Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
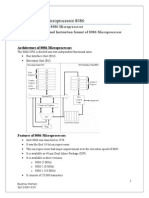
Lifo-Fifo Register (%R)
Hochgeladen von
nmulyonoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lifo-Fifo Register (%R)
Hochgeladen von
nmulyonoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Software Objects
Section 4.3
LIFO/FIFO Register (%R)
LIFO/FIFO Register (%R)
Using LIFO/FIFO Register Function Blocks
This section provides descriptions and programming guidelines for using LIFO/FIFO Register
function blocks.
What Is in This Section?
This section contains the following topics:
Topic
Page
Description
142
Configuration
144
LIFO Register Operation
145
FIFO Register Operation
146
Programming Example
147
EIO0000001474 11/2014
141
Software Objects
Description
Introduction
A LIFO/FIFO Register function block
is a memory block which can store up to 16 words
of 16 bits each in 2 different ways:
Queue (First In, First Out) known as FIFO.
Stack (Last In, First Out) known as LIFO.
Illustration
This illustration is the LIFO/FIFO Register function block.
Inputs
The LIFO/FIFO Register function block has the following inputs:
142
Label
Description
Value
Reset input (or
instruction)
At state 1, initializes the LIFO/FIFO Register.
Storage input (or
instruction)
On a rising edge, stores the contents of associated word %Ri.I in the
LIFO/FIFO Register.
Retrieval input (or
instruction)
On a rising edge, loads a data word of the LIFO/FIFO Register into
associated word %Ri.O.
EIO0000001474 11/2014
Software Objects
Outputs
The LIFO/FIFO Register function block has the following outputs:
Label
Description
Value
Empty output
(%Ri.E)
The associated bit %Ri.E indicates that the LIFO/FIFO Register is
empty. The value of %Ri.E can be tested, for example, in an animation
table or with an instruction.
Full output (%Ri.F) The associated bit %Ri.F indicates that the LIFO/FIFO Register is
full. The value of %Ri.F can be tested, for example, in an animation table
or with an instruction.
EIO0000001474 11/2014
143
Software Objects
Configuration
Parameters
To configure parameters, follow the Configuring a Function Block procedure (see page 133) and
read the description of Memory Allocation Modes in the SoMachine Basic Operating Guide.
The LIFO/FIFO Register function block has the following parameters:
Parameter
Description
Value
Used
Address used
If selected, this address is currently in use in a program.
Address
LIFO/FIFO Register
object address
A program can contain only a limited number of LIFO/FIFO
Register objects. Refer to the Programming Guide of the
hardware platform for the maximum number of registers.
Symbol
Symbol
The symbol associated with this object. Refer to the
SoMachine Basic Operating Guide, Defining and Using
Symbols for details.
Type
LIFO/FIFO Register
type
FIFO (queue) or LIFO (stack).
Comment
Comment
A comment can be associated with this object.
Objects
The LIFO/FIFO Register function block has the following objects:
Object
Description
Value
%Ri.I
LIFO/FIFO Register
input word
Can be read, tested, and written.
It can be modified in an animation table.
%Ri.O
LIFO/FIFO Register
output word
Can be read, tested, and written.
It can be modified in an animation table.
%Ri.E
Empty output
See Outputs table above.
%Ri.F
Full output
See Outputs table above.
Special Cases
This table contains a list of special cases for programming the LIFO/FIFO Register function
block:
Special Case
Description
Effect of a cold restart (%S0=1) or INIT
Initializes the contents of the LIFO/FIFO Register. The
output bit %Ri.E associated with the output E is set to 1.
Effect of a warm restart (%S1=1) or a controller
stop
Has no effect on the current value of the LIFO/FIFO
Register, nor on the state of its output bits.
NOTE: Effect of INIT is the same as %S0=1.
144
EIO0000001474 11/2014
Software Objects
LIFO Register Operation
Introduction
In LIFO operation (Last In, First Out), the last data item entered is the first to be retrieved.
Operation
This table describes LIFO operation:
Stage
Description
Storage:
When a storage request is received (rising edge at input
I or activation of instruction I), the contents of input
word %Ri.I are stored at the top of the stack (Fig. a).
When the stack is full (output F=1), no further storage is
possible.
