Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Windows and Doors
Hochgeladen von
Malith De SilvaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Windows and Doors
Hochgeladen von
Malith De SilvaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
GIP TRAINING REPORT
10. WINDOWS AND DOORS
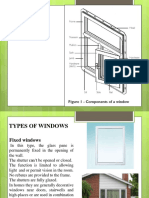
10.1. WINDOWS.
Window is an opening formed in a wall or roof to admit daylight through some transport or
translucent material fixed in the opening. The primary function of a window is served by a sheet of
glass fixed in a frame in the window opening. This simple type of window is termed a fixed light or
dead light because no part of the window can be opened. As the window is part of the wall or roof
envelope to the building, it should serve to exclude wind and rain, and act as a barrier to excessive
transfer of heat, sound, and spread of fire in much the same way as the surrounding wall or roof does.
The functional material of a endow, glass, is efficient in admitting daylight and excluding wind and
rain but is a poor barrier to the transfer of heat, sound and the spread of fire.
A traditional window is usually designed to ventilate rooms through one or more parts that open to
encourage an exchange of air between inside and outside. Ventilation is not a necessary function.
Ventilation can as well be provided through openings in walls and roofs that are either separate from
windows or linked to them to perform the separate function of ventilation. The advantage of
separating the functions of daylighting and ventilation is that windows may be made more effectively
wind and weathertight and ventilation can be more accurately controlled. The primary function of a
window is :
Admission of daylight
The secondary functions are :
A view out
Ventilation
10.2. ADMISSION OF DAY LIGHT.
The prime function of a daylight is to admit adequate daylight for the efficient performance of
daytime activities. The amount of light admitted depends in general terms on the size of the window
or windows in relation to the area of the room lit, and the depth inside the room to which useful light
will penetrate depends on the light of the head of windows above floor level.
CB/01/4573
CB/01/4573
GIP TRAINING REPORT
Common sense and observation suggest that the quantity of daylight in rooms is proportional to the
area of glass windows relative to floor area and this is confirmed by measurements. The shape, size
and position of windows affect the distribution of daylight in rooms and the view out. Tall windows
give a better penetration of light than low windows, separate windows give a less uniform
distribution of light than continuous windows.
10.2.1. VIEW OUT
As well as admitting daylight it is generally accepted that windows perform the useful function of
providing a view out of buildings as a link with the outside. When we are in the inside of the
building, by using glass windows always we can get the clear view of outside of the building without
going there. It is useful advantage in rainy days and is a one of the safety method. Because we can
clearly visible outside of the building without going out of the building.
10.2.2. VENTILATION
Ventilation means get fresh air inside to the building and remove dirt air from the building. Good
ventilation system requires for habitable rooms, kitchens, bathrooms, and sanitary accommodation to
provides air changes by natural or mechanical ventilation and also to reduce condensation in rooms
where worm, moisture vapor laden air may condense to water. The size of a ventilating opening, by
itself, gives no exact indication of the likely air changes as the ventilating effect of an opening
depends on air pressure difference between inside and outside and the size of the opening or
openings through which air will be evacuated to cause air flow.
The rate of exchange of air will depend on variations between inside and outside pressure and heat,
and the size and position of other openings in the room such as doors and open fireplaces that may
play a part in air exchange. The traditional method of ventilating is through opening lights in
windows. The advantage of opening lights is that they can be opened or closed to suit the individual
choice of the occupant of rooms regardless of notional optimum rates of air changes for comfort and
well being.
CB/01/4573
CB/01/4573
GIP TRAINING REPORT
10.3. MATERIALS USED FOR WINDOWS
Most of the time we used wood for make the windows and doors. But now a days other alternative
materials for prepare doors and windows. Followings are the materials that used for make windows.
Wood
Steel
Aluminium
Upvc
Fiber
Concrete
The advantage of wood as a material for framing windows was that the material was readily
available and could be cut, shaped and framed with traditional hand tools. The cost of labour and
materials in regular painting of these windows was accepted as a necessity to maintain the material
and enhance appearance. But now situation is change and there is no enough wood and it is very
expensive.
Therefore peoples are going for other alternative materials.
In our site we used
Aluminium as a material for windows and doors.
10.4. ALUMINIUM
Aluminium sections are introduced for substitute for steel section windows. This metal, though not
having the same advantageous weight to strength ratio as steel, does not suffer progressive, corrosive
rusting and can be formed in a wide variety of sections suitable for the whole windows with single or
double glazing. On exposure to air Aluminium forms an oxide that does not progressively corrode
but which has a coarse textured and unattractive appearance.
