Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lecture 1 PPC
Hochgeladen von
Keith Tanaka MagakaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lecture 1 PPC
Hochgeladen von
Keith Tanaka MagakaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lecture 1 PPC
Introduction
Production Planning is a managerial function which is mainly concerned with the following
important issues:
What production facilities are required?
How these production facilities should be laid down in the space available for
production? and
How they should be used to produce the desired products at the desired rate of
production?
Broadly speaking, production planning is concerned with two main aspects: (i) routing or
planning work tasks (ii) layout or spatial relationship between the resources. Production
planning is dynamic in nature and always remains in fluid state as plans may have to be
changed according to the changes in circumstances.
Production control is a mechanism to monitor the execution of the plans. It has several
important functions:
Making sure that production operations are started at planned places and planned
times.
Observing progress of the operations and recording it properly.
Analyzing the recorded data with the plans and measuring the deviations.
Taking immediate corrective actions to minimize the negative impact of deviations
from the plans.
Feeding back the recorded information to the planning section in order to improve
future plans.
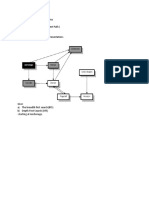
A block diagram depicting the architecture of a control system is shown in Figure1. Important
functions covered by production planning and control (PPC) function in any manufacturing
system are shown in Table1along with the issues to be covered.
Types of Production Systems
A production system can be defined as a transformation system in which a saleable product or
service is created by working upon a set of inputs. Inputs are usually in the form of men,
machine, money, materials etc. Production systems are usually classified on the basis of the
following:
Type of product,
Type of production line,
Rate of production,
Equipments used etc.
They are broadly classified into three categories:
Job shop production
Batch production
Mass production
Job Production
In this system products are made to satisfy a specific order. However that order may be
produced
only once
or at irregular time intervals as and when new order arrives
or at regular time intervals to satisfy a continuous demand
The following are the important characteristics of job shop type production system:
Machines and methods employed should be general purpose as product changes are
quite frequent.
Planning and control system should be flexible enough to deal with the frequent
changes in product requirements.
Man power should be skilled enough to deal with changing work conditions.
Schedules are actually non existent in this system as no definite data is available on
the product.
In process inventory will usually be high as accurate plans and schedules do not exist.
Product cost is normally high because of high material and labor costs.
Grouping of machines is done on functional basis (i.e. as lathe section, milling section
etc.)
This system is very flexible as management has to manufacture varying product types.
Material handling systems are also flexible to meet changing product requirements.
Batch Production
Batch production is the manufacture of a number of identical articles either to meet a specific
order or to meet a continuous demand. Batch can be manufactured either
only once
or repeatedly at irregular time intervals as and when demand arise
or repeatedly at regular time intervals to satisfy a continuous demand
The following are the important characteristics of batch type production system:
As final product is somewhat standard and manufactured in batches, economy of scale
can be availed to some extent.
Machines are grouped on functional basis similar to the job shop manufacturing.
Semi automatic, special purpose automatic machines are generally used to take
advantage of the similarity among the products.
Labor should be skilled enough to work upon different product batches.
In process inventory is usually high owing to the type of layout and material handling
policies adopted.
Semi automatic material handling systems are most appropriate in conjunction with
the semi automatic machines.
Normally production planning and control is difficult due to the odd size and non
repetitive nature of order.
Mass Production
In mass production, same type of product is manufactured to meet the continuous demand of
the product. Usually demand of the product is very high and market is going to sustain same
demand for sufficiently long time.
The following are the important characteristics of mass production system:
As same product is manufactured for sufficiently long time, machines can be laid
down in order of processing sequence. Product type layout is most appropriate for
mass production system.
Standard methods and machines are used during part manufacture.
Most of the equipments are semi automatic or automatic in nature.
Material handling is also automatic (such as conveyors).
Semi skilled workers are normally employed as most of the facilities are automatic.
As product flows along a pre defined line, planning and control of the system is much
easier.
Cost of production is low owing to the high rate of production.
In process inventories are low as production scheduling is simple and can be
implemented with ease.
