Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Obstetrics Sample
Hochgeladen von
medpgnotesCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Obstetrics Sample
Hochgeladen von
medpgnotesCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
OBSTETRICS
medpgnotes
OBSTETRIC ANATOMY
OBSTETRICS
CONTENTS
OBSTETRIC ANATOMY ................................................................................................................................................... 6
ANATOMY IN OBSTETRICS ........................................................................................................................................ 6
OBSTETRIC DIAMETERS ............................................................................................................................................. 7
FETAL DIAMETERS AND PRESENTATION ................................................................................................................... 7
PHYSIOLOGY OF OBSTETRICS ........................................................................................................................................ 8
HCG AND HPL ............................................................................................................................................................ 8
SIGNS OF PREGNANCY .............................................................................................................................................. 9
PHYSIOLOGICAL CHANGES IN PREGNANCY ............................................................................................................ 11
NUTRITION AND PREGNANCY ................................................................................................................................. 13
GESTATIONAL TROPHOBLASTIC DISEASES .................................................................................................................. 13
FEATURES OF GESTATIONAL TROPHOBLASTIC DISEASES ....................................................................................... 13
MANAGEMENT OF GESTATIONAL TROPHOBLASTIC DISEASES ............................................................................... 14
AMNIOTIC FLUID AND DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH AMNIOTIC FLUID...................................................................... 15
AMNIOTIC FLUID ..................................................................................................................................................... 15
DISEASES OF AMNIOTIC FLUID ................................................................................................................................ 16
ABORTION AND MEDICAL TERMINATION OF PREGNANCY ........................................................................................ 16
FEATURES OF ABORTION ........................................................................................................................................ 16
FIRST TRIMESTER ABORTION .................................................................................................................................. 17
SECOND TRIMESTER ABORTION ............................................................................................................................. 18
MEDICAL TERMINATION OF PREGNANCY ............................................................................................................... 18
INTRAUTERINE DEATH AND INDUCTION OF LABOR ................................................................................................... 19
INTRAUTERINE DEATH ............................................................................................................................................ 19
INDUCTION OF LABOR ............................................................................................................................................ 20
ECTOPIC PREGNANCY ................................................................................................................................................. 21
FEATURES OF ECTOPIC PREGNANCY ....................................................................................................................... 21
MANAGEMENT OF ECTOPIC PREGNANCY .............................................................................................................. 22
MULTIFETAL PREGNANCY ........................................................................................................................................... 23
FEATURES OF MULTIFETAL PREGNANCY ................................................................................................................ 23
COMPLICATIONS AND MANAGEMENT OF MULTIFETAL PREGNANCY .................................................................... 24
NORMAL LABOR .......................................................................................................................................................... 25
GENERAL FEATURES OF LABOR ............................................................................................................................... 25
MANAGEMENT OF LABOR ...................................................................................................................................... 26
www.medpgnotes.com
OBSTETRIC ANATOMY
OBSTETRICS
PRETERM LABOR AND PROLONGED PREGNANCY ...................................................................................................... 27
PRETERM LABOR ..................................................................................................................................................... 27
PROLONGED PREGNANCY ....................................................................................................................................... 28
ANTEPARTUM HEMORRHAGE .................................................................................................................................... 29
GENERAL FEATURES OF ANTEPARTUM HEMORRHAGE .......................................................................................... 29
PLACENTA PREVIA ................................................................................................................................................... 30
ABRUPTIO PLACENTA .............................................................................................................................................. 31
POSTPARTUM HEMORRHAGE ..................................................................................................................................... 32
FEATURES OF POSTPARTUM HEMORRHAGE .......................................................................................................... 32
MANAGEMENT OF POSTPARTUM HEMORRHAGE.................................................................................................. 32
INFECTIONS IN PREGNANCY ....................................................................................................................................... 33
GENERAL FEATURES OF INFECTIONS IN PREGNANCY ............................................................................................. 33
HIV INFECTION IN PREGNANCY ............................................................................................................................... 34
RUBELLA IN PREGNANCY ........................................................................................................................................ 34
HEPATITIS IN PREGNANCY ...................................................................................................................................... 34
CHICKEN POX IN PREGNANCY ................................................................................................................................. 34
TOXOPLASMOSIS IN PREGNANCY ........................................................................................................................... 35
MALPRESENTATIONS .................................................................................................................................................. 35
FEATURES OF BREECH PRESENTATION ................................................................................................................... 35
MANAGEMENT OF BREECH PRESENTATION ........................................................................................................... 35
TRANSVERSE LIE ...................................................................................................................................................... 36
OCCIPITOPOSTERIOR PRESENTATION AND DEEP TRANSVERSE ARREST ................................................................ 37
FACE PRESENTATION .............................................................................................................................................. 37
BROW PRESENTATION ............................................................................................................................................ 37
