Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Hochgeladen von
geetuaggarwalCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Hochgeladen von
geetuaggarwalCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN QUALITATIVE AND
QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
Its been said that every business issue ultimately boils down to an information problem.
Can the right information be delivered? The ultimate goal of research is to supply accurate
information that reduces the uncertainty in managerial decision making. Very often, decisions
are made with little information for various reasons, including cost considerations,
insufficient time to conduct research, or managements belief that enough is already known.
Relying on seat-of-the-pants decision making decision making without research is like
betting on a long shot at the racetrack because the horses name is appealing. Occasionally
there are successes, but in the long run, intuition without research lead to losses. Business
research helps decision makers shift from intuitive information gathering to systematic and
objective investigation.
Business research is the application of the scientific method in searching for the truth about
business phenomena. These activities include defining business opportunities and problems,
generating and evaluating alternative courses of action, and monitoring employee and
organizational performance. Business research is more than conducting surveys This process
includes idea and theory development, problem definition, searching for and collecting
information, analysing data, and communicating the findings and their implications. It
suggests that business research information is not intuitive or haphazardly gathered. Literally,
research (re-search) means to search again. The term connotes patient study and scientific
investigation wherein the researcher takes another, more careful look at the data to discover
all that is known about the subject. Ultimately, all findings are tied back to the underlying
theory.
The definition also emphasizes, through reference to the scientific method, that any
information generated should be accurate and objective. Research isnt performed to support
preconceived ideas but to test them. The researcher must be personally detached and free of
bias in attempting to find truth. If bias enters into the research process, the value of the
research is considerably reduced. It is clear that business research is designed to facilitate the
managerial decision-making process for all aspects of the business: finance, marketing,
human resources, and so on. Business research is an essential tool for management in
virtually all problem-solving and decision-making activities. By providing the necessary
information on which to base business decisions, research can decrease the risk of making a
wrong decision in each area. However, it is important to note that research is an aid to
managerial decision making, never a substitute for it.
As we have defined research, one must understand qualitative and quantitative research. As
the words imply, qualitative research is interested more in qualities than quantities. Therefore,
qualitative research is not about applying specific numbers to measure variables or using
statistical procedures to numerically specify a relationships strength.
Qualitative business research is research that addresses business objectives through
techniques that allow the researcher to provide elaborate interpretations of market phenomena
without depending on numerical measurement. Its focus is on discovering true inner
meanings and new insights.
Qualitative research is very widely applied in practice. Qualitative research is less structured
than most quantitative approaches. It does not rely on self-response questionnaires containing
structured response formats. Instead, it is more researcher-dependent in that the researcher
must extract meaning from unstructured responses, such as text from a recorded interview or
a collage representing the meaning of some experience, such as skateboarding. The
researcher interprets the data to extract its meaning and converts it to information.
Generally, the less specific the research objective, the more likely that qualitative research
tools will be appropriate. Also, when the emphasis is on a deeper understanding of
motivations or on developing novel concepts, qualitative research is very appropriate. Some
common situations where qualitative research is used:
When the research objective is to learn how a phenomena occurs in its natural setting
or to learn how to express some concept in colloquial terms. For example, how do
consumers actually use a product? Or, exactly how does the accounting department
process invoices? While a survey can probably ask many useful questions, observing
a product in use or watching the invoice process will usually be more insightful.
Qualitative research produces many product and process improvement ideas.
When some behaviour the researcher is studying is particularly context dependent
meaning the reasons something is liked or some behaviour is performed depend very
much on the particular situation surrounding the event.
