Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
MEC521 Tutorial 1 - DavidNV
Hochgeladen von
HilmyZulkifliOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MEC521 Tutorial 1 - DavidNV
Hochgeladen von
HilmyZulkifliCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Universiti Teknologi MARA
40450 Shah Alam, Selangor
MEC521
VIBRATIONS
NAME:
Group
UiTM I.D.:
TUTORIAL 1 (4TH WEEK)
SINGLE DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEMS: FREE VIBRATION
Instruction: Answer all questions in a group of two.
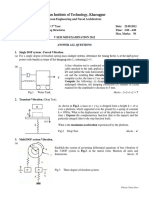
1.
A body of mass 1.25 kg is suspended from a spring with a scale of 2 kN/m. A dashpot is
attached between the mass and the ground and has a resistance of 0.5 N at a velocity of
50 mm/s. The initial displacement is 20 mm. Determine:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
the natural frequency of the system,
the critical damping factor of the dashpot,
the ratio of successive amplitudes,
the amplitude of the body 10 cycles after it was released from the initial
displacement, and
(e) the displacement of the body 1.25 s after it was released from the initial
displacement.
[Answers: (d) x10 = 0.036 mm; (e) x(1.25) = 0.1106 mm]
2.
A 5-kg mass is attached to a spring and makes damped oscillations. If the time 20 s is
needed to complete 50 complete oscillations and the ratio of the first downward
displacement to the sixth is found to be 22.5, calculate the spring stiffness and the
damping coefficient.
1 x
Hint: = ln o
n xn
[Answers: k = 1245.83 N/m; c = 15.64 Ns/m]
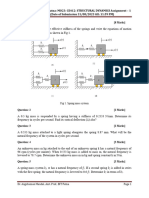
3.
A tightly wound helical coil spring is made from an 18 mm diameter bar of 0.2 %
hardened steel (G = 80 109 N/m2). The spring has 80 active coils with a coil diameter
of 16 cm. What is the change in length of the spring when it hangs vertically with one
end fixed and a 200-kg block attached to its other end?
(The stiffness of a helical coil spring is given by:
GD 4
64Nr 3
where D is the bar diameter, r is the coil radius, and N is the number of active turns.)
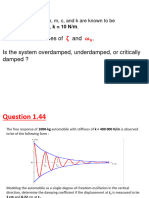
4.
The amplitude of a simple harmonic motion (SHM) is 0.20 cm and its oscillation
interval is 0.15 seconds. Determine the maximum velocity and maximum acceleration
of the motion.
Dr. David, N.V. 2014
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Worked Out Problems - Vibrations-DOMDokument103 SeitenWorked Out Problems - Vibrations-DOMTom TambeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Question BankDokument5 SeitenImportant Question BankChhagan kharolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assigment 1Dokument2 SeitenAssigment 1Pankhuri Kumari0% (1)
- Tutorial No. 1 Free VibrationDokument3 SeitenTutorial No. 1 Free VibrationNjuguna WaweruNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDOF Model: Non-Periodic Excitation MDOF ModelsDokument3 SeitenSDOF Model: Non-Periodic Excitation MDOF Modelssayan mukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solved Problems: Single Degree Free VibrationDokument14 SeitenSolved Problems: Single Degree Free Vibrationprem adhikariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test SokDokument14 SeitenTest SokFirzan100% (5)
- CL708 - Earthquake Engineering - Tutorial 3Dokument1 SeiteCL708 - Earthquake Engineering - Tutorial 3Rutvik ShethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 8Dokument2 SeitenTutorial 8fawwazfauzi2004Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prob Set 1Dokument2 SeitenProb Set 1bryanblooNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 CE5320 Assignment 2Dokument2 Seiten2019 CE5320 Assignment 2sayan mukherjee0% (1)
- DoM Tutorial Sheet 07 Mech VibrationsDokument1 SeiteDoM Tutorial Sheet 07 Mech VibrationsJerry RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Midterm 2012Dokument2 SeitenVibration Midterm 2012Aravind KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Engineering Department Mechanical Vibration (Met-351) Tutorial 1Dokument15 SeitenMechanical Engineering Department Mechanical Vibration (Met-351) Tutorial 1Aakash SinglaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07a72101-Vibrations and Structural DynamicsDokument8 Seiten07a72101-Vibrations and Structural Dynamicspoornima reddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Midterm 2012Dokument2 SeitenVibration Midterm 2012Aravind KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Previous Year QuestionsDokument9 SeitenModule 2 Previous Year QuestionsnikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Mechanics Department B.E-Sem.-Vi - Earthquake Engineering (160605) ASSIGNMENT - 3: Structural Dynamics (Module I)Dokument3 SeitenApplied Mechanics Department B.E-Sem.-Vi - Earthquake Engineering (160605) ASSIGNMENT - 3: Structural Dynamics (Module I)archan_daveNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICS - Research PapersDokument6 SeitenPHYSICS - Research PapersPATIL NISHANT SUNILNoch keine Bewertungen
- NV Tut 1 - Fundamental of VibrationsDokument6 SeitenNV Tut 1 - Fundamental of VibrationsMynxNoch keine Bewertungen
- MVSD Imp QstnsDokument5 SeitenMVSD Imp QstnsNobleSharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOM QuestionPaperPattern-IA-2 - PrintDokument4 SeitenDOM QuestionPaperPattern-IA-2 - PrintThamizh Selvan SNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMMV3043 TutorialDokument4 SeitenBMMV3043 TutorialKartik KrisnianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 2075Dokument5 SeitenPhysics 2075sujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mechanics Q.paperDokument8 SeitenEngineering Mechanics Q.paperYogeswara KayaguralaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erd Ta-I - SdofsystemDokument3 SeitenErd Ta-I - SdofsystemDeep ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1 Free VibrationDokument2 SeitenTutorial 1 Free VibrationMISKIR TADESSENoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1Dokument7 SeitenTutorial 1Shuvam Pyakurel33% (3)
- Homework 2Dokument7 SeitenHomework 2Chinny LyheangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit III Class Notes ProblemsDokument37 SeitenUnit III Class Notes Problemskumar km0% (2)
- Structural Dynamics Module 1 Assignment 1Dokument4 SeitenStructural Dynamics Module 1 Assignment 1Arpit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9A01101 Engineering MechanicsDokument8 Seiten9A01101 Engineering MechanicssivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech Eng 3028 Dynamics & Control II - Vibrations Assignment 1Dokument3 SeitenMech Eng 3028 Dynamics & Control II - Vibrations Assignment 1ehsanzkr_499329029Noch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank Unit I Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Vibrations: Type ADokument13 SeitenQuestion Bank Unit I Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Vibrations: Type AKanhaiyaPrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ed 651 Mechanical Vibrations Time: 3hours Maximum Marks: 100Dokument5 SeitenEd 651 Mechanical Vibrations Time: 3hours Maximum Marks: 100ssm_ssmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Aaug-Dec 2019 MVDokument5 SeitenAssignment 1Aaug-Dec 2019 MVkamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3Dokument5 SeitenTutorial 3mohd.a.alawadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anna University Madras Institute of Technology: 718 R.P.M N 843 R.P.M)Dokument4 SeitenAnna University Madras Institute of Technology: 718 R.P.M N 843 R.P.M)veeyeskay_2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 24Dokument25 SeitenCH 24Sanjay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems Sheet (2) : Damped Oscillations: X X B XDokument1 SeiteProblems Sheet (2) : Damped Oscillations: X X B XMahmoud RamadanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems Sheet (2) : Damped Oscillations: X X B XDokument1 SeiteProblems Sheet (2) : Damped Oscillations: X X B XMahmoud RamadanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model QuestionsDokument4 SeitenModel Questions6nkumar_vnrNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME313: Dynamics of Machinery: Sheet 4: Free Vibration ResponseDokument2 SeitenME313: Dynamics of Machinery: Sheet 4: Free Vibration ResponsePrasanna RajagopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alva'S Institute of Engineering and Technology: Department of Mechanical EnginrringDokument1 SeiteAlva'S Institute of Engineering and Technology: Department of Mechanical EnginrringenggsantuNoch keine Bewertungen
- VibrationDokument6 SeitenVibrationchandan_j4uNoch keine Bewertungen
- T1403 Mom Ii 24.6.14Dokument2 SeitenT1403 Mom Ii 24.6.14STUDENTS OF DOE CUSATNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial + Correction Mechanical Vibration Chapter 3Dokument15 SeitenTutorial + Correction Mechanical Vibration Chapter 3Mohammed Al HelaylNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final 2022 + SolutionDokument14 SeitenFinal 2022 + SolutionYoussef MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- DomDokument2 SeitenDomHari PraneethNoch keine Bewertungen
- M.Tech Sem-2 DYN Tutorial-1Dokument2 SeitenM.Tech Sem-2 DYN Tutorial-1Rutvik ShethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aipmt 2006 PrelimsDokument34 SeitenAipmt 2006 Prelimskajal100% (1)
- Topper Sample Paper 2 Xi - Physics Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 70Dokument6 SeitenTopper Sample Paper 2 Xi - Physics Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 70microdotcdmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midsemester2017 Solved PDFDokument4 SeitenMidsemester2017 Solved PDFHammad100% (1)
- Dynamics of Engineering Systems ENG432: Midsemester Test 2017Dokument4 SeitenDynamics of Engineering Systems ENG432: Midsemester Test 2017HammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy QP 4 PrescreeningDokument2 SeitenPhy QP 4 PrescreeningAbhinav MadheshiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum Mechanics QuestionsDokument20 SeitenQuantum Mechanics QuestionsSwetha PosamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anna University Mechanical Vibraction Question PaperDokument4 SeitenAnna University Mechanical Vibraction Question PaperAnand Ras100% (1)
- Physics Simple Harmonic MotionDokument3 SeitenPhysics Simple Harmonic MotionAhmed AshikNoch keine Bewertungen
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Von EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresVon EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- 6.4 Accident Investigation 6 Edit BDokument100 Seiten6.4 Accident Investigation 6 Edit BHilmyZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mec600 Kelas Test 1Dokument1 SeiteMec600 Kelas Test 1HilmyZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mec500 April2017 Assignment 2Dokument4 SeitenMec500 April2017 Assignment 2HilmyZulkifli0% (1)
- 5b (Digital System) Logic Gates & Boolean Expression - AminDokument29 Seiten5b (Digital System) Logic Gates & Boolean Expression - AminHilmyZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5a (Digital System) Number System - Amin - V.studentDokument50 Seiten5a (Digital System) Number System - Amin - V.studentHilmyZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mec500 (2012) Assignment 1Dokument6 SeitenMec500 (2012) Assignment 1HilmyZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slope DeflectionDokument2 SeitenSlope DeflectionHilmyZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Design For Strength - Fatigue Strength Variable LoadingDokument37 SeitenChapter 2 Design For Strength - Fatigue Strength Variable LoadingHilmyZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC435 Chapter6 v1.0Dokument22 SeitenMEC435 Chapter6 v1.0HilmyZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC435 Chapter4 v1.0Dokument56 SeitenMEC435 Chapter4 v1.0HilmyZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC551 Test 1 Solution (Sept2011-Feb2012) StudentDokument4 SeitenMEC551 Test 1 Solution (Sept2011-Feb2012) StudentHilmyZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1 AnswerDokument4 SeitenTest 1 AnswerHilmyZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen