Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Vesico Ureteral Reflux
Hochgeladen von
GerardLumCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Vesico Ureteral Reflux
Hochgeladen von
GerardLumCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
jslum.
com | Medicine
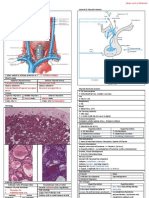
Vesico-Ureteral Reflux (VUR)
Definition Investigations
Urine flows back in a retrograde fashion from Bladder → Kidneys Ultrasound of Kidney
Can detect dilatation in cases of VUR
Significance of Reflux But may show normal ultrasound in VUR, Scarring
↑ Incidence MCU (Micturating Cysto Urethrogram) (Male)
Somewhat less than 1% Bladder is catheterised
In 40% of Infants with UTI Contrast given in Bladder
↑ Frequent in Younger patients Patient asked to pass urine
Sequelae • Nice visualisation of bladder outline
Recurrent UTI • Nice visualisation of urethra
Renal failure (Damaged Kidney in small children) • Normally – No contrast move up
Hypertension Advantages Disadvantages
Degree of reflux demonstrated Gonadal irradiation
VUR causes UTI Good outline of Bladder, Urethra Not very sensitive
Ascending (almost always) Invasive
During micturition
• Urine goes out (excreted via urethra)
• Urine goes up (ascend to ureter)
Micturition ends when bladder is empty
After micturition, urine comes back into bladder (previously ascend to ureter)
Perineal colonisation
Urethral colonisation
Bladder col onisation Isotope Cystogram (Female)
Infrequent passing of urine Bladder catheterised
Incomplete bladder emptying Isotopes given in bladder
Cystitis • Camera can monitor during 1h
Pyelonephritis • ↓ good outline of Bladder wall and Urethra
• ↓ Radiation
UTI causes Renal Damage Advantages Disadvantages
Bacteria in Kidney → Inflammatory response ↑ Sensitive ↓ good outline of structures
Release inflammatory mediators – Toxins, O2 radicals ↓ Radiation Invasive
Ischaemia → Damage Kidney tissue
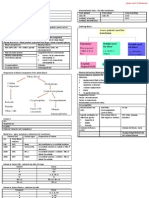
Immature Kidneys of Infants are more susceptible Management
Medical Surgical
Causes of VUR Correction & avoidance of risk factors Discuss with parents, surgeon
• Good Perineal Hygiene • Operation
• Normal Voiding Pattern • Laparoscopic (minimally
• Normal Bowel Habits invasive surgery)(keyhole)
• Endoscopi c
Antibiotics Prophylaxis Factors
(Once daily)(N octe – every night) • Age (Not in < 2 y/o with mild
• Trimetoprim reflux)
• Nitrofurantoin • Severity
• Cotrimoxazole • Persistence
• Cephalosporins • No. of breakthrough infections
Congenital Given until Reflux resolved • Bacterial resistance
Ureter enters bladder in oblique way Given until 7 y/o • Renal damage & progression
Congenital If fail, usually due to
Familial occurrence • Poor compliance
(Mother did not eat/ do anything wrong during pregnancy) • Resistant bacteria
Infrequent voiding
Neurogenic bladder
Cystitis
Clinical
Detected after UTI
Detected Antenally – Ultrasound shows dilated PC system
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Pathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisDokument5 SeitenPathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisGerardLum100% (1)
- Nephrology - Dr. Allam 2021Dokument42 SeitenNephrology - Dr. Allam 2021Alokh Saha RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Soft Tissue TumoursDokument8 SeitenSoft Tissue TumoursGerardLum100% (2)
- Pathology of Thyroid DiseasesDokument5 SeitenPathology of Thyroid DiseasesGerardLum100% (2)
- Pathology of DiabetesDokument4 SeitenPathology of DiabetesGerardLum100% (4)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Posterior Pituitary SyndromeDokument1 SeitePosterior Pituitary SyndromeGerardLumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paediatrics OrthopaedicsDokument5 SeitenPaediatrics OrthopaedicsGerardLumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prostate GlandsDokument3 SeitenProstate GlandsDragan PetrovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Urinary Tract Infections in ChildrenDokument1 SeiteUrinary Tract Infections in ChildrenGerardLumNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Pathology of TestesDokument4 SeitenPathology of TestesGerardLum100% (1)
- Urinary Tract InfectionDokument4 SeitenUrinary Tract InfectionGerardLum100% (2)
- Pituitary DysfunctionDokument2 SeitenPituitary DysfunctionGerardLum0% (1)
- Soft Tissue InfectionsDokument3 SeitenSoft Tissue InfectionsGerardLum100% (1)
- Pathology GlomerulonephritisDokument4 SeitenPathology GlomerulonephritisGerardLum100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Nerve InjuryDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Nerve InjuryGerardLum100% (1)
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDokument6 SeitenSexually Transmitted DiseasesGerardLum100% (3)
- Safer Oral Sex BrochureDokument2 SeitenSafer Oral Sex BrochureMichael_Bolen1306Noch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Excretion of DrugsDokument3 SeitenRenal Excretion of DrugsGerardLum100% (3)
