Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Copyofgrade 8 Dbqrubric
Hochgeladen von
api-328534846Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Copyofgrade 8 Dbqrubric
Hochgeladen von
api-328534846Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
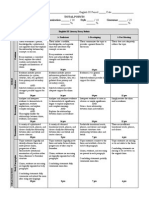
Grade 8 DBQ Rubric
Exceeding
Introduction
(background and
thesis)
Evidence
(to support the
claim)
LEAD:
The writer provides global context for his/her claim
(why it matters to the world at large).
LEAD:
The writer provides context and background that
explains the importance of the topic.
THESIS:
The thesis closes the lead paragraph.
THESIS:
The thesis closes the lead paragraph.
The thesis/claim:
specifically answers the question
gives clear reasons and an organized
structure and focus for the body
paragraphs
acknowledges a counter claim
The thesis/claim:
specifically answers the question
gives clear reasons and an organized
structure and focus for the body paragraphs
acknowledges a counter claim
The writer cites, paraphrases, and quotes various
primary and secondary sources/documents. The
evidence selected strongly supports and enhances
the thesis or claim.
The writer cites, paraphrases, and quotes various
primary and secondary sources/documents The
evidence selected supports the thesis or claim.
Style and
Development
THESIS:
The thesis closes the lead paragraph.
THESIS:
The thesis closes the lead paragraph.
The thesis/claim:
specifically answers the question
gives clear reasons that provide an
organized structure and focus for the
body paragraphs
The writer clearly states his/her claim and
answers the question.
gives clear reasons that introduce
the order of the body paragraphs.
The writer cites and paraphrases limited primary and
secondary sources/documents.
The evidence selected inconsistently supports the
thesis or claim.
The writer cites and paraphrases various
primary and secondary sources/documents,
but the evidence selected doesnt support the
thesis or claim.
The writer acknowledges a counterclaim, but
provides weak or no evidence to support the
counterclaim.
No counterclaim, and/or irrelevant evidence.
The writer explains the importance of the evidence in
relation to their claim.
The writer explains the importance of the evidence in
relation to their claim.
The writer does not explain the importance of
the evidence in relation to their claim.
The writer presents and explains a counterclaim with a
rebuttal.
The writer presents a counterclaim, but does not
provide a clear rebuttal, and/or their counterclaim is
confusing.
The writer presents no counterclaim, and/or
their counterclaim is too confusing to
understand.
The writer:
restates the thesis with included
counterclaim
summarizes the argument and,
offers unique additional insights, questions
or challenges.
The writer:
restates the thesis with included
counterclaim,
summarizes the argument and,
Attempts to offer additional insights,
questions or challenges.
The writer restates the thesis and summarizes their
argument, but does not offer additional insights,
questions or challenges.
The writer restates the thesis, but a summary
of their argument is missing and they offer no
additional insights, questions or challenges.
The writers argument is cohesive, relevant, and
persuasive.
The writers argument is clear, relevant, and persuasive.
The writers argument is clear and mostly relevant.
The writers argument is clear but not
consistently relevant.
The writer establishes and maintains a formal style, not
to include contractions and personal pronouns.
The writer establishes and maintains a formal style,
not to include personal pronouns.
The writer mostly uses academic vocabulary
appropriately to provide context.
The writer attempts to use academic vocabulary.
Some mechanical errors that do not interfere with
communication.
Some mechanical errors that d
o interfere with
communication.
The writer explains the importance of the evidence in
relation to their claim in depth (background
knowledge, inference).
The writer establishes and maintains a formal style,
not to include contractions and personal pronouns.
The writer uses academic vocabulary throughout.
Mechanics
/Covnevtions
Not Yet
LEAD:
The writer creates an introduction to interest
readers and helps them understand a topic or
text (what).
The writer explains why the evidence for their position
outweighs the counterclaim with clear rebuttal.
Conclusion
Approaching
LEAD:
The writer interests readers in his/her argument and
provides some basic context of the topic or text
(when and where of the topic).
The writer provides relevant evidence that strongly
supports a counterclaim.
Analysis of
Evidence
(explains evidence)
Meeting
Few mechanical errors.
The writer provides relevant evidence to support a
counterclaim.
The writer establishes and maintains a formal
style.
The writer uses limited academic vocabulary.