FIGURE 1
Table 1: Production Planning and control Functions
Functions
Issues to be covered
Product
Design& Customer needs, market needs, availability of similar product, demand-supply
Developme gap, functional aspects, operational aspects, environmental aspects etc.
nt
Demand
Forecasting
Capacity
Planning
Quantity, Quality, Demand pattern.
No. of machines, No. of tooling, workers, No.of flow lines, Quantity, Quality
and rate of production, demand pattern.
Equipment
s Selection No. of machines, type of M/c, Quality aspects, Quantity aspects, rate of
&
production, Cost of equipments, support from the supplier, maintenance policy,
Maintenanc storage of spare parts.
e
Tooling
Selection
Compactability between w/c steels, No. of tools, their cost, their material etc,
storage policy.
Material
Selection
Types, specification, quality aspect, quantity aspect, cost, supplies reputation ,
&
lot size, inventory levels, setup cost, mode of transportation etc.
Manageme
nt
Process
Planning
Generation of manufacture instruction, selection of M/c, tools, parameters,
sequence etc.
Loading
Division of work load, assignment of tasks, uniform loading, matching between
capability & capacity with job requirements.
Routing
Path selection for material movement as per the process plan and loading,
minimum material handling and waiting time.
Scheduling
Time based loading, start and finish times, due dates, dispatching rules, rescheduling.
Expediting Operation Scheduling and order and progress reporting.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Disadvantages Traditional File SystemsDokument4 SeitenDisadvantages Traditional File SystemsKeith Tanaka Magaka88% (17)
- Disadvantages Traditional File SystemsDokument4 SeitenDisadvantages Traditional File SystemsKeith Tanaka Magaka88% (17)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Data Structures and AlgorithmsDokument45 SeitenData Structures and AlgorithmsKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tino Radio ProfilingDokument3 SeitenTino Radio ProfilingKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Vitae Anesu ChimhiniDokument3 SeitenCurriculum Vitae Anesu ChimhiniKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two Dimensional ArrayDokument10 SeitenTwo Dimensional ArrayKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research on Graph Algorithms: Warshall, Dijkstra, BFS & DFSDokument1 SeiteResearch on Graph Algorithms: Warshall, Dijkstra, BFS & DFSKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Half-Way Line: Football PitchDokument1 SeiteHalf-Way Line: Football PitchKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter1 IntroductionDokument2 SeitenChapter1 IntroductionKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReferencesDokument1 SeiteReferencesKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mealie Brand: (A Division of Zimplow LTD)Dokument6 SeitenMealie Brand: (A Division of Zimplow LTD)Keith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impediments to Agricultural Development in Small-Scale FarmsDokument71 SeitenImpediments to Agricultural Development in Small-Scale FarmsKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Structures & AlgorithmsDokument4 SeitenData Structures & AlgorithmsKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TreesDokument4 SeitenTreesKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is A Tree in Which Every Node Other Than The Leaves Has Two ChildrenDokument11 SeitenIs A Tree in Which Every Node Other Than The Leaves Has Two ChildrenKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advantages of RecursionDokument2 SeitenAdvantages of RecursionKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Sorting MethodsDokument6 SeitenInternal Sorting MethodsKeith Tanaka Magaka100% (1)
- Data Structures and Alg#1B7Dokument59 SeitenData Structures and Alg#1B7Keith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Structures NotesDokument131 SeitenData Structures NotesKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Binary Trees: What Is A Binary Tree?Dokument6 SeitenBinary Trees: What Is A Binary Tree?Keith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlgorithmsDokument18 SeitenAlgorithmsKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Structures and Alg#1B7Dokument59 SeitenData Structures and Alg#1B7Keith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Structures NotesDokument131 SeitenData Structures NotesKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Structures and Alg#1B7Dokument59 SeitenData Structures and Alg#1B7Keith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Structures and Algorithms QuestionsDokument2 SeitenData Structures and Algorithms QuestionsKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- File