MENTOPOSTERIOR PRESENTATION ........................................................................................................................ 38
CORD PROLAPSE ..................................................................................................................................................... 38
COMPOUND PRESENTATION .................................................................................................................................. 38
CONTRACTED PELVIS AND CPD ............................................................................................................................... 38
TYPES OF PELVIS ...................................................................................................................................................... 38
OBSTRUCTED LABOR ................................................................................................................................................... 39
FEATURES OF OBSTRUCTED LABOR ........................................................................................................................ 39
SCAR DEHISCENCE ................................................................................................................................................... 40
UTERINE RUPTURE .................................................................................................................................................. 40
PUERPERIUM .............................................................................................................................................................. 40
www.medpgnotes.com
OBSTETRIC ANATOMY
OBSTETRICS
FEATURES OF PUERPERIUM .................................................................................................................................... 40
LOCHIA .................................................................................................................................................................... 41
LACTATION .............................................................................................................................................................. 41
PUERPERAL SEPSIS .................................................................................................................................................. 41
PREGNANCY IN RH NEGATIVE WOMEN ...................................................................................................................... 42
FEATURES OF RH ISOIMMUNISATION .................................................................................................................... 42
MANAGEMENT OF RH ISOIMMUNISATION ............................................................................................................ 43
OPERATIVE OBSTETRICS .............................................................................................................................................. 44
EXTERNAL CEPHALIC VERSION ................................................................................................................................ 44
INTERNAL PODALIC VERSION .................................................................................................................................. 44
FORCEPS DELIVERY.................................................................................................................................................. 44
VENTOUSE EXTRACTION ......................................................................................................................................... 45
AMNIOTOMY OR ARTIFICIAL RUPTURE OF MEMBRANES....................................................................................... 45
EPISIOTOMY ............................................................................................................................................................ 46
PARACERVICAL BLOCK ............................................................................................................................................ 46
LSCS AND VBAC ....................................................................................................................................................... 46
DISEASES COMPLICATING PREGNANCY ...................................................................................................................... 47
GENERAL FEATURES OF DISEASES COMPLICATING PREGNANCY ........................................................................... 47
ANEMIA IN PREGNANCY ......................................................................................................................................... 48
FEATURES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN PREGNANCY ................................................................................................ 49
MANAGEMENT OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN PREGNANCY ....................................................................................... 50
FEATURES OF HYPERTENSIVE DISEASES OF PREGNANCY ....................................................................................... 51
MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSIVE DISEASES OF PREGNANCY ............................................................................... 52
FEATURES OF HEART DISEASES IN PREGNANCY ..................................................................................................... 53
MANAGEMENT OF HEART DISEASES IN PREGNANCY ............................................................................................. 54
DRUGS IN PREGNANCY ............................................................................................................................................... 55
INDICATIONS OF DRUG IN PREGNANCY.................................................................................................................. 55
SAFE DRUGS IN PREGNANCY................................................................................................................................... 55
UNSAFE DRUGS IN PREGNANCY ............................................................................................................................. 55
TERATOGENECITY ................................................................................................................................................... 55
DRUGS OF OBSTETRICS ............................................................................................................................................... 56
DRUGS AND PLACENTA ........................................................................................................................................... 56
HEPARIN .................................................................................................................................................................. 56
OXYTOCICS .............................................................................................................................................................. 56
www.medpgnotes.com
OBSTETRIC ANATOMY
OBSTETRICS
NEWBORN DISEASES ................................................................................................................................................... 57
GENERAL FEATURES OF NEWBORN DISEASES ........................................................................................................ 57
GESTATIONAL WEEKS.............................................................................................................................................. 58
FETAL MONITORING ............................................................................................................................................... 58
FETAL DISTRESS ....................................................................................................................................................... 60
IUGR ........................................................................................................................................................................ 60
LARGE FOR DATE BABIES ........................................................................................................................................ 61
CAPUT ..................................................................................................................................................................... 61
CEPHALHEMATOMA ............................................................................................................................................... 62
ANENCEPHALY AND NEURAL TUBE DEFECTS .......................................................................................................... 62
AMNIOCENTESIS ..................................................................................................................................................... 62
CHORIONIC VILLI SAMPLING ................................................................................................................................... 62
www.medpgnotes.com
OBSTETRIC ANATOMY
OBSTETRICS
KEY TO THIS DOCUMENT
Text in normal font Must read point.
