Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Manifestation of Bacterial Endocarditis
Hochgeladen von
Kyra KhalidCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Manifestation of Bacterial Endocarditis
Hochgeladen von
Kyra KhalidCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MANIFESTATION OF BACTERIAL ENDOCARDITIS
4. RISK FACTORS
1. DEFINITION
1.
Bacterial endocarditis is
the:
Heart valves
Septal defects.
Mural endocardium.
2. SITE: Aortic valve > Mitral
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Rheumatic heart disease: Mitral, Aortic
valve
Prosthetic cardiac valves.
Congenital heart disease: VSD, PDA, PS,
Tetralogy of Fallot
History of RF
defined as inflammation of
[most common]
Hemodialysis
IV drug user
valve
3. ETIOLOGY
1.
2.
3.
4.
STREPTOCOCCI: Viridian / a-hemolytic streptococci
(70% of cases)
STAPHYLOCOCCUS: Aureus, Coagulase-negative
(20% of cases)
ENTEROCOCCI : E.feacalis, E.faecium
GRAM VE RODS: HACEK, E.coli, Klebsiella, Neisseria gonorrhoae
*Its usually occurs on top of underlying heart disease, but also can occur on top of a normal heart.
5. MANIFESTATIONS
SYMPTOMS
Low-grade fever
(common)
Headache
Sweating
Malaise
Loss weight
Pain in back, muscle joint
INVOLVEMENT
CARDIAC
SIGNS
General look: Earthy look, Pallor, Toxic face.
Hyperpyrexia.
Tachycardia, arrhythmia
Skin:
PETICHEAL HEMORRHAGES: On the legs & chest wall
SPLINTER HEMORRHAGES: Under the nails.
OSLERS NODES: On pads of fingers & toes, and thenar &
hypothenar eminences.
JANEWAY LESIONS: Hemorrhagic raised lesions in palms & soles.
Clubbing of the fingers & toes: In long-standing cases.
Absent pulsations (Embolic).
Eyes: Subconjunctival hemorrhages, Roth spots (Retinal petichae),
Unilateral blindness (embolic).
Spleen: Splenomegaly
CLINICALLY
Appearance new murmur
Change in previous murmur
Pericarditis
EYE
SKIN
Increase intracranial pressure
Neurological deficits
Petechiae
Petechiae
KIDNEY
SPLEEN
Hematuria
Splenomegaly
NEUROLOGICAL
6.INVESTIGATION
1.
2.
Blood: FBC, ESR, CRP, culture
Echo:
PATHOLOGICALLY
Endocardial: Vegetations.
Myocardial: Myocarditis, abscess, MI
Pericardial: Pericarditis
Rupture of: cusps, chordae, and/or papillary
muscles
Cerebral infarction & hemorrhage
Mycotic aneurysm
Roth spot
Oslers nodes
Janeway lesions
(pathognomonic)
Infarction
Infarction, abscess
3.
Transthoracic echo: Specificity 98% but poor sensitivity, non-invasive
Transesophageal echo: Sensitivity 95%, invasive
Rheumatoid factor
DUKE CRITERIA
1.
2.
MAJOR CRITERIA
Blood culture positive for typical IEcausing microorganism
Evidence of endocardial involvement
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
MINOR CRITERIA
Predisposition heart condition or i.v. drug abuse
Fever temp. >38 C
Vascular phenomena arterial emboli etc.
Immunologic phenomena glomerulonephritis, Oslers nodes,
Roths spots
Microbiological evidence positive blood cultures but do not
meet major criteria
RESULT:
2 major criteria
1 major and 3 minor criteria
5 minor criteria
Pathology/histology findings
7. THERAPY
1. ANTIMICROBIAL THERAPY
Bactericidal regimen depends on organism
2. SURGERY
INDICATION: Congestive heart failure, uncontrolled infection despite antimicrobial therapy, large
vegetation, major embolus, heart block
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- AndiDokument3 SeitenAndiKyra KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
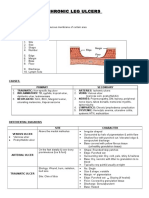
- Chronic Leg UlcersDokument2 SeitenChronic Leg UlcersKyra Khalid100% (1)
- Differential Diagnosis of Enlarged Abdomen in PediatricsDokument2 SeitenDifferential Diagnosis of Enlarged Abdomen in PediatricsKyra KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives Case 4 (Dermatology)Dokument3 SeitenObjectives Case 4 (Dermatology)Kyra KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- STDDokument7 SeitenSTDKyra KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Diagnosis of Tinea CapitisDokument3 SeitenDifferential Diagnosis of Tinea CapitisKyra KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congestive Heart Failure: Congenital Acquired OthersDokument2 SeitenCongestive Heart Failure: Congenital Acquired OthersKyra KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regulation of Body TemperatureDokument5 SeitenRegulation of Body TemperatureKyra KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- 2021-03 Trophy LagerDokument11 Seiten2021-03 Trophy LagerAderayo OnipedeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iec TR 61010-3-020-1999Dokument76 SeitenIec TR 61010-3-020-1999Vasko MandilNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlpaGasus: How To Train LLMs With Less Data and More AccuracyDokument6 SeitenAlpaGasus: How To Train LLMs With Less Data and More AccuracyMy SocialNoch keine Bewertungen
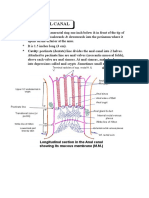
- Anatomy Anal CanalDokument14 SeitenAnatomy Anal CanalBela Ronaldoe100% (1)
- Radiation Safety Densitometer Baker PDFDokument4 SeitenRadiation Safety Densitometer Baker PDFLenis CeronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Law of EvidenceDokument14 SeitenLaw of EvidenceIsha ChavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turn Around Coordinator Job DescriptionDokument2 SeitenTurn Around Coordinator Job DescriptionMikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recommendations For Students With High Functioning AutismDokument7 SeitenRecommendations For Students With High Functioning AutismLucia SaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Space Hulk - WDDokument262 SeitenSpace Hulk - WDIgor Baranenko100% (1)
- Dynamics of Machinery PDFDokument18 SeitenDynamics of Machinery PDFThomas VictorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Movie Piracy in Ethiopian CinemaDokument22 SeitenMovie Piracy in Ethiopian CinemaBehailu Shiferaw MihireteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Talking Art As The Spirit Moves UsDokument7 SeitenTalking Art As The Spirit Moves UsUCLA_SPARCNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Derridean Différance - UsiefDokument16 SeitenOn Derridean Différance - UsiefS JEROME 2070505Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hima OPC Server ManualDokument36 SeitenHima OPC Server ManualAshkan Khajouie100% (3)
- Outdoor Air Pollution: Sources, Health Effects and SolutionsDokument20 SeitenOutdoor Air Pollution: Sources, Health Effects and SolutionsCamelia RadulescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2SB817 - 2SD1047 PDFDokument4 Seiten2SB817 - 2SD1047 PDFisaiasvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO 9001 2015 AwarenessDokument23 SeitenISO 9001 2015 AwarenessSeni Oke0% (1)
- FAMOUS PP Past TenseDokument21 SeitenFAMOUS PP Past Tenseme me kyawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test ScienceDokument2 SeitenTest Sciencejam syNoch keine Bewertungen
- WL-80 FTCDokument5 SeitenWL-80 FTCMr.Thawatchai hansuwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mastertop 1230 Plus PDFDokument3 SeitenMastertop 1230 Plus PDFFrancois-Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elements of ArtDokument1 SeiteElements of Artsamson8cindy8louNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizational ConflictDokument22 SeitenOrganizational ConflictTannya AlexandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTE Networks Engineering Track Syllabus Overview - 23 - 24Dokument4 SeitenLTE Networks Engineering Track Syllabus Overview - 23 - 24Mohamed SamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equivalent Fractions Activity PlanDokument6 SeitenEquivalent Fractions Activity Planapi-439333272Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.technical Specifications (Piling)Dokument15 Seiten1.technical Specifications (Piling)Kunal Panchal100% (2)
- DP 2 Human IngenuityDokument8 SeitenDP 2 Human Ingenuityamacodoudiouf02Noch keine Bewertungen
- School of Mathematics 2021 Semester 1 MAT1841 Continuous Mathematics For Computer Science Assignment 1Dokument2 SeitenSchool of Mathematics 2021 Semester 1 MAT1841 Continuous Mathematics For Computer Science Assignment 1STEM Education Vung TauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Costbenefit Analysis 2015Dokument459 SeitenCostbenefit Analysis 2015TRÂM NGUYỄN THỊ BÍCHNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISBN Safe Work Method Statements 2022 03Dokument8 SeitenISBN Safe Work Method Statements 2022 03Tamo Kim ChowNoch keine Bewertungen