These windows are made from Aluminium alloy that is extruded in channel and box sections with
flanges and grooves for rebates and weather stripping. These thin walled channel and box sections
give the material adequate strength and stiffness for use as window sections.
CB/01/4573
CB/01/4573
GIP TRAINING REPORT
The material can be readily welded and has good resistance to corrosion that might cause loss of
strength, yet the surface of the material will fairly rapidly loss luster owing to white corrosion
products and some pitting caused particularly in marine and industrially polluted atmospheres. This
corrosive effect may be inhabit by anodizing or liquid organic or power coating. To maintain the
initial luster of the surface of these windows it is necessary to wash them at regular intervals.
The advantage of Aluminium windows are the variety of sections available for the production of a
wide range of window types, and the freedom from destructive corrosion. The disadvantage is the
high thermal conductivity of the material which acts as a cold bridge to heat transfer. To prevent
Aluminium section windows acting as a thermal bridge, they are constructed as two sections
mechanically linked by a plastic bridge that acts as a thermal break. As an alternative the inner face
of the Aluminium is covered with a plastic facing.
10.4.1. ALUMINIUM CASEMENT WINDOWS
Aluminium windows were originally made as a substitute for hot rolled steel section windows, in
small sections similar to those of steel. Aluminium windows of small solid sections are less used
now than they were, partly due to changing fashion and more particularly because the small section,
which acts as a thermal bridge to encourage condensation, does not take the wider use today.
The majority of Aluminium windows that are made today are of sections extruded from Aluminium
alloy in a wide range of channel and box sections with grooves and lops for weatherstripping and
double glazing.
10.5. TYPES OF WINDOWS
There are two main types.
1. Fixed light
2. Opening light
Fixed light (Dead light) means is used to describe the whole or part of a window in which glass is
fixed so that no part of the glazing can be opened.
CB/01/4573
CB/01/4573
GIP TRAINING REPORT
Typically fixed lights are one sheet of glass, several sheets of glass in glazing bars, or led or copper
lights glazed (Fixed) directly to the window frame.
Open light is the whole or part of a window that can be opened by being hinged or pivoted to frame
or which cam slide open inside the frame. Windows with opening lights are classified according to
the manner in which the opening lights are arranged to open inside the frame.
Hinged
Pivoted
Sliding
Composite action
In our site we used Aluminium horizontally Sliding windows. This crude form of small window
comprised two Aluminium framed sashes that slid horizontally on Aluminium runners inside a solid
Aluminium frame. As there had to be clearance for moving the sashes it as impossible to make this
window weather tight and because of the tendency of the sashes to rack. The advantage of this type
of window is that there are no internal or external projections from opening sashes and it can be
opened to give close control of ventilation. It is difficult to clean the glass both sides from inside and
the clearance required for movement of the sashes makes it difficult to weatherseal for conditions of
severe exposure.
CB/01/4573
CB/01/4573
GIP TRAINING REPORT
10.6. DOORS
A door opening should be reasonably comfortable access of people. Door has mainly two functional
requirements. They are :
Access
Privacy
Access means, a door opening should be sufficiently wide and high for reasonably comfortable
access of people. The side on which the door is hung by hinges or pivots, its hand or handing and
whether it opens into or out of a space or room, are matter of convenience in use.
Privacy means doors should be serve to maintain privacy inside rooms to the same extent as the
enclosing walls or partitions.
For visual privacy, doors should be as obscure as the walls or
partitions.
Other functional requirements and materials that are used for manufacturing is as same as the
windows. In our site we use Aluminium Glaze panel doors. Doors with one or more glaze panel are
used to give some daylight to spaces such as halls that have no windows, and to give some borrowed
light from a window through an internal door to an otherwise unlit space. Doors are manufactured
from extruded Aluminium sections. These glaze doors commonly advertised as patio doors are
made as both single and multi leaf doors to hinge, slide or slide and fold to open. The particular use
of these doors is to provide a large area of clear glass for an unobstructed view out to gardens and to
give ready access from inside to outside.
An advantage of these doors is that they may be finished in a range of coloured powder or liquid
coatings that do not require periodic painting for maintenance. These doors are sufficiently robust
for use in domestic buildings and may be fabricated as thermal break construction to minimize
condensation on the internal faces of the Aluminium framing. A disadvantage of these doors is that
there may be appreciable condensation on the inside faces of the Aluminium framing. To minimize
condensation on the inside faces of these doors it is practice to fabricate them as thermal break doors.
