Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
42 Maximum PDF
Hochgeladen von
Engr Wahab MarwatOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
42 Maximum PDF
Hochgeladen von
Engr Wahab MarwatCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ISSN (Print) : 2320 3765
ISSN (Online): 2278 8875
International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Vol. 2, Issue 6, June 2013
Maximum Power Point Tracking For
Photovoltaic System by Perturb and Observe
Method Using Buck Boost Converter
M.S.Sivagamasundari1, Dr.P.Melba Mary2,V.K.Velvizhi3
Assistant Professor, Department of EEE,V V College of Engineering,Tisaiyanvilai,Tamilnadu, India 1
Principal, Department of EEE,V V College of Engineering,Tisaiyanvilai,Tamilnadu, India 1
Assistant Professor, Department of EEE,V V College of Engineering,Tisaiyanvilai,Tamilnadu, India 3
ABSTRACT: Energy , especially alternative source of energy is vital for the development of a country. In future, the
world anticipates to develop more of its solar resource potential as an alternative energy source to overcome the
persistent shortages and unreliability of power supply. In order to maximize the power output the system components of
the photovoltaic system should be optimized. For the optimization maximum power point tracking (MPPT) is a
promising technique that grid tie inverters , solar battery chargers and similar devices use to get the maximum possible
power from one or more solar panels. Among the different methods used to track the maximum power point, Perturb
and Observe method is a type of strategy to optimize the power output of an array. In this method, the controller adjusts
the voltage by a small amount from the array and measures power, if the power increases, further adjustments in that
direction are tried until power no longer increases. In this research paper the system performance is optimized by
perturb and observe method using buck boost converter. By varying the duty cycle of the buck boost converter, the
source impedance can be matched to adjust the load impedance to improve the efficiency of the system. The
Performance has been studied by the MATLAB/Simulink.
Keywords: Maximum power point tracking, Photovoltaic system, Buck boost converter, Perturb and Observe method,
Direct current
I.INTRODUCTION
The rapid increase in the demand for electricity and the recent change in the environmental conditions such as
global warming led to a need for a new source of energy that is cheaper and sustainable with less carbon emissions.
Solar energy has offered promising results in the quest of finding the solution to the problem. The harnessing of solar
energy using PV modules comes with its own problems that arise from the change in insulation conditions. These
changes in insulation conditions severely affect the efficiency and output power of the PV modules [1-3].A great deal
of research has been done to improve the efficiency of the PV modules. A number of methods of how to track the
maximum power point of a PV module have been proposed to solve the problem of efficiency and products using these
methods have been manufactured and are now commercially available for consumers [1-3]. As the market is now
flooded with varieties of these MPPT that are meant to improve the efficiency of PV modules under various insolation
conditions it is not known how many of these can really deliver on their promise under a variety of field conditions.
This research then looks at how a different type of converter affects the output power of the module and also
investigates if the MPPT that are said to be highly efficient and do track the true maximum power point under the
various conditions [1].
A MPPT is used for extracting the maximum power from the solar PV module and transferring that power to the
load [4, 5]. A dc/dc converter (step up/ step down) serves the purpose of transferring maximum power from the solar
PV module to the load. A dc/dc converter acts as an interface between the load and the module figure 1 [5]. By
changing the duty cycle the load impedance as seen by the source is varied and matched at the point of the peak power
with the source so as to transfer the maximum power[5]. Therefore MPPT techniques are needed to maintain the PV
arrays operating at its MPP [6]. Many MPPT techniques have been proposed in the literature; example are the Perturb
and Observe (P&O) methods [4, 6-9], Incremental Conductance (IC) methods [7, 10-12], Fuzzy Logic Method [2, 4, 6,
11], etc.,
In this research paper the system performance is optimized by perturb and observe method using buck boost
converter. By varying the duty cycle of the buck boost converter, the source impedance can be matched to adjust the
load impedance to improve the efficiency of the system. The Performance has been studied by the MATLAB/Simulink.
Copyright to IJAREEIE
www.ijareeie.com
2433
ISSN (Print) : 2320 3765
ISSN (Online): 2278 8875
International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Vol. 2, Issue 6, June 2013
II. PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEM
A Photovoltaic (PV) system directly converts solar energy into electrical energy. The basic device of a PV system
is the PV cell. Cells may be grouped to form arrays . The voltage and current available at the terminals of a PV device
may directly feed small loads such as lighting systems and DC motors or connect to a grid by using proper energy
conversion devices. This photovoltaic system consists of main parts such as PV module, charger, battery, inverter and
load.
