Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Repro in Humans
Hochgeladen von
VivlosophyCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Repro in Humans
Hochgeladen von
VivlosophyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Reproduction in Humans
PART ONE: UNTIL PAGE 11 (MENSTRUAL CYCLE)
Sexual Reproduction
- Definition: It is the fusion of the nuclei of gametes to form a zygote and produce genetically
dissimilar offspring
- Gametes: Haploid, produced by meiosis (4 dissimilar daughter cells)
- Zygote (+ normal body cells): Diploid, divide by mitosis (2 identical daughter cells)
-
Female Reproductive System
Ovary: Produces ova (eggs) and oestrogen + progesterone
Oviduct/Fallopian tube: A muscular tube leading from ovaries to uterus + site of fertilisation
Uterus/Womb: Site of metal development, has elastic + muscular walls, soft + smooth uterine
lining for implantation
Cervix: Enlarges to allow passage of foetus during birth
Vagina: Semen is deposited here
The Ovum
- Large nucleus: Haploid no. of chromosomes
- Plasma membrane surrounded by outer membrane (jelly layer)
THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
Follicle Development
- Primary follicle: Contains 1 potential egg cell + layer of follicle cells
- Each month, 1 primary follicle may develop into the Graafian follicle (stimulates secretion of
oestrgen > growth and repair of uterine lining)
- Graafian follicle will rupture and release the ovum during ovulation
- The remaining graafian follicle becomes the corpus luteum (secretes progesterone + some
oestrogen)
- No fertilisation > Corpus luteum persists for a while, then degenerates
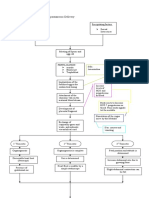
Stages of the Menstrual Cycle
MENSTRUAL PHASE FOLLICULAR PHASE
(DAY 1 - 5)
(DAY 6 - 13)
Uterine lining breaks
1 primary follicle will
down and flows out
through the vagina
develop into graafian
follicle
Graafian follicle
secretes oestrogen
Effect of oestrogen:
- Stimulate repair and
growth of uterine
lining > Becomes
thick and spongey
with blood vessels
OVULATION
(DAY 14)
Graafian follicle
ruptures and releases
the ovum
Corpus luteum formed
Coprpus luteum
secretes progesterone
and some oestrogen
LUTEAL PHASE
(DAY 15 - 28)
Effect of progesterone:
- Works together with
oestrogen to further
thicken, maintain and
supply uterine lining
with more blood
capillaries in
preparation for
implantation
FERTILE PERIOD: ??
No Fertilisation Occurs
1. Ovum breaks down
2. High conc. of progesterone inhibits LH production
3. LH production decreases > Corpus luteum breaks down > Progesterone secretion
decreases
4. Uterine lining not maintained > Breaks down (menstruation)
Questions:
1. With reference to graphs, describe how do changes in hormonal levels result in changes in the
uterine lining shown?