CB/01/4573
CB/01/4573
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- BQS 207 POWER POINT - Week 1,2,3,4 Introduction, Windows, DoorsDokument18 SeitenBQS 207 POWER POINT - Week 1,2,3,4 Introduction, Windows, DoorsZechariah OburuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Construction Materials and Structural System-IiiDokument25 SeitenBuilding Construction Materials and Structural System-IiishelmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fenestration DesignDokument2 SeitenFenestration Designsusmita sethi100% (1)
- Door and Window Fenestration System PDFDokument77 SeitenDoor and Window Fenestration System PDFEyob AleneNoch keine Bewertungen
- FenestrationDokument21 SeitenFenestrationCyril NitchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taman Siswa v2345Dokument14 SeitenTaman Siswa v2345aimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BuildingDokument7 SeitenBuildingprajwaldhungana506Noch keine Bewertungen
- Curtain WallDokument3 SeitenCurtain WalljitenderaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curtain Wall (Revise1)Dokument8 SeitenCurtain Wall (Revise1)Mohammad BurhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doors, Windows and Ventilation DetailsDokument6 SeitenDoors, Windows and Ventilation DetailsPratik GhimireNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.skylight ConstructionDokument54 Seiten7.skylight ConstructionMark Kristian Rocafor100% (4)
- Glass FinalDokument22 SeitenGlass Finalsithi_raihanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tilt&Turn Window CADokument1 SeiteTilt&Turn Window CAManuel TrentiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulated GlazingDokument35 SeitenInsulated GlazingSarath nair.sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study 2Dokument14 SeitenCase Study 2FazreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curtainwalls TextDokument18 SeitenCurtainwalls TextLuciana MimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fenestration in BuildingsDokument38 SeitenFenestration in Buildingsrohit14oct100% (1)
- Curtain WallsDokument10 SeitenCurtain WallsBhavana ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gelo Oral Report - Use of Insulation and Vapor BarriersDokument22 SeitenGelo Oral Report - Use of Insulation and Vapor BarriersAngelo LunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Technology - Doors and WindowsDokument75 SeitenBuilding Technology - Doors and WindowsacmoradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aluminium WindowDokument5 SeitenAluminium WindowAwang HakimieNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Application of Capillary Tube in Double Glazed Units PDFDokument3 SeitenThe Application of Capillary Tube in Double Glazed Units PDFHAN HANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curtain Wall NoAnswersDokument20 SeitenCurtain Wall NoAnswersLuiz CarlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Facade TreatmentDokument11 SeitenFacade TreatmentfakemasterkgpNoch keine Bewertungen
- StorefrontDokument5 SeitenStorefrontMary Mae JeremiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaca InsulasiDokument4 SeitenKaca InsulasiVeronica AngelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Window DetailsDokument24 SeitenWindow DetailsTarun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glass Aluminum Curtain Wall SystemsDokument20 SeitenGlass Aluminum Curtain Wall Systemsliuqian100% (1)
- Curtain WallDokument18 SeitenCurtain WallTushar JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Materials and Construction 15CV36: Doors, Windows and VentilatorsDokument22 SeitenBuilding Materials and Construction 15CV36: Doors, Windows and VentilatorsAnonymous Qm0zbNkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Northern SkylightDokument7 SeitenNorthern SkylightYash PrajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cembrit Facade Hidden Fixing AluminiumDokument12 SeitenCembrit Facade Hidden Fixing AluminiumBertrand LaffontNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Technology (CE1303) : Window: Lecturer: Madam FatinDokument19 SeitenBuilding Technology (CE1303) : Window: Lecturer: Madam FatinRazif AjibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Defects in Aluminium WindowsDokument4 SeitenDefects in Aluminium WindowsShankavi KandappuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Windows and DoorsDokument40 SeitenWindows and DoorsAdrielle LadazzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curtain WallsDokument34 SeitenCurtain WallsKotesh ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A WindowDokument6 SeitenA WindowShreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skylight Natural Light VentilationDokument4 SeitenSkylight Natural Light VentilationWilliam LiewNoch keine Bewertungen