Frequent mechanical errors interfere with
communication.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Essay WritingDokument13 SeitenEssay WritingMirela Dragos100% (2)
- AP WH GUIDEDokument7 SeitenAP WH GUIDEAP Stats BoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP English Language and Composition Exam: Guide for EssaysVon EverandAP English Language and Composition Exam: Guide for EssaysBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (3)
- Understanding Essay Writing: A Guide To Writing Essays By Someone Who Grades ThemVon EverandUnderstanding Essay Writing: A Guide To Writing Essays By Someone Who Grades ThemBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (4)
- Text-Based Lesson SequenceDokument9 SeitenText-Based Lesson Sequenceteacherasyikin100% (1)
- Argumentative Persuasive Essay - How To Write PDFDokument4 SeitenArgumentative Persuasive Essay - How To Write PDFJm HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Argumentative Essay Assignment Group 1Dokument3 SeitenArgumentative Essay Assignment Group 1nataly ceaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle Fusion Talent ManagementDokument26 SeitenOracle Fusion Talent ManagementmadhulikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Argumentative EssayDokument4 SeitenArgumentative EssayJanet100% (1)
- Argument Rubric and Feedback FormDokument3 SeitenArgument Rubric and Feedback Formapi-217459968Noch keine Bewertungen
- Literary Analysis Essay PacketDokument6 SeitenLiterary Analysis Essay Packetapi-328534846Noch keine Bewertungen
- Literary Analysis RubricDokument3 SeitenLiterary Analysis RubricCarmen912Noch keine Bewertungen
- How To Write An ArgumentDokument3 SeitenHow To Write An ArgumentNelitza CuadradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Game Based LearningDokument8 SeitenDigital Game Based Learningwmrouman8251Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ar Argumentative Essay RubricDokument3 SeitenAr Argumentative Essay Rubricapi-253896137Noch keine Bewertungen
- 11 and 12th Grade Writing Rubric and GoalsDokument6 Seiten11 and 12th Grade Writing Rubric and Goalsapi-222621642Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grades 7-8 Elkgrove RubricsDokument12 SeitenGrades 7-8 Elkgrove Rubricsapi-276801348Noch keine Bewertungen
- English Language Teaching in IndiaDokument51 SeitenEnglish Language Teaching in Indiaabhishek.mishraji88% (8)
- Rubric Opinion EssayDokument2 SeitenRubric Opinion EssayOlivia Nechita100% (5)
- Conquer the New SAT Essay: A Skilled Professor Teaches the 2016 SAT Essay SectionVon EverandConquer the New SAT Essay: A Skilled Professor Teaches the 2016 SAT Essay SectionBewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- Organize IWA ArgumentDokument4 SeitenOrganize IWA ArgumentLily ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knight Vs Samurai ProjectDokument2 SeitenKnight Vs Samurai Projectapi-334125776Noch keine Bewertungen
- Essay Outline From Santa Barbara City CollegeDokument2 SeitenEssay Outline From Santa Barbara City Collegeapi-32450147050% (2)
- Purposeful Writing 1Dokument48 SeitenPurposeful Writing 1JAZMIN JOY M. BAYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Framing: Toward Clarification Fractured Paradigm: Journal of Communication Autumn 1993 43, 4 ABI/INFORM GlobalDokument8 SeitenFraming: Toward Clarification Fractured Paradigm: Journal of Communication Autumn 1993 43, 4 ABI/INFORM GlobalMaría Del Rosario MillánNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Studies Laureate Essay RubricDokument1 SeiteAdvanced Studies Laureate Essay Rubricapi-294488294Noch keine Bewertungen
- Csss-Writing Rubric 7th 8thDokument2 SeitenCsss-Writing Rubric 7th 8thapi-205769831Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8th Grade Argumentative Essay Rubric Final 4Dokument1 Seite8th Grade Argumentative Essay Rubric Final 4api-233718532100% (2)
- Zionfinalpeet 2 GradeDokument1 SeiteZionfinalpeet 2 Gradeapi-287713332Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1984 Essay RubricDokument2 Seiten1984 Essay Rubricapi-246379833Noch keine Bewertungen
- Technology Argumentative EssayDokument2 SeitenTechnology Argumentative Essayapi-236556535Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis/Claim and Essential Questions: Essay Rubric Exceeds (4) Proficient (3) Emerging (2) Developing (1-0)Dokument2 SeitenThesis/Claim and Essential Questions: Essay Rubric Exceeds (4) Proficient (3) Emerging (2) Developing (1-0)api-278321671Noch keine Bewertungen
- English III Essay Rubric (11:14-Walz)Dokument2 SeitenEnglish III Essay Rubric (11:14-Walz)api-130859276Noch keine Bewertungen
- Immigration Argumentative Essay Rubric: Names: - ScoreDokument2 SeitenImmigration Argumentative Essay Rubric: Names: - Scoreapi-270513539Noch keine Bewertungen