Retrieval:
When a retrieval request is received (rising edge at input
O or activation of instruction O), the highest data word
(last word to be entered) is loaded into word %Ri.O (Fig.
b). When the LIFO/FIFO Register is empty (output
E=1), no further retrieval is possible. Output word %Ri.O
does not change and retains its value.
Reset:
The stack can be reset at any time (state 1 at input R or
activation of instruction R). The stack is empty after a
reset (%Ri.E =1).
EIO0000001474 11/2014
Example
145
Software Objects
FIFO Register Operation
Introduction
In FIFO operation (First In, First Out), the first data item entered is the first to be retrieved.
Operation
This table describes FIFO operation:
Stage
146
Description
Example
Storage:
When a storage request is received (rising edge at input
I or activation of instruction I), the contents of input word
%Ri.I are stored at the top of the queue (Fig. a). When
the queue is full (output F=1), no further storage is
possible.
Retrieval:
When a retrieval request is received (rising edge at input
O or activation of instruction O), the data word lowest in
the queue is loaded into output word %Ri.O and the
contents of the LIFO/FIFO Register are moved down
one place in the queue (Fig. b).
When the LIFO/FIFO Register is empty (output
E=1), no further retrieval is possible. Output word %Ri.O
does not change and retains its value.
Reset:
The queue can be reset at any time (state 1 at input R or
activation of instruction R). The queue is empty after a
reset (%Ri.E=1).
EIO0000001474 11/2014
Software Objects
Programming Example
Introduction
The following programming example shows the content of a memory word (%MW34) being loaded
into a LIFO/FIFO Register (%R2.I) on reception of a storage request (%I0.2) if LIFO/FIFO
Register %R2 is not full (%R2.F = 0). The storage request in the LIFO/FIFO Register is
made by %M1. The retrieval request is confirmed by input %I0.3, and %R2.O is loaded into %MW20
if the register is not empty (%R2.E = 0).
Programming
This example is a LIFO/FIFO Register function block with reversible instructions:
Rung
Reversible Instruction
BLK %R2
LD
%M1
I
LD
%I0.3
ANDN %R2.E
O
END_BLK
LD
%I0.3
[%MW20:=%R2.O]
LD
%I0.2
ANDN %R2.F
[%R2.I:=%MW34]
ST
%M1
This example is the same LIFO/FIFO Register function block with non-reversible instructions:
Rung
Non-Reversible Instruction
LD
I
LD
%I0.3
ANDN %R2.E
O
%R2
LD
%I0.3
[%MW20:=%R2.O]
LD
%I0.2
ANDN %R2.F
[%R2.I:=%MW34]
ST
%M1
%M1
%R2
NOTE: Refer to the reversibility procedure (see page 14) to obtain the equivalent Ladder Diagram.
EIO0000001474 11/2014
147
Software Objects
Section 4.4
Shift Bit Register (%SBR)
Shift Bit Register (%SBR)
Using Shift Bit Register Function Blocks
This section provides descriptions and programming guidelines for using Shift Bit Register
function blocks.
What Is in This Section?
This section contains the following topics:
Topic
148
Page
Description
149
Configuration
150
Programming Example
152
EIO0000001474 11/2014
Software Objects
Description
Introduction
The Shift Bit Register function block
or 1).
provides a left or right shift of binary data bits (0
Illustration
This illustration is the Shift Bit Register function block:
The current value of the Shift Bit Register is displayed in the centre of the function block:
Decimal value eg 7
Binary value eg 111
Hex value eg 16#7
Inputs
The Shift Bit Register function block has the following inputs:
Label
Description
Value
Reset input (or instruction)
When function parameter R is 1, this sets register bits 0 to 15
%SBRi.j to 0.
CU
Shift to left input (or instruction) On a rising edge, shifts a register bit to the left.
CD
Shift to right input (or
instruction)
EIO0000001474 11/2014
On a rising edge, shifts a register bit to the right.
149
Software Objects
Configuration
Parameters
To configure parameters, follow the Configuring a Function Block procedure (see page 133) and
read the description of Memory Allocation Modes in the SoMachine Basic Operating Guide.
The Shift Bit Register function block has the following parameters:
Parameter
Description
Value
Used
Address used
If selected, this address is currently in use in a program.
Address
Shift Bit Register object
address
A program can contain only a limited number of Shift Bit
Register objects. Refer to the Programming Guide of the
hardware platform for the maximum number of registers.
