Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Historical Background.: Baroque Art
Hochgeladen von
AlineOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Historical Background.: Baroque Art
Hochgeladen von
AlineCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Baroque Art
Historical background.
o 16th & 17th centuries were a time of great religious, scientific,
political and social changes.
o The catholic churchs influence diminished after the Protestant
Reformation and the Scientific Revolution.
o However, monarchies grew strong and became absolute, royal
authority was questioned by the bourgeoisie.
o 1517 Martin Luther published 95 Thesis, which refuted the
authority of the pope as well as many catholic dogmas and
traditions.
o
The Catholic Church answered with Counterreformation; it
summoned the Council of Trent (1545-1563) and Protestantism
was condemned.
o The Jesuit order was created as an effort to support the pope and
educate Catholics.
o Many rulers decided to become Protestant, and their choice had to
be adopted by their people. Along 16 th & 17th Centuries almost half
of Europe turned to Protestantism. England, Northern Netherlands,
Germany and some regions of France.
o Italy, Spain, Portugal, South Netherlands remained Catholic.
o The Thirty years war was fought largely as a religious war between
Protestants and Catholics in the Holy Roman Empire, although
disputes over internal politics and the balance of power within the
Empire played a significant part.
o 17th century Johannes Kepler affirmed that the planets had a
elliptical form and orbits.
o Galileo contradicted the Ptolemaic geocentric theory, and stated
that the Earth moved around the sun. These ideas denied the
traditional religious perception of the universe.
o Spain lived its Golden Age, supported by the silver and gold
obtained from the American colonies.
o Baroque art was demanded by three groups: a) the Catholic
Church (as propaganda); b) the absolute monarchies (to show their
power and for entertainment); and c) Protestants (for prestige).
o The Jesuit order needed temples, schools, convents, sacred images
etc. The kings, nobility and the bourgeoisie demanded places and
luxurious furniture and decoration.
Baroque Architecture
ELEMENTS
o Forms
change
according
to
country
and
region.
o Big
building
projects:
convents,
churches
and
palaces.
o Curved forms in
facades
and
plan
provided
undulating
movement
to
the building.
o Facades
were
decorated with
eye-catching
forms.
o Contrast
between
light
and shade.
o Materials: stone
cut in ashlars,
interiors
were
covered
with
colored marble,
details
in
bronze.
Decorative
elements: oval
windows,
niches, opened
pediments.
Organic
decoration.
Horror vacui
(fear for empty
space): most of
the surface is
covered with
o Carlo Madero.
o Gian Lorenzo
Bernini.
o Francesco
Borromini.
Baroque Sculpture
Baroque Painting
decoration.
Solomonic
columns:
helical column
(a spiraling
twisting shaft
like a
corkscrew).
Mixtilinear
figures: formed
angles and
curves.
Abundant
niches.
Sculptures were
created
Gian Lorenzo
together with a
Bernini.
scenography.
Movement.
Dramatic effects
and
expressions.
Undulating
clothes.
Helical
compositions.
Materials: white
and colored
marble, bronze,
polychrome
stone.
Asymmetrical
and diagonal
compositions.
Realism: full
naturalism.
Chiaroscuro.
Big formats.
Techniques: oil
on canvas and
fresco.
Michelangelo
Merisi
(Caravaggio).
Pedro Pablo
Rubens.
Rembrandt.
Velzquez.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Reformation without end: Religion, politics and the past in post-revolutionary EnglandVon EverandReformation without end: Religion, politics and the past in post-revolutionary EnglandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Royal Books and Holy Bones: Essays in Medieval ChristianityVon EverandRoyal Books and Holy Bones: Essays in Medieval ChristianityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Studies From Court and Cloister (Barnes & Noble Digital Library)Von EverandStudies From Court and Cloister (Barnes & Noble Digital Library)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elce Notes Unit I - VDokument37 SeitenElce Notes Unit I - VArijith Reddy JNoch keine Bewertungen
- Church History 101: The Highlights of Twenty CenturiesVon EverandChurch History 101: The Highlights of Twenty CenturiesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (13)
- Chapter 17Dokument103 SeitenChapter 17idkjittrippinNoch keine Bewertungen
- From Icons to Idols: Documents on the Image Debate in Reformation EnglandVon EverandFrom Icons to Idols: Documents on the Image Debate in Reformation EnglandNoch keine Bewertungen
- People and Their Contexts: A Chronology of the 16Th Century WorldVon EverandPeople and Their Contexts: A Chronology of the 16Th Century WorldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saints, Sacrilege and Sedition: Religion and Conflict in the Tudor ReformationsVon EverandSaints, Sacrilege and Sedition: Religion and Conflict in the Tudor ReformationsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Chapter 12, Lesson 1Dokument3 SeitenChapter 12, Lesson 1hopscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parallels of Power: An Introduction to Some Individualists of Church and StateVon EverandParallels of Power: An Introduction to Some Individualists of Church and StateNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Renaissance Thinkers: With History Projects for KidsVon EverandThe Renaissance Thinkers: With History Projects for KidsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Romantic Period NotesDokument1 SeiteRomantic Period NotesJeremy WebbNoch keine Bewertungen
- WHAP Chapter 16Dokument59 SeitenWHAP Chapter 16John LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mayflower: The Founding Myth of the United States of AmericaVon EverandThe Mayflower: The Founding Myth of the United States of AmericaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Great Ejectment of 1662: Its Antecedents, Aftermath, and Ecumenical SignificanceVon EverandThe Great Ejectment of 1662: Its Antecedents, Aftermath, and Ecumenical SignificanceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student's Friend 2 of 2Dokument28 SeitenStudent's Friend 2 of 2fwoobyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Medieval Church: From the Dawn of the Middle Ages to the Eve of the ReformationVon EverandThe Medieval Church: From the Dawn of the Middle Ages to the Eve of the ReformationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Empires of the Imagination: Politics, War, and the Arts in the British World, 1750-1850Von EverandEmpires of the Imagination: Politics, War, and the Arts in the British World, 1750-1850Noch keine Bewertungen
- The European RenaissanceDokument3 SeitenThe European RenaissanceCélia ZENNOUCHENoch keine Bewertungen
- Reformation Divided: Catholics, Protestants and the Conversion of EnglandVon EverandReformation Divided: Catholics, Protestants and the Conversion of EnglandNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Transformation of The West, 1450Dokument23 SeitenThe Transformation of The West, 1450Shakil Ahmad AligNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Catholic ChurchDokument9 SeitenHistory of Catholic ChurchNithiyarajan MasilamanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catholics x Protestants: The Thirty Years War (1618-1648)Von EverandCatholics x Protestants: The Thirty Years War (1618-1648)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Religious Transformations in the Early Modern AmericasVon EverandReligious Transformations in the Early Modern AmericasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcript of Renaissance and ReformationDokument3 SeitenTranscript of Renaissance and Reformationapi-217985483Noch keine Bewertungen
- Popes & Anti Popes: All the Popes, Good & Bad, from Sr. Peter to John Paul IiVon EverandPopes & Anti Popes: All the Popes, Good & Bad, from Sr. Peter to John Paul IiNoch keine Bewertungen
- American Jesuits and the World: How an Embattled Religious Order Made Modern Catholicism GlobalVon EverandAmerican Jesuits and the World: How an Embattled Religious Order Made Modern Catholicism GlobalBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- 0 - From Enlightment To RomanticismDokument11 Seiten0 - From Enlightment To RomanticismSarha FiorenzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mother ShipDokument24 SeitenMother ShipSteven TruongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second Year LMD Civilization Lesson 03Dokument3 SeitenSecond Year LMD Civilization Lesson 03GrX4 ChemsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Empires of God: Religious Encounters in the Early Modern AtlanticVon EverandEmpires of God: Religious Encounters in the Early Modern AtlanticBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Chapter 1 The Renaissance and HumanismDokument41 SeitenChapter 1 The Renaissance and Humanismapi-241427002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Key Concepts Unit 1 2020 EuroDokument2 SeitenKey Concepts Unit 1 2020 EuroKool BeansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Literary, Spiritual, and Political Crosscurrents of the Seventeenth CenturyVon EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Literary, Spiritual, and Political Crosscurrents of the Seventeenth CenturyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Henry VIII’s Narrow Escape: How Sawley Abbey nearly destroyed a king and changed the course of English historyVon EverandHenry VIII’s Narrow Escape: How Sawley Abbey nearly destroyed a king and changed the course of English historyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity: Renaissance Historical Background: Gad - Campaign Spanish&Gclid Cmql2Jhxysccfqguaqodo2CbkaDokument2 SeitenActivity: Renaissance Historical Background: Gad - Campaign Spanish&Gclid Cmql2Jhxysccfqguaqodo2CbkaAlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Groups ChartDokument1 SeiteFunctional Groups ChartAlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 14th Century in EuropeDokument2 SeitenThe 14th Century in EuropeAlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Formula: C H: IsomerismDokument3 SeitenMolecular Formula: C H: IsomerismAlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Background: Period Time Characteristics ArtistDokument3 SeitenBackground: Period Time Characteristics ArtistAlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proteins ExerciseDokument2 SeitenProteins ExerciseAlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkanes and CycloalkanesDokument5 SeitenAlkanes and CycloalkanesAlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proteins ExerciseDokument2 SeitenProteins ExerciseAlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Historical Background.: Baroque ArtDokument4 SeitenHistorical Background.: Baroque ArtAlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proteins ExerciseDokument2 SeitenProteins ExerciseAlineNoch keine Bewertungen
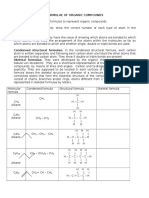
- Formulae Organic CompundsDokument2 SeitenFormulae Organic CompundsAlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Art of Calligraphy by David Harris PDFDokument128 SeitenThe Art of Calligraphy by David Harris PDFamandabraunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dante's InfernoDokument63 SeitenDante's InfernochathulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Carbon Atoms: Primary Carbon Atom: One Carbon NeighborDokument1 SeiteTypes of Carbon Atoms: Primary Carbon Atom: One Carbon NeighborAlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Booklet - 1989 (Deluxe) PDFDokument19 SeitenDigital Booklet - 1989 (Deluxe) PDFnidialysney3670Noch keine Bewertungen
- Waltz of The Flowers Piano SoloDokument3 SeitenWaltz of The Flowers Piano SoloBubi SilveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Write An EssayDokument3 SeitenHow To Write An EssayAlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ideal Trees To Plant in TolucaDokument6 SeitenIdeal Trees To Plant in TolucaAlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inequalities by RandomDokument23 SeitenInequalities by RandomRey VincentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biogeochemical Cycles (BB)Dokument22 SeitenBiogeochemical Cycles (BB)AlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Booklet - Red PDFDokument12 SeitenDigital Booklet - Red PDFAlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grande Amore - Piano Left HandDokument5 SeitenGrande Amore - Piano Left HandMauroScardiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Booklet - The Great GatsbyDokument9 SeitenDigital Booklet - The Great GatsbyACDC_oo_ooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethnic and Racial ConflictDokument17 SeitenEthnic and Racial ConflictAlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tchaikovsky Piotr Ilitch Children 039 S Album 59616 PDFDokument31 SeitenTchaikovsky Piotr Ilitch Children 039 S Album 59616 PDFAlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brahms Johannes Hungarian Dance F Minor 12Dokument3 SeitenBrahms Johannes Hungarian Dance F Minor 12da_vi_eba_neshtastniciteNoch keine Bewertungen