- Webquery RubricDokument2 SeitenWebquery Rubricapi-302024365Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quarter 1 Final Essay Assessment English 11Dokument5 SeitenQuarter 1 Final Essay Assessment English 11api-293165455Noch keine Bewertungen
- Persuasive Essay RubricDokument2 SeitenPersuasive Essay Rubricapi-284370701Noch keine Bewertungen
- English III Essay Rubric 1114-WalzDokument2 SeitenEnglish III Essay Rubric 1114-Walzapi-130859276Noch keine Bewertungen
- Civics Local Essay RubricDokument2 SeitenCivics Local Essay Rubricapi-240606759Noch keine Bewertungen
- Argumentative Essay PromptDokument2 SeitenArgumentative Essay Promptapi-261695648Noch keine Bewertungen
- Developing A Thesis StatementDokument4 SeitenDeveloping A Thesis StatementSilvi Orellana ManzanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExpozessayDokument2 SeitenExpozessayapi-275159576Noch keine Bewertungen
- Argumentive EssayDokument2 SeitenArgumentive EssayDiomedes ColarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rubric For CipDokument3 SeitenRubric For Cipapi-285628024Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rhetorical Analysis EssayDokument40 SeitenRhetorical Analysis EssayYuanshengNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Booklet Essay Outline Samples For Each Paragraph and TipsDokument6 SeitenHow To Booklet Essay Outline Samples For Each Paragraph and TipsphamhoanghienNoch keine Bewertungen
- CrucibleessaypromptDokument4 SeitenCrucibleessaypromptapi-286318385Noch keine Bewertungen
- How To Write A History Essay at CCADokument5 SeitenHow To Write A History Essay at CCAlfhurlburtNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE Structure of An APDokument15 SeitenAE Structure of An APOkiOkiOkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nicolasafinalpeet 3 GradeDokument2 SeitenNicolasafinalpeet 3 Gradeapi-256791739Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pahilanga, Janiel T.Dokument6 SeitenPahilanga, Janiel T.Joely VillaflorNoch keine Bewertungen
- RubicDokument2 SeitenRubicapi-239706245Noch keine Bewertungen
- English Literature Writing GuideDokument29 SeitenEnglish Literature Writing GuideAllen PayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wwii-A-Bomb Grading RubricDokument1 SeiteWwii-A-Bomb Grading Rubricapi-235628318Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grading Comments For Essays On LiteratureDokument5 SeitenGrading Comments For Essays On LiteratureNguyen Trung Kien (FE FPTU CT)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Workbook 1Dokument4 SeitenWorkbook 1api-257595875Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chamberlain Homs Essay Rubric ChallengeDokument3 SeitenChamberlain Homs Essay Rubric Challengeapi-273010677Noch keine Bewertungen
- Argumentative EssayDokument3 SeitenArgumentative EssayMohd ShaeezwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENG 101 Essay #4Dokument4 SeitenENG 101 Essay #4AliaStearns100% (1)
- Guidelines for Writing Coherent ParagraphsDokument31 SeitenGuidelines for Writing Coherent ParagraphsLany BalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EAPP StructureofacademictextDokument21 SeitenEAPP StructureofacademictextAl BurceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Brief Assignment 1Dokument4 SeitenAssessment Brief Assignment 1Yvonne IoanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steps For Writing An A.P. U.S. History Timed EssayDokument10 SeitenSteps For Writing An A.P. U.S. History Timed EssayMary Kelly FriedmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 MercantilismdbqDokument3 Seiten5 Mercantilismdbqapi-328534846Noch keine Bewertungen
- Age of Exploration DBQDokument10 SeitenAge of Exploration DBQapi-328534846100% (1)
- Soaps Method Od Document AnalysisDokument1 SeiteSoaps Method Od Document Analysisapi-328534846Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Guide To Ungoogleable Question CreationDokument4 SeitenA Guide To Ungoogleable Question Creationapi-328534846Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Sentence: Sample Historical Writing Sentence StemsDokument3 SeitenBasic Sentence: Sample Historical Writing Sentence Stemsapi-328534846Noch keine Bewertungen
- SoapsdocumentanalysisrubricDokument2 SeitenSoapsdocumentanalysisrubricapi-328534846Noch keine Bewertungen
- WhatisthecenteroftheuniverseposterrubricDokument1 SeiteWhatisthecenteroftheuniverseposterrubricapi-328534846Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thescientificrevolution AnnotationDokument3 SeitenThescientificrevolution Annotationapi-328534846Noch keine Bewertungen
