Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
DC and Semiconductors
Hochgeladen von
Kirz SerranoCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DC and Semiconductors
Hochgeladen von
Kirz SerranoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DC
Chapter 1: Basic Concepts Of Electricity
o
Static electricity
Conductors, insulators, and electron flow
Electric circuits
Voltage and current
Resistance
Voltage and current in a practical circuit
Conventional versus electron flow
Contributors
Chapter 2: Ohm's Law
o
How voltage, current, and resistance relate
An analogy for Ohm's Law
Power in electric circuits
Calculating electric power
Resistors
Nonlinear conduction
Circuit wiring
Polarity of voltage drops
Computer simulation of electric circuits
Contributors
Chapter 3: Electrical Safety
o
The importance of electrical safety
Physiological effects of electricity
Shock current path
Ohm's Law (again!)
Safe practices
Emergency response
Common sources of hazard
Safe circuit design
Safe meter usage
Electric shock data
Contributors
Chapter 4: Scientific Notation And Metric
Prefixes
o
Scientific notation
Arithmetic with scientific notation
Metric notation
Metric prefix conversions
Hand calculator use
Scientific notation in SPICE
Contributors
Chapter 5: Series And Parallel Circuits
o
What are "series" and "parallel" circuits?
Simple series circuits
Simple parallel circuits
Conductance
Power calculations
Correct use of Ohm's Law
Component failure analysis
Building simple resistor circuits
Contributors
Chapter 6: Divider Circuits And Kirchhoff's
Laws
o
Voltage divider circuits
Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL)
Current divider circuits
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)
Contributors
Chapter 7: Series-parallel Combination
Circuits
o
What is a series-parallel circuit?
Analysis technique
Re-drawing complex schematics
Component failure analysis
Building series-parallel resistor circuits
Contributors
Chapter 8: DC Metering Circuits
o
What is a meter?
Voltmeter design
Voltmeter impact on measured circuit
Ammeter design
Ammeter impact on measured circuit
Ohmmeter design
High voltage ohmmeters
Multimeters
Kelvin (4-wire) resistance measurement
Bridge circuits
Wattmeter design
Creating custom calibration resistances
Contributors
Chapter 9: Electrical Instrumentation Signals
o
Analog and digital signals
Voltage signal systems
Current signal systems
Tachogenerators
Thermocouples
pH measurement
Strain gauges
Contributors
Chapter 10: Dc Network Analysis
o
What is network analysis?
Branch current method
Mesh current method
Node voltage method
Introduction to network theorems
Millman's Theorem
Superposition Theorem
Thevenin's Theorem
Norton's Theorem
Thevenin-Norton equivalencies
Millman's Theorem revisited
Maximum Power Transfer Theorem
-Y and Y- conversions
Contributors
Chapter 11: Batteries And Power Systems
Electron activity in chemical reactions
Battery construction
Battery ratings
Special-purpose batteries
Practical considerations
Contributors
Chapter 12: Physics Of Conductors And
Insulators
o
Introduction
Conductor size
Conductor ampacity
Fuses
Specific resistance
Temperature coefficient of resistance
Superconductivity
Insulator breakdown voltage
Data
Contributors
Chapter 13: Capacitors
o
Electric fields and capacitance
Capacitors and calculus
Factors affecting capacitance
Series and parallel capacitors
Practical considerations
Contributors
Chapter 14: Magnetism And Electromagnetism
o
Permanent magnets
Electromagnetism
Magnetic units of measurement
Permeability and saturation
Electromagnetic induction
Mutual inductance
Contributors
Chapter 15: Inductors
o
Magnetic fields and inductance
Inductors and calculus
Factors affecting inductance
Series and parallel inductors
Practical considerations
Contributors
Chapter 16: Rc And L/r Time Constants
o
Electrical transients
Capacitor transient response
Inductor transient response
Voltage and current calculations
Why L/R and not LR?
