Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
What Is Adsorption
Hochgeladen von
i1607282Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
What Is Adsorption
Hochgeladen von
i1607282Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
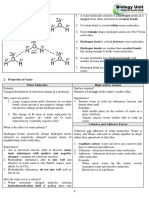
What is Adsorption?
Adsorption is the phenomenon of accumulation of large number of molecular species at the surface of liquid or solid phase
in comparison to the bulk.
How Adsorption occurs?
The process of adsorption arises due to presence of unbalanced or residual forces at the surface of liquid or solid phase.
These unbalanced residual forces have tendency to attract and retain the molecular species with which it comes in contact
with the surface. Adsorption is essentially a surface phenomenon.
Adsorption process involves two components Adsorbent and Adsorbate. Adsorbent is the substance on the surface of which
adsorption takes place.Adsorbate is the substance which is being adsorbed on the surface of adsorbent. Adsorbate gets
adsorbed.
Adsorption process takes place by adsorbate getting adsorbed on adsorbent .Forces of attraction exist between adsorbate and
adsorbent and due to these forces of attraction, heat energy is released. So adsorption is an exothermic process.
Types of Adsorption
Forces of attraction exist between adsorbate and adsorbent. These forces of attraction can be due to Vanderwaal forces of
attraction which are weak forces or due to chemical bond which are strong forces of attraction. On the basis of type of forces
of attraction existing between adsorbate and adsorbent, adsorption can be classified into two types: Physical Adsorption or
Chemical Adsorption.
Physical Adsorption or Physisorption
When the force of attraction existing between adsorbate and adsorbent are weak Vanderwaal forces of attraction, the process
is called Physical Adsorption or Physisorption.
Chemical Adsorption or Chemisorption
When the force of attraction existing between adsorbate and adsorbent are chemical forces of attraction or chemical bond,
the process is called Chemical Adsorption or Chemisorption
Adsorption Isotherm
The process of Adsorption is usually studied through graphs called as adsorption isotherm. It is the graph between the
amounts of adsorbate (x) adsorbed on the surface of adsorbent (m) and pressure at constant temperature.
Applications of Adsorption
Charcoal is used as a decoloriser as it adsorbs the coloring matter from the coloured solution of sugar.
Silica and alumina gels are used as adsorbents for removing moisture and for controlling humidity of rooms.
Activated charcoal is used in gas masks as it adsorbs all the toxic gases and vapours and purifies the air for
breathing.
Absorption is the process in which a fluid is dissolved by a liquid or a solid (absorbent). Adsorption is the process in
which atoms, ions or molecules from a substance (it could be gas, liquid or dissolved solid) adhere to a surface of the
adsorbent. Adsorption is a surface-based process where a film of adsorbate is created on the surface while absorption
involves the entire volume of the absorbing substance.
Absorption versus Adsorption comparison chart
Absorption
Definition Assimilation of
molecular species
throughout the bulk
of the solid or liquid
is termed as
absorption.
Phenomenon It is a bulk
phenomenon
Adsorption
Accumulation of
the molecular
species at the
surface rather than
in the bulk of the
solid or liquid is
termed as
adsorption.
It is a surface
phenomenon.
Heat Endothermic process Exothermic process
exchange
Temperature It is not affected by It is favoured by
temperature
low temperature
Absorption versus Adsorption comparison chart
Absorption
Rate of It occurs at a
reaction uniform rate.
Concentratio It is same
n throughout the
material.
Adsorption
It steadily increases
and reach to
equilibrium
Concentration on
the surface of
adsorbent is
different from that
in the bulk
Process
Adsorption and absorption are both sorption processes.
Absorption occurs when atoms pass through or enter a bulky material. During absorption, the molecules are entirely
dissolved or diffused in the absorbent to form a solution. Once dissolved, the molecules cannot be separated easily from
the absorbent.
Adsorption is generally classified into physisorption (weak van der Waals forces) and chemisorption (covalent bonding). It
can also be caused by electrostatic attraction. The molecules are held loosely on the surface of the adsorbent and can be
easily removed.
Uses
Absorption: The common commercial uses of absorption cycle are absorption chillers for space cooling applications, ice
production, cold storage, turbine inlet cooling. Highefficiency operation, environmentally friendly refrigerants, cleanburning fuels and few moving parts that require maintenance make absorption a very good choice for consumers.
The process of gas absorption by a liquid is used in hydrogenation of oils and carbonation of beverages.
Adsorption: Some of the industrial applications for adsorption are air-conditioning, adsorption chillers, synthetic resin
and water purification. An adsorption chiller does not require moving parts and hence is quiet. In pharmaceutical industry
applications, adsorption is used as a means to prolong neurological exposure to specific drugs or parts thereof. Adsorption
of molecules onto polymer surfaces is used in various applications such as in the development of non-stick coatings and in
various biomedical devices.
Absorption is when one substance enters completely into another. Think of people walking into and sitting down in a car
trolley.
Adsorption is when one substance just hangs onto the outside of another. Think of people holding onto a car trolley with one
hand and leaning off the side. Theyre along for the ride but not inside.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Adsorption (Surface Chemistry)Dokument15 SeitenAdsorption (Surface Chemistry)Salman AshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colloidal State: Crystalloids: Crystalloids Were Those Substances Which Could Be Obtained inDokument29 SeitenColloidal State: Crystalloids: Crystalloids Were Those Substances Which Could Be Obtained inPiyushSinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stationary Phase, Which Separates The Analyte To Be Measured From Other MoleculesDokument15 SeitenStationary Phase, Which Separates The Analyte To Be Measured From Other MoleculesJatinChadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sociology Is The Scientific Study of SocietyDokument6 SeitenSociology Is The Scientific Study of SocietyJethro Tigno0% (1)
- Section 3 Discovering Life MeaningDokument2 SeitenSection 3 Discovering Life Meaningrose belle garciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThixotropyDokument13 SeitenThixotropyAnonymous JMuM0E5YONoch keine Bewertungen
- Polyurethane: Partial Fulfillment in Physical Science Submitted To: Mrs. Filamae J. MapareDokument11 SeitenPolyurethane: Partial Fulfillment in Physical Science Submitted To: Mrs. Filamae J. MapareTrishia SeñoronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Political ScienceDokument3 SeitenPolitical ScienceSunshine Baclaan100% (1)
- Exp. 6 Biuret Test For The Presence of ProteinsDokument4 SeitenExp. 6 Biuret Test For The Presence of ProteinsClarice CatorceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal TissueDokument3 SeitenAnimal TissueAkmal MusyaffaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Lipids and Dietary LipidsDokument33 SeitenIntroduction To Lipids and Dietary LipidsAtif Amin BaigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomical Terms of MovementDokument16 SeitenAnatomical Terms of MovementMari Carreon TulioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disaster Risk ReductionDokument30 SeitenDisaster Risk ReductionRoselyn Estrada MunioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Membrane TransportDokument4 SeitenMembrane TransportNiharika GhoshalNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHBP Prelims - ReviewerDokument39 SeitenPHBP Prelims - ReviewerAia RohaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terminologies: Common Terms Used in Animal Nutrition and FeedingDokument10 SeitenTerminologies: Common Terms Used in Animal Nutrition and FeedingArkham Phari100% (1)
- Common Apparatus and ProceduresDokument7 SeitenCommon Apparatus and ProceduresNorazrina Abdul Aziz0% (1)
- Lec 1 Enzyme and Its ClassificationDokument30 SeitenLec 1 Enzyme and Its ClassificationSadia DinNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdaptationsDokument4 SeitenAdaptationsJack BarkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell CycleDokument5 SeitenThe Cell CycleBrandon Alforque EsmasNoch keine Bewertungen
- HomeostasisDokument16 SeitenHomeostasisDr M K GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of CarbohydratesDokument25 SeitenClassification of CarbohydratesMeleny BallesterosNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Respiratory System PDFDokument47 SeitenThe Respiratory System PDFNicole LumbreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy FlowDokument40 SeitenEnergy FlowHeather ClarchickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knowing The Unknown Determination of DensitiesDokument8 SeitenKnowing The Unknown Determination of DensitiesKath kathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Rates of ReactionDokument14 SeitenIntroduction To Rates of Reactionash4evaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Affecting The State of Equilibrium - Angela TanghalDokument17 SeitenFactors Affecting The State of Equilibrium - Angela TanghalTomTanghalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Terminology Slides: Musculatory SystemDokument62 SeitenMedical Terminology Slides: Musculatory Systemsolovchik0% (1)
- Universal Properties of CellsDokument6 SeitenUniversal Properties of CellsMELISSA ANNE WASSMERNoch keine Bewertungen
- BasketballDokument13 SeitenBasketballKyle AtinonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assingment PharmaDokument2 SeitenAssingment PharmaCagabcab Canibel MelanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell MembraneDokument20 SeitenCell MembraneSarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific ReportDokument6 SeitenScientific Reportapi-334750388Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basketball Court DimensionsDokument1 SeiteBasketball Court DimensionsKristine Mae MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter7 Gases Liquids SolidsDokument86 SeitenChapter7 Gases Liquids SolidsBriyan Ibnu HusnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Darca & Dimapasoc Roy's Adaptation Theory PresentationDokument26 SeitenDarca & Dimapasoc Roy's Adaptation Theory PresentationJandrew Gomez DimapasocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buffer and Isotonic SolutionDokument25 SeitenBuffer and Isotonic SolutionShipra Singhal100% (2)
- Functions of BloodDokument5 SeitenFunctions of BloodsecretNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis and DialysisDokument1 SeiteOsmosis and DialysisNicole PastoresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacodynamics3 161031154812Dokument43 SeitenPharmacodynamics3 161031154812Adeel Khan100% (1)
- Diff Osmosis Lab Sp11Dokument8 SeitenDiff Osmosis Lab Sp11Kelly TrainorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of Nerve ImpulseDokument7 SeitenPhysiology of Nerve ImpulseBryan tsepang Nare100% (1)
- Respiratory System: StructureDokument29 SeitenRespiratory System: StructureDr. Abir Ishtiaq100% (1)
- Study MaterialDokument39 SeitenStudy Materialrutwick100% (1)
- Chemistry of CarbohydratesDokument6 SeitenChemistry of CarbohydratesTaimoor HameedNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThrombophlebitisDokument10 SeitenThrombophlebitisapi-3797941Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 01 Edited PDFDokument10 SeitenCH 01 Edited PDFabbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipids PDFDokument71 SeitenLipids PDFmiallyannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PlatyhelminthesDokument7 SeitenPlatyhelminthesJam-jam N. AyongaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.1 The Nervous System and Nerve ImpulsesDokument60 Seiten8.1 The Nervous System and Nerve ImpulsesAmber Michaels100% (1)
- ANPH-M1-CU4. Skeletal SystemDokument26 SeitenANPH-M1-CU4. Skeletal SystemajdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Properties of LiquidsDokument7 SeitenPhysical Properties of LiquidsSubhamshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Lipids: Bio-Molecules Categorized As Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids and Nucleic Acids LipidsDokument5 SeitenClassification of Lipids: Bio-Molecules Categorized As Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids and Nucleic Acids Lipidsjoi orpillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ads or PtionDokument9 SeitenAds or PtionAnonymous QPwPG3DNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdsorptionDokument6 SeitenAdsorptionSathiyamoorthy SithurajNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdsoptionDokument18 SeitenAdsoptionmrskhan jalalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ads or PtionDokument29 SeitenAds or PtionAli UsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absorption & AdsorptionDokument16 SeitenAbsorption & Adsorptionparagaloni8365Noch keine Bewertungen
- Surface ChemistryDokument22 SeitenSurface ChemistryiycbrthoratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes ADSORPTIONDokument15 SeitenLecture Notes ADSORPTIONtony frankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - GasesDokument72 SeitenChapter 5 - GasesAmbar WatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 191020countertop Catalogue QUADRA-1Dokument41 Seiten191020countertop Catalogue QUADRA-1ZamzamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- FoldernamesDokument10 SeitenFoldernamesLEADER VISANoch keine Bewertungen
- Bom of Studs & Nuts For Balance SystemDokument4 SeitenBom of Studs & Nuts For Balance SystemmishtinilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Structural Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, M.B.M. Engineering College, Jai Narain Vyas University, JodhpurDokument10 SeitenDepartment of Structural Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, M.B.M. Engineering College, Jai Narain Vyas University, JodhpurAjayvidyanand SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cleanfreak® Tm4 15" CRB Scrubber With Renovators: Product DetailsDokument1 SeiteCleanfreak® Tm4 15" CRB Scrubber With Renovators: Product DetailsMartin JacoboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part - A: by Density Bottle MethodDokument7 SeitenPart - A: by Density Bottle MethodGorantla Ravi TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gold Recovery Resins Q & A 03Dokument3 SeitenGold Recovery Resins Q & A 03JendayiNoch keine Bewertungen
- WaterSaver Faucet CTBT Lab Service Fittings OnlineDokument146 SeitenWaterSaver Faucet CTBT Lab Service Fittings OnlineXavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Chaaban & Muzze, 1991) - Finite Element Analysis of Residual Stresses in Threaded End ClosuresDokument4 Seiten(Chaaban & Muzze, 1991) - Finite Element Analysis of Residual Stresses in Threaded End Closureschristos032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Astm B 330-2007Dokument5 SeitenAstm B 330-2007Ramsi Ankzi100% (1)
- Industrial Waste Management: Che 3101 G1 1/N 00 1/1Dokument2 SeitenIndustrial Waste Management: Che 3101 G1 1/N 00 1/1JAN JERICHO MENTOYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry: Classifying MatterDokument3 SeitenChemistry: Classifying MatterMa. Filipina AlejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Info Librel RMX 26Dokument4 SeitenTechnical Info Librel RMX 26Rijalul AuthonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Calculations Practice 2 PDFDokument2 SeitenHeat Calculations Practice 2 PDFRizqi HidayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shear Walls-Frame DesignDokument150 SeitenShear Walls-Frame Designsaikiran100% (5)
- Stability of ColumnsDokument45 SeitenStability of ColumnsjemnesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.4 Transition Metals Formation of Coloured Ions QsDokument27 Seiten2.4 Transition Metals Formation of Coloured Ions QsJesulayomi BolajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCD Chapter 3Dokument58 SeitenRCD Chapter 3jereck loquisoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TLE 9 READING MATERIALS 13 and 14Dokument2 SeitenTLE 9 READING MATERIALS 13 and 14Jeff LacasandileNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSDS PPCPDokument4 SeitenMSDS PPCPSivakumar AmbikapathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ceramic Brush On: Technical Reference InformationDokument2 SeitenCeramic Brush On: Technical Reference InformationAbdul RafiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Rules and SafetyDokument9 SeitenLaboratory Rules and SafetyMehul KhimaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fermi Surface: Notes By: Shahzaib ShahidDokument7 SeitenFermi Surface: Notes By: Shahzaib ShahidShazaib MirzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 19-Bulk Deformation Processes IIDokument38 SeitenChapter 19-Bulk Deformation Processes IIMuhammad Qasim QureshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weldability of Austenitic Manganese Steel: J. Mendez, M. Ghoreshy, W.B.F. Mackay, T.J.N. Smith, R.W. SmithDokument7 SeitenWeldability of Austenitic Manganese Steel: J. Mendez, M. Ghoreshy, W.B.F. Mackay, T.J.N. Smith, R.W. Smithนรวิชญ์ กาญจนามัยNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSDS - Avesta Passivator 601Dokument8 SeitenMSDS - Avesta Passivator 601geoanburajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Management Plan (Draft)Dokument18 Seiten1 - Management Plan (Draft)Sahil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitosek1993 Article OscillatoryLiquidFlowInElasticDokument15 SeitenMitosek1993 Article OscillatoryLiquidFlowInElasticbaja2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- LR Weld Certification Guide v1.3 SubscribeDokument24 SeitenLR Weld Certification Guide v1.3 SubscribeSergio Jesus SanjurjoNoch keine Bewertungen