Quantitative business research can be defined as business research that addresses research
objectives through empirical assessments that involve numerical measurement and analysis
approaches. Qualitative research is more apt to stand on its own in the sense that it requires
less interpretation. For example, quantitative research is quite appropriate when a research
objective involves a managerial action standard. For example, a salad dressing company
considered changing its recipe. The new recipe was tested with a sample of consumers. Each
consumer rated the product using numeric scales. Management established a rule that a
majority of consumers rating the new product higher than the old product would have to be
established with 90 percent confidence before replacing the old formula. A project like this
can involve both quantitative measurement in the form of numeric rating scales and
quantitative analysis in the form of applied statistical procedures.1
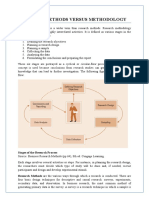
Contrasting Qualitative and Quantitative Methods
The following table illustrates some differences between qualitative and quantitative
research:
11 Zikmund, Babin, Carr, Adhikari, & Griffin. (2012). Business Research Methods (8 ed.). Delhi:
Cengage Learning
Table: Comparing Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Qualitative Research
Discover Ideas, Used in
Exploratory Research with
General Research Objects
Research Aspect
Common Purpose
Quantitative Research
Test Hypotheses or
Specific Research
Questions
Observe and Interpret
Unstructured, Free-Form
Approach
Data Collection
Approach
Measure and Test
Structured Response
Categories Provided
Researcher Is
Intimately Involved.
Results Are Subjective.
Researcher
Independence
Researcher Uninvolved
Observer. Results Are
Objective.
Small SamplesOften
in Natural Settings
Samples
Large Samples to
Produce Generalizable
Results (Results That
Apply to Other
Situations)
Exploratory Research
Designs
Most Often Used
Descriptive and Causal
Research Design
Source: Business Research Methods (pp 148), 8th ed. Cengage Learning.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Quantitative and Qualitative ApproachesDokument9 SeitenQuantitative and Qualitative ApproachesLeow Chee SengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative and Quantitative ResearchDokument7 SeitenQualitative and Quantitative ResearchKabutu ChuungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research DesignDokument3 SeitenResearch DesignChariztelle LacsamanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review SHDokument7 SeitenLiterature Review SHapi-430633950Noch keine Bewertungen
- Discuss The Differences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research...Dokument5 SeitenDiscuss The Differences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research...Calvin Mandivavarira80% (5)
- Descriptive ResearchDokument25 SeitenDescriptive Researchtuannn123100% (2)
- Qualitative and Quantitative Method of ResearchDokument15 SeitenQualitative and Quantitative Method of Researchsylviaukah82% (17)
- Mixed MethodsDokument1 SeiteMixed MethodsJM Jesalva BalanquitNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Descriptive ResearchDokument7 SeitenWhat Is Descriptive ResearchEden EscaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Approaches and Their Methodological ConcequencesDokument9 SeitenResearch Approaches and Their Methodological ConcequenceszefergNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graduate Student Research Proposal ExampleDokument3 SeitenGraduate Student Research Proposal ExampleHeatherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Educ 630 Research Proposal Final Sarah TerryDokument29 SeitenEduc 630 Research Proposal Final Sarah Terryapi-370442620Noch keine Bewertungen
- Differences Between Qualitative and Quantative ResearchDokument8 SeitenDifferences Between Qualitative and Quantative ResearchLori Perez100% (1)
- Differences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research MethodsDokument2 SeitenDifferences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research MethodsJonathan Wilder100% (4)
- Inferential StatisticsDokument23 SeitenInferential StatisticsAki StephyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Flaws in ResearchDokument9 SeitenCommon Flaws in ResearchJohn Koetsier100% (1)
- Non Probability SamplingDokument9 SeitenNon Probability SamplingmubbunNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Qualitative and Quantitative Research ApproachesDokument8 SeitenThe Qualitative and Quantitative Research ApproachesJosef CesarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mixed Methods Research DesignDokument7 SeitenMixed Methods Research DesignBayissa BekeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied and Basic ResearchDokument1 SeiteApplied and Basic ResearchPRINTDESK by Dan100% (1)
- Three Types of ResearchDokument8 SeitenThree Types of Researchasghaznavi95% (19)
