Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
Hochgeladen von
api-330092916Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
Hochgeladen von
api-330092916Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
page 480
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and use your book to find the answers.
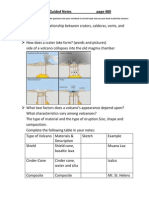
What is the relationship between craters, calderas, vents, and
magma?
The relationship between craters, calderas, vents, and magma is the structure of a
volcano.
How does a crater lake form? (words and pictures)
The Mount Mazama erupted many times. The top of partially empty magma chamber
collapsed. The steam activated multiple explosions. Lastly, the cadera filled with water
to form the crater lake.
What two factors does a volcanos appearance depend upon?
The appearance of a volcano depends on two factors: the type of material that forms
the volcano and the volcano and the type of eruptions that occur.
What characteristics vary among volcanoes?
They differ in size, shape, and composition.
Complete the following table in your notes:
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
page 480
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and use your book to find the answers.
Type of Volcano
Shield
Materials &
Description
Cinder-Cone
Sketch
Example
Usually built
by flowing
magma.
Named for
large size and
low profile.
Product of
hotspot
volcanism.
Almost
exclusively
basalt
Kilauea
Most active
shield volcano in
the Hawaiian
Islands
Elevation- 4,091
Most
common
type of
volcano
Wizard Island
West end of the
Crater Lake.
Elevation-6,932
Composed of
volcanic
cinders, or
small, rough
particles of
hardened
lava.
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
page 480
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and use your book to find the answers.
Composite
(Stratovolcano)
Constructed
from
multiple
eruptions
Made of
hardened
rock and
volcano ash
from
previous
eruptions.
Mount Fuji
Japans tallest
peak
Elevation12,338
How do the volcanoes compare in terms of size and slope?
They all discharge lava and magma.
They all have slopes that place magma/lava on earths surface.
They all have a large size.
What factors cause differences in size and slope?
The volume of the volcanic products.
The interval length between eruptions.
The composition of volcanic products.
The variety of volcanic eruption types.
The geometry of the vent.
The environment where the volcanoes erupt.
The climate.
The vegetation that grows on the volcano.
What is tephra?
Rock fragments thrown into the air during a volcanic eruption.
What is a pyroclastic flow?
Violent volcanic eruptions can send clouds of gas, ash, and other tephra down slope at
incredible speeds.
Where are most volcanoes found?
Most volcanoes are found at plate boundaries.
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
page 480
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and use your book to find the answers.
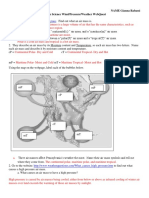
Use the maps provided to show: (1) the Circum Pacific Belt and the
Mediterranean Belt where convergent volcanism occur and (2) the
Hawaiian Emperor Volcanic Chain.
How do hotspots form?
Hotspots form when heat from deep within the earth causes the mantle rock
directly beneath the crust to melt and form the hotspot.
What do hotspots tell us about tectonic plates?
Hotspots tell us where tectonic plates are located, they occur beneath tectonic
plates.
Hotspots are not affected by plate movements.
Most tectonic plates occur on hotspots.
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
page 480
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and use your book to find the answers.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Volcanoes NotesDokument4 SeitenVolcanoes Notesapi-264874516Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDokument5 SeitenTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330049903Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDokument5 SeitenTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330050027Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDokument5 SeitenTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330050095Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDokument2 SeitenTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-264220672Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDokument4 SeitenTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330085018Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDokument3 SeitenTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-264090670Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDokument5 SeitenTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330464848Noch keine Bewertungen
- Volcano Guided NotesDokument4 SeitenVolcano Guided Notesapi-330490538100% (1)
- Types of VolcanoesDokument3 SeitenTypes of Volcanoesapi-265544103Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDokument3 SeitenTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-264099976Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDokument4 SeitenTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330049909Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDokument4 SeitenTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330042011Noch keine Bewertungen
- Voolcanoes Guided NotesDokument3 SeitenVoolcanoes Guided Notesapi-264885511Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDokument4 SeitenTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330102217Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes 1Dokument4 SeitenTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notes 1api-330067833Noch keine Bewertungen
- Volcanoes The Ultimate Book: Experience the Heat, Power, and Beauty of VolcanoesVon EverandVolcanoes The Ultimate Book: Experience the Heat, Power, and Beauty of VolcanoesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Science Tarbuck 14th Edition Solutions ManualDokument11 SeitenEarth Science Tarbuck 14th Edition Solutions ManualAntonioCohensirt100% (32)
- Term Paper On VolcanoesDokument9 SeitenTerm Paper On Volcanoesea6mkqw2100% (1)
