Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Google 1
Hochgeladen von
Andi Trisnawaty InhaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Google 1
Hochgeladen von
Andi Trisnawaty InhaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Edition: ENGLISH DEUTSCH ESPAOL FRANAIS PORTUGUS
News & Perspective
Drugs & Diseases
CME & Education
HYPERLINK
Print
Log In
Register
"E:\\PRINT\\javascript:ReferencePrint();"
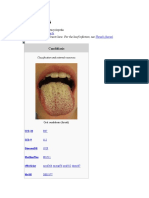
Candidiasis
Author: Jose A Hidalgo, MD; Chief Editor: Michael Stuart Bronze, MD more...
Overview
Presentation
DDx
Workup
Treatment
Medication
Follow-up
Updated: Aug 22, 2016
Practice Essentials
Background
Pathophysiology
Frequency
Mortality/Morbidity
Show All
Multimedia Library
References
Practice Essentials
Candidiasis (see the image below) is a fungal infection caused by yeasts from the
genus Candida. Candida albicans is the predominant cause of the disease.
HYPERLINK
"E:\\PRINT\\javascript:refimgshow(7)" Soreness and cracks at the lateral angles of
the mouth (angular cheilitis) are a frequent expression of candidiasis in elderly
individuals. Courtesy of Matthew C. Lambiase, DO.
Signs and symptoms
Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis
Findings reveal disfiguring lesions of the face, scalp, hands, and nails. Chronic
mucocutaneous candidiasis is occasionally associated with oral thrush and vitiligo.
Oropharyngeal candidiasis
Individuals with oropharyngeal candidiasis (OPC) usually have a history of HIV
infection, wear dentures, have diabetes mellitus, or have been exposed to broadspectrum antibiotics or inhaled steroids. Although patients are frequently
asymptomatic, when symptoms do occur, they can include the following:
Sore and painful mouth
Burning mouth or tongue
Dysphagia
Thick, whitish patches on the oral mucosa
Physical examination reveals a diffuse erythema and white patches that appear on the
surfaces of the buccal mucosa, throat, tongue, and gums.
The following are the 5 types of OPC:
Membranous candidiasis - One of the most common types; characterized by
creamy-white, curdlike patches on the mucosal surfaces
Chronic atrophic candidiasis (denture stomatitis) - Also thought to be one of the
most common forms of the disease; presenting signs and symptoms include
chronic erythema and edema of the portion of the palate that comes into
contact with dentures
Erythematous candidiasis - Associated with an erythematous patch on the hard
and soft palates
Angular cheilitis - Inflammatory reaction characterized by soreness, erythema,
and fissuring at the corners of the mouth
Mixed - A combination of any of the above types is possible
Esophageal candidiasis
Patients with esophageal candidiasis may be asymptomatic or may have 1 or more of
the following symptoms:
Normal oral mucosa (>50% of patients)
Dysphagia
Odynophagia
Retrosternal pain
Epigastric pain
Nausea and vomiting
Physical examination almost always reveals oral candidiasis.
Nonesophageal gastrointestinal candidiasis
The following symptoms may be present:
Epigastric pain
Nausea and vomiting
Abdominal pain
Fever and chills
Abdominal mass (in some cases)
Genitourinary tract candidiasis
The types of genitourinary tract candidiasis are as follows:
Vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) - Erythematous vagina and labia; a thick, curdlike
discharge; and a normal cervix upon speculum examination [1]
Candida balanitis - Penile pruritus and whitish patches on the penis
Candida cystitis - Many patients are asymptomatic, but bladder invasion may
result in frequency, urgency, dysuria, hematuria, and suprapubic pain
Asymptomatic candiduria - Most catheterized patients with persistent candiduria
are asymptomatic
Ascending pyelonephritis - Flank pain, abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting,
fever, chills and hematuria
Fungal balls - Intermittent urinary tract obstruction with subsequent anuria and
ensuing renal insufficiency
See Clinical Presentation for more detail.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic tests for candidiasis include the following:
Mucocutaneous candidiasis - For a wet mount, scrapings or smears obtained
from skin, nails, or oral or vaginal mucosa are examined under the microscope; a
potassium hydroxide smear, Gram stain, or methylene blue is useful for direct
demonstration of fungal cells
Cutaneous candidiasis - Using a wet mount, scrapings or smears obtained from
skin or nails can be examined under the microscope; potassium hydroxide
smears are also useful
Genitourinary candidiasis - A urinalysis should be performed; evidence of white
blood cells (WBCs), red blood cells (RBCs), protein, and yeast cells is common;
urine fungal cultures are useful
Gastrointestinal candidiasis - Endoscopy with or without biopsy
See Workup for more detail.
Management
See the list below:
Cutaneous candidiasis - Most localized cutaneous candidiasis infections can be
treated with any number of topical antifungal agents (eg, clotrimazole,
econazole, ciclopirox, miconazole, ketoconazole, nystatin)
Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis - This condition is generally treated with oral
azoles
Oropharyngeal candidiasis - This can be treated with either topical antifungal
agents or systemic oral azoles
Esophageal candidiasis - Treatment requires systemic therapy with fluconazole
VVC - Topical antifungal agents or oral fluconazole can be used
[2]
Candida cystitis - In noncatheterized patients, Candida cystitis should be treated
with fluconazole; in catheterized patients, the Foley catheter should be removed
or replaced; if the candiduria persists after the catheter change, then patients
can be treated with fluconazole
See Treatment and Medication for more detail.
Next Section: Background
READ MORE ABOUT CANDIDIASIS ON MEDSCAPE
RELATED REFERENCE TOPICS
Candidiasis Empiric Therapy
Cutaneous Candidiasis
Pediatric Candidiasis
RELATED NEWS AND ARTICLES
Yeast Infections in Pregnancy:
Recommended Treatments
Diagnosis and Management of Invasive
Candidiasis in the ICU
Induction Immunosuppression and
Clinical Outcomes in Kidney Transplant
Recipients Infected With Human
Immunodeficiency Virus
About Medscape Drugs & Diseases
HYPERLINK
"https://profreg.medscape.com/px/registration.do?src=ban_acq_ref_stm6"
ABOUT
About Medscape
Privacy Policy
Terms of Use
Advertising Policy
Help Center
MEMBERSHIP
Become a Member
Email Newsletters
Manage My Account
APPS
Medscape
MedPulse News
CME & Education
WebMD NETWORK
WebMD
MedicineNet
eMedicineHealth
RxList
WebMD Corporate
EDITIONS
English
Deutsch
Espaol
Franais
Portugus
All material on this website is protected by copyright, Copyright 1994-2016 by
WebMD LLC. This website also contains material copyrighted by 3rd parties.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Candidiasis MedscapeDokument36 SeitenCandidiasis MedscapesummiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Candida Info UptodateDokument40 SeitenCandida Info UptodateRamona RahimianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral CandidiasisDokument22 SeitenOral CandidiasisSherlocknovNoch keine Bewertungen
- CandidiasisDokument51 SeitenCandidiasisLincy JohnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esophagitis, Achalasia & Esophageal CancerDokument50 SeitenEsophagitis, Achalasia & Esophageal CancerhibaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Candidiasis: International Class MakalahDokument16 SeitenCandidiasis: International Class MakalahIrwan AzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Winter 1Dokument6 SeitenWinter 1Jam Knows RightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 2Dokument32 SeitenPresentation 2Dr. Bashir MehrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19 - Mycotic Infections FinalDokument18 Seiten19 - Mycotic Infections FinalMohammed GamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIDS and PeriodontiumDokument25 SeitenAIDS and PeriodontiumKarthik Krishna M100% (1)
- Genital Tract Infections Guide: TV, VVC, BV, CervicitisDokument70 SeitenGenital Tract Infections Guide: TV, VVC, BV, CervicitisAygulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Oral and Dental Manifestations of HIV InfectionDokument7 SeitenCommon Oral and Dental Manifestations of HIV InfectionGhaniyyatul KhudriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Candidiasis: Causes, Types, Symptoms & TreatmentDokument17 SeitenCandidiasis: Causes, Types, Symptoms & TreatmentSana KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genital Tract InfectionsDokument4 SeitenGenital Tract Infectionsmed.progressNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Causes and Treatment of BalanitisDokument5 SeitenThe Causes and Treatment of BalanitisHugo RanziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Candidiasis (Brut)Dokument6 SeitenCandidiasis (Brut)Ilyes FerenczNoch keine Bewertungen
- CandidiasisDokument6 SeitenCandidiasisNabrazz SthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CandidiasisDokument11 SeitenCandidiasisShakti RathodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Background LimfadenitisDokument29 SeitenBackground LimfadenitisWahyu Permata LisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Ibd)Dokument28 SeitenInflammatory Bowel Disease (Ibd)suhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Candidiasis (Hasznalt)Dokument4 SeitenCandidiasis (Hasznalt)Ilyes FerenczNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vih GastrointestinalDokument51 SeitenVih GastrointestinalRommel YánacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mucocutaneus Candidiasis: Dosen Pembimbing: DR - Dr.anni Andriani, SP - KK Pembimbing Residen: Dr. EvelynDokument37 SeitenMucocutaneus Candidiasis: Dosen Pembimbing: DR - Dr.anni Andriani, SP - KK Pembimbing Residen: Dr. EvelynHamizah Hasbullah100% (1)
- Clinical Microbiology MrcsDokument17 SeitenClinical Microbiology MrcsDeen MohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 961 Atharav CandidiasisDokument25 Seiten961 Atharav CandidiasisDevender MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opportunistic MycosesDokument31 SeitenOpportunistic MycosesMaxamed Faarax XaashiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Report OnDokument56 SeitenA Report OnweepauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hiv and GitDokument64 SeitenHiv and GitIsaac MwangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mucormycosis XyzzzDokument56 SeitenMucormycosis XyzzzMaliha TahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases/InfectionsDokument1 SeiteSexually Transmitted Diseases/InfectionsAnthony HartonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBD Guide: Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative ColitisDokument57 SeitenIBD Guide: Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative ColitissitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Fungal InfectionsDokument23 SeitenCommon Fungal Infections180045Noch keine Bewertungen
- CandidiasisDokument20 SeitenCandidiasisMoustafa Hazzaa100% (1)
- Oral Candidiasis: Madhu Priya.MDokument4 SeitenOral Candidiasis: Madhu Priya.MinventionjournalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral CandidiasisDokument18 SeitenOral CandidiasisRose DawoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBD Guide: Causes, Symptoms & Treatments for Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDokument4 SeitenIBD Guide: Causes, Symptoms & Treatments for Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseJustisia PadmiyatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Survey On Candida Drugs and ProbioticsDokument27 SeitenMarket Survey On Candida Drugs and ProbioticsStephen MooreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument51 SeitenPelvic Inflammatory Disease Diagnosis and TreatmentNorman AjxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Candidiasis: Epidemiology and MicrobiologyDokument5 SeitenCandidiasis: Epidemiology and MicrobiologyDeco BulaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDokument71 SeitenPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseGraceline Margaretha Marsintauly SianiparNoch keine Bewertungen
- Referat KonjungtivitisDokument21 SeitenReferat KonjungtivitisWyendae CliquersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fungal Diseases of The Oral MucosaDokument5 SeitenFungal Diseases of The Oral MucosaManar AlsoltanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dermnet NZ: Vulvovaginal CandidiasisDokument4 SeitenDermnet NZ: Vulvovaginal CandidiasismirrandapsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide to Oral Candidosis: Types, Causes and TreatmentsDokument39 SeitenGuide to Oral Candidosis: Types, Causes and TreatmentsArmada Eka FredianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goljan Notes Part 2Dokument166 SeitenGoljan Notes Part 2YU Ren Hua0% (1)
- Diseases of Oral Cavity: - Dr. Amar KumarDokument61 SeitenDiseases of Oral Cavity: - Dr. Amar KumarSudhanshu ShekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pemicu 1: Cornelius Kevin 405110022Dokument49 SeitenPemicu 1: Cornelius Kevin 405110022kheluwisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Candidiasis Kandidiasis/ KandidosisDokument19 SeitenCandidiasis Kandidiasis/ KandidosisAulya ArchuletaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MoniliasisDokument2 SeitenMoniliasis4gen_7100% (1)
- Gynecology StudyguideDokument39 SeitenGynecology StudyguideGameron777Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fungal InfectionsDokument20 SeitenFungal Infectionsallymyly88Noch keine Bewertungen
- AIDS and Periodontal DiseaseDokument25 SeitenAIDS and Periodontal DiseasePathivada LumbiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBD Obat Ganguan Saluran CernaDokument13 SeitenIBD Obat Ganguan Saluran CernaKhumairah mohtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- AudioDokument50 SeitenAudioshortysdavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gonorrhea - Practice Essentials, Background, Pathophysiology Sumber 13Dokument15 SeitenGonorrhea - Practice Essentials, Background, Pathophysiology Sumber 13Anizha AdriyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal Manifestation of HIVDokument16 SeitenGastrointestinal Manifestation of HIVashuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ludwig’s Angina, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandLudwig’s Angina, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ideal Candida Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Alleviate Candida Symptoms And Restore Gut Health With Nutritious RecipesVon EverandThe Ideal Candida Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Alleviate Candida Symptoms And Restore Gut Health With Nutritious RecipesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Article: Cerebral Malaria: A ReviewDokument6 SeitenReview Article: Cerebral Malaria: A ReviewAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stabilisasi GlukosaDokument23 SeitenStabilisasi GlukosaAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SK Ujian Komprehensif Thalliya Mabrukqay - 20190420180432Dokument3 SeitenSK Ujian Komprehensif Thalliya Mabrukqay - 20190420180432Andi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kak Cinta Daftar Pustaka: Animal Population. Australia: Charles Darwin University 2007. Accepted OnDokument4 SeitenKak Cinta Daftar Pustaka: Animal Population. Australia: Charles Darwin University 2007. Accepted OnAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cutaneous Candidiasis: BackgroundDokument4 SeitenCutaneous Candidiasis: BackgroundAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kak Cinta Daftar Pustaka: Animal Population. Australia: Charles Darwin University 2007. Accepted OnDokument4 SeitenKak Cinta Daftar Pustaka: Animal Population. Australia: Charles Darwin University 2007. Accepted OnAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Referat GgaDokument3 SeitenReferat GgaAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2Dokument2 Seiten2Andi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scabies Diagnosis and ManagementDokument5 SeitenScabies Diagnosis and ManagementAbdul Rauf ZakariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 Article 836Dokument11 Seiten2017 Article 836Andi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Referat Gga PDFDokument3 SeitenReferat Gga PDFAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Google 1Dokument8 SeitenGoogle 1Andi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Article: Cerebral Malaria: A ReviewDokument6 SeitenReview Article: Cerebral Malaria: A ReviewAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Referat GgaDokument3 SeitenReferat GgaAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 95 PDFDokument6 Seiten95 PDFAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CXCL4 and CXCL10 Predict Risk of Fatal Cerebral Malaria: A B C D e B e F D B, G ADokument12 SeitenCXCL4 and CXCL10 Predict Risk of Fatal Cerebral Malaria: A B C D e B e F D B, G AAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kak Cinta Daftar Pustaka: Animal Population. Australia: Charles Darwin University 2007. Accepted OnDokument4 SeitenKak Cinta Daftar Pustaka: Animal Population. Australia: Charles Darwin University 2007. Accepted OnAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cutaneous Candidiasis: BackgroundDokument4 SeitenCutaneous Candidiasis: BackgroundAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scabies Diagnosis and ManagementDokument5 SeitenScabies Diagnosis and ManagementAbdul Rauf ZakariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scabies Diagnosis and ManagementDokument5 SeitenScabies Diagnosis and ManagementAbdul Rauf ZakariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kak Cinta Daftar Pustaka: Animal Population. Australia: Charles Darwin University 2007. Accepted OnDokument4 SeitenKak Cinta Daftar Pustaka: Animal Population. Australia: Charles Darwin University 2007. Accepted OnAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kak Cinta Daftar Pustaka: Animal Population. Australia: Charles Darwin University 2007. Accepted OnDokument4 SeitenKak Cinta Daftar Pustaka: Animal Population. Australia: Charles Darwin University 2007. Accepted OnAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scabies Diagnosis and ManagementDokument5 SeitenScabies Diagnosis and ManagementAbdul Rauf ZakariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Program Studi S1 Ilmu Keperawatan Universitas Airlangga Kampus C Unair Mulyorejo Surabaya 6011 Telp. (031) 5913752, 5913754, Fax. (031) 5913257 EmailDokument12 SeitenProgram Studi S1 Ilmu Keperawatan Universitas Airlangga Kampus C Unair Mulyorejo Surabaya 6011 Telp. (031) 5913752, 5913754, Fax. (031) 5913257 EmailnindyNoch keine Bewertungen
- GoogleDokument4 SeitenGoogleAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cutaneous Candidiasis: BackgroundDokument4 SeitenCutaneous Candidiasis: BackgroundAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cutaneous Candidiasis: BackgroundDokument4 SeitenCutaneous Candidiasis: BackgroundAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kak Cinta Daftar Pustaka: Animal Population. Australia: Charles Darwin University 2007. Accepted OnDokument4 SeitenKak Cinta Daftar Pustaka: Animal Population. Australia: Charles Darwin University 2007. Accepted OnAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cutaneous Candidiasis: BackgroundDokument4 SeitenCutaneous Candidiasis: BackgroundAndi Trisnawaty InhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Analysis of Biosensors For Food Safety: Industry ReviewDokument6 SeitenMarket Analysis of Biosensors For Food Safety: Industry ReviewHai HuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach To Fever: History and Clinical ExaminationDokument6 SeitenApproach To Fever: History and Clinical Examinationdrbhaskar100% (1)
- EBOLA Virus DiseaseDokument5 SeitenEBOLA Virus DiseaseLeah Malate100% (1)
- Coronavirus PandemicDokument3 SeitenCoronavirus Pandemicmysterium slayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapeh 8 Q3Dokument5 SeitenMapeh 8 Q3Sarah Jane PescadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kingdom Fungi NotesDokument4 SeitenKingdom Fungi NotesAmi GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Virology Manual (PDFDrive)Dokument639 SeitenClinical Virology Manual (PDFDrive)Shweta KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARI: Acute Respiratory Infection GuideDokument29 SeitenARI: Acute Respiratory Infection GuideJam Knows RightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimum Medical Solutions CatalogueDokument20 SeitenOptimum Medical Solutions CatalogueOptimum Medical SolutionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ari Full ThesisDokument116 SeitenAri Full Thesisarti gaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resistance of Human Cytomegalovirus To Ganciclovirvalganciclovir ADokument14 SeitenResistance of Human Cytomegalovirus To Ganciclovirvalganciclovir ABianca GamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of Parasited (Parasitology)Dokument9 SeitenTable of Parasited (Parasitology)abcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Candida Species and Oral ThrushDokument11 SeitenCandida Species and Oral ThrushHukjvccx JjyfdxxvbNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADA Medications PDFDokument24 SeitenADA Medications PDFRoshni GehlotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To BacteriologyDokument1 SeiteIntroduction To BacteriologySeon u 'Noch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Genetic Engineering: Medicine IndustriesDokument4 SeitenApplications of Genetic Engineering: Medicine Industries19ucha023 19ucha023Noch keine Bewertungen
- Remedies of The Talmud: A Second Look at The Medical Benefits of HoneyDokument2 SeitenRemedies of The Talmud: A Second Look at The Medical Benefits of Honeyoutdash2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instielts TravellerDokument2 SeitenInstielts TravellerKamolpan Jammapat57% (7)
- Hiv Aids in Neonatology - LPDokument36 SeitenHiv Aids in Neonatology - LPMallika JoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communicable Disease Prevention GuideDokument197 SeitenCommunicable Disease Prevention Guidedennisjamesbartz100% (1)
- BIO 205 Chapter 8 PowerpointDokument16 SeitenBIO 205 Chapter 8 PowerpointDrPearcyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA CHN Post TestDokument3 SeitenCA CHN Post TestKristaMaeC.LazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Report: Management of Dairy Farm: Klebsiella SPP Mastitis On ADokument9 SeitenCase Report: Management of Dairy Farm: Klebsiella SPP Mastitis On ApramiswariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumonia Case: 35-Year-Old Male with Fever and CoughDokument11 SeitenPneumonia Case: 35-Year-Old Male with Fever and CoughDale Maninantan De DiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) : B.Sc. I Botany Unit - I Lecture - 3Dokument5 SeitenTobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) : B.Sc. I Botany Unit - I Lecture - 3vineetvishal73100% (1)
- Homeopathic Approach To COVID-19 A ReviewDokument6 SeitenHomeopathic Approach To COVID-19 A ReviewAgasthya anikiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Pakai 2 (Diagnosis, Tatalaksana) Efusi PerikardiumDokument9 SeitenJurnal Pakai 2 (Diagnosis, Tatalaksana) Efusi PerikardiumSatrya DitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal Examination Guide - MRCPCH Clinical RevisionDokument16 SeitenAbdominal Examination Guide - MRCPCH Clinical Revisionbairdman12Noch keine Bewertungen
- 107 Studies On VaccineDokument65 Seiten107 Studies On VaccineiRepair Gold Coast100% (1)
- A Case Study of Ankylosing SpondylitisDokument10 SeitenA Case Study of Ankylosing SpondylitisVenkatesan VidhyaNoch keine Bewertungen