Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Leads The Current By: T Sin E e T Sin I I
Hochgeladen von
physicspalanichamyOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Leads The Current By: T Sin E e T Sin I I
Hochgeladen von
physicspalanichamyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
12 -PHY-UNIT-4 (2/3)1
Palanichamy
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
PART-I :
Physics M.
(P151---164)
Time: 1.15 Hour
Max Marks: 50
4.
(20 x 1 = 20)
ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS
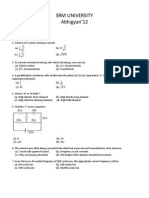
1. Transformer works with
(a) AC only
(b) DC only
(c) both AC and DC
(d) more effectively with AC than with DC.
2. In an AC circuit the applied emf e E 0 Sin( t ) leads the current I I 0 Sin ( t ) by
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) zero
3. Which of the following can not be stepped by a transformer
(a)
input current
(b) input voltage
(c) input power
(d) all
4. In any AC circuit
(a) the average value of current is zero
(b) the average value of square of current is zero
(c) the average power dissipation is zero
(d) the rms current is times the peak current
5. In a step-up transformer
(a) the input power is equal to the out put power
(b) emf induced per turn in the primsry is equal to the emf induced per turn in the secondary
(c) both the statement (a) and (b) are correct
(d) the out put current is larger than the input current
6. For an ideal transformer
(a)
efficiency = 1 (b) transformer ratio k = 1
(c) k < 1
(d) k > 1
7. In a transformer hyteresis loss is reduced by using the core of
(a) mumetal or stelloy
(b) stelloy
(c) silicon steel
(d) all the above
8. When electrical energy is transmitted at high current
(a) energy loss is reduced
(b) both energy loss and cost of transmission is reduced
(c) cost of transmission is reduced
(d) both energy loss and cost of transmission is increased
9. In electric power transmission, outside the city 230,000 V is stepped down to
(a) 110,000 V using a step-down transformer
(b)11,000 V using a step-down auto transformer
(c)220 V /440 V using a step-down transformer
(d) 110,000 V using a step-down auto transformer
10. Domestic electric power in India is supplied at a frequency of
(a) 50 Hz
(b) 60 Hz
(c) 100 KHz to 100 MHz
(d) 400 MW
11. A resistor offers 50 ohm resistance for an ac current of frequency 100 Hz. What will be the
resistance offered by the same resistor for an angular frequency of 100 Radian per second?
(a) 100
(b) 50
(c) 100/2
(d) 2/100
12. In an AC current varies
(a) in magnitude only
(b) in direction only
(c) in magnitude and direction independent of time
(d) in magnitude and direction with time
13. The unit of inductive reactance is
(a) henry
(b) Ohm
(c) Farad
(d) Wb m
14. The value inductive reactance is
(a) XL = L
(b) XL = 2L
(c) both (a) and(b) are correct
(d) (a) only correct
15. The capacitative reactance offered by a capacitor for DC is
1
(a) X C C
(b) X C 2 C
(c) XL = 2C
(d) infinity
16. In a RLC series circuit the impedance of the circuit increases XL increases. The statement is
(a) always true
(b)never true
(c) true only for very high frequencies
(d) true only for very low frequencies
Physics M.PALANICHAMY,M.Sc.,M.Ed.,M.Phil., P.G TEACHER IN PHYSICS,
(CELL:94421 - 36775)
12 -PHY-UNIT-4 (2/3)2
Physics M.
Palanichamy
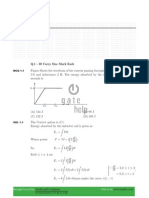
17. The effective reactance of a series RLC circuit is
(a)
R2 X L X C
(b) X L X C 2
18. The phenomenon of resonance is used in
(a) amplifier
(b) transformer
19. The Q-factor is given by
(a) Q
1
2
(b) Q
LC
(c) R
(d)
(c) capacitor
1
LC
(c) Q
1
R
XL XC
R
(d) radio and television
C
L
(d) Q
1
R
L
C
20. The power factor for an ideal chock is
(b) Cos
(a) zero
PART-II:
r
r C
2
(c) Cos
1
r C
2
r 2 2C 2
r
(d) Cos
Answer all the questions
(5 x 3 = 15)
21. Mention the difference between step-up transformer and step-down transformer.
22. Why a DC ammeter connected in an AC circuit gives zero deflection
23. What happens to the value of AC current in a series RLC circuit when the frequency of the source is
increased?
24. Differentiate between self-inductance and mutual inductance.
25. Define Q-factor of an RLC series resonance circuit.
PART-III:
Answer the following question
(1 x 5 = 5)
26. What is a choke coil? Explain the construction and working of a choke coil
PART-IV:
Answer the following question
(1x 10= 10)
27. A source of EC emf is connected to a series combination of R, L and C. Obtain with the help of a vector
diagram and impedance diagram, an expression for (i) the effective voltage (ii) the impedance (iii) the
phase relationship between the current and the voltage.
