Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Bio2 91156 DNA Replication PDF
Hochgeladen von
Abir OmarOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Bio2 91156 DNA Replication PDF
Hochgeladen von
Abir OmarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
No Brain Too Small BIOLOGY
AS91156
Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level
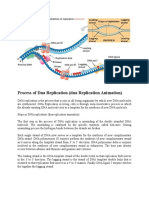
Steps in DNA replication
NOTE:
DNA replication is the copying of the DNA before the cell divides so that each generation receives a
complete set of genetic information.
DNA replication occurs during the S stage (synthesis stage) of the cell cycle.
DNA replication is semi-conservative because one side of the final DNA strand is made up of original
DNA and one strand is new.
DNA strands are anti-parallel: this means that the two sides of the DNA run in opposite directions.
Head to Tail (3 to 5) and Tail to Head (5 to 3). This anti-parallel nature is due to the numbering of
the carbons in the sugar (see diagram below)
Steps in DNA replication.
DNA molecule is unzipped by the enzyme helicase breaking the hydrogen bonds between the
complementary base pairs.
Nucleotides from within the nucleus are used to produce the new strands of DNA.
Leading Strand:
As the DNA is unzipped the enzyme DNA polymerase III adds new nucleotides (A bonds with T and C
bonds with G) to the 3 end of the original strand producing a continuous strand.
No Brain Too Small BIOLOGY
Lagging strand:
DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the 3 end of the original strand therefore DNA
polymerase must work from the replication fork down the strand producing small fragments
Okazaki that are later joined together.
As the DNA molecule unwinds a RNA primer is produced so the DNA polymerase can attach to the
strand and copy.
DNA polymerase III adds nucleotides using the complementary base pairing rule until it reaches a
primer where it is released. The piece of DNA is now known as an Okazaki fragment.
DNA polymerases I comes in and removes the primer and fills the gap with nucleotides, ready for
DNA ligase to join the fragments together.
This process continues until the whole strand of DNA has been copied.
Factors that effect DNA replication:
Because this process is controlled by enzymes, any factor that affect enzymes will affect the ratetemperature, amount of nucleotides present (substrate), amount of enzymes present.
Plants grow more in spring (cells divide more) because its warm with unlimited resources for all cell
processes including DNA replication.
Animals grow more at certain stages of their life cycle e.g. foetus.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Drawing Skills Booklet For A Level BiologyDokument16 SeitenDrawing Skills Booklet For A Level BiologyRaShid KhAn100% (1)
- 5-10 - Grasshopper - Dissection AsDokument7 Seiten5-10 - Grasshopper - Dissection AsAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio001 Balag, MayreisDokument11 SeitenBio001 Balag, MayreisMay Reis BalagNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Replication NotesDokument2 SeitenDNA Replication NotesMart Tin100% (1)
- DNA ReplicationDokument13 SeitenDNA ReplicationLisha AnbanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA ReplicationDokument7 SeitenDNA ReplicationMuhammad QayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 DnaDokument6 Seiten4 Dnadr_47839666Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dna Replication NotesDokument11 SeitenDna Replication NotesJanine San LuisNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA ReplicationDokument13 SeitenDNA ReplicationJoanne NgauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Bio 2 Module 1Dokument5 SeitenGen Bio 2 Module 1Kimberly MercadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 56404332dna ReplicationDokument4 Seiten56404332dna ReplicationKaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic: How Cells Work - DNA Replication, Metabolic RegulationDokument3 SeitenTopic: How Cells Work - DNA Replication, Metabolic RegulationDeitherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process of Dna ReplicationDokument3 SeitenProcess of Dna ReplicationLaiba AsimNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA ReplicationDokument5 SeitenDNA ReplicationNikki SStarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA ReplicationDokument4 SeitenDNA ReplicationYasmin ShaheenNoch keine Bewertungen
- BPH 2203, Bio-Molecular Pharmacy: Topic: DNA ReplicationDokument19 SeitenBPH 2203, Bio-Molecular Pharmacy: Topic: DNA ReplicationNazninNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ReportDokument12 SeitenLab ReportJISAS CLIMAXNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Genes WorkDokument47 SeitenHow Genes WorkJelly Joy CampomayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA ReplicationDokument2 SeitenDNA ReplicationFrancoise AngeliqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Replication of DNA in Prokaryo1tesDokument7 SeitenThe Replication of DNA in Prokaryo1teshgkutjutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz Discussion - ReplicationDokument2 SeitenQuiz Discussion - ReplicationDree SermanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Replication 101Dokument14 SeitenDNA Replication 101Ilac Tristan BernardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HLF Dna ReplicationDokument8 SeitenHLF Dna ReplicationPriyanka ChughNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dna ReplicationDokument18 SeitenDna ReplicationOguh AugustineNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReplicationDokument5 SeitenReplicationAtika ZulfiqarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 3 - DNA Replication - Notes Sp18-1Dokument8 SeitenWeek 3 - DNA Replication - Notes Sp18-1Alabhya DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cytogenetics Seatwork No. 4 DNA ReplicationDokument4 SeitenCytogenetics Seatwork No. 4 DNA ReplicationKemverly RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Notes DddxfymcfmcghDokument7 SeitenBiology Notes Dddxfymcfmcghthirumalaivasan GNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.7, 7.1, 7.2, 7.3 DNA Replication, Transcription and Translation Biology HLDokument91 Seiten2.7, 7.1, 7.2, 7.3 DNA Replication, Transcription and Translation Biology HLmunir sehwai.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined Style 20240314 1Dokument26 SeitenStructure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined Style 20240314 1leighariazbongsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem QuinDokument4 SeitenBiochem QuinKingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA ReplicationDokument11 SeitenProkaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA ReplicationSarmistha NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Replication: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument10 SeitenDNA Replication: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRahul GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dna ReplicationDokument26 SeitenDna ReplicationJerric Cristobal100% (3)
- DNA Replication Notes: Purpose: To Make An Identical Copy of DNA For Cell Division Process: BackgroundDokument3 SeitenDNA Replication Notes: Purpose: To Make An Identical Copy of DNA For Cell Division Process: BackgroundLuke HughesNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Replication: DefinitionDokument6 SeitenDNA Replication: DefinitionZEE zeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Definition: Shape, Replication, and Mutation: Nucleic Acid Double HelixDokument8 SeitenDNA Definition: Shape, Replication, and Mutation: Nucleic Acid Double HelixRishikesh BhintadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ScienceDokument7 SeitenScienceRonald Alexandrei TropelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Biology Study MaterialDokument58 SeitenMolecular Biology Study MaterialchitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Replication: DNA Replication Is A Biological Process That Occurs in AllDokument11 SeitenDNA Replication: DNA Replication Is A Biological Process That Occurs in AllKomal SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentationprint TempDokument27 SeitenPresentationprint TempGandepelli SwetchaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - Molecular Biology and GeneticsDokument14 Seiten2 - Molecular Biology and Geneticsarahunt253Noch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Biology Unit IV and VDokument60 SeitenMolecular Biology Unit IV and VchitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process of Dna Replication, Transcription, TranslationDokument8 SeitenProcess of Dna Replication, Transcription, TranslationBenedictus YohanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dna Replication: By: Group 3Dokument26 SeitenDna Replication: By: Group 3Jesse Kate GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes 8Dokument5 SeitenLecture Notes 8rishabhNoch keine Bewertungen
- GENETICSDokument37 SeitenGENETICSJohn KennedyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ObjectivesDokument36 SeitenObjectivesMARIAN SABENECIONoch keine Bewertungen
- The Biological Information Flows From DNA To RNA and From There To ProteinsDokument38 SeitenThe Biological Information Flows From DNA To RNA and From There To Proteinsfentaw melkieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem Group ProjDokument21 SeitenBiochem Group ProjYves Christian PineNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA ReplicationDokument21 SeitenDNA ReplicationP Santosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA ReplicationDokument27 SeitenDNA ReplicationJeniNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA ReplicationDokument47 SeitenDNA ReplicationYSOBELLATHERESE BILOLONoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes DNA ReplicationDokument11 SeitenNotes DNA ReplicationMary Lyndie BorgoniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Genetics