- Methods of Data Collection in Qualitative Research - Interviews and Focus Group PDFDokument5 SeitenMethods of Data Collection in Qualitative Research - Interviews and Focus Group PDFRianaDyahPrameswariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mixed Method Research: An OverviewDokument16 SeitenMixed Method Research: An Overviewshumon2657100% (1)
- Chap 1-3 (Part 1)Dokument22 SeitenChap 1-3 (Part 1)Jerine BenedictoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research DesignDokument6 SeitenResearch DesignVineet AbrahamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research DesignDokument34 SeitenResearch DesignPriyanka Soni0% (1)
- A Correlational StudyDokument7 SeitenA Correlational StudyvalenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are The Types of ResearchDokument3 SeitenWhat Are The Types of ResearchSelenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mixed Research MethodologyDokument7 SeitenMixed Research MethodologyDr. Nisanth.P.MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research ApproachDokument1 SeiteResearch ApproachomairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Descriptive Research Is Used To Describe Characteristics of A Population or Phenomenon BeingDokument2 SeitenDescriptive Research Is Used To Describe Characteristics of A Population or Phenomenon BeingkevzcOde09100% (1)
- Mixed MethodDokument26 SeitenMixed MethodFirdaus AzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study As A Research Method in EducationDokument23 SeitenCase Study As A Research Method in EducationDorota Oakley MatuszykNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Three: Research MethodologyDokument20 SeitenChapter Three: Research MethodologyRogerKYChan100% (1)
- Concept of Research and Research ProblemDokument12 SeitenConcept of Research and Research Problemjessa villaruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Descriptive and Inferential StatisticsDokument3 SeitenDescriptive and Inferential StatisticsHimraj Bachoo100% (2)
- Positivism in Cross Sectional SurveysDokument12 SeitenPositivism in Cross Sectional SurveysStephen KokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Conceptual Framework of The Evolution of School PsychologyDokument17 SeitenA Conceptual Framework of The Evolution of School PsychologyFernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of ResearchDokument6 SeitenDefinition of Researchayush_GARG1234567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Contemporary Issues in PMDokument26 SeitenContemporary Issues in PMBobb Ketter0% (1)
- Narrative Study Experience of An Engineer Pursuing Another CareerDokument33 SeitenNarrative Study Experience of An Engineer Pursuing Another CareerGherbe CastañaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Validity and Reliability in A Qualitative StudyDokument3 SeitenValidity and Reliability in A Qualitative StudyGheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 A - Research DesignDokument22 SeitenModule 3 A - Research DesignsafssimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research DesignDokument6 SeitenResearch DesignPallavi PalluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Descriptive and Inferential StatisticsDokument31 SeitenDescriptive and Inferential Statisticsabusroor2008100% (1)
- Methods of Data CollectionDokument11 SeitenMethods of Data Collectiongeetarose100% (2)
- Research DesignDokument10 SeitenResearch DesignBalaji N92% (13)
- HypothesisDokument25 SeitenHypothesisVenkatachalam Mohanasundaram100% (1)
- Business ResearchDokument81 SeitenBusiness ResearchREMIGIUS MARIOE100% (1)
- Research Is The Systematic Process of Collecting and Analyzing Information To Increase OurDokument19 SeitenResearch Is The Systematic Process of Collecting and Analyzing Information To Increase OurMaruf AmaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRM NotesDokument16 SeitenBRM Notesclick bank100% (1)
- What Is RecesrhDokument3 SeitenWhat Is RecesrhCanggu Chic FamilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 BRMDokument30 Seiten4 BRMSayeeshwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 BRMDokument5 SeitenChapter 1 BRMagragamidegree collegeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Research: Types, Benefits, and Its ImportanceDokument6 SeitenBusiness Research: Types, Benefits, and Its ImportanceRana100% (1)
- Module 1 - Research MethodologyDokument22 SeitenModule 1 - Research MethodologyPRATHAM MOTWANINoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Research Method The Series of Essay Essay OneDokument6 SeitenBusiness Research Method The Series of Essay Essay OneNidhi PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRES-C1-Introduction-to-Business-Research 2Dokument20 SeitenBRES-C1-Introduction-to-Business-Research 2Jhonissa LasquiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Quantitative Research SampleDokument4 SeitenWhat Is Quantitative Research SampleMikmik Channel TvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reserach MethodologyDokument2 SeitenReserach MethodologygeetuaggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative and Quantitative ResearchDokument3 SeitenQualitative and Quantitative ResearchgeetuaggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Murray 93 Drunk and DogDokument3 SeitenMurray 93 Drunk and Doganshuljain785Noch keine Bewertungen
