Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mito
Hochgeladen von
abeer adel0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
42 Ansichten30 Seiten66666
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument melden66666
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
42 Ansichten30 SeitenMito
Hochgeladen von
abeer adel66666
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 30
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Mitosis
Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Mitosis
Splitsville!
Why do cells divide?
Cell division takes place for different reasons.
Cell division is important for asexual
reproduction, which involves only one parent
organism.
Most growth in a multicellular organism
happens because cell division produces new
cells.
Cell division also produces cells for repair.
Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Mitosis
What happens to genetic material
during cell division?
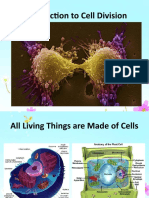
The genetic material in cells is called DNA
(deoxyribonucleic acid).
In eukaryotic cells, DNA is found in the nucleus.
A DNA molecule contains the information that
determines the traits that a living thing
inherits and needs to live.
Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Mitosis
What happens to genetic material
during cell division?
During most of a cells life cycle, DNA is found in a
mass of loose strands called chromatin.
Before cell division, DNA is duplicated.
As cell division begins, the chromatin
is compacted into visible structures
called chromosomes.
Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Mitosis
What happens to genetic material
during cell division?
A duplicated chromosome is made of two identical
structures called chromatids.
Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Mitosis
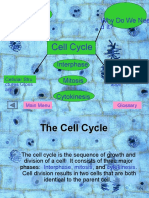
Around and Around
What are the stages of the cell cycle?
The life cycle of a eukaryotic cell, called the cell
cycle, can be divided into three stages:
interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis.
Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Mitosis
What are the stages of the cell cycle?
Interphase is the stage in the cell cycle
during which the cell is not dividing.
The cell grows to about twice the size it was
when it was first produced. It produces various
organelles and engages in normal life activities.
Changes that occur during interphase prepare a
cell for division.
Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Mitosis
What are the stages of the cell cycle?
In eukaryotic cells, mitosis is the part of the cell
cycle during which the nucleus divides.
Prokaryotes do not undergo mitosis because they
do not have a nucleus.
Mitosis results in two nuclei that are identical to
the original nucleus.
When mitosis is complete, the cell has two
identical sets of chromosomes in two separate
nuclei.
Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Mitosis
What are the stages of the cell cycle?
Cytokinesis is the division of the parent cells
cytoplasm.
Cytokinesis starts during the last step of
mitosis and eventually forms two complete
cells.
In cells that have a cell wall, a cell plate forms
during cytokinesis. The cell plate separates the
cell into two new cells.
Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Mitosis
Phasing Out
What are the phases of mitosis?
There are four phases of mitosis: prophase,
metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
By the end of the four phases, the cell will have
two identical nuclei.
Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Mitosis
What are the phases of mitosis?
In prophase, the chromatin in the nucleus
condenses into chromosomes. The
membrane around the nucleus breaks down.
Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Mitosis
What are the phases of mitosis?
In metaphase, the chromosomes line up in
the middle of the cell.
Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Mitosis
What are the phases of mitosis?
In anaphase, the chromatids of each
chromosome are pulled to opposite sides of the
cell.
Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Mitosis
What are the phases of mitosis?
In telophase, a new nuclear membrane
forms around each group of chromosomes,
which become less condensed.
Cytokinesis begins during this phase.
Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Mitosis
What are the phases of mitosis?
After mitosis, cytokinesis results in two new
cells, and the two new cells start the cell cycle
again.
Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 8.2 The Cell CycleDokument23 Seiten8.2 The Cell Cycleapi-520057338Noch keine Bewertungen
- High School Biology: Comprehensive Content for Cell & Molecular BiologyVon EverandHigh School Biology: Comprehensive Content for Cell & Molecular BiologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular ReproductionDokument26 SeitenCellular ReproductionIftikhar Hussain RizviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio-101 Cell DivisionDokument42 SeitenBio-101 Cell DivisionGabriel NdandaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Cell DivisionDokument43 Seiten4 Cell DivisionPrem ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Division: by Aouni Kaaki, Abbas AlawieDokument12 SeitenCell Division: by Aouni Kaaki, Abbas Alawiekarim karakiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Cell DivisionDokument24 Seiten4 Cell DivisionAbhishek SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Cell DivisionDokument24 Seiten4 Cell DivisionAbhinav AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- FSC 111 Mitosis and Meiosis ClassDokument41 SeitenFSC 111 Mitosis and Meiosis Classtolubabatunde06Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 Lesson 4: Cell DivisionDokument26 SeitenTopic 1 Lesson 4: Cell Divisionomar deebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Cell Division and Cell Cycle Lesson 4 and 5Dokument39 SeitenLesson Cell Division and Cell Cycle Lesson 4 and 5silvajunjosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Division NoteDokument12 SeitenCell Division NoteAidah AmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Division Note PDFDokument12 SeitenCell Division Note PDFAishaizl100% (1)
- Mitosis PowerpointDokument55 SeitenMitosis PowerpointAbegail CahatianNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument42 SeitenUntitledJazzmine C. RubricoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDokument14 SeitenChapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionPhoenix RockiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio NotesDokument6 SeitenBio NotesHuck KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitosis and Meiosis: Bio Lab-131 Session-Fall 2021 Section-001Dokument27 SeitenMitosis and Meiosis: Bio Lab-131 Session-Fall 2021 Section-001Satya NadellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3 & 2.5 Cell DivisionDokument14 Seiten2.3 & 2.5 Cell DivisionJhonnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Division Mitosis 29Dokument52 SeitenCell Division Mitosis 29Zelian ShcwienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Division: MitosisDokument52 SeitenCell Division: MitosisZelian ShcwienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 GED BioDokument52 SeitenChapter 1 GED BioKhant ZawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell DivisionDokument85 SeitenCell DivisionGlendel DimaculanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.2 Mitosis: Unit 5: Cell ReproductionDokument17 Seiten8.2 Mitosis: Unit 5: Cell Reproductionapi-520057338Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology G 10 - Lesson - 1 - Cellular+ReproductionDokument41 SeitenBiology G 10 - Lesson - 1 - Cellular+ReproductionQbasantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy& Physiology BY Adeniyi M. OlatoyeDokument59 SeitenAnatomy& Physiology BY Adeniyi M. OlatoyeAdeniyi OlatoyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell Cycle: MitosisDokument36 SeitenThe Cell Cycle: MitosisEllen Jane RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Division Mitosis MeiosisDokument49 SeitenCell Division Mitosis MeiosisKeaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Division Mitosis MeiosisDokument49 SeitenCell Division Mitosis MeiosisRoldan BihayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Division Mitosis MeiosisDokument49 SeitenCell Division Mitosis Meiosisleve lester navarra100% (2)
- Cell Division and CycleDokument16 SeitenCell Division and CycleAnaJeanJumawidMarananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Division Mitosis MeiosisDokument49 SeitenCell Division Mitosis MeiosisAli Namialus100% (1)
- Introduction To Cell Division: Animated Mitosis Actual Cells Going Through Cell Division Animated MitosisDokument49 SeitenIntroduction To Cell Division: Animated Mitosis Actual Cells Going Through Cell Division Animated MitosisKatrina RomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Division Mitosis MeiosisDokument49 SeitenCell Division Mitosis MeiosisCharles IbusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle MitosisDokument27 SeitenCell Cycle MitosisKate Clancy NugaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology: Form 4: Chapter 5 Cell DivisionDokument32 SeitenBiology: Form 4: Chapter 5 Cell DivisionAsim HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Veron Cell DivisionDokument32 SeitenVeron Cell Divisionveronica francisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Cell Cycle and Mitosis Student VersionDokument35 Seiten3 Cell Cycle and Mitosis Student VersionIshu SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SciFusTX Grade7 U03L04 PowerNoteDokument14 SeitenSciFusTX Grade7 U03L04 PowerNoteEsther SaraviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell DivisionDokument48 SeitenCell DivisionMichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 5-1 5-2 Cell CycleDokument28 SeitenCH 5-1 5-2 Cell Cycleapi-270681199Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4.1Dokument41 SeitenChapter 4.1Sofia GranicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle Part 1 (Mitosis)Dokument25 SeitenCell Cycle Part 1 (Mitosis)Awais GulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2Dokument11 SeitenWeek 2IRIS CHRISTINE SENONoch keine Bewertungen
- W3-4 Introduction To Cell DivisionDokument46 SeitenW3-4 Introduction To Cell DivisionMaricel YamatNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell Cycle and MitosisDokument40 SeitenThe Cell Cycle and MitosisStifany Dianne VillasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.6 FR StudentsDokument28 Seiten1.6 FR StudentsAkshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis FinalDokument16 SeitenCell Cycle and Mitosis FinalCamille Sison-AlmirolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cytogenetics, Mitosis and MeiosisDokument17 SeitenCytogenetics, Mitosis and MeiosisdomeniclwandileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2 - Cellular ReproductionDokument25 SeitenWeek 2 - Cellular Reproductionansammohame2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson-Plan-in-Science-8 - Cell DivisionDokument18 SeitenLesson-Plan-in-Science-8 - Cell DivisionMaricris Ranara100% (1)
- Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionDokument120 SeitenCell Cycle & Cell DivisionGanesh Patil100% (1)