Complex voltage and current calculations
Complex circuits
Solving for unknown time
Contributors
Semiconductors
Chapter 1: Amplifiers And Active Devices
o
From electric to electronic
Active versus passive devices
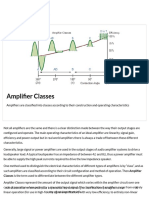
Amplifiers
Amplifier gain
Decibels
Absolute dB scales
Attenuators
Contributors
Chapter 2: Solid-state Device Theory
o
Introduction
Quantum physics
Valence and Crystal structure
Band theory of solids
Electrons and ``holes''
The P-N junction
Junction diodes
Bipolar junction transistors
Junction field-effect transistors
Insulated-gate field-effect transistors (MOSFET)
Thyristors
Semiconductor manufacturing techniques
Superconducting devices
Quantum devices
Semiconductor devices in SPICE
Contributors
Chapter 3: Diodes And Rectifiers
o
Introduction
Meter check of a diode
Diode ratings
Rectifier circuits
Peak detector
Clipper circuits
Clamper circuits
Voltage multipliers
Inductor commutating circuits
Diode switching circuits
Zener diodes
Special-purpose diodes
Other diode technologies
SPICE models
Contributors
Chapter 4: Bipolar Junction Transistors
o
Introduction
The transistor as a switch
Meter check of a transistor
Active mode operation
The common-emitter amplifier
The common-collector amplifier
The common-base amplifier
The cascode amplifier
Biasing techniques
Biasing calculations
Input and output coupling
Feedback
Amplifier impedances
Current mirrors
Transistor ratings and packages
BJT quirks
Chapter 5: Junction Field-effect Transistors
o
Introduction
The transistor as a switch
Meter check of a transistor
Active-mode operation
The common-source amplifier -- PENDING
The common-drain amplifier -- PENDING
The common-gate amplifier -- PENDING
Biasing techniques -- PENDING
Transistor ratings and packages -- PENDING
JFET quirks -- PENDING
Chapter 6: Insulated-gate Field-effect
Transistors
o
Introduction
Depletion-type IGFETs
Enhancement-type IGFETs -- PENDING
Active-mode operation -- PENDING
The common-source amplifier -- PENDING
The common-drain amplifier -- PENDING
The common-gate amplifier -- PENDING
Biasing techniques -- PENDING
Transistor ratings and packages -- PENDING
IGFET quirks -- PENDING
MESFETs -- PENDING
IGBTs
Chapter 7: Thyristors
o
Hysteresis
Gas discharge tubes
The Shockley Diode
The DIAC
The Silicon-Controlled Rectifier (SCR)
The TRIAC
Optothyristors
The Unijunction Transistor (UJT)
The Silicon-Controlled Switch (SCS)
Field-effect-controlled thyristors
Chapter 8: Operational Amplifiers
o
Introduction
Single-ended and differential amplifiers
The "operational" amplifier
Negative feedback
Divided feedback
An analogy for divided feedback
Voltage-to-current signal conversion
Averager and summer circuits
Building a differential amplifier
The instrumentation amplifier
Differentiator and integrator circuits
Positive feedback
Practical considerations
Operational amplifier models
Data
Contributors
Chapter 9: Practical Analog Semiconductor
Circuits
ElectroStatic Discharge
Power supply circuits -- INCOMPLETE
Amplifier circuits -- PENDING
Oscillator circuits -- INCOMPLETE
Phase-locked loops -- PENDING
Radio circuits -- INCOMPLETE
Computational circuits
Measurement circuits -- INCOMPLETE
Control circuits -- PENDING
Contributors
Chapter 10: Active Filters
Chapter 11: DC Motor Drives
o
Pulse Width Modulation
Contributors
Chapter 12: Inverters And Ac Motor Drives
Chapter 13: Electron Tubes
o
Introduction
Early tube history
The triode
The tetrode
Beam power tubes
The pentode
Combination tubes
Tube parameters
Ionization (gas-filled) tubes
Display tubes
Microwave tubes
Tubes versus Semiconductors
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- E-Book Guide Radio TransmittersDokument10 SeitenE-Book Guide Radio TransmittersJCNoch keine Bewertungen
- EI2203 - Electronic Devices and Circuits - 2 Marks With AnswersDokument16 SeitenEI2203 - Electronic Devices and Circuits - 2 Marks With AnswersASPCN 2017Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECE Department's Electronic Circuits CourseDokument27 SeitenECE Department's Electronic Circuits CourseklnayaagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eecim02 Course MaterialDokument42 SeitenEecim02 Course Materialsmahesh_1980Noch keine Bewertungen
- 09ec304 Electronic Circuits I 3 1 0 4Dokument2 Seiten09ec304 Electronic Circuits I 3 1 0 4Balaji DuraiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec 2 MARKSDokument0 SeitenEc 2 MARKScalinshabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDC Question Bank 18Dokument33 SeitenEDC Question Bank 18kalaiselvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Engineering SyllabusDokument1 SeiteElectronics Engineering Syllabuspcjoshi02Noch keine Bewertungen
- Common To E&C and EI&C: Department of Technical EducationDokument10 SeitenCommon To E&C and EI&C: Department of Technical EducationVikram RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BANNARI AMMAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ELECTRON DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LABDokument3 SeitenBANNARI AMMAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ELECTRON DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LABnandhakumarmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer The FollowingDokument12 SeitenAnswer The FollowingPrabhat SagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electronics 131101Dokument2 SeitenBasic Electronics 131101Sanjay AdwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec1 SyllabusDokument2 SeitenEc1 SyllabusVinoth Kumar MNoch keine Bewertungen
- HISTORY OF ELECTRONICSDokument8 SeitenHISTORY OF ELECTRONICSTrinidad TalanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment6ManualDokument6 SeitenExperiment6ManualAiden PierceNoch keine Bewertungen
- REC101 / REC201 Electronics EngineeringDokument1 SeiteREC101 / REC201 Electronics EngineeringAmit GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edc Unit 1Dokument62 SeitenEdc Unit 1raghul100% (1)
- Syllabus For Written Examination of Work Experience TeacherDokument8 SeitenSyllabus For Written Examination of Work Experience TeacherAnkitvats VatsNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Converters in Equilibrium: 2. Principles of Steady State Converter AnalysisDokument4 SeitenI. Converters in Equilibrium: 2. Principles of Steady State Converter AnalysisJiaweiDuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesDokument128 SeitenEee-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesraghudatheshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2: Electricity and Magnetism, Ac Theory & Electronics and Atomic & Nuclear PhyDokument3 SeitenUnit 2: Electricity and Magnetism, Ac Theory & Electronics and Atomic & Nuclear PhyJodie HowellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Made Easy Previous Year SSC Je Question PapersDokument14 SeitenMade Easy Previous Year SSC Je Question PapersSyedsaqibali100% (1)
- Study of Clipper and Clamper CircuitDokument5 SeitenStudy of Clipper and Clamper Circuitmabrur nabilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Components HandDokument12 SeitenElectronic Components HandjainkamalkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus For Kvs TGT We ExamDokument9 SeitenSyllabus For Kvs TGT We ExamsaralabitmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological University: B.E Semester: 3 Electronics & Telecommunication EngineeringDokument2 SeitenGujarat Technological University: B.E Semester: 3 Electronics & Telecommunication EngineeringChirag PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics (Basics Diodes)Dokument130 SeitenElectronics (Basics Diodes)ramanaidu1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eto Handout1 DiodeDokument20 SeitenEto Handout1 DiodedawitNoch keine Bewertungen
- C-Viva Report2 For EceDokument206 SeitenC-Viva Report2 For EceSunil Setty MalipeddiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TERMSDokument14 SeitenTERMSArnel Pamaos Lopiba MontañezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThiristorDokument10 SeitenThiristorNarasimhaPrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE4532 Part A Lecture - pdf0Dokument83 SeitenEE4532 Part A Lecture - pdf0Denise Isebella LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus For Written Examination of TGT (Work Experience)Dokument4 SeitenSyllabus For Written Examination of TGT (Work Experience)Sandhya DeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Device Circuit Lab SheetDokument27 SeitenElectronics Device Circuit Lab Sheetjimfinch512Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesDokument128 SeitenEee-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesDilip TheLipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senkottai Village, Madurai - Sivagangai Main Road, Madurai - 625 020. (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution)Dokument23 SeitenSenkottai Village, Madurai - Sivagangai Main Road, Madurai - 625 020. (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution)Raji SharmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Circuit Lab ReportDokument9 SeitenElectrical Circuit Lab Reportapi-297082885100% (1)
- E&M Question BankDokument18 SeitenE&M Question BankEzhilya VenkatNoch keine Bewertungen
- TGT Work ExperiewnceDokument5 SeitenTGT Work ExperiewnceHƏÞƏŘŒ ĐŒXÝNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMS LAB PLAN TITLEDokument56 SeitenEMS LAB PLAN TITLEKrishna Kolanu83% (6)
- Measurements Lab Manual PDFDokument56 SeitenMeasurements Lab Manual PDFAnnie Rachel100% (2)