- Murray 93 Drunk and DogDokument3 SeitenMurray 93 Drunk and Doganshuljain785Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class ActionDokument4 SeitenClass ActiongeetuaggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barriers To CommunicationDokument20 SeitenBarriers To CommunicationgeetuaggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10.2 Recent Amendments: Tenure From 1 To 3 Years (Other Than A Unit of Equity Oriented Fund)Dokument1 Seite10.2 Recent Amendments: Tenure From 1 To 3 Years (Other Than A Unit of Equity Oriented Fund)geetuaggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Standard 9Dokument13 SeitenAccounting Standard 9MANJEET PANGHALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Warren BuffettDokument2 SeitenWarren BuffettgeetuaggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature ReviewDokument2 SeitenLiterature Reviewmingren93100% (1)
- The Importance of Statistics To Criminal Justice and CriminologyDokument20 SeitenThe Importance of Statistics To Criminal Justice and CriminologyAneelaMalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Engineering Data AnalysisDokument4 SeitenNotes On Engineering Data Analysismae hope bangloyNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLEMING Balagot GT2Dokument7 SeitenFLEMING Balagot GT2Kirk AndrewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final 315Dokument43 SeitenFinal 315Angelica mae TabilisimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Management Assignment Morales E. MA332Dokument2 SeitenProject Management Assignment Morales E. MA332LJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 1: Strategic and Extensive Form Games SolutionsDokument11 SeitenProblem Set 1: Strategic and Extensive Form Games SolutionsAmmi JulianNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effect of Climate Change On Food Security in Gedo, Jubaland, SomaliaDokument17 SeitenThe Effect of Climate Change On Food Security in Gedo, Jubaland, SomaliaKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essentials of Marketing Research Putting Research Into Practice 1st Edition Clow Test BankDokument10 SeitenEssentials of Marketing Research Putting Research Into Practice 1st Edition Clow Test BankDebbieCollinsokpzd100% (13)
- Pre Test Practical Research 2 IDokument4 SeitenPre Test Practical Research 2 IKris NeyraNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.S B.S B.S B.S Nishat EducationDokument32 SeitenB.S B.S B.S B.S Nishat EducationQamar ZamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- What We Know About ResearchDokument16 SeitenWhat We Know About Researchcarlosmontes21Noch keine Bewertungen
- DOCUMENT 5-6 - Research Paper TemplateDokument13 SeitenDOCUMENT 5-6 - Research Paper TemplateKreshia Kyrelle BundalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Three Research Methodology 3.0. Introduction: March 2020Dokument6 SeitenChapter Three Research Methodology 3.0. Introduction: March 2020Danica SoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RHandbookProgramEvaluation PDFDokument759 SeitenRHandbookProgramEvaluation PDFflorin100% (1)
- Annexure-I - Research Analyst PDFDokument2 SeitenAnnexure-I - Research Analyst PDFmahantaratan123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Research OnionDokument5 SeitenResearch OnionVolvereneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Research Q3Dokument2 SeitenPractical Research Q3mary joy v, chiquilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Evolution of Management Accounting Research in The United StatesDokument13 SeitenThe Evolution of Management Accounting Research in The United Stateshanna rosydaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perales - Kent Benedict - Reflection Paper 1 - 3CHEM1Dokument1 SeitePerales - Kent Benedict - Reflection Paper 1 - 3CHEM1KENT BENEDICT PERALESNoch keine Bewertungen
- TriangulationDokument19 SeitenTriangulationMarkWeber100% (1)
- Creswell 2009Dokument97 SeitenCreswell 2009Anonymous fPode9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Research in CurriculumDokument9 SeitenTypes of Research in CurriculumgoldenfeathersfootballclubNoch keine Bewertungen
- PR1Dokument14 SeitenPR1Kenneth Rodriguez HerminadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ErrosDokument13 SeitenErrosMd AmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kajian Tentang Perumusan Hipotesis Statistik Dalam Pengujian Hipotesis PenelitianDokument4 SeitenKajian Tentang Perumusan Hipotesis Statistik Dalam Pengujian Hipotesis PenelitianMeylan HusinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book Ics Part-I 2019Dokument70 SeitenBook Ics Part-I 2019Rajput Prince50% (2)
- Abubeker HajiDokument52 SeitenAbubeker HajikalebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Writing Research ApproachesDokument5 SeitenThesis Writing Research ApproachessylvesterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pr1 St3q1 Summative TestDokument3 SeitenPr1 St3q1 Summative TestEsther EdaniolNoch keine Bewertungen