Asked in any previous medical entrance
examinations
Text in bold font Point from Harrisons
text book of internal medicine 18th
edition
Text in italic font Can be read if
you are thorough with above two.
www.medpgnotes.com
OBSTETRIC ANATOMY
OBSTETRICS
OBSTETRIC ANATOMY
ANATOMY IN OBSTETRICS
Motor Nerve supply of detrusor
Weight of normal uterus
Cholinergic fibres of uterus travel via
Nerve root blocked in pudendal nerve block
Uterine blood flow at term
Motile spermatozoa found in wet mount of vaginal
secretion are indicative of intercourse within past
Thickness of endometrium at the time of implantation
Fetal circulation is first established and separated from
maternal circulation at the age of
Oxygen content of blood sent to upper
body during fetal life is higher than that
sent to lower body
Persistence of fetal circulation (persistent
pulmonary hypertension)
How many days after ovulation placental circulation is
established
Trophoblast give rise to
Syncitotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast differentiate on
Separate fetal blood from synctiotrophoblast
Does NOT separate fetal blood from synctiotrophoblast
Umbilical cord is covered by
Oxygenated blood from placenta to heart in utero by
Do NOT carry deoxygenated blood in fetal circulation
Fetal blood is returned to umbilical
arteries and placenta through
Single umbilical artery on examination of umbilical cord
after delivery
Umbilical artery catheter is removed only
if
Folds of Hoboken are found in
No of vessels in cut section of umbilical cord
Umbilical cord usually fall after
Placenta has
Weight of placenta at term
Placenta is formed by
Blood flow in intervillous space at term
Bleeding into deciduas basalis leads to
Fetal blood loss in abnormal cord insertion is seen in
Marginal insertion of cord into placenta
S2,S3,S4
45 60 gm
S2,S3,S4
S2,S3,S4
500 750 ml/min
24 hours
5-6 mm
21 days
Oxygenated blood passes through foramen
ovale to left ventricle
Presence of cyanosis, common in babies
having meconium staining of liquor, paO2
in right radial artery is often higher than
lower limb arteries
18 21 days
Placenta, Chorion, Amnion
8 days
Fetal capillary membrane, Mesenchyme of intervillous
blood space, Cytotrophoblast
Deciduas parietalis
Amnion
Umbilical vein, IVC
Umbilical vein
Two hypogastric arteries
Indicator of considerably increased incidence of major
malformation of fetus
PiO2 > 0.4
Umbilical cord
3
5-10 days
2 arteries and 1 vein
500 gm
Decidua basalis, Chorion frondosum
500 ml
Separation of placenta
Vasa previa
Battledore placenta
www.medpgnotes.com
OBSTETRIC ANATOMY
OBSTETRICS
Succenturiate placenta is commonly
associated with
Amniotic membrane
Fetal membranes include
NOT a fetal membrane
Internal organs in fetus develops at
Insulin secreted by fetal pancreas by
Urine formation in intrauterine life starts at
Lanugo hair appears at
After 28 weeks of gestation
Phosphatidyl glycerol appears in amniotic fluid at
Retained placenta
AVASCULAR, Provides maximum tensile strength,
Develops after 2-7 days of gestation, Fetal ectoderm
Amnion, chorion, decidua capsularis
Yolk sac
6 weeks
12 weeks
3 months
4 months
Alive, >1000 gm, Phosphatidyl glycerol present
35 weeks
OBSTETRIC DIAMETERS
True pelvis refer to
Sacral promontory
Smallest diameter of true pelvis
Most important diameter of pelvis during labor
Shortest anteroposterior diameter of pelvic inlet
Obstetric conjugate definition
Obstetric conjugate
Critical obstetric conjugate for trial of labor
Diagonal conjugate is defined as distance between
Obstetric conjugate is computed by separating 1.5 to 2
cm from
Can be assessed directly
Diagonal conjugate
Maximum diameter of pelvic inlet
Shortest diameter of pelvic outlet
Shortest diameter of fetal head
Most important plane in obstructed labor
Lower part of pelvis
Anterior margin of first sacral vertebra
Interspinous diameter