Symbol
Symbol
The symbol associated with this object. Refer to the SoMachine
Basic Operating Guide, Defining and Using Symbols for details.
Comment
Comment
A comment can be associated with this object.
Objects
The Shift Bit Register function block has the following objects:
Object
Description
Value
%SBRi
Register number
0 to 7
It can be modified in an animation table.
%SBRi.j Register bit
Bits 0 to 15 (j = 0 to 15) of the shift register can be tested by a test
instruction and written using an Assignment instruction.
Operation
This illustration shows a bit pattern before and after a shift operation:
This is also true of a request to shift a bit to the right (bit 15 to bit 0) using the CD instruction. Bit 0
is lost.
If a 16-bit register is not adequate, it is possible to use the program to cascade several Register.
150
EIO0000001474 11/2014
Software Objects
Special Cases
This table contains a list of special cases for programming the Shift Bit Register function
block:
Special Case
Description
Effect of a cold restart (%S0=1)
Sets all the bits of the register word to 0.
Effect of a warm restart (%S1=1)
Has no effect on the bits of the register word.
EIO0000001474 11/2014
151
Software Objects
Programming Example
Introduction
The Shift Bit Register function block provides a left or right shift of binary data bits (0 or 1).
Programming
In this example, a bit is shifted to the left every second while bit 0 assumes the state to bit 15.
In reversible instructions:
Rung
Reversible Instruction
BLK %SBR0
LD
%S6
CU
END_BLK
LD
ST
%SBR0.15
%SBR0.0
In non-reversible instructions:
Rung
Non-Reversible Instruction
LD
CU
LD
ST
%S6
%SBR0
%SBR0.15
%SBR0.0
NOTE: Refer to the reversibility procedure (see page 14) to obtain the equivalent Ladder Diagram.
152
EIO0000001474 11/2014
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Problem Solving in C and Python: Programming Exercises and Solutions, Part 1Von EverandProblem Solving in C and Python: Programming Exercises and Solutions, Part 1Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Want To Buy & Sell Expired Domain Names-Follow These 3 StepsDokument6 SeitenWant To Buy & Sell Expired Domain Names-Follow These 3 StepsEmiemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Assembly Language Programming with the ARM ProcessorVon EverandModern Assembly Language Programming with the ARM ProcessorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microprocessor 8085 Lab ManualDokument29 SeitenMicroprocessor 8085 Lab Manualmichaeledem_royal100% (1)
- Microprocessor Notes For JNTUH ECE IIIDokument82 SeitenMicroprocessor Notes For JNTUH ECE IIIManoj KollamNoch keine Bewertungen
- OBD AT Commnads ELM327DS PDFDokument94 SeitenOBD AT Commnads ELM327DS PDFclick2klic100% (1)
- Fifo Verif PlanDokument20 SeitenFifo Verif PlanPrabakaran Ellaiyappan0% (1)
- Euroleague Basketball: Change Pays Off ForDokument36 SeitenEuroleague Basketball: Change Pays Off ForNikos TagalnikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akta-332 Copyright Act 1987Dokument50 SeitenAkta-332 Copyright Act 1987Kartigesan999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Snubbing PDFDokument134 SeitenSnubbing PDFNavin SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coa Unit 5Dokument73 SeitenCoa Unit 5Shiv Patel 18-38Noch keine Bewertungen
- Control Loop 13Dokument15 SeitenControl Loop 13nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8085 Instruction SetDokument122 Seiten8085 Instruction SetgokulchandruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Studies Public LibraryDokument4 SeitenCase Studies Public LibraryHimalya Kaim83% (6)
- Sky 1Dokument14 SeitenSky 1Vũ Quang HưngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Z80 - Instruction SetDokument36 SeitenZ80 - Instruction SetHaddouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shift Bit Register (%SBR)Dokument5 SeitenShift Bit Register (%SBR)nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module-6 COMPUTER ARCHITECTUREDokument25 SeitenModule-6 COMPUTER ARCHITECTUREpranaykumarghosh41Noch keine Bewertungen
- Execution Unit (EU) : Instruction Queue, and The Instruction Pointer. It Has The Task of Making Sure That The BusDokument10 SeitenExecution Unit (EU) : Instruction Queue, and The Instruction Pointer. It Has The Task of Making Sure That The BusPradeep RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 3Dokument12 SeitenActivity 3api-548516280Noch keine Bewertungen
- Logical OperationsDokument6 SeitenLogical OperationsLysergic WarNrumorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual # 03 Implementation of Flag RegistersDokument4 SeitenLab Manual # 03 Implementation of Flag RegistersMuhammad FaizanNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Notes Compiled SrinathDokument24 SeitenE-Notes Compiled SrinathArjun SvNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABAP - 4 Programming PDFDokument13 SeitenABAP - 4 Programming PDFShiva AnnaldasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sewp Zc413 Computer Organization & ArchitectureDokument16 SeitenSewp Zc413 Computer Organization & Architectureshravanr500Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Architecture Unit 1Dokument35 SeitenComputer Architecture Unit 1agamer43387Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module IV LOCDokument21 SeitenModule IV LOCrahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programmingwith8085 130826055747 Phpapp01Dokument55 SeitenProgrammingwith8085 130826055747 Phpapp01Malviya RohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIFODokument4 SeitenFIFORitesh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MP Instruction SetDokument15 SeitenMP Instruction SetKannan MuthusamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aim: Apparatus: Theory:: 8086 Trainer KitDokument8 SeitenAim: Apparatus: Theory:: 8086 Trainer Kitdeepa9bhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 5 Sem QPDokument35 SeitenCE 5 Sem QPJCT DesigningNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARM ArchitectureDokument9 SeitenARM Architectureultimatekp144Noch keine Bewertungen
- COA Answers Question by MahamatDokument6 SeitenCOA Answers Question by Mahamatsurajadine001Noch keine Bewertungen
- (Updated) Rajan Microprocessor Lab Manual-1 (16!11!2012)Dokument113 Seiten(Updated) Rajan Microprocessor Lab Manual-1 (16!11!2012)Thiagu RajivNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Computer System Organization Unit 1Dokument11 SeitenNotes Computer System Organization Unit 1Grace PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coa 4th LessonDokument23 SeitenCoa 4th LessonMukeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programming With 8085: Introduction To 8085 InstructionsDokument25 SeitenProgramming With 8085: Introduction To 8085 Instructionssukirti guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intel 8085Dokument80 SeitenIntel 8085vsalaiselvamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mplab 1Dokument68 SeitenMplab 1Avast FreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-Vi Lecture Notes: - 8086 MICROPROCESSOR: 8086 ArchitectureDokument29 SeitenUnit-Vi Lecture Notes: - 8086 MICROPROCESSOR: 8086 Architectureramarao pagadalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 4 Rev. 2.4 Parallel I/O and Keyboard ScanningDokument13 SeitenLab 4 Rev. 2.4 Parallel I/O and Keyboard ScanningEduardo GuzmánNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 8051 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems: 8051 Addressing ModesDokument81 SeitenThe 8051 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems: 8051 Addressing ModesChindam Hari PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPU Registers (Registers Commonly Used by The CPU)Dokument18 SeitenCPU Registers (Registers Commonly Used by The CPU)Moorthy ManikandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2Dokument9 SeitenAssignment 2irum khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequenlty Asked Questions - ABAP/4 Reporting: Sy-IndexDokument2 SeitenFrequenlty Asked Questions - ABAP/4 Reporting: Sy-IndexSultanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Command Index: Basic Instructions Timer & Counter CompareDokument5 SeitenCommand Index: Basic Instructions Timer & Counter CompareRitesh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec2002 8085 L2,3,4Dokument35 SeitenEc2002 8085 L2,3,4himadeepthi sayaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPU Instruction Set DetailsDokument244 SeitenCPU Instruction Set Detailsiamsue1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- BBasic ManualDokument560 SeitenBBasic ManualTedi DarusmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAT II Answer Key Year/Sem: III/VI Part A: Institute of TechnologyDokument27 SeitenCAT II Answer Key Year/Sem: III/VI Part A: Institute of TechnologyHusamHaskoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microprocessor Lab ManualDokument85 SeitenMicroprocessor Lab ManualReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALU MISSDV0716 G.kaladhar Design PlanDokument16 SeitenALU MISSDV0716 G.kaladhar Design Plangourishettikaladhar562Noch keine Bewertungen