1
a
11
b
2
c
12
d
3
c
13
b
4
a
14
c
5
c
15
d
6
a
16
c
7
c
17
b
8
d
18
d
9
d
19
d
10
a
20
a
Physics M.PALANICHAMY,M.Sc.,M.Ed.,M.Phil., P.G TEACHER IN PHYSICS,
(CELL:94421 - 36775)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ac Network Work BookDokument9 SeitenAc Network Work Bookrakesh chaturvediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis - Ac CircuitsDokument16 SeitenSinusoidal Steady State Analysis - Ac Circuitsvivek kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- QUIZ - Alternating Current Level - IDokument3 SeitenQUIZ - Alternating Current Level - ISankar KumarasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online EE Test Series 2017Dokument23 SeitenOnline EE Test Series 2017sayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC 1 Mark QuestionsDokument16 SeitenAC 1 Mark Questionsmilonee lNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock GateDokument11 SeitenMock GateSandeep Guha NiyogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Engineering Questions & AnswersDokument7 SeitenElectrical Engineering Questions & Answersnprobo1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Synchronous Motor McqsDokument93 SeitenSynchronous Motor McqsDineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ On Emi & AcDokument23 SeitenMCQ On Emi & AcmanishphyNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE Electrical Engineering - 2001Dokument15 SeitenGATE Electrical Engineering - 2001Pramod ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE EE Sample Test Questions & AnswersDokument12 SeitenGATE EE Sample Test Questions & AnswersNayan MannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE GATE 1998 Question and AnswersDokument9 SeitenEE GATE 1998 Question and AnswersUTKAL.45Noch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit Debugging Questions - 1Dokument3 SeitenCircuit Debugging Questions - 1Hareesh Pillai88% (8)
- Smart Screen 6Dokument11 SeitenSmart Screen 6leslie94Noch keine Bewertungen
- This Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingDokument8 SeitenThis Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE EE 2002 Actual Paper PDFDokument24 SeitenGATE EE 2002 Actual Paper PDFKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE GATE 2000 Question and AnswersDokument8 SeitenEE GATE 2000 Question and AnswersUTKAL.45Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Engineering Questions & AnswersDokument10 SeitenElectrical Engineering Questions & Answersnprobo1Noch keine Bewertungen
- GATE 2009 Paper Q1-20Dokument16 SeitenGATE 2009 Paper Q1-20mass1984Noch keine Bewertungen
- ch31 PDFDokument26 Seitench31 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alternating Current Class 12 Physics MCQsDokument84 SeitenAlternating Current Class 12 Physics MCQsSrishti PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question - Bank - Ee201Dokument16 SeitenQuestion - Bank - Ee201joydeep12Noch keine Bewertungen
- EE GATE 1999 Question and AnswersDokument7 SeitenEE GATE 1999 Question and AnswersUTKAL.45Noch keine Bewertungen
- BSNL JTO Exam 2006 Question PaperDokument17 SeitenBSNL JTO Exam 2006 Question PaperROHITCHOURASIYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock Gate EEEDokument13 SeitenMock Gate EEEnaga01013ee022Noch keine Bewertungen
- GATE EE 2005 Q1-30 one mark questionsDokument17 SeitenGATE EE 2005 Q1-30 one mark questionsvims124Noch keine Bewertungen
- GATE EE 2011 With SolutionsDokument52 SeitenGATE EE 2011 With SolutionsAbhishek MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gate Model PaperDokument32 SeitenGate Model PapererjayprakashpatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital-to-Analog Converter Resolution and DC Motor Speed CalculationDokument13 SeitenDigital-to-Analog Converter Resolution and DC Motor Speed Calculationsanjujoshhi7550Noch keine Bewertungen
- MTC Test Nescom 14 May, 2019 AM ElectronicsDokument9 SeitenMTC Test Nescom 14 May, 2019 AM ElectronicsIsha Hussain86% (14)
- 00 - Electrical Machines - 1Dokument7 Seiten00 - Electrical Machines - 1Bskster BskNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE engineering exam bookletDokument16 SeitenEE engineering exam bookletSrimannarayana NandamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformers Objective Type Questions and AnswersDokument11 SeitenTransformers Objective Type Questions and AnswersJabir Sijas100% (1)
- Electrical TransformersDokument10 SeitenElectrical TransformersSindhu ManchukondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ InverterDokument25 SeitenMCQ InverterrajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSSPDCL Aee2015 QP PDFDokument17 SeitenTSSPDCL Aee2015 QP PDFSbshshxhddhdhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 025ea9953e193-CSEB AE Paper 2018Dokument14 Seiten025ea9953e193-CSEB AE Paper 2018Aviz XalxoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wapda Hydel Junior Engineer Test - 13 November 2016: Blue BookDokument11 SeitenWapda Hydel Junior Engineer Test - 13 November 2016: Blue BookabdulNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH4B01U Electronics 2Dokument4 SeitenPH4B01U Electronics 2AsjathNoch keine Bewertungen
- JE Model Paper ElectricalDokument16 SeitenJE Model Paper ElectricalParveen JangraNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Transformer MasterDokument12 SeitenMCQ Transformer MasterDeepak Choudhary DC67% (3)
- AC CurrentsDokument4 SeitenAC CurrentsRajat AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- A CDokument84 SeitenA Cgurdeepsingh1296100% (1)
- Alternating Current Circuits ExplainededucDokument12 SeitenAlternating Current Circuits Explainededucpavan_marthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDCDokument28 SeitenEDCzuberbashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Find Total Current in Circuit ProblemsDokument1 SeiteFind Total Current in Circuit ProblemsVijay PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 6334696854562799858 PDFDokument32 Seiten5 6334696854562799858 PDFAtul ShingadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE EE 2003 MCQ QuestionsDokument72 SeitenGATE EE 2003 MCQ QuestionssdmtsndNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac TestDokument2 SeitenAc TestAdarsh DhawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 Physics - Alternating Current - McqsDokument15 SeitenClass 12 Physics - Alternating Current - Mcqskhushi GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEE MCQ Unit IVDokument16 SeitenBEE MCQ Unit IVUmesh PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOCK TEST PAPERDokument13 SeitenMOCK TEST PAPERALLU ARJUNNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE EE 2004 With SolutionsDokument57 SeitenGATE EE 2004 With Solutionsamrit40367% (6)
- Forum Attachment 5Dokument19 SeitenForum Attachment 5gauthamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-EE-Objective Paper-II-2010 PDFDokument20 Seiten2-EE-Objective Paper-II-2010 PDFyash97140% (1)
- NE SPACE APPLICATION CENTRE TECHNICAL ASSISTANT EXAMDokument15 SeitenNE SPACE APPLICATION CENTRE TECHNICAL ASSISTANT EXAMumaira arifNoch keine Bewertungen
- IESCO Past PaperDokument13 SeitenIESCO Past Paperfaisal amin60% (5)
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)Von EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesVon EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: Higher Secondary First YearDokument320 SeitenPhysics: Higher Secondary First YearphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- KP Astrology BasicDokument16 SeitenKP Astrology BasicSaini Varun100% (3)
- Name: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsDokument4 SeitenName: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsDokument4 SeitenName: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsDokument5 SeitenName: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bga® TF Ò Ãçî Gÿë Nj®Î V©: Nkšãiy Ïu©Lh M©L - Ïa ÃašDokument4 SeitenBga® TF Ò Ãçî Gÿë Nj®Î V©: Nkšãiy Ïu©Lh M©L - Ïa ÃašphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bga® TF Ò Ãçî Gÿë Nj®Î V©: Nkšãiy Ïu©Lh M©L - Ïa ÃašDokument4 SeitenBga® TF Ò Ãçî Gÿë Nj®Î V©: Nkšãiy Ïu©Lh M©L - Ïa ÃašphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsDokument3 SeitenName: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bga® TF Ò Ãçî Gÿë Nj®Î V©: Nkšãiy Ïu©Lh M©L - Ïa ÃašDokument5 SeitenBga® TF Ò Ãçî Gÿë Nj®Î V©: Nkšãiy Ïu©Lh M©L - Ïa ÃašphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bga® TF Ò Ãçî Gÿë Nj®Î V©: Nkšãiy Ïu©Lh M©L - Ïa ÃašDokument5 SeitenBga® TF Ò Ãçî Gÿë Nj®Î V©: Nkšãiy Ïu©Lh M©L - Ïa ÃašphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsDokument4 SeitenName: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsDokument6 SeitenName: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsDokument5 SeitenName: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsDokument4 SeitenName: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsDokument4 SeitenName: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsDokument5 SeitenName: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEEDokument12 SeitenJEEphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsDokument4 SeitenName: Standard: Section: School: Exam No: Higher Secondary Second Year-PhysicsphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sura Publications: MathematicsDokument4 SeitenSura Publications: MathematicsMoorthi SemmalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Paper II 11th Model Question PaperDokument9 SeitenEnglish Paper II 11th Model Question PaperjknewworldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nkšãiy Kjyh M©L Mwïaš Khâç Édh JhÿDokument4 SeitenNkšãiy Kjyh M©L Mwïaš Khâç Édh JhÿphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Income Tax ExcemptedDokument26 SeitenIncome Tax ExcemptedphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Paper I 11th Model Question PaperDokument8 SeitenEnglish Paper I 11th Model Question PaperjknewworldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geography (English)Dokument4 SeitenGeography (English)physicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communicative EnglishDokument3 SeitenCommunicative EnglishphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics EnglishDokument5 SeitenEconomics EnglishphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics Tamil 11th Model Question PaperDokument6 SeitenEconomics Tamil 11th Model Question PaperjknewworldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics Tamil 11th Model Question PaperDokument6 SeitenEconomics Tamil 11th Model Question PaperjknewworldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commerce - EnglishDokument4 SeitenCommerce - EnglishphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commerce - TamilDokument4 SeitenCommerce - TamilphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power BJTDokument19 SeitenPower BJTSamay GoenkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Islamic University of Technology (Iut)Dokument2 SeitenIslamic University of Technology (Iut)shiamNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSI 700 Control Spec PDFDokument3 SeitenDSI 700 Control Spec PDFMARCO PEREZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 7Dokument6 SeitenLab Report 7api-534904948Noch keine Bewertungen
- IL NT MRS3,4 AMF8,9 2.2 Reference GuideDokument86 SeitenIL NT MRS3,4 AMF8,9 2.2 Reference GuideoveladoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Design Interview Questions 1Dokument14 SeitenDigital Design Interview Questions 1Mohit TopiwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kalai Mohan Lab ManualDokument35 SeitenKalai Mohan Lab Manualrskumar.eeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microwave Systems Document SummaryDokument16 SeitenMicrowave Systems Document SummaryAmeya KadamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Architecture (OrCAD) Laboratory File Simulation ProceduresDokument29 SeitenComputer Architecture (OrCAD) Laboratory File Simulation ProceduresHarman SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sync OlnDokument4 SeitenSync OlnhomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 1Dokument4 SeitenExercise 1Nico RobinNoch keine Bewertungen
- PIC16C5X - EPROM/ROM-Based 8-Bit CMOS Microcontroller Series - 30453cDokument158 SeitenPIC16C5X - EPROM/ROM-Based 8-Bit CMOS Microcontroller Series - 30453cGuillermo HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Control SystemsDokument21 SeitenIntroduction to Control Systemsنورشان محمدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - 2 - 3 FINALDokument15 SeitenChapter 1 - 2 - 3 FINALNin Ninjoe JoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- JBL Control 5 SpeakersDokument2 SeitenJBL Control 5 SpeakersbenshihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smaw200 NN LG TV Power Board ConnectorDokument1 SeiteSmaw200 NN LG TV Power Board Connectormichael DoddNoch keine Bewertungen
- POWER AMPLIFIER Owner's ManualDokument12 SeitenPOWER AMPLIFIER Owner's ManualAlberto PimentelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Veracity VLS-1N-L Data SheetDokument4 SeitenVeracity VLS-1N-L Data SheetJMAC SupplyNoch keine Bewertungen
- APEC 2011 Seminar ACDC ACAC Final Inclusive Swiss Rectifier As Sent 010211Dokument268 SeitenAPEC 2011 Seminar ACDC ACAC Final Inclusive Swiss Rectifier As Sent 010211Cristian BandilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IRMCS2011: Complete Encoder Based Servo Drive Design Platform Imotion Development SystemDokument24 SeitenIRMCS2011: Complete Encoder Based Servo Drive Design Platform Imotion Development SystemNevenko ArlovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philips 29pfl4508-f8 29pfl4908-f7 Chassis pl13.7Dokument75 SeitenPhilips 29pfl4508-f8 29pfl4908-f7 Chassis pl13.7fiuxy webNoch keine Bewertungen
- Omron Programming ManualDokument1.175 SeitenOmron Programming ManualHaroDavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On Integrated CircuitDokument20 SeitenProject Report On Integrated CircuitSushil Kumar67% (6)
- Datasheet Diodo 250 Amperes PowerexDokument4 SeitenDatasheet Diodo 250 Amperes PowerexwallersonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Behringer MIC200 Mic Tube Preamp User ManualDokument12 SeitenBehringer MIC200 Mic Tube Preamp User ManualJean-Pierre DesrochersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Czujnik Indukcyjny RN04 NP Firmy RIKO PDFDokument1 SeiteCzujnik Indukcyjny RN04 NP Firmy RIKO PDFLuis OrtizNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM1188 Product Briefv 1Dokument2 SeitenFM1188 Product Briefv 1ahmad104Noch keine Bewertungen
- Birla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani: Analog AssignmentDokument24 SeitenBirla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani: Analog AssignmentRahamtulla MohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tertiary Windings in Autotransformers - When Needed and Proper SizingDokument1 SeiteTertiary Windings in Autotransformers - When Needed and Proper Sizingravi474Noch keine Bewertungen
- ParadoxDokument7 SeitenParadoxLisa FloresNoch keine Bewertungen