Resume: 1. DNA ReplicationDokument2 SeitenPlant Genetics Resume: 1. DNA ReplicationEbri Yosia ManikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem Task 9 BocalanbethinnaDokument4 SeitenBiochem Task 9 BocalanbethinnaANA MARIA BETHINNA BOCALANNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Replication: Molecular Biology DNA Living Organisms Biological InheritanceDokument2 SeitenDNA Replication: Molecular Biology DNA Living Organisms Biological InheritancePretty UNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dianne D. Mariano BSN 101Dokument9 SeitenDianne D. Mariano BSN 101Dianne MarianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: Midterm: Week 3Dokument8 SeitenLesson 3: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: Midterm: Week 3ROGELIO COLUMNANoch keine Bewertungen
- Sci10 q3w4L1Dokument26 SeitenSci10 q3w4L1Cedric BaldozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetic Research PaperDokument10 SeitenGenetic Research PaperDev raj regmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Circulatory System2Dokument5 SeitenWorksheet Circulatory System2Abir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 2005 QP - Paper 6 CIE Biology IGCSE PDFDokument12 SeitenJune 2005 QP - Paper 6 CIE Biology IGCSE PDFAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Grade 9 American Division Miss AlaaDokument14 SeitenRevision Grade 9 American Division Miss AlaaAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steven Fady Fayez Mehany: Youssef Ahmed Abdelmohsen YoussefDokument8 SeitenSteven Fady Fayez Mehany: Youssef Ahmed Abdelmohsen YoussefAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aies Trial Multiple Choice MsDokument2 SeitenAies Trial Multiple Choice MsAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 2003 QP - Paper 6 CIE Biology IGCSEDokument12 SeitenJune 2003 QP - Paper 6 CIE Biology IGCSEAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steven Fady Fayez Mehany: Youssef Ahmed Abdelmohsen YoussefDokument8 SeitenSteven Fady Fayez Mehany: Youssef Ahmed Abdelmohsen YoussefAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Behavior Chapter NotesDokument27 SeitenBehavior Chapter NotesAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mixed Questions Genetics1Dokument11 SeitenMixed Questions Genetics1Abir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP 08 - Tensile Strength of Plant FibresDokument2 SeitenCP 08 - Tensile Strength of Plant FibresAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP 03 - Calculating Mitotic IndexDokument3 SeitenCP 03 - Calculating Mitotic IndexAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Which Stats Test Should I UseDokument2 SeitenWhich Stats Test Should I Useaby251188Noch keine Bewertungen
- MeasurementDokument4 SeitenMeasurementAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set 2 Cell Biology Grades 4 5 PDFDokument18 SeitenSet 2 Cell Biology Grades 4 5 PDFAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specimen Paper 1 Mark Scheme PDFDokument2 SeitenSpecimen Paper 1 Mark Scheme PDFAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eukaryotic Cell Cycle & Division 1 MSDokument6 SeitenEukaryotic Cell Cycle & Division 1 MSAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set 1 Bioenergetics Grades 4 6Dokument19 SeitenSet 1 Bioenergetics Grades 4 6Abir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set 1 Infection Grades 7 9Dokument19 SeitenSet 1 Infection Grades 7 9Abir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Notes - Topic 2 Cells and Control - Edexcel Biology GCSEDokument10 SeitenDetailed Notes - Topic 2 Cells and Control - Edexcel Biology GCSEAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP 07 - Plant Mineral DeficienciesDokument3 SeitenCP 07 - Plant Mineral DeficienciesAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Questions and AnswersDokument472 SeitenBiology Questions and Answersbusybeefreedom100% (1)
- SAPS - Chromatography of Photosynthetic Pigments - Student NotesDokument5 SeitenSAPS - Chromatography of Photosynthetic Pigments - Student NotesHaruka SuzukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis Respiration and Nutrient Cycle AnswersDokument14 SeitenPhotosynthesis Respiration and Nutrient Cycle AnswersAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP 06 - Water Potential of Plant CellsDokument3 SeitenCP 06 - Water Potential of Plant CellsAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muscles 1Dokument5 SeitenMuscles 1Abir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cell Structure & Function 5 MSDokument7 SeitenEukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cell Structure & Function 5 MSAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface Area To Volume Ratio QPDokument3 SeitenSurface Area To Volume Ratio QPAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry Part One Mxed AnswersDokument7 SeitenBiochemistry Part One Mxed AnswersAbir OmarNoch keine Bewertungen