- Ece-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesDokument238 SeitenEce-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesShubhesh SwainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - I Electrical - BeeeDokument27 SeitenUnit - I Electrical - BeeeBubblee BennuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - NotesDokument170 SeitenEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - NoteschaitanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FEE Module 4Dokument10 SeitenFEE Module 4fasnamditNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics ComponentsDokument51 SeitenElectronics ComponentsMarlon AranasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Circuit 1Dokument23 SeitenChapter 2 Circuit 1peterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slides Lec 1-2Dokument26 SeitenSlides Lec 1-2ali tariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological University: Course Name: Electronic Devices and Circuits - IDokument3 SeitenGujarat Technological University: Course Name: Electronic Devices and Circuits - IadeliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components 1. Diode: Semiconductor DiodesDokument8 SeitenComponents 1. Diode: Semiconductor DiodesVaranasi RamakrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics: Switches and ConvertersVon EverandPower Electronics: Switches and ConvertersBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Ii YearDokument27 SeitenElectronic Devices and Circuits - Ii YearT ThirumuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fybscit Arun Sir ElectronicsDokument31 SeitenFybscit Arun Sir Electronicssaleem_almaqashiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonVon EverandSolid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- Nonlinear Electronics 1: Nonlinear Dipoles, Harmonic Oscillators and Switching CircuitsVon EverandNonlinear Electronics 1: Nonlinear Dipoles, Harmonic Oscillators and Switching CircuitsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Calculus NotesDokument10 SeitenDifferential Calculus NotesKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: - : Summative Test Grade & Section: Date: Subject: Earth and Life ScienceDokument1 SeiteName: - : Summative Test Grade & Section: Date: Subject: Earth and Life ScienceKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1:: Republic Act 9292Dokument5 SeitenTopic 1:: Republic Act 9292Kirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra 1&2 ReviewerDokument4 SeitenAlgebra 1&2 ReviewerKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB CommandsDokument6 SeitenTB CommandsKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Thesis Chapter 1Dokument6 SeitenSample Thesis Chapter 1van7wicca93% (54)
- Letter of RecoDokument1 SeiteLetter of RecoKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Mensuration ReviewDokument8 SeitenSolid Mensuration ReviewKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Segment ReportingDokument2 SeitenSegment ReportingDhan MarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conceptual FrameworkDokument5 SeitenConceptual Frameworkchaleen23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Amplifier Classes and The Classification of AmplifiersDokument11 SeitenAmplifier Classes and The Classification of AmplifiersKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elecs Final ExamDokument6 SeitenElecs Final ExamKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- w9 234 HDokument30 Seitenw9 234 HKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active FilterDokument3 SeitenActive FilterKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnhydrousDokument2 SeitenAnhydrousKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certification For InterviewDokument1 SeiteCertification For InterviewKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lightning ArresterDokument2 SeitenLightning ArresterKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object StorageDokument10 SeitenObject StorageKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus I, Section 3.9, #20: Baseball Diamond RatesDokument2 SeitenCalculus I, Section 3.9, #20: Baseball Diamond RatesKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- External StorageDokument3 SeitenExternal StorageKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiplexing 7 Segment Display Using PIC Microcontroller PDFDokument7 SeitenMultiplexing 7 Segment Display Using PIC Microcontroller PDFKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Superheterodyne TransmitterDokument3 SeitenSuperheterodyne TransmitterKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- QAM Error RatesDokument1 SeiteQAM Error RatesKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate of Parental/Guardian Consent: Noted byDokument5 SeitenCertificate of Parental/Guardian Consent: Noted byKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposal Defense Panel Comments and RevisionsDokument1 SeiteProposal Defense Panel Comments and RevisionsKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus I, Section 3.9, #20: Baseball Diamond RatesDokument2 SeitenCalculus I, Section 3.9, #20: Baseball Diamond RatesKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ordinary Differential Equations PDFDokument26 SeitenOrdinary Differential Equations PDFdivyasatthishNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB CommandsDokument6 SeitenTB CommandsKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Proposal Writing PDFDokument3 Seiten06 Proposal Writing PDFKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- KBP Broadcast CodeDokument3 SeitenKBP Broadcast CodeKirz SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ed Lab ManualDokument27 SeitenEd Lab ManualBonnieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Year Project ReportDokument61 SeitenFinal Year Project ReportKibetfredrick100% (1)
