Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Psychology Lecture 3
Hochgeladen von
shamim3261Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Psychology Lecture 3
Hochgeladen von
shamim3261Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lecture #3
Chapter 2
Neuroscience and Behavior
-Basic premise: everything psychological is simultaneously biological
-Behavior, thought, mood, etc... is the product of activity among billions and billions of
interconnected cells called neurons.
___________ myelin sheath terminal branches of axon
__________| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||/-------------<
__________|cell body |_____axon _______________________-----------------<
__________|___________|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||\__________
dendrites ->->neural impulses->->
-How do neurons communicate?
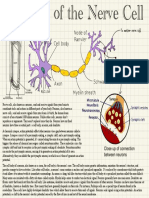
-Each neuron contains:
-a cell body
-two types of branching fibers
-dendrites: receive messages from other cells and pass it to
the cell body
-short bushes of fiber
-axon: passes neural message (information) from the cell
body and passes it to the other neurons, muscles or
glands
-can be short or long (e.g. short in brain, long in leg)
-extensions of the neuron
-usually end in terminal branch
-many axons are covered in a fatty substance, called
myelin (the myelin sheath)
-increases speed of neural message traveling along
the axon (neural conduction)
-as you get older, you get more and more myelin
-cells with no myelin = gray matter, cells with
myelin = white matter
-Multiple Sclerosis - decay of the myelin - causes
lots of problems: loss of motor and mental
abilities
How do neurons work?
- the neuron fires a brief electrical impulse when stimulated by heat, light, sound,
pressure, chemicals, etc. (e.g. you put your finger near a flame)
-the impulse is called an action potential
-Occurs in one part of the neuron, then travels the length of the neuron (down the
axon) to the next cell
-the brain is bathed in salt water - inside and outside each cell are ions (charged
particles)
+ + + sodium and chloride + + + (outside axon)
- - - - potassium- - - - - - - (inside axon)
+ + + sodium and chloride + + + (outside axon)
-when the cell is at rest, the inside o f the cell is more negatively charged than the
outside, because the positively charged sodium ions are kept outside the cell
-the cell becomes less negative when stimulated, because channels in the cell
open up allowing positive sodium ions outside to flow inside -> this causes the
cell to depolarize -> if it depolarizes enough, it triggers an action potential
-e.g.
+++++++++ - ---++++++
- - - - - - - - - - - - - -> +++++-------
++++++++++ -------+++++
-once a cell depolarizes in one part, it triggers the next part to open its sodium
channels to depolarize that part - this carries the action potential down the length
of the cell
-an action potential in one part of the cell triggers succeeding action potentials in
adjacent parts of the cell, which is how the neural message is carried along the
cell
-after the action potential: pumps move the sodium outside and the potassium
inside so the cell is polarized once again
-How does a message communicate with the next cell?
-the axon terminals of the sending cell are filled with round sacks (vesicles) which
contain a chemical (neurotransmitter)
-an action potential causes the vesicles to move down the terminal fibers and
release the neurotransmitter
-the axon terminals of the sending cell almost but not quite touch the surface of
the receiving cell - the gap is called a synapse
-the neurotransmitter travels across the synapse into the receptors in the dendrites
of the next cell
The axon terminals of one cell almost, but not quite, tough the surface of another cell -
the gap is called the synapse - when an action potential reaches the axon terminal, the
even causes vesicles, containing neurotransmitters, to release the neurotransmitter,
which flows out of the sending neuron, across the synapse to the receptor sites on the
receiving neuron - that process can trigger an action potential in the receiving neurons
-different neurotransmitters fit into particular receptors “like a key in a lock”
-how do they know what path to take?
-paths are laid down by genetics
-memory/experience can also lay down neural paths
-There are at least seventy -five types of neurotransmitters
-e.g. serotonin and dopamine
-both are related to mood disorders
-both are in the limbic system
-both have their own neurons that they like to stimulate
-neurotransmitters have receptor sites that they fit into like a key in a lock
-the two effects a neurotransmitter can have:
1.) Excitatory - makes an action potential more likely to happen - allows
sodium to flow into the cell e.g. acetylcholine (ACh) is released at
muscle junctures and activates the movements of muscles
2.) Inhibitory - makes an action potential less likely to happen-
hyperpolarizes the cell, e.g. GABA makes cells stop firing to
inhibit activity
The all or none principle
-any given cell can receive both excitory and inhibitory neurotransmitters
-to fire, a receiving cell must receive more excitatory than inhibitory
neurotransmitters and they must exceed the threshold
- if it does not exceed the threshold the cell will not fire
-strong excitation does not case stronger action potentials
-like a gun: the trigger must be pulled past a certain point in order for it to fire,
and it will not fire differently depending on how the trigger is pulled
-it explains a lot of our behavior when we take chemicals that affect
neurotransmitters
Drugs and Poisons
-Poisons that affect ACh
1)Curare - poison used in hunting by natives - paralyses prey
-is chemically similar to ACh - it fits into the ACh receptor sites but will
not cause the sodium channels to open - blocks ACh from working
-ACh antagonist - it blocks the action of ACh
2)Botulin (botulinum toxin)
-comes from improperly canned food
-blocks release of ACh from the axon terminal
-causes paralysis, loss of feeling, and sometimes death (the heart and lungs
are paralyzed)
-used in bo-tox cosmetic treatments - smoothes out wrinkles by paralyzing
the face
-can also relieve some diseases
3)Venom of the Black Widow spider
-causes convulsions
-causes ACh to flood across the axon terminal - mass activation of
muscles
-you can convulse to violently that you die
-take home point: these 3 poisons have 3 different effects on the same
neurotransmitter
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Depression and Coronary Heart DiseaseDokument2 SeitenDepression and Coronary Heart Diseaseshamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology Recitation - 13Dokument2 SeitenPsychology Recitation - 13shamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- ObicityDokument2 SeitenObicityshamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Disease SpeechDokument3 SeitenHeart Disease Speechshamim326150% (2)
- Psychology Test 1 Practice QuestionsDokument6 SeitenPsychology Test 1 Practice Questionsshamim326180% (5)
- Psychology Test 2 Practice QuestionsDokument15 SeitenPsychology Test 2 Practice Questionsshamim3261100% (3)
- Psychology Test 3 Practice QuestionsDokument15 SeitenPsychology Test 3 Practice Questionsshamim326175% (4)
- Psychology Recitation - 12Dokument2 SeitenPsychology Recitation - 12shamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology Recitation - 9Dokument2 SeitenPsychology Recitation - 9shamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology Recitation - 10Dokument2 SeitenPsychology Recitation - 10shamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology Recitation - 8Dokument2 SeitenPsychology Recitation - 8shamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology Recitation - 11Dokument2 SeitenPsychology Recitation - 11shamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology Recitation - 6Dokument2 SeitenPsychology Recitation - 6shamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology Recitation - 7Dokument1 SeitePsychology Recitation - 7shamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology Recitation - 2Dokument2 SeitenPsychology Recitation - 2shamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology Lecture 2Dokument4 SeitenPsychology Lecture 2shamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology Recitation - 3Dokument1 SeitePsychology Recitation - 3shamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Recitation Sections Learning Objectives: Measures of Central Tendency and Measures of VariationDokument4 SeitenRecitation Sections Learning Objectives: Measures of Central Tendency and Measures of Variationshamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology Recitation - 4Dokument2 SeitenPsychology Recitation - 4shamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution in Action: Medicine'S Challenge in Countering Resistant Strains of Harmful BacteriaDokument8 SeitenEvolution in Action: Medicine'S Challenge in Countering Resistant Strains of Harmful Bacteriashamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Work of Alexander GlazunovDokument6 SeitenComplete Work of Alexander Glazunovshamim3261100% (2)
- Lecture 1 OutlineDokument1 SeiteLecture 1 Outlineshamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Preview of "Chapter 12 PPT Pot"Dokument16 SeitenPreview of "Chapter 12 PPT Pot"shamim3261100% (1)
- Cerebral CortexDokument5 SeitenCerebral Cortexshamim3261Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modified Test 2 ReviewDokument9 SeitenModified Test 2 Reviewshamim3261100% (1)
- Cow Eye DissectionDokument8 SeitenCow Eye Dissectionshamim3261100% (4)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Chapter 22 - Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems - Nursing Test BanksDokument36 SeitenChapter 22 - Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems - Nursing Test BanksNeLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 15 Man-Machine Systems: StructureDokument21 SeitenUnit 15 Man-Machine Systems: StructureNikhil PrasannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson # 8 - The Nerve ImpulseDokument4 SeitenLesson # 8 - The Nerve ImpulseSmith PennanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System ReviewerDokument9 SeitenNervous System ReviewerPlacido Edgar MagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To PsychopharmacologyDokument48 SeitenIntro To PsychopharmacologyKhadija ArshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ion ChannelsDokument6 SeitenIon ChannelsNicolas IsformermynameNoch keine Bewertungen
- WBI05 01 MSC 20180124Dokument24 SeitenWBI05 01 MSC 20180124Asem BarhoushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen BioDokument86 SeitenGen BioPaul MagbagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Electrophysiology Signaling and ResponsesDokument381 SeitenPlant Electrophysiology Signaling and ResponsesGradina PovestilorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiological Response To Electrical StimuliDokument19 SeitenPhysiological Response To Electrical StimuliArathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Quest 9Dokument76 SeitenScience Quest 9Naushin HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PharmacologyDokument7 SeitenPharmacologyraquel maniegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boettiger 1960. Insect Flight Muscles and Their Basic PhysiologyDokument16 SeitenBoettiger 1960. Insect Flight Muscles and Their Basic PhysiologyRenan Nascimento LeiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 .Intro of Biosignal ProcessingDokument38 Seiten1 .Intro of Biosignal ProcessingAmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- StrychnineDokument20 SeitenStrychnineMarc DuqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.5 Neurons SynapsesDokument57 Seiten6.5 Neurons SynapsesTae Soo LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practico para Revisar Labaxon 5.2 WorkbookDokument44 SeitenPractico para Revisar Labaxon 5.2 WorkbookMARIA JOSE RODRIGUEZ BARONANoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - Nerve - MuscleDokument11 Seiten5 - Nerve - Musclesame200100% (1)
- Biology PosterDokument1 SeiteBiology PosterNoobmaster666Noch keine Bewertungen
- GABA ReceptorDokument6 SeitenGABA ReceptorAthena NocetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 7 The Muscular SystemDokument13 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 7 The Muscular System俺気健人Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing Neurologic System: Mabini CollegesDokument25 SeitenAssessing Neurologic System: Mabini CollegesNicole NipasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument64 SeitenNervous SystemRiyas AfdalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument2 SeitenNervous SystemShanel Aubrey AglibutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phyp211 - Week 2Dokument2 SeitenPhyp211 - Week 2KHRIZZA PAULETTE ANTIFORDA VEGANoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology - Module 5Dokument12 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology - Module 5JayR MendonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Psychology 1st Edition Ebook PDFDokument41 SeitenPrinciples of Psychology 1st Edition Ebook PDFwillie.dorich827100% (38)
- ERR Holiday HomeworkDokument6 SeitenERR Holiday HomeworkJefferyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analyse Signal EMGDokument12 SeitenAnalyse Signal EMGAlfonso Molina RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 Coordination and Response (Repaired)Dokument18 SeitenChapter 12 Coordination and Response (Repaired)yokekeannNoch keine Bewertungen