2. Describe how hormonal level and uterine lining change if egg was fertilised at ovulation.
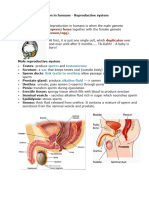
Male Reproductive System
Functions
Testis(s)/Testes(pl): Produces sperms and testosterone
Scrotum: Lie outside of the main body cavity to lower the temperature: essential for sperm
development
Sperm duct (Vas deferens): Conducts sperm to the urethra
Urethra: A tube that transports urine and semen through penis out of body (at diff times)
Penis: An erectile organ that deposits sperms into vagina
Prostate gland: Secretes seminal fluid which contains nutrients and enzymes to nourish +
activate sperms
The Sperm
Head: Contains nucleus (haploid) + Acrosome contains enzymes
that break down ovum membrane to allow sperm to penetrate
during fertilisation
Midpiece: Contains numerous mitochondria to release energy for
the sperm to swim to the ovum
Flagellum: To propel the sperm forward
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Susan Bratton Personalized Sex Life Bucket ListDokument11 SeitenSusan Bratton Personalized Sex Life Bucket ListArturNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Class:: Natural Science Primary 6 - Downloadable and Printable © Ediciones Bilingües, S.LDokument2 SeitenName: Class:: Natural Science Primary 6 - Downloadable and Printable © Ediciones Bilingües, S.LMªDolores86% (14)
- Physiology of Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDokument2 SeitenPhysiology of Normal Spontaneous DeliverySummer Rain100% (2)
- How To Please A Woman in BedDokument1 SeiteHow To Please A Woman in BedJohn Smith0% (1)
- Previous IB Exam QuestionsDokument12 SeitenPrevious IB Exam QuestionsJohn OsborneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preclinical Anatomy Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1Von EverandPreclinical Anatomy Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Sexual AttractionDokument5 SeitenSexual Attractionnathan100% (1)
- The Reproductive SystemDokument25 SeitenThe Reproductive SystemCoran St Nicholi Beckford INoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive System: Dr. Dicky Moch. Rizal, Mkes, Spand Bag. Ilmu Faal, FK UgmDokument94 SeitenReproductive System: Dr. Dicky Moch. Rizal, Mkes, Spand Bag. Ilmu Faal, FK UgmNi Made Dwiki AndriyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sexual Reproduction NotesDokument35 SeitenSexual Reproduction NotesZelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Menstrual Cycle:: MenarcheDokument21 SeitenMenstrual Cycle:: MenarcheAlpesh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human reproduction overviewDokument30 SeitenHuman reproduction overviewfirstclassNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Reproductive System MyguruDokument7 SeitenThe Reproductive System MygurumfaizchejamriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch. 38 Human ReproductionDokument38 SeitenCh. 38 Human ReproductionERIC ASAMAMLEH KLEMEHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repro. - NursingDokument79 SeitenRepro. - NursingARAK Aldarwish100% (1)
- 8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesDokument13 Seiten8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesAndre KachigambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wa0020Dokument52 SeitenWa0020michaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormon Reproduksi: Dr. Septi Handayani, M.SiDokument133 SeitenHormon Reproduksi: Dr. Septi Handayani, M.SiYusuf Almalik SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human ReproductionDokument17 SeitenHuman ReproductionGeorge Oswald Junior CarringtonNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 13 Reproduction UnitDokument27 SeitenWEEK 13 Reproduction UnitRina FakhryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.5.3.1 - Perkembangan Janin Intrauterin Dan Gangguan Yang Mungkin TimbulDokument54 Seiten1.5.3.1 - Perkembangan Janin Intrauterin Dan Gangguan Yang Mungkin TimbulMuhammad Fatkhi100% (1)
- 6.7 Reproduction IB BiologyDokument3 Seiten6.7 Reproduction IB Biologyamber_straussNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproduction (M, F) : Lecturer: Dr. R. Ahangari University of Central Florida, OrlandoDokument10 SeitenReproduction (M, F) : Lecturer: Dr. R. Ahangari University of Central Florida, Orlandokuku411Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Endocrine 6Dokument16 Seiten4 Endocrine 6ShenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of The SystemDokument14 SeitenParts of The SystembookonscribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 10 3rd Q ReviewerDokument8 SeitenBiology 10 3rd Q Revieweryxcz.rzNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Embryology 1Dokument34 SeitenGeneral Embryology 1asenathderlene27Noch keine Bewertungen