- Urinary System PDFDokument27 SeitenUrinary System PDFfiona100% (3)
- Pathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesDokument5 SeitenPathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesGerardLum100% (1)
- Obstructive UropathyDokument3 SeitenObstructive UropathyGerardLum100% (1)
- ThalassaemiaDokument4 SeitenThalassaemiaGerardLum100% (4)
- ThrombophiliaDokument3 SeitenThrombophiliaGerardLum100% (1)
- CAUTIDokument46 SeitenCAUTImahesh sivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathogenesis Bleeding DisordersDokument4 SeitenPathogenesis Bleeding DisordersGerardLumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urology MCQDokument16 SeitenUrology MCQChristian Jara80% (5)
- Pituitary Gland PathologyDokument4 SeitenPituitary Gland PathologyGerardLumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid PhysiologyDokument2 SeitenThyroid PhysiologyGerardLum100% (2)
- Skeletal Muscle RelaxantsDokument1 SeiteSkeletal Muscle RelaxantsGerardLum100% (2)
- Principles of Blood TransfusionDokument2 SeitenPrinciples of Blood TransfusionGerardLum100% (3)
- Renal Function in Disease StateDokument2 SeitenRenal Function in Disease Statedamai140390Noch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of AnaemiaDokument2 SeitenOverview of AnaemiaGerardLumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nsaids DrugsDokument2 SeitenNsaids DrugsIrene Zae MwandotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nocturnal EnuresisDokument1 SeiteNocturnal EnuresisGerardLumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Urinary EliminatonDokument5 SeitenImpaired Urinary EliminatonLoriejae Marie DesulocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology and Manifestation of Prostate CancerDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology and Manifestation of Prostate CancerAndreas LaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pencegahan HivDokument17 SeitenPencegahan HivJH ELIS RNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Ayurveda and Pharma Research: Case StudyDokument3 SeitenInternational Journal of Ayurveda and Pharma Research: Case StudyakhilkgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Hospital Near DarbhangaDokument5 SeitenBest Hospital Near DarbhangaShubh ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory 15Dokument5 SeitenLaboratory 15Isabel Maxine DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Most Common Hospital Departments: Breast CancerDokument7 SeitenMost Common Hospital Departments: Breast Cancerdeddy ramadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) : Pharmacotherapeutics II YrDokument20 SeitenUrinary Tract Infection (UTI) : Pharmacotherapeutics II YrpawannnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rupture Urethra Anterior DR Sule FixDokument36 SeitenRupture Urethra Anterior DR Sule FixkadinfathiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflex Facilitation: Vol Control of Micturition (Corticol Areas) Control EUS & Abd MDokument1 SeiteReflex Facilitation: Vol Control of Micturition (Corticol Areas) Control EUS & Abd MTharani KumaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unite 6Dokument17 SeitenUnite 6Surafel TamratNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASE REPORT-Devyana Enggar TaslimDokument24 SeitenCASE REPORT-Devyana Enggar TaslimvivitaslimNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Doctors Diagnose Bladder Stones in DogsDokument6 SeitenHow Doctors Diagnose Bladder Stones in DogshiralkchauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medullary Sponge KidneyDokument3 SeitenMedullary Sponge KidneyAmrAliTahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BAUS Student Guide To UrologyDokument4 SeitenBAUS Student Guide To UrologyTasya Aulia PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doxy PEPDokument2 SeitenDoxy PEPDoverocks7Noch keine Bewertungen
- HematuriaDokument9 SeitenHematuriaTel Avid YaredNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Hospitals and ClinicsDokument4 SeitenList of Hospitals and ClinicsArdi UkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AKI in ChildrenDokument43 SeitenAKI in ChildrenYonas AwgichewNoch keine Bewertungen
- NLM Classification: Worldwide Source of Medical Library ClassificationDokument1 SeiteNLM Classification: Worldwide Source of Medical Library ClassificationFrancisca CuellarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Groupd Ebp PresentationDokument38 SeitenGroupd Ebp Presentationapi-384226081Noch keine Bewertungen
- Catheter-Associated UTIDokument54 SeitenCatheter-Associated UTIAmeng GosimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karl Storz - Leaflet - True BipolarDokument2 SeitenKarl Storz - Leaflet - True BipolarHuy Thịnh NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- SyphilisDokument1 SeiteSyphilisdanice-magbanua-2668Noch keine Bewertungen
- Male Genetal OrganDokument7 SeitenMale Genetal OrgantomiNoch keine Bewertungen