Interspinous diameter of outlet
Obstetric conjugate
Distance between promontory of sacrum to point
above pubic symphysis
10 cm
10 cm
Lower border of symphysis pubis and the sacral
promontory
Diagonal conjugate
Diagonal conjugate
12 cm
Transverse diameter
Posterior sagittal diameter
Bitemporal diameter
Plane of least pelvic dimension
FETAL DIAMETERS AND PRESENTATION
Normal fetal heart rate at 37 40 weeks of pregnancy
Longest diameter of fetal skull
Diameter in face presentation
Shortest diameter of fetal skull
Fully extended face
Bitemporal diameter of fetus
Shortest diameter of fetal skull
Fetal weight can be assessed by
Commonest diameter of engagement
Suboccipitofrontal diameter
120 160 per minute
Mentovertical > Submentovertical
Occipitofrontal
Submentobregmatic, Submentovertical
Submentobregmatic
Submentobregmatic
8 cm
Bitemporal
Biparietal diameter
Suboccipitofrontal
10 cm
www.medpgnotes.com
PHYSIOLOGY OF OBSTETRICS
OBSTETRICS
Largest Fetal Diameter corresponding to Pelvis
Engaging diameter in deflexed head is
Fetal diameter NOT measuring 9.5 cm
When vertex is well flexed, presentation is
Commonest type of presentation
MC type of vertex presentation
Abnormal attitude
NOT a USG fetal growth diameter
Occipitofrontal
Occipitofrontal diameter
Occipitofrontal
Vertex
Vertex
Left occipitotransverse
Face presentation
Transcerebellar diameter
PHYSIOLOGY OF OBSTETRICS
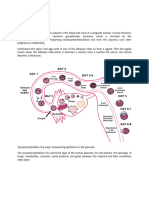
HCG AND HPL
Human placenta
Placenta develops from
Decidua at site of implantation
Placental hormone
NOT true about placental hormone
Insulin like growth factor is secreted by
Role of human placental lactogen
Hormones secreted by placenta exclusively
Schwangershaft protein
NOT secreted by placenta
Chemical pregnancy
HCG
HCG is secreted by
Hcg is secreted by
HCG
Doubling time of hcg
In early pregnancy, doubling time of hcg concentration
in plasma is
Highest hCG levels seen in
Peak level of HCG in pregnancy at
NOT a function of HCG
At what level of beta HCG, normal pregnancy can be
detected by Transvaginal ultrasound
Earliest diagnostic test of pregnancy
Minimum level of beta HCG detected by
radioimmunoassay
Most sensitive method of quantitative measurement of
hcg
Positive pregnancy test with serum
progesterone level of less than 5 ng/ml
Haemochorial
Chorion frondosum & Decidua basalis
Decidua basalis
hCS is diabetogenic, hCG rise leads to nausea
luteal placental shift at 8 10 weeks
Progesterone production require fetal steroidogenic
tissue
Trophoblast
Growth of fetus
HCG, HPL
Pregnancy specific beta 1 glycoprotein
Prolactin
Positive beta HCG and absent gestational sac
Non specific alpha and specific beta subunit
Placenta
Syncitiotrophoblast
Alpha subunit is identical to LH, FSH and TSH, Maximum
level is seen at 60 70 days of gestation
1.4 2 days
48 hours
60 70 days
Early gestation
Inhibition of relaxin
1000 IU/ml
Beta Hcg
0.001 IU/ml
Radioimmunoassay
Non viable pregnancy
www.medpgnotes.com
PHYSIOLOGY OF OBSTETRICS
OBSTETRICS
SIGNS OF PREGNANCY
Minimum number of antenatal visits
Minimum three antenatal visits
Ideal number of antenatal visits
Antenatal visits after 36 weeks should be made
Position used for bimanual examination in OPD
Per rectal palpation of uterus in
Associated with increased risk of normal pregnancy
Vagina in normal pregnancy
Short statured primigravida has height less than
Urine collected in pregnant female by
Wied test is used to differentiate
Placental localization is done by
USG of umbilical artery is to know about
Uterine souffl
Radiological investigation in a female of reproductive
age should be restricted to
Clinical feature of Pseudocyesis
NOT a feature of Pseudocyesis
Most diagnostic sign of pregnancy
Positive sign of pregnancy
Most striking symptom of pregnancy
Pathognomic sign in abdominal pregnancy
NOT a definite sign of pregnancy
Changes that occur in second trimester of pregnancy