2.1.Equivalent model
A Photovoltaic cell is a device used to convert solar radiation directly into electricity. It consists of two or more
thin layers of semiconducting material, most commonly silicon. When the silicon is exposed to light , electrical charges
are generated. A PV cell is usually represented by an electrical equivalent one-diode model shown in fig.1.
Fig. 1. Single PV cell model
The model contains a current source , one diode, internal shunt resistance and a series resistance which represents
the resistance inside each cell. The net current is the difference between the photo current and the normal diode current
is given by the equation.[13].
ID = IO [
-1]
(1)
I=I I [
L O
1]-
(2)
where
I is the cell current (A).
q is the charge of electron (coul).
K is the Boltzmann's constant (j/K).
T is the cell temperature (K).
I is the photo current (A).
L
Io is the diode saturation current.(A)
Rs , Rsh are cell series and shunt resistances (ohms). V is the cell output voltage (V).
2.2.Current Voltage curve for PV cell
Copyright to IJAREEIE
www.ijareeie.com
2434
ISSN (Print) : 2320 3765
ISSN (Online): 2278 8875
International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Vol. 2, Issue 6, June 2013
Fig.2.Current Voltage curve
The Current Voltage characteristic curve of a PV cell for a certain irradiance at a fixed cell temperature is shown in
fig.2. The current from a PV cell depends on the external voltage applied and the amount of sunlight on the cell. When
the PV cell circuit is short, the current is at maximum and the voltage across the cell is zero. When the PV cell circuit is
open, the voltage is at maximum and the current is zero.
2.3. Power Voltage curve for PV cell
Fig.3.Power Voltage curve
The Power Voltage curve for PV cell is shown in fig.3. Here P is the power extracted from the PV array and V is
the voltage across the terminals of the PV array. This curve varies due to the current insolation and temperature. When
insolation increases , the power available from PV array increases whereas when temperature increases the power
available from PV array decreases.[14]
III. BUCK BOOST CONVERTER
Fig.3.Buck Boost Converter
Copyright to IJAREEIE
www.ijareeie.com
2435
ISSN (Print) : 2320 3765
ISSN (Online): 2278 8875
International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Vol. 2, Issue 6, June 2013
A buck boost converter is a DC-to-DC power converter with an output voltage either greater or smaller than its
input voltage. It is a combination of the buck converter topology and a boost converter topology in cascade. The output
to input conversion ratio is also a product of ratios in buck converter and the boost converter. The output voltage is
controlled by controlling the switch-duty cycle. The term D is the duty ratio and defined as the ratio of the on time of
the switch to the total switching period. This shows the output voltage to be hgher or lower than the input voltage,
based on the duty-ratio D.
IV. MAXIMUM POWER POINT TRACKING
Maximum power point plays an important role in photovoltaic system because they maximize the power output
from a PV system for a given set of conditions, and therefore maximize the array efficiency. There are different
methods used to track the maximum power point are
1. Perturb and Observe method
2. Incremental Conductance method
3. Parasitic Capacitance method
4. Constant Voltage method
Among the different methods used to track the maximum power point, Perturb and Observe method is the most
widely used method in PV MPPTs and is highly competitive against other MPPT methods.
4.1. Perturb and Observe method
In this method a slight perturbation is introduce system [7]. This perturbation causes the power of the solar module
changes. If the power increases due to the perturbation then the perturbation is continued in that direction [15]. After
the peak power is reached the power at the next instant decreases and hence after that the perturbation reverses. When
the steady state is reached the method oscillates around the peak point. In order to keep the power variation small the
perturbation size is kept very small. The method is developed in such a manner that it sets a reference voltage of the
module corresponding to the peak voltage of the module. A PI controller then acts moving the operating point of the
module to that particular voltage level. It is observed that there some power loss due to this perturbation also the fails to
track the power under fast varying atmospheric conditions. But still this
method is very popular and simple[7].
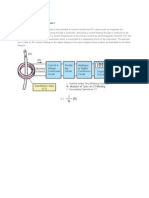
V. BLOCK DIAGRAM OF THE PROPOSED METHOD
Photovoltaic
Array
Buck Boost Converter
I,V
AC
load
PI D
Controller
MPPT
Perturb and
Observe
Method
Fig.4.shows the block diagram of the proposed method
Figure.4 shows the block diagram of the proposed method. It uses buck boost converter to adjust the output
voltage of PV panel. Buck Boost Converter is capable of step up or step down the output voltage from the source
voltage. The converter is controlled by PID with 2 inputs and 1 output and the system performance is optimized by
perturb and observe method. The inputs are fed by voltage and current of the PV terminals, while the output provides
Copyright to IJAREEIE
www.ijareeie.com
2436
ISSN (Print) : 2320 3765
ISSN (Online): 2278 8875
International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Vol. 2, Issue 6, June 2013
duty cycle for the buck boost converter. Buck Boost converter controls the output voltage by varying the duty cycle k,
of the switch. Duty cycle refers to ratio of the conduction time and the total switching period . During its operations,
the semiconductor switch turns-on for ton milliseconds and turns-off for toff milliseconds periodically. By adjusting k
at pre-defined value depending on the PV voltage and current, the output power of PV canbe maintained at the
maximum point. The value of k is determined by the PID controller.
VI. SIMULATION RESULTS
In this paper, the simulation model is developed with MATLAB/SIMULINK. The simulation model of the
proposed method is shown in Fig.5 and the waveforms are shown in fig .6. The proposed circuit needs independent
dc source which is supplied from photovoltaic cell . The inputs are fed by voltage and current of the PV terminals,
while the output provides duty cycle for the buck boost converter. The input voltage is 24V and the output voltage
after being buck boosted up is 48.2V and shown in fig.6. Buck Boost converter controls the output voltage by
varying the duty cycle k, of the switch and the value of k is 0.67 which is calculated using the formulae Vo = Vs*k / 1k. If we vary the pulse width of the pulse generator various voltage ranges at the output can be obtained. Once the buck
boost converter injected the power from the pv panel and the PID controller starts function, it varies the value of duty
cycle which will change the input value that is sensed by the PID controller . By using the PID controller the error has
been minimized in the system and the efficiency is improved.Table.1. below shows the output values for PV panel.
Table.1.Output value for PV panel
MPPT
METHOD
Perturb and
Observe
Output Voltage(V)
Output Current(A)
Output Power(W)
Efficiency(%)
48.2
4.82
232.32
90
The PV cell temperature is maintained constant at 25 degree Celsius and the solar intensity is varied in steps up to
the rated value of 1200W/meter square. It is seen from the figure .7 that the current slightly increase with increasing
intensity thereby increasing the power output of the solar cell.
Fig.5. Simulation circuit of the proposed method
Copyright to IJAREEIE
www.ijareeie.com
2437
ISSN (Print) : 2320 3765
ISSN (Online): 2278 8875
International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Vol. 2, Issue 6, June 2013
Fig.6. Waveforms
power and current
5000000
4500000
4000000
3500000
3000000
2500000
power
2000000
current
1500000
1000000
500000
0
800
1000
1200
irradiance
Fig.7.Power versus Current
VII. CONCLUSION
In the Present Work, the maximum power point tracking is successfully carried out by this research using perturb
and observe method. The PV module working on photovoltaic effect actually improves the system efficiency.
Compared to other methods of maximum power point tracking, the perturb and observe method seems to be easy for
the optimization of the photovoltaic system using buck boost converter. By varying the duty cycle of the buck boost
converter, the source impedance can be matched to adjust the load impedance which improves the efficiency of the system. The
Performance has been studied by the MATLAB/Simulink. In future, the maximum power point tracking could be
carried out without the use of controllers in order to reduce the cost and complications of hardware can be removed.
Copyright to IJAREEIE
www.ijareeie.com
2438
ISSN (Print) : 2320 3765
ISSN (Online): 2278 8875
International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Vol. 2, Issue 6, June 2013
REFERENCES
[1] R. S.Lewis, "Antartic Research and Relevant of Science," in Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, vol. 26, 1970, pp. 2.
[2] Y.-H. Chang and C.-Y. Chang, "A Maximum Power Point Tracking of PV System by Scaling Fuzzy Control," presented at International
MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists, Hong Kong, 2010.
[3] S.Mekhilef, "Performance of grid connected inverter with maximum power point tracker and power factor control," International Journal of
Power Electronics, vol. 1, pp. 49-62, 2008.