- The Cell Cycle and Mitosis PDFDokument77 SeitenThe Cell Cycle and Mitosis PDFRonzie EstrellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell CycleDokument32 SeitenCell Cyclewakinn lezgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle: Two Important Characteristics of All Living FormsDokument16 SeitenCell Cycle: Two Important Characteristics of All Living FormsNiamat UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 202 2nd Exam TopicsDokument29 SeitenBio 202 2nd Exam TopicsEdel John SivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle: What Is It? Why Do We Nee D It?Dokument28 SeitenCell Cycle: What Is It? Why Do We Nee D It?suvendumitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDokument31 Seiten2-Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionElias KangwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4 Cell Division Mitosis and CancerDokument74 SeitenLecture 4 Cell Division Mitosis and CancerGerald AdolfoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiador y Sus Partes, Motor Diesel 504BDTDokument3 SeitenRadiador y Sus Partes, Motor Diesel 504BDTRamón ManglesNoch keine Bewertungen
- LNG Simulation PDFDokument28 SeitenLNG Simulation PDFRobert WatersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screenshot 2019-10-30 at 12.44.00Dokument25 SeitenScreenshot 2019-10-30 at 12.44.00Miền VũNoch keine Bewertungen
- Education - Khóa học IELTS 0đ Unit 3 - IELTS FighterDokument19 SeitenEducation - Khóa học IELTS 0đ Unit 3 - IELTS FighterAnna TaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNICEF Annual Report - Water 2018Dokument20 SeitenUNICEF Annual Report - Water 2018Ross WeistrofferNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dosage Calculations, CH 10 ProblemsDokument1 SeiteDosage Calculations, CH 10 ProblemsJacqueline GreerNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument2 SeitenUntitledapi-236961637Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ciac - HW Brochure Seer 16Dokument2 SeitenCiac - HW Brochure Seer 16Tatiana DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ens TecDokument28 SeitenEns TecBorja CanalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anesthesia 3Dokument24 SeitenAnesthesia 3PM Basiloy - AloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naming Alcohols, Aldehydes. EtcDokument1 SeiteNaming Alcohols, Aldehydes. Etcim_mikezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phyilosophy of Midwifery Care 2Dokument13 SeitenPhyilosophy of Midwifery Care 2Noella BezzinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis Knowledge OrganiserDokument1 SeitePhotosynthesis Knowledge Organiserapi-422428700Noch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance CodeDokument18 SeitenInsurance CodeKenneth Holasca100% (1)
- Marantz - dv-4200 DVD Player PDFDokument60 SeitenMarantz - dv-4200 DVD Player PDFH.V KayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nfpa Training - Nfpa 72Dokument107 SeitenNfpa Training - Nfpa 72yusuf.ahmediutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retrenchment in Malaysia Employers Right PDFDokument8 SeitenRetrenchment in Malaysia Employers Right PDFJeifan-Ira DizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interventional Cardiology and SurgeryDokument19 SeitenInterventional Cardiology and SurgeryDEV NANDHINI RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Umali v. Estanislao (1992, 209 SCRA 446)Dokument12 SeitenUmali v. Estanislao (1992, 209 SCRA 446)KTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses Các NămDokument4 SeitenTenses Các NămAnh MinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB ActivityDokument2 SeitenLAB ActivityNicole AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dyestone Blue MX SDS SA-0186-01Dokument5 SeitenDyestone Blue MX SDS SA-0186-01gede aris prayoga mahardikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA02 ParchamentoJVMDokument6 SeitenCA02 ParchamentoJVMJohnrey ParchamentoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Pollution Emissions 2008-2018 From Australian Coal Mining: Implications For Public and Occupational HealthDokument11 SeitenAir Pollution Emissions 2008-2018 From Australian Coal Mining: Implications For Public and Occupational HealthMaria Stephany CalisayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soduim Prescription in The Prevention of Intradialytic HypotensionDokument10 SeitenSoduim Prescription in The Prevention of Intradialytic HypotensionTalala tililiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EarthWear Clothier MaterialsDokument1 SeiteEarthWear Clothier MaterialsZhining LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diablo LED Wall LightDokument2 SeitenDiablo LED Wall LightSohit SachdevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet Cofraplus 60Dokument2 SeitenDatasheet Cofraplus 60Žarko JanjićNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Mono Channel BurnerDokument1 Seite01 Mono Channel BurnerSelwyn MunatsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review On Coconut MilkDokument4 SeitenLiterature Review On Coconut Milkea6mkqw2100% (1)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceVon EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (517)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerVon EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (393)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincVon EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (137)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessVon EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseVon EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (69)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesVon EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (397)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsVon EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeVon EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessVon Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (33)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionVon EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (812)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomVon EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (216)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceVon EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (18)
- Water: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationVon EverandWater: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (37)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Von EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (411)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainVon EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (110)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseVon EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (52)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperVon EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (16)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorVon EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedVon EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (11)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainVon EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (65)