- 009 - Reproductive HistologyDokument10 Seiten009 - Reproductive HistologycharlieholdenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rep NotesDokument8 SeitenRep NotesizzyguyNoch keine Bewertungen
- OB Exam 1 Study GuideDokument23 SeitenOB Exam 1 Study GuideAlvin ManiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio T4 DLP KSSM Chapter15Dokument99 SeitenBio T4 DLP KSSM Chapter15Nurasyikin SaidinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fertilization and PregnancyDokument5 SeitenFertilization and PregnancyMSANITYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reprodcution in Humans 3Dokument10 SeitenReprodcution in Humans 3thraaaladyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fertilization and Implantation Copy To StudentsDokument40 SeitenFertilization and Implantation Copy To StudentsRiya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aspek Fisiologi Organ Genetalia Prp2017Dokument58 SeitenAspek Fisiologi Organ Genetalia Prp2017komang nickoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fetal DevelopmentDokument60 SeitenFetal DevelopmentElaine Malzan De GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female Reproductive System PhysiologyDokument16 SeitenFemale Reproductive System Physiologysami loveNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEW Physiology PAP 2 Ovarian and Uterine CyclesDokument33 SeitenNEW Physiology PAP 2 Ovarian and Uterine CyclesbhumeekakhadayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apbioch46animalreproduction 1Dokument5 SeitenApbioch46animalreproduction 1api-310813720Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hormones and ReproductionDokument4 SeitenHormones and ReproductionJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive HormonesDokument26 SeitenReproductive HormonesInji IdupalagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionDokument22 SeitenFemale Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionAngela NeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionDokument22 SeitenFemale Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionAecille VillarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Reproduction GuideDokument11 SeitenHuman Reproduction Guidehi100% (1)
- Dasar2 Biomolekuler Repro WanitaDokument51 SeitenDasar2 Biomolekuler Repro WanitaFitriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 9 - Reproduction in HumansDokument46 SeitenBiology 9 - Reproduction in HumansDelvonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sexual Reproduction in Human Beings (Part 1)Dokument40 SeitenSexual Reproduction in Human Beings (Part 1)puspita8967628Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 5 Bio F5 (Module)Dokument5 SeitenChap 5 Bio F5 (Module)Nurfatin JamaludinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test #5 Notes 2Dokument29 SeitenTest #5 Notes 2api-3723612Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physiological Breast Development and Involution - CompressedDokument7 SeitenPhysiological Breast Development and Involution - CompressedmohamedhazemelfollNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18 ReproductionDokument7 Seiten18 ReproductionAmandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ovarian Functions and Hormonal ControlDokument9 SeitenOvarian Functions and Hormonal ControlUloko ChristopherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing: Menstruation, Fertilization, and ImplantationDokument45 SeitenMaternal and Child Health Nursing: Menstruation, Fertilization, and ImplantationKaye OrtegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EOT - 9 Adv T3 - Yr 22-23Dokument83 SeitenEOT - 9 Adv T3 - Yr 22-23NKANoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Reproduction: © Lisa MichalekDokument30 SeitenHuman Reproduction: © Lisa MichalekMj Briones100% (2)
- Sexual Reproduction FullDokument46 SeitenSexual Reproduction FullSharara YMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female Reproductive System: A Complete GuideDokument65 SeitenFemale Reproductive System: A Complete GuideLidiya TeshomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLS224 Lecture 13 1 PDFDokument30 SeitenCLS224 Lecture 13 1 PDFmike RNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Reproductive Systems 2016Dokument43 SeitenThe Reproductive Systems 2016nurul dwi ratihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mammalian Reproductive SystemDokument50 SeitenMammalian Reproductive SystemLeena MuniandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pregnancy - Human ReproductionDokument36 SeitenPregnancy - Human ReproductionDICKSONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproduction NotesDokument27 SeitenReproduction NotesAyra AlbairaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - Notes: Human ReproductionDokument25 SeitenBiology - Notes: Human ReproductionDan LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oogenesis and The Ovarian Cycle: Angelbert R. Bacongco Justin Rhea M. BandiolaDokument19 SeitenOogenesis and The Ovarian Cycle: Angelbert R. Bacongco Justin Rhea M. BandiolaJustin Rhea BandiolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRSPT in Plants 2013.5Dokument3 SeitenTRSPT in Plants 2013.5VivlosophyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repro in Plants O LevelsDokument3 SeitenRepro in Plants O LevelsVivlosophyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current ElectricityDokument1 SeiteCurrent ElectricityVivlosophyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS Mock Cabinet MeetingDokument12 SeitenSS Mock Cabinet MeetingVivlosophyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormones & Endocrine GlandsDokument2 SeitenHormones & Endocrine GlandsVivlosophyNoch keine Bewertungen
- After: History Notes: Chapter 8Dokument1 SeiteAfter: History Notes: Chapter 8VivlosophyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS Mock Cabinet MeetingDokument12 SeitenSS Mock Cabinet MeetingVivlosophyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post-War: History Notes: Chapter 7Dokument2 SeitenPost-War: History Notes: Chapter 7VivlosophyNoch keine Bewertungen
- I JustDokument6 SeitenI JustVivlosophyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Truth About Female Ejaculation Free Report1Dokument16 SeitenThe Truth About Female Ejaculation Free Report1Thirdy HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20 Hard-Knock Life Lessons From Orgasmic Meditation.: Candice HoldorfDokument6 Seiten20 Hard-Knock Life Lessons From Orgasmic Meditation.: Candice HoldorfGeorgianna StrungaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE ReproductionDokument77 SeitenIGCSE ReproductionTonkaaw KatayouwongchareonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sexual Disorders PDFDokument3 SeitenSexual Disorders PDFJenny SisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Form 5 Reproduction & GrowthDokument3 SeitenBiology Form 5 Reproduction & GrowthM I K R A MNoch keine Bewertungen
- 30 Minutes in HeavenDokument11 Seiten30 Minutes in HeavenValpo Valparaiso100% (1)
- GAD PresentationDokument32 SeitenGAD PresentationMelymay Palaroan Remorin100% (1)
- InfertilityDokument10 SeitenInfertilityits_piks7256Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Biology of Menstruation in Homo Sapies. StrassmannDokument8 SeitenThe Biology of Menstruation in Homo Sapies. Strassmannlucre88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Task CardsDokument22 SeitenBiology Task Cardsapi-257668156100% (1)
- 1 800 805 7837Dokument124 Seiten1 800 805 7837Same Day STD TestingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Should Sex Ed be taught in schoolsDokument1 SeiteShould Sex Ed be taught in schoolsFish RamenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetrics and Gynecology WordsDokument1 SeiteObstetrics and Gynecology WordsDiah Wardana0% (1)
- Supporting Residents' Gender and Sexual IdentitiesDokument2 SeitenSupporting Residents' Gender and Sexual IdentitiesHoward VickridgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal InfeertilitasDokument9 SeitenJurnal InfeertilitasFaradila TadoranteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explanatorium of NatureDokument362 SeitenExplanatorium of NatureMaria Cobos100% (4)
- Background of The StudyDokument3 SeitenBackground of The StudyTrisha Nicole SangriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGL 202C: Technical Definition or Description AssignmentDokument6 SeitenENGL 202C: Technical Definition or Description AssignmentMegan MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- The G-Zone HandoutDokument1 SeiteThe G-Zone Handoutapi-646865632Noch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple OrgasmDokument11 SeitenMultiple OrgasmSheila ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH7 Sex Positions Kama Sutra and Oral PleasuresDokument23 SeitenCH7 Sex Positions Kama Sutra and Oral PleasuresTheVeiledGarden100% (2)
- LP Menstrual CycleDokument3 SeitenLP Menstrual CycleKaren Joy LendayaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LM S s5lt Iia 1 s5lt Iib 2Dokument4 SeitenLM S s5lt Iia 1 s5lt Iib 2Judith Alojado Colanggo100% (1)
- Fission: Molds, Lichens, Many Plants, and Animals Such As Sponges, Acoel Flatworms, Some Annelid Worms and Sea StarsDokument2 SeitenFission: Molds, Lichens, Many Plants, and Animals Such As Sponges, Acoel Flatworms, Some Annelid Worms and Sea StarsKARENNoch keine Bewertungen
- Women's Sexual Fulfilment - Osho NewsDokument6 SeitenWomen's Sexual Fulfilment - Osho NewsPalanisamy Balasubramani100% (1)