Braxton hick contraction
Braxton hick contraction
NOT true about Braxton hick contraction
Braxton hicks contractions are absent in
Pregnancy is confirmed by
Quickening felt at
Internal ballotment
External ballotment
Carunculae Myrtiformes is diagnostic of
Test done for routine pregnancies
Absolute diagnosis of pregnancy
NOT used for establishing antenatal diagnosis
NOT a presumptive sign of pregnancy
Signs positive in early pregnancy
In early pregnancy, clinical signs of feeling cervix and
body of bulky uterus separated because of softened
isthmus at 6-10 weeks of gestation
3
20, 32, 36 weeks
12-14
Once a week
Dorsal position with thighs flexed
Virgins
Increased production of clotting factors by liver
Increased number of lactobacilli
140 cm
Early morning sample
Cytohormonal study to differentiate perimenopause
from pregnancy
Placentography
Heat beat
Due to increase in blood flow through dilated uterine
vessels
First 10 days of menstrual cycle
Quickening, amenorrhea, false labor
Enlargement of UTERUS
Fetal heart sounds
Detection of fetal parts in USG/X-ray
Cessation of Menstruation
Weinberg sign
Amenorrhea
Braxton Hicks contraction, Quickening
Occurs during most months of pregnancy
Painless, rules out abdominal pregnancy,
seen in hematometra
They aid in cervical dilatation during
first stage of labor
Abdominal pregnancy
Fetal heart activity, Fetal movement by examiner, Fetal
sac in USG
16 20 weeks
th
th
16 week to 28 week
20 weeks
Previous child birth
Syphilis
Fetal heart rate, Fetal movements, fetal skeleton in X
ray
Deciduas
Fetal movement perception by examiner
Hegar sign, Palmer sign, Goodell sign, Osiander sign
Hegar sign
www.medpgnotes.com
PHYSIOLOGY OF OBSTETRICS
OBSTETRICS
Hegar sign of pregnancy is
Hegar sign elicited in
Hegar sign elicited by
Triad of enlarged upper part of uterus,
soft middle part of uterus, firm cervix
Softening of cervix with lateral implantation (one half is
more firm than other half)
Chadwick sign
Jacquimer sign
Osiander sign
Palmer sign elicit
Palmer sign in pregnancy related to
Laden sign
Von Fernvard sign
NOT an early sign of pregnancy
Best investigation to diagnose fetal age
Earliest sign of gestation evidenced by deciduochorionic
thickness by USG
20 weeks pregnancy diagnosed by
Earliest detection of pregnancy by USG is by
Manual appreciation of fetal parts and fetal movements
by examination is earliest possible by
Study of fetal parts in first trimester with least radiation
hazard
Fetal heart can be detected earliest with transvaginal
sonography at (from last menstrual period)
Transvaginal USG can detect fetal cardiac activity in
In transvaginal USG, earliest detection of gestational sac
by
Finding seen earliest in USG
Earliest ultrasound sign of pregnancy in a
transabdominal ultrasound scan is
Transabdominal USG can detect fetal cardiac activity in
USG done at 18-20 weeks mainly to
Antenatal Doppler
Earliest sign of fetal life is detected by
6 weeks of pregnancy, safest method to confirm
pregnancy
32 weeks of gestation, Decreased uterus size, Fetal
Movements Diminished, Investigation of Choice
Doppler finding in USG in IUGR associated with worst
prognosis
Most reliable indicator for measurement of gestational
age in first trimester
Normal crown rump length at birth
Crown rump length 120 mm
Best parameter for estimation of fetal age by USG in
Softening of isthumus
Early pregnancy
8 weeks
Hegar sign
Piskacek sign
Bluish discolouration of vagina
Bluish hue of vagina
Pulsation in lateral vaginal fornix
Intermittent uterine contraction
Rhythmic contractions of uterus
Central part of isthumus is soft
Fundus is soft
Cullen sign, Lemon sign
Serial ultrasound
29 35 days
USG
Gestational sac
20 weeks
Ultrasound
46 days
6 weeks
14 days after ovulation
Yolk sac
Fundal endometrial thickening
8 weeks
Detect fetal anomaly
In normal pregnancy, placental resistance is low.
Reduction in end diastolic flow is associated with poor
outcome, Reduction in EDF is associated with IUGR, S/D
ratio is high in IUGR, Flow velocities and S/D ratio are
useful to evaluate high risk pregnancies
Real time USG
Doppler for fetal cardiac activity
USG Doppler
Reversal of diastolic flow
Crown rump length
38 50 cm
14 weeks
Femur length
www.medpgnotes.com
10
PHYSIOLOGY OF OBSTETRICS
OBSTETRICS
third trimester
Parameters used to estimate gestational age in last
trimester
Abdominal circumference, BPD, Femur length
PHYSIOLOGICAL CHANGES IN PREGNANCY
Total duration of Pregnancy
Term delivery
Pregnant woman not allowed for international travel after
nd
Overdistended uterus in 2 trimester
Average weight gain during pregnancy in poor Indian
woman
Net weight gain in pregnancy
Net weight gain in pregnancy
Weight gain in pregnancy NOT related to
Best method for assessing fetal well being at term by
serial estimation of
Prolactin levels highest during
Alpha and beta subunits NOT seen in
Intermediate cell predominance on vaginal cytology
Character of vagina in normal pregnancy
Oxytocin sensitivity during delivery
Decidual reaction and Arias stella reaction
Hormone essential for maintaining pregnancy
Arias stella reaction
Aris stella reaction seen in
Arias stella reaction NOT seen in
During pregnancy, increased respiratory sensitivity to
CO2 due to higher circulatory levels of
Changes during pregnancy
Changes during pregnancy
Truly physiological in pregnancy
Features of Pregnancy
During fetal life, maximum growth is caused by
Insulin resistance in pregnancy because of
Characteristic lesion of pregnancy
Dissection of which artery is common in
pregnancy
Blood cells increasing in pregnancy
Clotting factors increasing in pregnancy
Renal changes increasing in pregnancy
Respiratory changes increasing in
280 days/40 weeks/10 lunar months
40 weeks
32 weeks
Wrong date, Hydramnios, Distended bladder, Twins,
Fibromyoma
6.5 kg
10-12 kg
24 lb (24 pounds)
Smoking
Estriol
Pregnancy and falls during lactation
Prolactin
Pregnancy
Increase in number of lactobacilli
Increase
Progesterone
Progesterone
Loss of polarity of nucleus, Presence of hyperchromatic
nucleus, Specific to ectopic pregnancy
Ovarian pregnancy, Molar pregnancy, Interstitial
pregnancy
Salpingitis isthmica noda
Progesterone
Hyperplasia of thyroid and parathyroid, Increased
pigmentation, Increased insulin
Increased cardiac output, Increased tidal volume,
Decreased plasma protein concentration, Decreased
residual volume, Decreased hematocrit
Mild pedal edema, Increased GFR
Serum potassium decreased and sodium retention,
Insulin level increase, Increased BMR
Insulin
Human placental lactogen, Progesterone, Estrogen
Chloasma
Aorta
WBC
All clotting factors except 11 and 13
GFR and renal blood flow
Tidal volume, minute volume, airway
www.medpgnotes.com
11
PHYSIOLOGY OF OBSTETRICS
OBSTETRICS
pregnancy
Protein changes in pregnancy
Iron related parameters increasing in
pregnancy
Cardiovascular change in last trimester of pregnancy
Aggravated by pregnancy
Maximum increase in cardiac output by which stage of
pregnancy
Maximum cardiac output in pregnancy
During uterine contraction of labor, uterine blood flow
Normal changes during pregnancy
During pregnancy, maternal blood volume increased by
Peripheral vascular resistance in pregnancy
Abnormal CVS change in pregnancy
Abnormal finding in pregnancy
Cardiovascular change in last trimester of pregnancy
Last to occur in pregnancy
Uterine snouffle is due to
Changes in respiratory system in
pregnancy
Level of hormone unchanged in pregnancy
Supine hypotension is characteristic of
Supine hypertension syndrome
Least likely physiological change in pregnancy
Treatment for edema in pregnancy
Plasma fibrinogen in pregnancy
Increased pregnancy
Cause of increased risk of thromboembolism in
pregnancy
Increase in blood volume by
Increase in RBC volume
Maximum plasma volume increase
NOT increased in pregnancy
NOT increased in pregnancy
NOT increasing in pregnancy
Clotting factor NOT increased in pregnancy
Clotting factor decreased in pregnancy
MC cause of decreased platelet in pregnancy
Changes NOT occurring in pregnancy
Urinary system during pregnancy
Urinary retention in pregnancy as early as
GFR in pregnancy increased by
Normally present in urine of pregnant woman in third
trimester
conductance
Total plasma protein, globulin, fibrinogen
Serum transferring, TIBC
Shift of apical impulse lateral and upwards in left 4th
intercostal space
Carditis
32 weeks
Immediate postpartum period
Decreases
Increased stroke volume, Increased intravascular
volume
50%
Decreased
Right axis deviation, Early diastolic murmur
Supraclavicular murmur
th
Shift of apical impulse laterally and upwards in left 4
intercostal space
Uterine snouffle
Increase in blood flow through dilated uterine vessels
Tidal volume increases
Vasopressin
rd
3 trimester
Compression of aorta and vena cava by gravid uterus
when lying supine
Increase in peripheral vascular resistance
Bed rest
Increases
Globulin, Fibrinogen, Leucocytes, Transferrin
Increased production of clotting factor by liver
40%
20%
50%
Vital capacity
Plasma osmolality
Platelets
11
13
Benign gestational
Increase in blood viscosity
Increased GFR, Increased Renal blood flow,
Hypertrophy of bladder musculature, Decreased activity
of ureter
10 16 weeks
50%
Glucose
www.medpgnotes.com
12
GESTATIONAL TROPHOBLASTIC DISEASES
OBSTETRICS
Pregnancy is associated with reduced risk
of
Couvade syndrome
Relapse of multiple sclerosis
Partner experiences some of the symptoms
of pregnant woman
NUTRITION AND PREGNANCY
Daily calorie requirement in pregnancy
Iron supplementation in pregnant women for
Calcium requirement per day during third trimester of
pregnancy
Folic acid supplement reduces risk of
Folic acid initiated
Demand NOT increased in pregnancy
NOT a criteria for fetal growth
2500 Kcal
3 months
1000 mg
Neural tube defects
Before conception
Vitamin B12
Maternal weight gain
GESTATIONAL TROPHOBLASTIC DISEASES
FEATURES OF GESTATIONAL TROPHOBLASTIC DISEASES
Highest incidence of gestational trophoblastic disease
Gestational trophoblastic disease is of high risk, if it
follows
MC cause of persistent trophoblastic
disease after evacuation of hydatidiform
mole evacuation
Condition associated with H.mole
NOT associated with H.mole
Uterine height more than corresponding
gestational age with complains of
vomiting and per vaginal bleeding favors
the diagnosis of
Hydatidiform mole is due to
Hydatidiform mole
Chromosome number of H.mole
Luteal cysts
Doughy feel of uterus is associated with
H.mole
In hydatidiform mole, blood cells do not develop
because of defect in
MC complication of molar pregnancy
Sequale of vesicular mole
Abortion in H.mole often occurs at
Conversion of complete hydatidiform mole to invasive
mole in indicated by
MC GTD following H.mole
Asia
Normal pregnancy
Residual mole
Hyperthyroidism
Gestational diabetes
Hydatidiform mole
Degeneration of Chorionic villi
Trophoblastic proliferation, Hydropic degeneration
46XX
Molar pregnancy
Gestational trophoblastic diseases
Hysterectomy in selected cases, Thyrotoxicosis rare
Mesoderm
Hemorrhage
Chorioadenoma destruens (invasive mole)
4-6 months
Plateau hcg, enlarged uterine size, persistence of theca
lutein cyst
Invasive mole
www.medpgnotes.com
13
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- General Embryology PDFDokument9 SeitenGeneral Embryology PDFmedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physiology PDFDokument11 SeitenGeneral Physiology PDFmedpgnotes100% (4)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Female Reproductive System SampleDokument15 SeitenFemale Reproductive System SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gestational Trophoblastic Diseases (GTD)Dokument39 SeitenGestational Trophoblastic Diseases (GTD)moreen kipkemoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDokument27 SeitenSeminar Gestational Trophoblastic Diseasehusnajihah18Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10-Obstetric UltrasoundDokument179 Seiten10-Obstetric UltrasoundFisiha FikiruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetrics - GynaecologyDokument137 SeitenObstetrics - GynaecologyCiel100% (1)
- Hydatidiform Mole/ Molar Pregnancy: College of Health SciencesDokument11 SeitenHydatidiform Mole/ Molar Pregnancy: College of Health SciencesAngelu Gabrielle CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social and Preventive Medicine SampleDokument11 SeitenSocial and Preventive Medicine SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology PDFDokument103 SeitenMicrobiology PDFmedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical NuggetsDokument8 SeitenMedical NuggetsDrGandhi Bhaskar Patrudu LankaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical InvestigationsDokument7 SeitenMedical InvestigationsmedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Pathology SampleDokument10 SeitenGeneral Pathology SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orthopedics SampleDokument14 SeitenOrthopedics Samplemedpgnotes100% (1)
- General Pharmacology SampleDokument13 SeitenGeneral Pharmacology SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System SampleDokument18 SeitenRespiratory System SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ophthalmology SampleDokument14 SeitenOphthalmology SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Otorhinolaryngology SampleDokument9 SeitenOtorhinolaryngology SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiology Sample PDFDokument5 SeitenRadiology Sample PDFmedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatry SampleDokument8 SeitenPsychiatry SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition SampleDokument6 SeitenNutrition SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Male Reproductive System SampleDokument4 SeitenMale Reproductive System SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System SampleDokument18 SeitenNervous System SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology SampleDokument7 SeitenImmunology SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Pediatrics SampleDokument7 SeitenGeneral Pediatrics SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Surgery SampleDokument9 SeitenGeneral Surgery Samplemedpgnotes100% (1)
- Genetics SampleDokument7 SeitenGenetics SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forensic Medicine and Toxicology SampleDokument9 SeitenForensic Medicine and Toxicology SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretory System SampleDokument13 SeitenExcretory System SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Points About Medical Topics SampleDokument7 SeitenPoints About Medical Topics SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal System SampleDokument14 SeitenGastrointestinal System SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System SampleDokument12 SeitenCardiovascular System SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids and Electrolyte Abnormalities SampleDokument7 SeitenFluids and Electrolyte Abnormalities SamplemedpgnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: Di WenDokument40 SeitenGestational Trophoblastic Disease: Di WenarshadmraziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ectopic Molar Pregnancy A Case ReportDokument4 SeitenEctopic Molar Pregnancy A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Nidhi Blood ReportDokument1 SeiteNidhi Blood ReportSmitha GowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDokument27 SeitenSeminar Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseCourtney Dela FierraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uterine Arteriovenous Malformation: Hilwati H, Ouzreiah NDokument5 SeitenUterine Arteriovenous Malformation: Hilwati H, Ouzreiah NM Iqbal EffendiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interesting Case V2Dokument56 SeitenInteresting Case V2Kaye Villania-OctavioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Downloadfile 2Dokument416 SeitenDownloadfile 2SayanDuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDokument30 SeitenGestational Trophoblastic DiseaseInstrukcije Seminari100% (1)
- Gestational ConditionsDokument148 SeitenGestational ConditionsEsvinch EsvinchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trofoblasto IntermedioDokument17 SeitenTrofoblasto IntermedioNestor FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) : Ahmed Refaat Abd ElzaherDokument41 SeitenGestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) : Ahmed Refaat Abd ElzaherJessica NadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydatidiform Mole: PGI Sia, Kevin PGI Tan, SheilaDokument80 SeitenHydatidiform Mole: PGI Sia, Kevin PGI Tan, SheilaSheila Mary TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complications of PregnancyDokument33 SeitenComplications of PregnancyMilagros Maglasang100% (1)
- New Full Case Report 2017Dokument6 SeitenNew Full Case Report 2017Yudha GanesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Interactionist Approach: Client Individual or Group System Group, Agency, or OtherDokument27 SeitenThe Interactionist Approach: Client Individual or Group System Group, Agency, or OtherRonie Bongolo Dacuba0% (1)
- Mola Hidatidosa NcbiDokument4 SeitenMola Hidatidosa NcbiRekno DwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midwifery Management of First Trimester Bleeding and Early Pregnancy LossDokument17 SeitenMidwifery Management of First Trimester Bleeding and Early Pregnancy LossliopergonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mola HidatidosaDokument53 SeitenMola HidatidosaJeanyanty Yoesteyn DjaranjoeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- AUBF Lec LESSON 1 - Pregnancy TestDokument12 SeitenAUBF Lec LESSON 1 - Pregnancy TestnkbmanaliliNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOLAR Pregnancy V2 2021Dokument5 SeitenMOLAR Pregnancy V2 2021CassNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Products of Conception - Libre PathologyDokument8 Seiten1 Products of Conception - Libre PathologyfadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ectopic PregnancyDokument14 SeitenEctopic PregnancyPrashanta PahariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuretase Case Report 2Dokument3 SeitenKuretase Case Report 2Lydia AmaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ's 3 Flashcards - QuizletDokument12 SeitenMCQ's 3 Flashcards - Quizletbmhsh100% (1)
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Pt2Dokument75 SeitenGestational Trophoblastic Disease Pt2RiosNoch keine Bewertungen