1 SeiteSocial Agents and Its ImpactsMiles HacheroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychological Changes of PregnancyDokument30 SeitenPsychological Changes of PregnancyyuddNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Three Mental OperationsDokument12 Seiten5 Three Mental OperationsSherwin Pazzibugan100% (1)
- Nursing Leadership and Management 2Dokument8 SeitenNursing Leadership and Management 2Maybelyn JoradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1) Cardiac Muscle: 3 Types of Muscle TissueDokument7 Seiten1) Cardiac Muscle: 3 Types of Muscle TissueAira PayadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definitions of NursingDokument5 SeitenDefinitions of NursingA CNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of PHN in The PhilippinesDokument3 SeitenHistory of PHN in The PhilippinesMia ZendayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- System Wise Physiological ChangesDokument24 SeitenSystem Wise Physiological ChangesKinjal VasavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- F. Y. B. Sc. (Zoology) Question BankDokument51 SeitenF. Y. B. Sc. (Zoology) Question BankHassan Ahmed100% (2)
- National Geographic Little Kids - 03 2019 - 04 2019Dokument35 SeitenNational Geographic Little Kids - 03 2019 - 04 2019florenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WonderlandDokument2 SeitenWonderlandJohn WilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chaparrí: Ubicación: Región Lambayeque. Provincia de Chiclayo, Distrito de Chongoyape, Caserío TierrasDokument3 SeitenChaparrí: Ubicación: Región Lambayeque. Provincia de Chiclayo, Distrito de Chongoyape, Caserío TierrasAlexs TomapascaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cat and Mouse 2Dokument2 SeitenCat and Mouse 2Da MiánNoch keine Bewertungen
- HAYDUKE, George - ''Make'Em Pay - Ultimate Revenge Techniques From The Master Trickster''Dokument125 SeitenHAYDUKE, George - ''Make'Em Pay - Ultimate Revenge Techniques From The Master Trickster''Mitko Krumov100% (3)
- Comidas Que Me Gustan ActividadDokument2 SeitenComidas Que Me Gustan ActividadAngelica HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosis of Viral Infections in Animal TissuesDokument3 SeitenDiagnosis of Viral Infections in Animal TissuesRandy Butternubs100% (2)
- Jurnal Katak PDFDokument5 SeitenJurnal Katak PDF31122007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Horse Welfare CompendiumDokument76 SeitenHorse Welfare CompendiumbodnarencoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Hygiene and Proper HandwashingDokument50 SeitenPersonal Hygiene and Proper HandwashingVincent Jay Dominguez MaatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study 2 - Maria Snyder - Magic StudyDokument283 SeitenStudy 2 - Maria Snyder - Magic StudySharlene WhitakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument41 SeitenUntitledReham Ricka ValmonteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laktosa Mempertahankan Daya Hidup Spermatozoa Kambing Peranakan Etawah Yang Dipreservasi Dengan Plasma Semen Domba PrianganDokument8 SeitenLaktosa Mempertahankan Daya Hidup Spermatozoa Kambing Peranakan Etawah Yang Dipreservasi Dengan Plasma Semen Domba Prianganachmad setiyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reanimation of Rats From Body Temperatures Between 0 and 1°c by Microwave DiathermyDokument6 SeitenReanimation of Rats From Body Temperatures Between 0 and 1°c by Microwave DiathermyLJNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIS LunchDokument20 SeitenCIS LunchCIS AdminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science of The Heart Vol 2Dokument118 SeitenScience of The Heart Vol 2karinadaparia75% (4)
- Taban Lo Liyong Fixions and Other StoriesDokument27 SeitenTaban Lo Liyong Fixions and Other StoriesStacy Hardy100% (1)
- 7 Free Knit Scarf PatternsDokument21 Seiten7 Free Knit Scarf PatternsCarlota ViglizzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Face and ScalpDokument31 SeitenThe Face and ScalpRobin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Perfect - Past Simple - Extensive PracticeDokument13 SeitenPresent Perfect - Past Simple - Extensive PracticeDan TeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mixed Dentition AnalysisDokument6 SeitenMixed Dentition AnalysisJess JesiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cómo Hacer FigurasDokument8 SeitenCómo Hacer FigurasAlberto Delfino100% (1)
- About VaginaDokument13 SeitenAbout VaginaRazend Muhd0% (1)
- Test Dos InglesDokument4 SeitenTest Dos Inglesgbøniillaa75% (4)
- NEF PRE-int UNIT 1Dokument11 SeitenNEF PRE-int UNIT 1Ma Gabriela Ojeda CasellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Millipedes & Centipedes: DescriptionDokument2 SeitenMillipedes & Centipedes: Descriptionralf casagdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AmulDokument36 SeitenAmulvahid100% (1)
- Paul Loeb's Complete Book of Dog Training (1E) (1974)Dokument169 SeitenPaul Loeb's Complete Book of Dog Training (1E) (1974)John AdamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurulation Refers To The Folding Process in Vertebrate Embryos, Which Includes TheDokument6 SeitenNeurulation Refers To The Folding Process in Vertebrate Embryos, Which Includes Theaaliya saaheenNoch keine Bewertungen