Based SystemDokument10 SeitenFile Based SystemKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- On The Job Yearly ReportDokument34 SeitenOn The Job Yearly ReportKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- QueuesDokument2 SeitenQueuesKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is DbmsDokument3 SeitenWhat Is DbmsKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pointers Sequential Access: Base CaseDokument4 SeitenPointers Sequential Access: Base CaseKeith Tanaka MagakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Project Report: Uop, LLCDokument165 SeitenFinal Project Report: Uop, LLCSiddharth KishanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatizari Complexe - Laborator Nr. 4: Wind (M/S)Dokument1 SeiteAutomatizari Complexe - Laborator Nr. 4: Wind (M/S)Alexandru AichimoaieNoch keine Bewertungen
- A K A G .: RUN Umar Shok UptaDokument2 SeitenA K A G .: RUN Umar Shok UptaArun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sound Wave Interference and DiffractionDokument79 SeitenSound Wave Interference and DiffractionMuhammad QawiemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitamin D3 5GDokument7 SeitenVitamin D3 5GLuis SuescumNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOLE AEP Rule 2017Dokument2 SeitenDOLE AEP Rule 2017unhoopterenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- HetNet Solution Helps Telcos Improve User Experience & RevenueDokument60 SeitenHetNet Solution Helps Telcos Improve User Experience & RevenuefarrukhmohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT: 01 Housekeeping SupervisionDokument91 SeitenUNIT: 01 Housekeeping SupervisionRamkumar RamkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Merlin Gerin Medium VoltageDokument10 SeitenMerlin Gerin Medium VoltagekjfenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap Fi/Co: Transaction CodesDokument51 SeitenSap Fi/Co: Transaction CodesReddaveni NagarajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nmea Components: NMEA 2000® Signal Supply Cable NMEA 2000® Gauges, Gauge Kits, HarnessesDokument2 SeitenNmea Components: NMEA 2000® Signal Supply Cable NMEA 2000® Gauges, Gauge Kits, HarnessesNuty IonutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sec of Finance Purisima Vs Philippine Tobacco Institute IncDokument2 SeitenSec of Finance Purisima Vs Philippine Tobacco Institute IncCharlotte100% (1)
- 5030si PDFDokument2 Seiten5030si PDFSuperhypoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Memento Mori: March/April 2020Dokument109 SeitenMemento Mori: March/April 2020ICCFA StaffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Homeopathic Doctor in SydneyDokument8 SeitenBest Homeopathic Doctor in SydneyRC homeopathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippines Taxation Scope and ReformsDokument4 SeitenPhilippines Taxation Scope and ReformsAngie Olpos Boreros BaritugoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FEM IntroductionDokument47 SeitenFEM IntroductionShanmuga RamananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pike River Case StudyDokument7 SeitenPike River Case StudyGale HawthorneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Javascript: What You Should Already KnowDokument6 SeitenJavascript: What You Should Already KnowKannan ParthasarathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- (EMERSON) Loop CheckingDokument29 Seiten(EMERSON) Loop CheckingDavid Chagas80% (5)
- Resona I9 Neuwa I9 FDADokument2 SeitenResona I9 Neuwa I9 FDAMarcos CharmeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp19 Excel Ch08 HOEAssessment Robert's Flooring InstructionsDokument1 SeiteExp19 Excel Ch08 HOEAssessment Robert's Flooring InstructionsMuhammad ArslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Borneo United Sawmills SDN BHD V Mui Continental Insurance Berhad (2006) 1 LNS 372Dokument6 SeitenBorneo United Sawmills SDN BHD V Mui Continental Insurance Berhad (2006) 1 LNS 372Cheng LeongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iqvia PDFDokument1 SeiteIqvia PDFSaksham DabasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easyjet Group6Dokument11 SeitenEasyjet Group6Rishabh RakhechaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HandoverDokument2 SeitenHandoverKumaresh Shanmuga Sundaram100% (1)
- Assignment 2 - p1 p2 p3Dokument16 SeitenAssignment 2 - p1 p2 p3api-31192579150% (2)
- NDU Final Project SP23Dokument2 SeitenNDU Final Project SP23Jeanne DaherNoch keine Bewertungen
- M Series CylindersDokument61 SeitenM Series CylindersAndres SantanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Cycle Refrigeration:-Bell - Coleman CycleDokument21 SeitenAir Cycle Refrigeration:-Bell - Coleman CycleSuraj Kumar100% (1)