- Mountains of Fire: Exploring the Science of Volcanoes: The Science of Natural Disasters For KidsVon EverandMountains of Fire: Exploring the Science of Volcanoes: The Science of Natural Disasters For KidsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Explosive World of Volcanoes with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceVon EverandThe Explosive World of Volcanoes with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of VolcanoesDokument26 SeitenTypes of VolcanoesMatt PayawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science-6 Q4 W2 the Effects of Volcanic EruptionDokument8 SeitenScience-6 Q4 W2 the Effects of Volcanic Eruptionkiandizon12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Volcano ReadingsDokument16 SeitenVolcano Readingsapi-251355123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Volcanoes EarthquakeDokument83 SeitenVolcanoes EarthquakeMeshal M ManuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading Comprehension Worksheet VolcanoesDokument2 SeitenReading Comprehension Worksheet VolcanoesMohammad ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesDokument16 SeitenPlate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesDemon bbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5b. VolcanismDokument44 Seiten5b. VolcanismGaurav KapseNoch keine Bewertungen
- VolcanoDokument3 SeitenVolcanoRhienzane L. MarasiganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaboom! What Happens When Volcanoes Erupt? Geology for Beginners | Children's Geology BooksVon EverandKaboom! What Happens When Volcanoes Erupt? Geology for Beginners | Children's Geology BooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth ScienceDokument12 SeitenEarth ScienceJames DJmanahan AnuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- P PPPPPP P: P PP PP P' P P PP' P $P' P P ('P P"Dokument4 SeitenP PPPPPP P: P PP PP P' P P PP' P $P' P P ('P P"bpmojapeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcanoes PDF Format 5912b8dcDokument4 SeitenVolcanoes PDF Format 5912b8dcsukesh sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-Assessment: Choose The Letter of The Best AnswerDokument60 SeitenPre-Assessment: Choose The Letter of The Best AnswerheartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcano WebquestDokument3 SeitenVolcano WebquestRichard Muchow100% (1)
- VOLCANOESDokument10 SeitenVOLCANOESYesha ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcano Features & TypesDokument8 SeitenVolcano Features & TypesShah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcanic EruptionsDokument4 SeitenVolcanic Eruptionspatrick201050428Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesDokument17 SeitenPlate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesChristle NgoveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcano TriviaDokument22 SeitenVolcano TriviaEman VidalloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcanic Eruptions and HazardsDokument44 SeitenVolcanic Eruptions and HazardsLevy GerpacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- VolcanoDokument12 SeitenVolcanoEibar AcostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcanic LandformDokument12 SeitenVolcanic LandformJoseph ZotooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcano DissertationDokument8 SeitenVolcano DissertationWriteMyPapersDiscountCodeSingapore100% (1)
- Lecture Notes Study Guide: Volcanoes and Volcanic Activity: ObjectivesDokument7 SeitenLecture Notes Study Guide: Volcanoes and Volcanic Activity: ObjectivesRonaldo ManaoatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcanic EruptionsDokument7 SeitenVolcanic EruptionsmusicatworkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wonders of Creation: A Descriptive Account of Volcanoes and Their PhenomenaVon EverandWonders of Creation: A Descriptive Account of Volcanoes and Their PhenomenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepared By: Mrs. Amany Adel Gaber HussienDokument127 SeitenPrepared By: Mrs. Amany Adel Gaber Hussienmalakelghamry743Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geography?Dokument13 SeitenGeography?haneefa yusufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinds of VolcanoesDokument50 SeitenKinds of VolcanoesJust onceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcano at Hazard and Disaster: Narciso School Inc. 4-4 Maya St. Sta. Maria Village II, Balibago Angeles CityDokument5 SeitenVolcano at Hazard and Disaster: Narciso School Inc. 4-4 Maya St. Sta. Maria Village II, Balibago Angeles CityRyley GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- VOLCANIC ERUPTIONSDokument16 SeitenVOLCANIC ERUPTIONSTadiwa MawereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1: Introduction to VolcanoesDokument12 SeitenLesson 1: Introduction to VolcanoesNeneth Saguin SionomioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Intervention Material VolcanoDokument26 SeitenStrategic Intervention Material VolcanoShena Jalalon Peniala100% (2)
- Invasive SpeciesDokument1 SeiteInvasive Speciesapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Renewable ResourcesDokument1 SeiteRenewable Resourcesapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Severe Weather Guided NotesDokument2 SeitenSevere Weather Guided Notesapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- AtmosphericbasicwebquestDokument2 SeitenAtmosphericbasicwebquestapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Climate Guided NotesDokument4 SeitenClimate Guided Notesapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dam and DiversionsDokument2 SeitenDam and Diversionsapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- SevereweatherwebquestDokument5 SeitenSevereweatherwebquestapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- ClimatechangewqDokument3 SeitenClimatechangewqapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Climate ChangeDokument2 SeitenClimate Changeapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Severe WeatherDokument1 SeiteSevere Weatherapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- MeteorologyDokument4 SeitenMeteorologyapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- AirmassesandfrontwqDokument5 SeitenAirmassesandfrontwqapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- WastewaterttreatmentactivityDokument4 SeitenWastewaterttreatmentactivityapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atmosphere NotesDokument3 SeitenAtmosphere Notesapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Water QualityDokument2 SeitenWater Qualityapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Holt Environmental Science Section 5.2, Pg. 131Dokument5 SeitenHolt Environmental Science Section 5.2, Pg. 131api-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Surface WaterDokument3 SeitenSurface Waterapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sewage V SepticDokument2 SeitenSewage V Septicapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- WatershedandriverbasinactivityDokument4 SeitenWatershedandriverbasinactivityapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Water PropertiesDokument2 SeitenWater Propertiesapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Urbanization NotesDokument2 SeitenUrbanization Notesapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Water Cycle WebquestDokument7 SeitenWater Cycle Webquestapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rangeland NotesDokument2 SeitenRangeland Notesapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Non Renewable Resources NotesDokument3 SeitenNon Renewable Resources Notesapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Matrix QuestionsDokument2 SeitenMatrix Questionsapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- TruaxquestionsDokument1 SeiteTruaxquestionsapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Waste Guided NotesDokument4 SeitenSolid Waste Guided Notesapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Feeding The World NotesDokument4 SeitenFeeding The World Notesapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coastal ManagementDokument3 SeitenCoastal Managementapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mining NotesDokument2 SeitenMining Notesapi-330092916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Disasters 10th Edition Abbott Test BankDokument23 SeitenNatural Disasters 10th Edition Abbott Test Banksamuelhammondbzksifqnmt100% (24)
- Grade 9 Science (K To 12)Dokument6 SeitenGrade 9 Science (K To 12)Christine DinglasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- La Caldera TilzapotlaDokument23 SeitenLa Caldera TilzapotlaAeriseRainiersNoch keine Bewertungen
- How It Works Annual 2013 PDFDokument224 SeitenHow It Works Annual 2013 PDFLampZOS100% (4)
- Six Types of Volcanoes ClassifiedDokument3 SeitenSix Types of Volcanoes ClassifiedBenes Salamanca BolascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Hazards and Disasters 5th Edition Hyndman Solutions Manual DownloadDokument7 SeitenNatural Hazards and Disasters 5th Edition Hyndman Solutions Manual DownloadRex Pynes100% (26)
- Summative TestDokument4 SeitenSummative Testmenchie ismaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cashman2014 PDFDokument18 SeitenCashman2014 PDFLola LolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welcome To NervDokument13 SeitenWelcome To NervMark JanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth's Layers ExplainedDokument251 SeitenEarth's Layers ExplainedShaneal100% (1)
- Geology of Ethiopia - An OverviewDokument33 SeitenGeology of Ethiopia - An OverviewAnonymous 6C0GArxPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Storonkin - Sophie - 7b - HUM Eruption of Krakatoa News Report ScriptDokument3 SeitenStoronkin - Sophie - 7b - HUM Eruption of Krakatoa News Report ScriptMichelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geo2 2e ch01Dokument17 SeitenGeo2 2e ch01Don FeckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcanoes, Magma & PlutonsDokument37 SeitenVolcanoes, Magma & Plutonswonder-chef-4677100% (1)
- Plutonism & Volcanism: Nica B. Raymundo STEM 11-1ADokument13 SeitenPlutonism & Volcanism: Nica B. Raymundo STEM 11-1ATina YusonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sir20105070q 2Dokument30 SeitenSir20105070q 2Ahmet ÇelikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ziway-Shala Lake Basin Main Ethiopian Rift PDFDokument24 SeitenZiway-Shala Lake Basin Main Ethiopian Rift PDF류태하100% (1)
- 7e Lesson Plan Types of Volcano and Volcanic EruptionDokument13 Seiten7e Lesson Plan Types of Volcano and Volcanic EruptionIel FedericoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcanoes Grade 9 Third QuarterDokument50 SeitenVolcanoes Grade 9 Third QuarterChelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- VolcanoesDokument36 SeitenVolcanoesjhoms8Noch keine Bewertungen
- PAS Inggris Kls 3Dokument9 SeitenPAS Inggris Kls 3MushoffaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A VolcanoDokument2 SeitenWhat Is A VolcanoBrenda AurelliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLPDokument8 SeitenDLPDanika Mae PondangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcanoes: Lecture 16 - Introduction To VolcanoesDokument13 SeitenVolcanoes: Lecture 16 - Introduction To VolcanoesumzzNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT NOTES FOR GEOGRAPHY 11th Standard Fundamentals of Physical GeographyDokument120 SeitenNCERT NOTES FOR GEOGRAPHY 11th Standard Fundamentals of Physical GeographyRamesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yellow Stone Super Volcano Getting Ready To Blow Its Cork.2009.152 PagesDokument152 SeitenYellow Stone Super Volcano Getting Ready To Blow Its Cork.2009.152 PagesMircea Ionel Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Volcanoes IIDokument49 SeitenVolcanoes IIAsfandyar KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geologic Processes Within The Earth 4Dokument10 SeitenGeologic Processes Within The Earth 4Luz OrtalizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Publications: Reviews of GeophysicsDokument37 SeitenPublications: Reviews of GeophysicsBagas JuniarNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Hot Is LavaDokument9 SeitenHow Hot Is LavamaggieNoch keine Bewertungen