- Revealing Hidden Interfaces in Organic SemiconductorsDokument7 SeitenRevealing Hidden Interfaces in Organic SemiconductorsalkanderiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 01Dokument18 SeitenLecture 01priyasonu049Noch keine Bewertungen
- Inelastic Mean Free PathDokument50 SeitenInelastic Mean Free Pathace7721Noch keine Bewertungen
- Temperature Controlled Fan SpeedDokument4 SeitenTemperature Controlled Fan Speedsgrao2010549Noch keine Bewertungen
- Field Strength MeterDokument9 SeitenField Strength MeterVinod JagdaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gallium Nitride 28V, 100W RF Power TransistorDokument10 SeitenGallium Nitride 28V, 100W RF Power TransistorJohan BecerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- System On Chips Soc'S & Multiprocessor System On Chips MpsocsDokument42 SeitenSystem On Chips Soc'S & Multiprocessor System On Chips MpsocsAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fully Reused VLSI Architecture of FMO/Manchester Encoding Using SOLS Technique For DSRC ApplicationsDokument16 SeitenFully Reused VLSI Architecture of FMO/Manchester Encoding Using SOLS Technique For DSRC ApplicationssnehaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14-Bit Digital-To-Synchro Converter High Efficiency: Powered From Reference InputDokument6 Seiten14-Bit Digital-To-Synchro Converter High Efficiency: Powered From Reference InputMHS DuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines BookDokument263 SeitenElectrical Machines BookYo Molo MazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low-Frequency Antennas (Chapter 19) by C.A. Martin and Phillip S. Carter (RCA Laboratories)Dokument19 SeitenLow-Frequency Antennas (Chapter 19) by C.A. Martin and Phillip S. Carter (RCA Laboratories)Bob Laughlin, KWØRLNoch keine Bewertungen
- TH 37phd8gk TH 37phd8gs TH 37phd8uk TH 42phd8gk TH 42phd8gs TH 42phd8ukDokument235 SeitenTH 37phd8gk TH 37phd8gs TH 37phd8uk TH 42phd8gk TH 42phd8gs TH 42phd8ukLuis MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MG5241 X-Band Magnetron Technical SpecificationsDokument4 SeitenMG5241 X-Band Magnetron Technical SpecificationsFernando EtchegarayNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Best IC Crack and IC Decipher Services in ChinaDokument15 SeitenThe Best IC Crack and IC Decipher Services in ChinajackNoch keine Bewertungen
- 00001560a PDFDokument20 Seiten00001560a PDFjoseluisblanco69100% (1)
- Electrical Properties of Kevlar-Carbon Fiber Epoxy CompositesDokument7 SeitenElectrical Properties of Kevlar-Carbon Fiber Epoxy CompositesJorge RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intraband TransitionsDokument8 SeitenIntraband TransitionsnikithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor ControllerDokument7 SeitenMotor ControllerOnupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 30gx PDFDokument36 Seiten30gx PDFVinod NairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ug470 7series ConfigDokument176 SeitenUg470 7series ConfigRakesh KhannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Nanotechnology: 1.1 Nanotechnology - Definition and ExamplesDokument15 SeitenIntroduction To Nanotechnology: 1.1 Nanotechnology - Definition and ExamplesMustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CT For Protection: Prof.O.V.Gnana SwathikaDokument24 SeitenCT For Protection: Prof.O.V.Gnana SwathikaSarthak VatsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MB3773Dokument28 SeitenMB3773Morteza BaratzadehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Current Transformer: Applications and AdvantagesDokument20 SeitenOptical Current Transformer: Applications and Advantagesshubham jaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- (3143512) Diffusion WeldingDokument29 Seiten(3143512) Diffusion Weldingsushil sandhu100% (1)
- Technical Data Sheet - SDCDokument4 SeitenTechnical Data Sheet - SDCnailulfalah17Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2N2369A Silicon NPN Transistor DescriptionDokument4 Seiten2N2369A Silicon NPN Transistor DescriptionReymondJosuéArgüelloRojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2009 RI Prelims Physics H2 P2lDokument14 Seiten2009 RI Prelims Physics H2 P2lcjcsucksNoch keine Bewertungen