- TEACHING PLAN FOR BUILDING TECHNOLOGY AND ARCHITECTURAL PLANNINGDokument44 SeitenTEACHING PLAN FOR BUILDING TECHNOLOGY AND ARCHITECTURAL PLANNINGKhan MujahidKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Tightness of Building Envelope Design SystemDokument7 SeitenAir Tightness of Building Envelope Design SystemYolanda SelgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Facade LectureDokument71 SeitenFacade LectureYigezu YehombaworkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curtain Wall Systems: A Comprehensive GuideDokument32 SeitenCurtain Wall Systems: A Comprehensive Guidenikita singhalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curtain Wall and Glazing Report SummaryDokument14 SeitenCurtain Wall and Glazing Report SummarysuhailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Glazing in Modern ArchitectureDokument9 SeitenApplication of Glazing in Modern ArchitectureLenard UsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMC V - Unit-1-GlassDokument12 SeitenBMC V - Unit-1-Glassnivi100% (1)
- Joinery and Fitting (Wooden Windows Detail - Casement) : Department of Interior & Furniture Design LsadDokument19 SeitenJoinery and Fitting (Wooden Windows Detail - Casement) : Department of Interior & Furniture Design LsadAnmol MehanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Windows Used in ConstructionDokument13 SeitenTypes of Windows Used in ConstructionAnshuman SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doors & WindowsDokument20 SeitenDoors & WindowsJustine Pearl SibugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homeowner'S Window: Maintenance & Operation ManualDokument5 SeitenHomeowner'S Window: Maintenance & Operation Manualpandey008Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5.0 Windows and Window FramesDokument29 Seiten5.0 Windows and Window FramesvictorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infill WallDokument54 SeitenInfill WallnickNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIY - Window Buying GuideDokument9 SeitenDIY - Window Buying GuideormondsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Conservation: Lecture Eleven Minimizing Heat and Infiltration LossesDokument12 SeitenEnergy Conservation: Lecture Eleven Minimizing Heat and Infiltration Lossesjulia saleemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Curtain WallingDokument16 SeitenPrinciples of Curtain Wallingjewon100% (1)
- Family Handyman Whole House Repair GuideVon EverandFamily Handyman Whole House Repair GuideFamily HandymanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family Handyman Quick & Easy ProjectsVon EverandFamily Handyman Quick & Easy ProjectsFamily HandymanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Manual of Glass-BlowingVon EverandLaboratory Manual of Glass-BlowingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- KPK 1Dokument1 SeiteKPK 1Malith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12.1 Site and Site Office ManagementDokument8 Seiten12.1 Site and Site Office ManagementMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 327-Engineering ManagementDokument5 Seiten327-Engineering ManagementMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject - Request To Fulfill The Requirement of Superintendent (Civil) - Trainee - 07 Nos For UDA ProjectsDokument1 SeiteSubject - Request To Fulfill The Requirement of Superintendent (Civil) - Trainee - 07 Nos For UDA ProjectsMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Introduction To The Training EstblishmentDokument10 Seiten1-Introduction To The Training EstblishmentMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vehicle Movement BooksDokument3 SeitenVehicle Movement BooksMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Project Management SystemDokument7 SeitenIntroduction to Project Management SystemMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document Maintain at SiteDokument2 SeitenDocument Maintain at SiteMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 SurveyDokument7 Seiten6 SurveyMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Store ManagementDokument4 SeitenChapter 10 Store ManagementMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MarkingDokument6 SeitenMarkingMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.1.2.2. Role of Engineering StaffDokument3 Seiten11.1.2.2. Role of Engineering StaffMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summery of The Training PerformanceDokument2 SeitenSummery of The Training PerformanceMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Site LocationDokument1 SeiteSite LocationMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3Dokument4 Seiten3Malith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NDIPLOMA BASIC INDUSTRIAL TRAININGDokument2 SeitenNDIPLOMA BASIC INDUSTRIAL TRAININGMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Site LocationDokument1 SeiteSite LocationMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Store ManagementDokument3 SeitenStore ManagementMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12.3 Stores Management: IntrtoductionDokument4 Seiten12.3 Stores Management: IntrtoductionMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Storage: Storing of Fine and Course AggregatesDokument2 SeitenMaterial Storage: Storing of Fine and Course AggregatesMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument2 SeitenChapter 1Malith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summery of The Training PerformanceDokument2 SeitenSummery of The Training PerformanceMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.3 Ceiling WorkDokument1 Seite8.3 Ceiling WorkMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tiling Guide: Tools, Advantages, and Installation ProcessDokument4 SeitenTiling Guide: Tools, Advantages, and Installation ProcessMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.0 TillingDokument4 Seiten5.0 TillingMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Light Is The Whole or Part of A Window That Can Be Opened by Being Hinged or Pivoted To Frame or Which Cam Slide Open Inside The FrameDokument1 SeiteOpen Light Is The Whole or Part of A Window That Can Be Opened by Being Hinged or Pivoted To Frame or Which Cam Slide Open Inside The FrameMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel truss construction and applicationsDokument3 SeitenSteel truss construction and applicationsMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Durra Board Celling and Aluminum Ceiling Grid InstallationDokument4 SeitenDurra Board Celling and Aluminum Ceiling Grid InstallationMalith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9Dokument4 Seiten9Malith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sri Lanka Standard 1247-2003Dokument34 SeitenSri Lanka Standard 1247-2003piyalaravinnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabrication and Testing of Natural Fiber Reinforced Hybrid Composites Banana/PineappleDokument5 SeitenFabrication and Testing of Natural Fiber Reinforced Hybrid Composites Banana/PineappleIJMERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Painting Procedure For Ball ValveDokument7 SeitenPainting Procedure For Ball ValveBhisamS Salleh100% (2)
- Ohwt D1Dokument4 SeitenOhwt D1Mayur SonkusareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stainless Steel Structure Design HandbookDokument20 SeitenStainless Steel Structure Design Handbookgnino2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Polyken 936 TapeDokument2 SeitenPolyken 936 TapeKyaw Kyaw AungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mil HDBK 695d Change 2Dokument45 SeitenMil HDBK 695d Change 2dhoo_babyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete RepairDokument7 SeitenConcrete RepairjjahaddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marapur PU Screen Printing Ink: Simple Print, Fabric 100-40 (T)Dokument4 SeitenMarapur PU Screen Printing Ink: Simple Print, Fabric 100-40 (T)m_malhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bamboo Reinforced ConcreteDokument9 SeitenBamboo Reinforced ConcreteE.m. Karishma E MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cepz FactoriesDokument3 SeitenCepz Factoriessalauddin77% (13)
- Finishing and polishing dental restorationsDokument32 SeitenFinishing and polishing dental restorationsbukya002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Piping: Kevin D. Rafferty, P.E. Geo-Heat Center Klamath Falls, Oregon 97601Dokument19 SeitenPiping: Kevin D. Rafferty, P.E. Geo-Heat Center Klamath Falls, Oregon 97601danianpdNoch keine Bewertungen
- CeramographyDokument6 SeitenCeramographyRomer John DetubioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naked Raku and Related Bare Clay TechniquesDokument25 SeitenNaked Raku and Related Bare Clay Techniquesferisitav100% (1)
- Technical Data:: Oasis Epoxy TL 8758Dokument2 SeitenTechnical Data:: Oasis Epoxy TL 8758Maurice DavisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plastic Mark SpecificationsDokument16 SeitenPlastic Mark SpecificationszuconjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemrite - 303 SPDokument2 SeitenChemrite - 303 SPghazanfar100% (3)
- 3M Electrical Products & Cold Shrink CatalogueDokument116 Seiten3M Electrical Products & Cold Shrink Cataloguewiyasatama100% (1)
- Module 1Dokument47 SeitenModule 1greatrijuvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM D 6083-97aDokument6 SeitenASTM D 6083-97aJOsé Ratónciitop R Gil0% (1)
- Macro EtchingDokument2 SeitenMacro EtchingAdeel IkhlaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pile InfoDokument1 SeitePile InfoArvin BhurtunNoch keine Bewertungen
- NERDC COST EFFECTIVE HOUSING TECHNOLOGY Sri LankaDokument6 SeitenNERDC COST EFFECTIVE HOUSING TECHNOLOGY Sri LankaSriyanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masonry Quick Reference Pocket GuideDokument62 SeitenMasonry Quick Reference Pocket GuideRonald KahoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sika PDS - E - Sika FastFix - 138 TPDokument2 SeitenSika PDS - E - Sika FastFix - 138 TPlwin_oo2435Noch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Fly Ash and Silica Fume On The Resistance of Mortar To Sulfuric Acid and Sulfate AttackDokument10 SeitenEffects of Fly Ash and Silica Fume On The Resistance of Mortar To Sulfuric Acid and Sulfate AttackMaziar Mehravar100% (1)
- Plasguard 5302 PDFDokument3 SeitenPlasguard 5302 PDFNageswara Rao BavisettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansymss SP-69: Standard PracticeDokument16 SeitenAnsymss SP-69: Standard PracticekjhgNoch keine Bewertungen