- First 100 Days: Donald Trump's Contract With The American VoterDokument2 SeitenFirst 100 Days: Donald Trump's Contract With The American VoterJames JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renaissance Versus Middle Ages DocsDokument5 SeitenRenaissance Versus Middle Ages Docsapi-328534846Noch keine Bewertungen
- Social Studies Sentence Starters-StemsDokument2 SeitenSocial Studies Sentence Starters-Stemsapi-328534846Noch keine Bewertungen
- RenaissanceDokument9 SeitenRenaissanceapi-328534846Noch keine Bewertungen
- Letterhome 1Dokument3 SeitenLetterhome 1api-328534846Noch keine Bewertungen
- Humanitiessyllabus2016 2017Dokument3 SeitenHumanitiessyllabus2016 2017api-328534846Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Case Formulation - BronDokument4 Seiten1 Case Formulation - BronGrace Marie100% (1)
- Ethics and Values in Engineering Profession 2020Dokument18 SeitenEthics and Values in Engineering Profession 2020Ram Chandra MeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unsettling Race and Language Toward A RaDokument27 SeitenUnsettling Race and Language Toward A Ra1dennys5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar Log Book - Computer Engineering - SPPUDokument19 SeitenSeminar Log Book - Computer Engineering - SPPUAnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan in Media and Information Literacy: (Have A Brief Description)Dokument7 SeitenLesson Plan in Media and Information Literacy: (Have A Brief Description)Dandreb SardanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 34 Expressing Opinions: (6.6 Speaking)Dokument2 Seiten34 Expressing Opinions: (6.6 Speaking)Алена Андреевна ПыкоNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mcv4u Course Outline 16Dokument4 SeitenMcv4u Course Outline 16api-323266544Noch keine Bewertungen
- (Descargado) ACCURACY AND FLUENCY BRUMFITDokument10 Seiten(Descargado) ACCURACY AND FLUENCY BRUMFITMiss AbrilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eat Your Vegetables and Do Your Homework: A Design-Based Investigation of Enjoyment and Meaning in LearningDokument8 SeitenEat Your Vegetables and Do Your Homework: A Design-Based Investigation of Enjoyment and Meaning in LearningInês SacaduraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Project: Choose A Topic. Grade 4 Grade 5 Minerals Digestive SystemDokument4 SeitenScience Project: Choose A Topic. Grade 4 Grade 5 Minerals Digestive Systemapi-266184438Noch keine Bewertungen
- Undergraduate ExamsDokument2 SeitenUndergraduate ExamsEverlyn Glenys Tall TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Significance of The StudyDokument4 SeitenSignificance of The StudyJames TangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nama: Sri Wulandari Oktarida NIM: 1181001055: Title: TheDokument3 SeitenNama: Sri Wulandari Oktarida NIM: 1181001055: Title: TheSri Wulan Dari OktaridaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tiered Task From Pre-AssessmentDokument8 SeitenTiered Task From Pre-Assessmentapi-313765228Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Last Year I Spoke On A Panel During A CampusDokument1 Seite1 Last Year I Spoke On A Panel During A CampusLEYENDKILLER ALBERTONoch keine Bewertungen
- Svenson - Preventing Help-Negation - SPA July 2013 PDFDokument1 SeiteSvenson - Preventing Help-Negation - SPA July 2013 PDFdiogocarreiras1345Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Meaning and Value of Supervision in Social Work Field EducationDokument18 SeitenThe Meaning and Value of Supervision in Social Work Field EducationmohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-SAT/SBM Data Collection-PCPGTVSFA: EmailDokument15 SeitenE-SAT/SBM Data Collection-PCPGTVSFA: Emailromil saloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Reflection on Developing Teaching MaterialsDokument3 SeitenCritical Reflection on Developing Teaching MaterialsObjek PelikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strong administrator seeks network roleDokument1 SeiteStrong administrator seeks network roleAbidullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Local Language Maintenance in Kolaka Through Mekongga FolkloreDokument10 SeitenLocal Language Maintenance in Kolaka Through Mekongga Folklorewarda elfiantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 5 NavigateDokument3 SeitenTest 5 NavigateVolodymyr ZakharkivNoch keine Bewertungen
- OD Network Tools - Weisbord Six-Box ModelDokument2 SeitenOD Network Tools - Weisbord Six-Box ModelSameer AllyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Parts, Format and Discussions: Immaculate Conception College of Balayan, IncDokument19 SeitenResearch Parts, Format and Discussions: Immaculate Conception College of Balayan, IncGemma AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen