Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Exam 2012 PDF
Hochgeladen von
YuChenQianOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Exam 2012 PDF
Hochgeladen von
YuChenQianCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Final Examination
Term: Fall Year: 2012
Student Name:
Student Identification Number:
Division Number:
Instructor:
Course: ECE105
Course Title: Physics for Electrical Engineering
Date of Exam: Mon, Dec 10, 2012
Exam Period Start time: 4:00pm End time: 6:30pm
Duration of Exam: 2.5h
Number of Exam Pages: 13 (includes cover page and equation sheet)
Exam Type:
Closed
Book
Special
Materials
Open
Book
Materials allowed are listed below:
Programmable calculator
Select this box if second side of paper is to be used for rough work calculations.
Instructions:
1. Mark your computer card in dark lead PENCIL only. Mark your ID number in the space provided.
IT IS VERY IMPORTANT that you fill in the correct ovals for your ID number.
2. Questions in Part A are worth 1.5 marks each; questions in Part B are worth 4 marks each. These
are multiple choice questions: mark your answers on the computer card provided. There
is no penalty for selecting an incorrect answer. Ignore any round-off errors and pick the closest
answer.
3. Questions in Part C are worth 12 marks each. Answer only 5 of the 6 questions. If you
answer more than five, only the first five will be marked. Write full solutions directly in the
exam booklet, and put your final answer in the boxes provided. Use the back of the opposite page if
necessary; indicate clearly if you have done so. These will be hand-marked, with partial credit given
for correct procedure.
4. Check that this booklet has 21 questions and 13 pages including the equation sheet, which you may
tear off.
5. COMPUTER SHEETS WILL BE COLLECTED AFTER 2 HOURS
Marking scheme: For office use only - do not fill in.
C16
C17
C18
C19
C20
C21
Total
ECE105 Final Exam
Page 2
Concept Questions: Answer all questions on the computer
card provided.
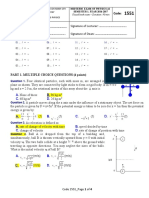
1. (1.5 marks) In the diagram below, a block of mass m is attached by a string to a block of unknown
mass M2 on an inclined plane. What is the magnitude of the normal force acting on mass m?
a) N = mg
b) N > mg
c) N < mg
d) N = 0
e) N = mg cos
2. (1.5 marks) A bead is free to travel around a vertical, circular hoop of radius R, without friction.
Gravity is present. At some point, shown in the diagram, the bead is at the bottom of the hoop,
with speed v . At what angle , measured counterclockwise from the vertical, does the normal force
on the bead have its maximum value? Answer in degrees.
a) = 0
b) = 90
c) = 180
d) 0 < < 90
e) 90 < < 180
3. (1.5 marks) A mass m hangs from a rope wound around a pulley. The mass is then allowed to fall
under the effect of gravity. You have three choices of pulleys: a uniform disk, a uniform ring, or a
disk that is thicker near the centre than at the edge. All pulleys have the same mass M and radius
R. Which pulley would you choose to make the mass reach the highest possible speed after falling
distance h?
a) The uniform disk
b) The uniform ring
c) The non-uniform disk
d) All will be the same, because they have the same mass (the radius is irrelevant)
e) All will be the same, because they have the same mass and radius.
ECE105 Final Exam
Page 3
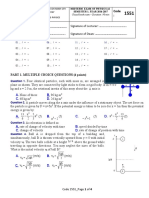
4. (1.5 marks) For a rotating object,
a) If the angular speed is positive the angular acceleration must be positive as well.
b) A zero angular acceleration is possible with non-zero angular speed
c) If the angular speed is zero then the angular acceleration must be zero as well
d) All of the above are true
e) None of the above are true
5. (1.5 marks) A ladder leans against a wall at angle . The other end rests on a horizontal surface.
The ladder will be in static equilibrium if
a) There is sufficient friction between the ladder and the wall
b) There is sufficient friction between the ladder and the floor
c) There is sufficient friction between the ladder and either the wall or the floor. You need friction
on at least one surface, but it doesnt matter which one.
d) There is sufficent friction between the ladder and both surfaces. If either surface is frictionless,
the ladder will slip.
e) None of the above
6. (1.5 marks) A torque acts on a disk, which can pivot about its centre of mass, as shown. The
magnitude of the torque increases linearly with time. Which of the following statements must be
true?
a) The disk is rotating in the clockwise direction
b) The disks angular speed will change at a constant rate.
c) The disks angular acceleration is in the counterclockwise direction.
d) At some point in the future, the disk will be rotating in the clockwise direction.
e) Either none of the above, or more than one of the above, are true.
7. (1.5 marks) A simple harmonic oscillator with period T has speed v at some point in time. The
next time it has the same speed
a) Must be a period T later
b) Must be half a period later
c) Must be one quarter of a period later.
d) Can occur at any value of t between zero and T /2 (inclusive).
e) None of the above.
8. (1.5 marks) If you superpose two waves with the same amplitude and wavelength, the resulting
amplitude will be
a) Twice the amplitude of each wave
b) Four times the amplitude of each wave
c) Some value between zero and four times the amplitude of each wave
d) Some value between zero and twice the amplitude of each wave
e) Any of the above is possible.
ECE105 Final Exam
Page 4
B Short Calculation Questions: Answer all questions on the
computer card provided.
9. (4 marks) The hockey stick shown below has a total mass M , uniformly distributed. The shaft
has length L, and the blade has length L/4, as shown. It can pivot freely about the point P, in the
middle of the shaft. What will be the magnitude of its angular acceleration, if it is subject to a net
torque of 2 Nm acting in the counter-clockwise direction?
a) 1.9/(M L2 )
b) 5.6/(M L2 )
c) 7.5/(M L2 )
d) 16.5/(M L2 )
e) None of the above
10. (4 marks) A spring of spring constant k = 200 N/m has one end fixed to a wall as it sits unstretched
on a horizontal, frictionless surface. The other end is attached to a mass M1 =2 kg. Another mass
M2 is moving toward M1 and collides with it in a perfectly elastic collision. Immediately after the
collision M2 stops moving, while M1 compresses the spring by an unknown distance x. When M1
rebounds back, it strikes the now stationary mass M2 . Find M2 , in kg.
a) 1
b) 2
c) 0.5
d) Not enough information to tell
e) None of the above
11. (4 marks) A spring of spring constant k = 200 N/m has one end fixed to a wall, and the other
attached to a block of mass m. The spring is initially compressed by 10 cm. The block is then moved
until the spring is stretched by 20 cm. What is the work done by the spring on the block, in J?
a) -3
b) -1
c) 1
d) 9
e) None of the above or impossible to tell
ECE105 Final Exam
Page 5
12. (4 marks) Block m2 = 5kg rests on a larger block of mass M = 10kg. A rope attached to m2 passes
over a pulley to m1 = 2kg. There is no friction between M and the ground. As a constant force
F = 20N is applied to M , m1 and m2 remain in the configuration shown, relative to each other and
block M . The pulley is massless and frictionless. Find the angle , in degrees.
a) 11.5
b) 84.3
c) 0
d) 6.8
e) None of the above.
13. (4 marks) A 2.0m long string fixed at both ends vibrates at its m = 3 harmonic frequency, with a
maximum amplitude of 3.0cm. Find the oscillation amplitude in cm, a distance x = 10cm from one
end of the string.
a) 3.0
b) 2.72
c) 4.2
d) 1.36
e) None of the above
ECE105 Final Exam
Page 6
14. (4 marks) Mass m = 0.75 kg is released from rest in the system shown, when the spring is stretched
by 15 cm. The pulley is a uniform disk with mass mp = 1kg and radius r = 20cm, and the spring
has k = 200N/m. Find the amplitude of oscillation, in cm.
a) 16.3
b) 15.0
c) 26.3
d) 7.6
e) None of the above
15. (4 marks) A wave moves through otherwise still water, at speed v = 1.5m/s. The wave has an
amplitude of 0.5m, and you measure the distance between successive crests to be 2.5m. Two buoys,
each of mass m = 5kg, float on the water, separated by 4m. The direction of wave propagation is
from buoy A to buoy B. Find the net force acting on A, 3s after the crest of a wave passes by B.
Answer in N. (Watch your precision: keep at least 4 significant figures through your calculations).
a) 28.7
b) 33.8
c) 11
d) 2.2
e) 12
ECE105 Final Exam
Page 7
Problems: Answer only 5 of the 6 questions!!
16. (12 marks) A 12 m tall, 2000 kg pillar is broken at the base. Originally vertical, the pillar begins
to swing. Indiana Jones stands at the top; he is 2m tall and has a mass of 100 kg. Assume enough
friction between the pillar and Jones to ensure Jones does not slide off the pillar, and assume Jones
maintains his orientation relative to the pillar. Assume both the pillar and Jones can be approximated
as thin rods.
(a) (6 marks) How high above the ground is the top of the pillar, when Jones is just about to lose
contact with the pillar?
h=
(b) (3 marks) Find Jones angular acceleration at the instant he is about to leave the pillar.
rad/s2
(c) (3 marks) Find the total linear acceleration at the top of Jones head, the instant he is about
to leave the pillar
a=
m/s2
ECE105 Final Exam
Page 8
17. 12 marks)
The bar in the figure is 3m long, with mass m = 2kg, and rests on the surfaces shown. The contact
with the surface on the right is frictionless. The incline on the left makes an angle of 23 degrees with
the horizontal. The incline on the right makes an angle of 62 degrees with the horizontal. The bar
makes an angle of 45 degrees with the incline on the right. Assume the bar does not slip.
a) (3 marks) Draw a correct free-body diagram for
the rod. Indicate all forces acting on the rod.
b) (3 marks) Calculate the normal force from the frictionless surface (on the right).
c) (6 marks) Find the force of friction acting on the left end of the bar.
f=
ECE105 Final Exam
Page 9
18. (12 marks)
A uniform rod with mass M and length L = 3m is pivoted
at one end as shown. The free end is attached to a vertical
spring fixed to the floor, which is unstretched when the
rod is perfectly horizontal. The rod is raised so it makes
an angle of 5 degrees relative to horizontal, and released
from rest. The tip of the rod is then seen to fall a total
vertical distance of L/5, before bouncing back. Hint: use
the small angle approximation.
a) (3 marks) At what angle from the horizontal, E , is the system in equilibrium? Answer in
degrees.
E =
deg
b) (4 marks) What is the ratio of spring constant to the mass of the rod, k/M ? (Hint: consider
the net torque acting on the system when it is at the equilibrium position found in b).
k/M =
s2
c) (5 marks) Find the frequency of small oscillations, in rad/s.
rad/s2
ECE105 Final Exam
Page 10
19. (12 marks) Many corners on Formula One race circuits are reverse-camber they are sloped
such that the track is higher on the inside of the corner, as shown. This example has a radius of
curvature R = 100m and = 15 degrees.
a) (3 marks)Draw a free-body diagram for the car as shown on the left, traveling into the page
at speed v without slipping, on this track. Identify all forces and the direction of acceleration.
b) (3 marks) Find the minimum possible value for the coefficient of static friction s , if the car
is to make the corner without slipping.
s,min =
c) (3 marks) If the maximum coefficient of static friction is 2.5 times larger than the minimum
you found in part b, what is the maximum speed with which a car could round this corner
without slipping?
vmax =
m/s
d) (3 marks) Inside the car, a spider (m = 10g) hangs from a thread attached to the roof. What
angle does the thread make, relative to the roof, if the car is traveling at the speed found in
part c?
degrees
ECE105 Final Exam
Page 11
20. (12 marks)
a) (3 marks) A rubber bullet of mass m1 is fired with horizontal speed v at a stationary block
of mass m2 . If no kinetic energy is lost in the collision, show that, after the collision, the speed
1
of block m2 is given by v2 = m2m
v .
1 +m2
b) (2 marks) Now consider the case where m2 is initially moving with speed v. Write an expression
for its final speed following the collision with the bullet (which is still moving at v ).
v2 =
c) (3 marks) Assume the block has m2 = 2kg and the bullets (m1 = 50g) are fired with speed
v = 10 m/s, at a rate of 3/s. Calculate the average force of the bullets acting on m2 , at the
instant when m2 is at rest. (Neglect any motion of m2 during the time over which the force is
averaged).
F =
d) (4 marks) You continue to fire bullets at the block at the same rate of 3/s. The block speeds
up until it reaches v = 5m/s, at which point it continues to move with constant speed. Find the
coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface. (Assume the bullets continue
to strike the block with a horizontal speed of v = 10m/s, relative to the ground).
k =
ECE105 Final Exam
Page 12
21. (12 marks) A particle of mass m = 300g, initially at rest, is attached to a unstretched horizontal
spring whose other end is attached to a wall. A constant horizontal force is applied to the mass such
that it comes to rest momentarily 0.4 seconds later, after having travelled 4cm.
a) (4 marks) Find the applied force
F =
b) (2 marks) When the spring is at maximum extension the force is reduced by a factor of 2.
How long does it take the mass to go back to equilibrium?
t=
c) (6 marks) With the force in part b still applied, find the time it takes the particle to go from
a point x1 = A2 , moving in the direction of increasing x at speed v1 , to a point x2 where it has
v2 = vmax /7 and a positive acceleration for the first time since leaving x1 .
t=
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Last Name: - : University of Waterloo Final Examination Fall 2014Dokument13 SeitenLast Name: - : University of Waterloo Final Examination Fall 2014YuChenQianNoch keine Bewertungen
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Von EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Final Exam 2009 SPDokument15 SeitenFinal Exam 2009 SPNick SnyderNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCS120 Final ExamDokument10 SeitenPCS120 Final ExamBetty WangNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE-ADVANCED - Part Test 1 Paper - 2013Dokument11 SeitenJEE-ADVANCED - Part Test 1 Paper - 2013Apex Institute100% (1)
- WWW - Colorado.edu Physics Phys1110 Phys1110 Fa14 Homeworks Phys1110 Fa14 Exam3 PracticeDokument10 SeitenWWW - Colorado.edu Physics Phys1110 Phys1110 Fa14 Homeworks Phys1110 Fa14 Exam3 PracticemikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYS1534 Exam 2018 MainDokument16 SeitenPHYS1534 Exam 2018 MainGiftNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phys 201 Practice Questions For Exam 2Dokument19 SeitenPhys 201 Practice Questions For Exam 2SawarSagwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 1 2016-17 Quiz3Dokument6 SeitenPhysics 1 2016-17 Quiz3Khoa TrầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter09 Practice QuestionsDokument29 SeitenChapter09 Practice Questionsaisha alsuwaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics SolvedDokument16 SeitenPhysics SolvedAbhijeet Singh PanwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- National University Physics Midterm ExamDokument4 SeitenNational University Physics Midterm ExamBá Phong LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- The second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of an isolated system always increases over timeDokument30 SeitenThe second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of an isolated system always increases over timeMahmoud QousiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2009T1Dokument8 Seiten2009T1smk1992Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fiitjee Phase Test 1 (Class 11th), Jee Advance Paper 1Dokument12 SeitenFiitjee Phase Test 1 (Class 11th), Jee Advance Paper 1Shlok Sah71% (77)
- Question Paper JeeDokument20 SeitenQuestion Paper JeeSourabhThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 Static Equilibrium Elasticity and Fracture: Physics: Principle and Applications, 7e (Giancoli)Dokument24 SeitenChapter 9 Static Equilibrium Elasticity and Fracture: Physics: Principle and Applications, 7e (Giancoli)KarissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebook College Physics A Strategic Approach 3Rd Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokument44 SeitenEbook College Physics A Strategic Approach 3Rd Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFkennethalandlj1f100% (11)
- College Physics A Strategic Approach 3rd Edition Knight Test BankDokument23 SeitenCollege Physics A Strategic Approach 3rd Edition Knight Test Bankpaullanb7nch100% (30)
- Ebook College Physics A Strategic Approach Technology Update 3Rd Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokument39 SeitenEbook College Physics A Strategic Approach Technology Update 3Rd Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFStevenMillersqpe100% (10)
- Sample Paper Physics Class XiDokument6 SeitenSample Paper Physics Class XiBhaskar JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 211 Exam 1 ReviewDokument14 SeitenPhysics 211 Exam 1 ReviewGeorge KongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 9th Edition Cutnell Test BankDokument27 SeitenPhysics 9th Edition Cutnell Test Bankchristinaperezsdoiftcjbk100% (28)
- This Test Contains A Total of 10 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingDokument19 SeitenThis Test Contains A Total of 10 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE Markingvarunkohliin100% (1)
- 10jan M2Dokument8 Seiten10jan M2Ahmed NurulNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 SJPO-2013-GenDokument19 Seiten4 SJPO-2013-Genronghui009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Phys 1D03 Test 2 Online F20 Ave PDFDokument5 SeitenPhys 1D03 Test 2 Online F20 Ave PDFMarc YorkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aapt United States Physics Team AIP 2014: 2014 F Ma Contest 25 Questions - 75 Minutes InstructionsDokument13 SeitenAapt United States Physics Team AIP 2014: 2014 F Ma Contest 25 Questions - 75 Minutes InstructionsMadeleine BeliveauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex3mech 2019Dokument8 SeitenEx3mech 2019Nasim RazaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- General PhysicsmidDokument4 SeitenGeneral Physicsmidkoket engidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SJPO General Round 2009 With AnswersDokument21 SeitenSJPO General Round 2009 With AnswersHaha XiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Final TestDokument9 SeitenOpen Final Testneerajnitin0110% (1)
- Test Bank For Physics Principles With Applications 7th Edition Douglas C Giancoli DownloadDokument38 SeitenTest Bank For Physics Principles With Applications 7th Edition Douglas C Giancoli Downloadmarissaarmstrongpbfzemcsji100% (18)
- Midterm Exam 2016-2017-01Dokument4 SeitenMidterm Exam 2016-2017-01Gia Hân EmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 1. Multiple Choice Questions (4 Points) : CodeDokument4 SeitenPart 1. Multiple Choice Questions (4 Points) : Codeminh nguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- National University Physics Midterm ExamDokument4 SeitenNational University Physics Midterm ExamMAI TRẦN THANHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Exam with SolutionsDokument10 SeitenPhysics Exam with SolutionsTOPKEKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Old Exam With Solutions 051Dokument11 SeitenPhysics Old Exam With Solutions 051poker100% (1)
- Center of Mass and The Motion of A SystemDokument13 SeitenCenter of Mass and The Motion of A SystemNitin SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDokument10 SeitenMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionAlejandro Torrico MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naf Yad: PrepaDokument5 SeitenNaf Yad: Prepanasru hajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Final ExamDokument7 SeitenPractice Final ExamChetanya SinglaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Review 3Dokument24 SeitenExam Review 3api-223793512Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach With Modern Physics 4Th Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokument37 SeitenPhysics For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach With Modern Physics 4Th Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFwadeperlid9d98k86% (7)
- MorroofdDokument2 SeitenMorroofdAnonymous ym7PJCj0% (1)
- Exam1a KeyDokument7 SeitenExam1a KeySaeed AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ms101 MTA FormB Answer Key Fall2014Dokument5 SeitenMs101 MTA FormB Answer Key Fall2014rofamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Midterm 2Dokument8 SeitenPractice Midterm 2Chetanya SinglaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Physics Eng PP 2023 24 2Dokument9 Seiten11 Physics Eng PP 2023 24 2guptadeepka168100% (2)
- Midterm Exam A1Dokument3 SeitenMidterm Exam A1Bá Phong LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Test 2Dokument7 SeitenPractice Test 2Maria YurlovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final 1a03 Winter 2017 Version 1 WatermarkDokument18 SeitenFinal 1a03 Winter 2017 Version 1 Watermarkproplayer910Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 12 Final QPDokument8 SeitenGrade 12 Final QPfazeelm24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jee 2014 Booklet3 HWT Energy & MomentumDokument19 SeitenJee 2014 Booklet3 HWT Energy & MomentumvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample FinalDokument15 SeitenSample FinalGeoff HattNoch keine Bewertungen
- PracticeExam2 BlankDokument5 SeitenPracticeExam2 Blanklestyouforget0% (1)
- p.1 FizDokument12 Seitenp.1 FizredroseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iit PaceDokument19 SeitenIit PaceabhishekjanjalkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low-Altitude Dynamics of Very Flexible AircraftDokument20 SeitenLow-Altitude Dynamics of Very Flexible AircraftTestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Coil SizingDokument21 SeitenSteam Coil SizingMildogg100% (1)
- Poisson TermodinamicaDokument97 SeitenPoisson TermodinamicaJoshua WrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projectile Motion 1Dokument52 SeitenProjectile Motion 1Ayman EidNoch keine Bewertungen
- CET I 4. Second Law 2021Dokument63 SeitenCET I 4. Second Law 2021Dhruv AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics analysis debunks myth that dropped and fired bullets hit ground simultaneouslyDokument11 SeitenPhysics analysis debunks myth that dropped and fired bullets hit ground simultaneouslyMichael DyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Dynamics of RotationDokument11 Seiten05 Dynamics of RotationCONIX- TVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demonstration of Euler Buckling: Description Learning Objectives/experimentsDokument3 SeitenDemonstration of Euler Buckling: Description Learning Objectives/experimentsDiego AvendañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE207 Assignment 1Dokument7 SeitenEE207 Assignment 1Anuranan DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 (DESIGN THEORY: LIMIT STATES AND BENDING)Dokument23 SeitenUnit 3 (DESIGN THEORY: LIMIT STATES AND BENDING)Zara Nabilah100% (7)
- On Fracture MechanicsDokument81 SeitenOn Fracture MechanicsDEEPAK100% (1)
- Baupanel Application Standard Seismic-Resistant ConstructionDokument11 SeitenBaupanel Application Standard Seismic-Resistant Constructionİhsan TazeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Newton Second Law-ForMATDokument5 Seiten1-Newton Second Law-ForMATVAIBHAV KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reinforcement Modeling in Nonlinear Analysis of RC and RCHS Columns Subjected to Axial CompressionDokument6 SeitenReinforcement Modeling in Nonlinear Analysis of RC and RCHS Columns Subjected to Axial CompressionAdolfo Gálvez VillacortaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Machines FundamentalsDokument25 SeitenTheory of Machines FundamentalsMd. Zillur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tyre As Car ComponentDokument113 SeitenTyre As Car ComponenttsegayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Stages and Column Shortening Analysis in Tall Buildings PDFDokument49 SeitenConstruction Stages and Column Shortening Analysis in Tall Buildings PDFPhu NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- KOM Unit IIDokument68 SeitenKOM Unit IIVinoth KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laue EquationsDokument3 SeitenLaue EquationsVinodh SrinivasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of The Application of Newton's Third Law in PhysicsDokument50 SeitenReview of The Application of Newton's Third Law in PhysicslawlietcullenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposals For New One-Way Shear Equations For The 318 Building CodeDokument4 SeitenProposals For New One-Way Shear Equations For The 318 Building CodepicottNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDokument5 SeitenStatics of Rigid BodiesUwu WehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Analysis Freestanding Wall and SignDokument21 SeitenWind Analysis Freestanding Wall and SignJheremae DeypalubosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orthopaedic Biomechanics Made EasyDokument226 SeitenOrthopaedic Biomechanics Made EasyCiara Caldwell98% (41)
- Laser Engineering PhysicsDokument27 SeitenLaser Engineering PhysicsPavan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- FHSC1014 Additional Tutorial 5Dokument5 SeitenFHSC1014 Additional Tutorial 5Zheng Kit OoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SFD and BMD (Questions)Dokument22 SeitenSFD and BMD (Questions)Mayank ShelarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elastic Foundations - Beams - Materials - Engineering Reference With Worked ExamplesDokument3 SeitenElastic Foundations - Beams - Materials - Engineering Reference With Worked Examplessebastian9033Noch keine Bewertungen
- LAWS OF MOTIONDokument22 SeitenLAWS OF MOTIONArijit MondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determining Moment-Curvature Relationship of Reinforced Concrete ColumnsDokument8 SeitenDetermining Moment-Curvature Relationship of Reinforced Concrete Columnspaulami das choudhuryNoch keine Bewertungen