- Features of 8086 MicroprocessorDokument20 SeitenFeatures of 8086 MicroprocessorZana JarallahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec501 Practical Work 4 PDFDokument25 SeitenEc501 Practical Work 4 PDFAdam DmcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sim RimDokument13 SeitenSim RimKalai VaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Win PostDokument42 SeitenWin PostpetroviccaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microprocessors & Microcontrollers Most Important Questions SolutionsDokument34 SeitenMicroprocessors & Microcontrollers Most Important Questions SolutionsSrijal GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question: Describe The 8085 Programming Model in Detail. Answer: Following Is The Answer To The Above QuestionDokument9 SeitenQuestion: Describe The 8085 Programming Model in Detail. Answer: Following Is The Answer To The Above QuestionSidh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- MicropblDokument5 SeitenMicropblpawarvedant4646Noch keine Bewertungen
- EE6502 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers 16 MARK QA 1Dokument36 SeitenEE6502 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers 16 MARK QA 1umramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee6502 MM Eee VST Au Units IIDokument19 SeitenEe6502 MM Eee VST Au Units IIRaad AljuboryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 4Dokument3 SeitenLab 4BIR GORKHALI OFFICIALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eeeb371 Pic Exp1newDokument8 SeitenEeeb371 Pic Exp1newSalemAbaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8085 Microprocessor Architecture and Programming-1Dokument92 Seiten8085 Microprocessor Architecture and Programming-1ShubhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank 1Dokument18 SeitenQuestion Bank 1heligolwala1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3Dokument14 SeitenUnit 3Riza Pahama MananaongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8086 MicroprocessorDokument32 Seiten8086 Microprocessorsheham ihjamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Protection Fundamentals 5Dokument26 SeitenMotor Protection Fundamentals 5nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Protection Fundamentals 1Dokument30 SeitenMotor Protection Fundamentals 1nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Protection Fundamentals 5Dokument26 SeitenMotor Protection Fundamentals 5nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Protection Fundamentals 1Dokument30 SeitenMotor Protection Fundamentals 1nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Protection Fundamentals 4Dokument27 SeitenMotor Protection Fundamentals 4nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Protection Fundamentals 3Dokument28 SeitenMotor Protection Fundamentals 3nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Protection Fundamentals 2Dokument29 SeitenMotor Protection Fundamentals 2nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Protection Fundamentals 3Dokument28 SeitenMotor Protection Fundamentals 3nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Protection Fundamentals 4Dokument27 SeitenMotor Protection Fundamentals 4nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Protection Fundamentals 2Dokument29 SeitenMotor Protection Fundamentals 2nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LV Circuit Breaker (AC, DC)Dokument1 SeiteLV Circuit Breaker (AC, DC)nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overload HeaterDokument1 SeiteOverload HeaternmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feedforward Signal Characterizer: AC 104 FT 105 FC 105Dokument6 SeitenFeedforward Signal Characterizer: AC 104 FT 105 FC 105nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vessel, Jacketed Vessel, Reactor Atmospheric Tank, Storage: 7.8 Documentation ExamplesDokument7 SeitenVessel, Jacketed Vessel, Reactor Atmospheric Tank, Storage: 7.8 Documentation ExamplesnmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.8.2 Example - Basic Column Control: Chapter 7 - C F I DDokument4 Seiten7.8.2 Example - Basic Column Control: Chapter 7 - C F I DnmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuse (AC, DC)Dokument1 SeiteFuse (AC, DC)nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELM327 at CommandsDokument4 SeitenELM327 at CommandsnmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- C L F: B A C P: Ontrol OOP Oundation Atch ND Ontinuous RocessesDokument5 SeitenC L F: B A C P: Ontrol OOP Oundation Atch ND Ontinuous RocessesnmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.6 Line and Function SymbolsDokument11 Seiten7.6 Line and Function SymbolsnmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Loop 20Dokument8 SeitenControl Loop 20nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Symbol: Figure 7-12. Excerpt From ISA-5.1 Valve Body and Damper SymbolsDokument9 SeitenGeneral Symbol: Figure 7-12. Excerpt From ISA-5.1 Valve Body and Damper SymbolsnmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 - C F I DDokument12 SeitenChapter 7 - C F I DnmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Loop 20Dokument8 SeitenControl Loop 20nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 - C F I D: Figure 7-8. ISA-5.1 Tag Number ConventionDokument14 SeitenChapter 7 - C F I D: Figure 7-8. ISA-5.1 Tag Number ConventionnmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 - C F I D: Figure 7-8. ISA-5.1 Tag Number ConventionDokument14 SeitenChapter 7 - C F I D: Figure 7-8. ISA-5.1 Tag Number ConventionnmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 - C F I D: Ontrol AND Ield Nstrumentation OcumentationDokument16 SeitenChapter 7 - C F I D: Ontrol AND Ield Nstrumentation Ocumentationnmulyono100% (1)
- Control Loop 11Dokument17 SeitenControl Loop 11nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enterprise Management System: Reference W.S.JawadekarDokument34 SeitenEnterprise Management System: Reference W.S.JawadekarPolice stationNoch keine Bewertungen
- RTP Cap III GR I June 2022Dokument92 SeitenRTP Cap III GR I June 2022मदन कुमार बिस्टNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix: Dhuts-Phase Ii Dhaka Urban Transport Network Development Study-Phase IIDokument20 SeitenAppendix: Dhuts-Phase Ii Dhaka Urban Transport Network Development Study-Phase IIhhbeckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relevé: Partie 6: Vidéo "Le Blues en Jazz"Dokument1 SeiteRelevé: Partie 6: Vidéo "Le Blues en Jazz"santiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Engineering: Scheme of Undergraduate Degree CourseDokument2 SeitenElectrical Engineering: Scheme of Undergraduate Degree CourseSuresh JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject: Industrial Marketing Topic/Case Name: Electrical Equipment LTDDokument4 SeitenSubject: Industrial Marketing Topic/Case Name: Electrical Equipment LTDRucha ShirudkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- GT Reading Test 5, 2Dokument2 SeitenGT Reading Test 5, 2Muzammel Hossian MatinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casio Aq140w UputstvoDokument1 SeiteCasio Aq140w UputstvoalazovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Paper About Charter ChangeDokument5 SeitenResearch Paper About Charter Changegz46ktxrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 201805graphene PDFDokument204 Seiten201805graphene PDFMohammad RezkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEVERAGE SERVICE INDUSTRY Lesson 1Dokument18 SeitenBEVERAGE SERVICE INDUSTRY Lesson 1milyn maramagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Warman Slurry Correction Factors HR and ER Pump Power: MPC H S S L Q PDokument2 SeitenWarman Slurry Correction Factors HR and ER Pump Power: MPC H S S L Q Pyoel cueva arquinigoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ION Architecture & ION ModulesDokument512 SeitenION Architecture & ION ModulesAhmed RabaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometric Latent Diffusion ModelDokument18 SeitenGeometric Latent Diffusion ModelmartaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Health 10 Q1-W7Dokument8 SeitenDLL Health 10 Q1-W7Robert ManiboNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Handout 1 (Midterms)Dokument14 Seiten04 Handout 1 (Midterms)Emmanuel DelarosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intermediate Course Study Material: TaxationDokument34 SeitenIntermediate Course Study Material: TaxationMd IbrarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution: Wireshark Lab: HTTPDokument7 SeitenSolution: Wireshark Lab: HTTPHaoTian YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Download Test Bank For Accounting Information Systems Hall 8th Edition PDF Full ChapterDokument36 SeitenFull Download Test Bank For Accounting Information Systems Hall 8th Edition PDF Full Chapterfluiditytrenail7c8j100% (16)
- 17 Farley Fulache Vs ABS-CBN G.R. No. 183810Dokument7 Seiten17 Farley Fulache Vs ABS-CBN G.R. No. 183810SDN HelplineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Laws ProjectDokument4 SeitenService Laws ProjectRaman PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pk-Kredit Finanzierung-Db International Opening A Bank Account For Foreign StudentsDokument19 SeitenPk-Kredit Finanzierung-Db International Opening A Bank Account For Foreign StudentsBoűmřãh FōüĀdNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 FundamentalsDokument20 Seiten01 FundamentalsTay KittithatNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Disaster Recovery Planning ChecklistDokument2 SeitenIT Disaster Recovery Planning ChecklistYawe Kizito Brian PaulNoch keine Bewertungen