[4] M.E.Ahmad and S.Mekhilef, "Design and Implementation of a Multi Level Three-Phase Inverter with Less Switches and Low Output Voltage
Distortation,"Journal of Power Electronics, vol. 9, pp. 594-604, 2009.
[5] S. Chin, J. Gadson, and K. Nordstrom, "Maximum Power Point Tracker," Tufts University Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer
Science, 2003, pp. 1-66.
[6] R. Faranda and S. Leva, "Energy Comparison of MPPT techniques for PV Systems," WSES Transaction on Power Systems, vol. 3, pp.446-455,
2008.
[7] Vikrant.A.Chaudhari, "Automatic Peak Power Traker for Solar PV Modules Using dSpacer Software.," in Maulana Azad National Institute Of
Technology vol. Degree of Master of Technology In Energy. Bhopal: Deemed University, 2005, pp. 98.
[8] T. P. Nguyen, "Solar Panel Maximum Power Point Tracker," in Department of Computer Science & Electrical Engineering:University of
Queensland, 2001, pp. 64.
[9] B. S, Thansoe, N. A, R. G, K. A.S., and L. C. J., "The Study and Evaluation of Maximum Power Point Tracking Systems," International
Conference on Energy and Environment 2006 (ICEE 2006), pp. 17-22, 2006.
[10] C. S. Lee, " A Residential DC Distribution System with Photovoltaic Array Integration.," vol. Degree of Honors Baccalaureate of Science in
Electrical and Electronics Engineering, 2008, pp. 38.
[11] T. Esram and P. L.Chapman, "Comparison of Photovoltaic Array Maximum Power Point Tracking Techniques," in 9. Urbana.
[12] E. I and O. Rivera, "Maximum Power Point Tracking using the Optimal Duty Ratio for DC-DC Converters and Load Matching in Photovoltaic
Applications," IEEE, pp. 987-991, 2008.
[13] L. M. Tolbert, F. Z. Peng, T. G. Habetler, Multilevel converters for large electric drives, IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, vol. 35,
no. 1, Jan./Feb. 1999, pp. 36-44.
[14] K.Surya Suresh , M.Vishnu Prasad, PV Cell Based Five Level Inverter Using Multicarrier PWMInternational Journal of Modern Engineering
Research,Vol.1, Issue.2, pp-545-551.
[15] Hairul Nissah Zainudin, Saad Mekhilef,Comparison study of maximum power point tracker techniques for pv systems Proceedings of the 14th
International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON10), Cairo University, Egypt, December 19-21, 2010.
Copyright to IJAREEIE
www.ijareeie.com
2439
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Beg Esl GuideDokument20 SeitenBeg Esl GuideDali Soares De Sá NardeliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Higher Education in Scientific WorldDokument33 SeitenImportance of Higher Education in Scientific WorldEngr Wahab MarwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Leakage DetectionDokument7 SeitenGas Leakage DetectionEngr Wahab MarwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel Management SystemDokument6 SeitenFuel Management SystemEngr Wahab MarwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Conversion 4Dokument35 SeitenEnergy Conversion 4kapsicumadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel Management SystemDokument7 SeitenFuel Management SystemShweta KompaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei Mate S ManualDokument99 SeitenHuawei Mate S ManualEngr Wahab MarwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 555 TimerDokument26 Seiten555 TimerEngr Wahab MarwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 555 IcDokument7 Seiten555 IcEngr Wahab MarwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation PhrasebookDokument11 SeitenPresentation PhrasebookSergio RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of A Charge Controller Circuit PDFDokument70 SeitenDesign of A Charge Controller Circuit PDFÇağatay AktenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 57i9-New Perturb and ObserveDokument13 Seiten57i9-New Perturb and ObserveIJAET JournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation PhrasebookDokument11 SeitenPresentation PhrasebookSergio RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical & Electronics Measurement Lab ManualDokument64 SeitenElectrical & Electronics Measurement Lab ManualHari Krish100% (1)
- Characterisitcs of LightDokument9 SeitenCharacterisitcs of LightEngr Wahab MarwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schering BridgeDokument13 SeitenSchering BridgeEngr Wahab Marwat100% (2)
- Eee-Iii-Electrical and Electronicmeasurements and Instrume (10ee35) - Notes PDFDokument90 SeitenEee-Iii-Electrical and Electronicmeasurements and Instrume (10ee35) - Notes PDFavrhankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clamp MeterDokument1 SeiteClamp MeterEngr Wahab MarwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 7Dokument17 SeitenLecture 7Engr Wahab MarwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment RC FiltersDokument11 SeitenExperiment RC FiltersingeniouNoch keine Bewertungen
- 555 IcDokument7 Seiten555 IcEngr Wahab MarwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clamp MeterDokument1 SeiteClamp MeterEngr Wahab MarwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 555 IcDokument7 Seiten555 IcEngr Wahab MarwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Lab Manual 1Dokument27 SeitenElectronics Lab Manual 1divyajdiv100% (1)
- Cutoff FrequencyDokument2 SeitenCutoff Frequencythap_dinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Informed Choices 2016 PDFDokument35 SeitenInformed Choices 2016 PDFRamshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Somebody Wanted But SoDokument3 SeitenSomebody Wanted But Soapi-415881667Noch keine Bewertungen
- COM 165 - Speech To PersuadeDokument3 SeitenCOM 165 - Speech To PersuadeNazirah FauziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan: 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDokument4 SeitenSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan: 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldMary Joy CasillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 11 Extra Practice Activities Life AdvancedDokument2 SeitenUnit 11 Extra Practice Activities Life AdvancedEsther LópezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResumeDokument2 SeitenResumeMa. Yedda BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Models of Organizing The Training Department: Training and Development Research TeamDokument9 SeitenModels of Organizing The Training Department: Training and Development Research TeamNarmeen KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- COT - LP For GerundsDokument3 SeitenCOT - LP For GerundsRalph LegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intra Uterine Growth RetardationDokument46 SeitenIntra Uterine Growth RetardationIba Ghannam100% (1)
- NCM 111-Nursing Research 1 Theoretical and Conceptual FrameworksDokument3 SeitenNCM 111-Nursing Research 1 Theoretical and Conceptual FrameworksKrizle AdazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Main SRTDokument10 SeitenMain SRTVigneshwar SaratharamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brumfit AwardDokument8 SeitenBrumfit AwardDrGeePeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poster IdeasDokument3 SeitenPoster Ideaszuzifalakhe.mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eoa Donna Johnson EnvpDokument4 SeitenEoa Donna Johnson Envpapi-264005033Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cici, Devi, Ayu, IvanDokument2 SeitenCici, Devi, Ayu, Ivanayu suhestiNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of The East - College of EngineeringDokument2 SeitenUniversity of The East - College of EngineeringPaulAndersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Listening, Speaking, Reading, and Writing Effectively, Are His Most Important Accomplishment andDokument1 SeiteListening, Speaking, Reading, and Writing Effectively, Are His Most Important Accomplishment andChristine Joy LaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 091 51 Final Biologi t5 Dlp-6-26Dokument21 Seiten091 51 Final Biologi t5 Dlp-6-26risya mariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 WholeDokument156 Seiten02 WholeNgvinh PieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aspen Posting Grades mp1Dokument10 SeitenAspen Posting Grades mp1api-346876984Noch keine Bewertungen
- Other ActivitiesDokument2 SeitenOther ActivitiesdarshanasgaikwadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Valuation-DeweyDokument75 SeitenTheory of Valuation-Deweyyuxue1366100% (1)
- Republic of The Philippines Davao Oriental State College of Science and Technology Institute of Education and Teacher TrainingDokument1 SeiteRepublic of The Philippines Davao Oriental State College of Science and Technology Institute of Education and Teacher TrainingJaysonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Let Review 2023 Teaching Profession Legal Issues in EducationDokument10 SeitenLet Review 2023 Teaching Profession Legal Issues in EducationJeah Asilum Dalogdog100% (2)
- Guidelines For Curriculum Planning: Jose Y. Cueto JR., MD, Mhped Member Board of MedicineDokument25 SeitenGuidelines For Curriculum Planning: Jose Y. Cueto JR., MD, Mhped Member Board of MedicineBuried_ChildNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lost Spring Study MaterialDokument3 SeitenLost Spring Study Materialmedha karraNoch keine Bewertungen
- July 2020 Zadankai Speaker Emcee ScriptDokument1 SeiteJuly 2020 Zadankai Speaker Emcee ScriptMMilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReferenciasDokument5 SeitenReferenciasyesica aguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDETDokument4 SeitenSDETjaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Russell Budd Sponsorship Proposal March 9 2014Dokument18 SeitenRussell Budd Sponsorship Proposal March 9 2014api-251471298100% (1)