Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Exam#1 (1) Solution
Hochgeladen von
digerOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Exam#1 (1) Solution
Hochgeladen von
digerCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Principles of Microeconomics
ECON 101
Exam 1
7-3-06
Name:___Solution____________
Student ID:_________________
1. Economics deals with how
a. individuals make decisions to use scarce resources in order to satisfy their
unlimited wants.
b. to run a business.
c. individuals become rich.
d. society can eliminate scarcity.
e. how to increase the profits of firms.
2. The opportunity cost of a choice is the
a. cost associated with making a choice.
b. value of the next best alternative which was not chosen.
c. fair market price of whatever is chosen.
d. amount paid to purchase whatever is chosen.
e. value of all the forgone alternatives not chosen.
3. Which of the following would shift the production
possibilities curve from curve "W" to "R"?
an improvement in the technology for
producing ink
b. an improvement in the technology for
producing paper
c. an improvement in widely applicable
technology
d. an increase in the unemployment rate
e. people demand more ink
4. The opportunity cost of moving from Point B to Point D is
a. 4 units of X.
b. 6 units of X.
c. 10 units of Y.
d. 3 units of Y.
e. 4 units of X and 3 units of Y.
da.
5. Point E would most likely represent?
a. an unattainable point.
b inefficiency.
c. the best possible choice.
d. an equally acceptable alternative available to
society.
6. The demand curve for pizza is downward sloping because
a. as the price of pizza rises, people will seek other, relatively cheaper alternatives,
like hamburgers or tacos.
b. pizza is popular and there are more pizza parlors.
c. when fewer pizzas are produced, the money in peoples pizza budgets does not
have to stretch as far.
d. when pizza prices rises, the price of other goods must also be rising, so people
cannot afford to buy as much.
7. Which of the following will not increase the demand for hotdogs (i.e., which will not
shift demand to the right)?
a. An expectation of a decline in the price of hotdogs in the future.
b. The price of hotdogs fall.
c. An increase in the price of a substitute, such as hamburgers.
d. A decrease in the price of a complement, such as hotdog buns.
e. A celebrity effectively promotes the healthful attributes of hotdogs.
8. When incomes are rising, new car sales increase while used car sales decrease.
This indicates that
a. new and used cars are both normal goods.
b. new cars are normal goods while used cars are inferior goods.
c. new and used cars are complements.
d. new and used cars are both inferior goods.
e. new cars are inferior goods and used cars are normal goods.
9. Due to the recent success of ISU athletic teams, lets say Cyclones T-Shirts become
more popular. We would expect
a. both the equilibrium price and quantity to increase.
b. both the equilibrium price and quantity to decrease.
c. the equilibrium price to increase and the equilibrium quantity will decrease..
d. the equilibrium price to decrease and the equilibrium quantity will increase..
10.If nothing changes except that producers sell more of a good or service when the
price increases, we know this is an example of the law of
a. increasing profit.
b. supply.
c. demand.
d. opportunity cost.
e. reduced real income.
11. If a drought in Ecuador reduces the amount of bananas grown, then
a. the demand curve of Ecuador bananas shifts to the left.
b. the demand curve of Ecuador bananas shifts to the right.
c. the supply curve of Ecuador bananas shifts to the left.
d. the supply curve of Ecuador bananas shifts to the right.
12. If technology improves in producing computers, what will happen to the equilibrium price
and quantity of computers?
a. both the equilibrium price and quantity will increase.
b. both the equilibrium price and quantity will decrease.
c. the equilibrium price will increase and the equilibrium quantity will decrease.
d. the equilibrium price will decrease and the equilibrium quantity will increase.
Price
$.90
$.80
$.70
$.60
$.50
Quantity Demanded
20
25
30
35
40
Quantity Supplied
50
40
30
20
10
13.If price is $.50 in the table, there is
a. a surplus of 30 units.
b. a surplus of 40 units.
c. a shortage of 40 units.
d. a shortage of 30 units.
e. neither a surplus or shortage; the market is in equilibrium.
14.In the market represented in the table above, there will be upward pressure on
prices, or in other words, a tendency for the price to increase, at which price level?
a. $.90
b. $.80
c. $.70
d. $.60
15.Refer to the figure to the right. A shortage of
______ units will result at a price of ______.
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
d
4
4
34; $9
32; $18
30; $27
5; $27
7; $9
16.Refer to the diagram again. The equilibrium price in the market is
a. $27. b. $18.
c. $9.
d. approximately $42.
17.Refer to the diagram again. The equilibrium quantity is
a. 27 units.
b. 30 units. c. 32 units.
18. T
F
shortages.
Price
$.90
$.80
$.70
$.60
$.50
d. 34 units.
e. 35 units.
Price ceilings, e.g., Rent controls on apartments typically cause
Quantity Demanded
20
25
30
35
40
Quantity Supplied
50
40
30
20
10
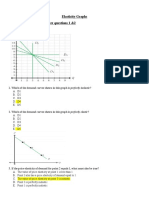
19.Refer to the table. Calculate the elasticity of supply between $.80 and $.70. Indicate
whether the supply curve is elastic, inelastic or unitary here. Write down the formula
you are using before you begin your calculations, and show at least some work for
partial credit.
Q2 Q1
10
Q2 Q1
2
es
35 2.14 Hence supply is elastic here.
P2 P1
.1
P2 P1
.75
2
20.Create your own supply and demand curves, and then assume that either supply or
demand changes, but not both. Indicate the direction and change in either supply or
9 demand that must have occurred to produce a decrease in equilibrium price and a
decrease in equilibrium quantity. Your answer need not include numbers; however,
the best answers will include a diagram with the curves and axes labeled.
The original supply and demand curves are
shown in black. We can see that
in order to produce a reduction in both P
equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity we
know this must have been caused by a
decrease in demand. (i.e., the demand curve
shifted to the left.)
Q
4
22,2
14,9
10,11
17,3
21.Suppose the production possibility frontiers above are the corn, electronics ppfs for
the United States and China, respectively. Also, suppose each country is producing
at the points indicated in the graphs, and not trading with each other.
10
Your task is to suggest a trade that would likely be accepted by both parties. You
dont have to make up numbers to go along with your answer; however, but you
might find it helpful. The best answers will use phrases like, opportunity cost, and
comparative advantage.
We can see from the slopes of the two ppfs that the United States has a
comparative advantage in producing corn, and China has a comparative advantage
in producing electronics. That is, the United States has a lower opportunity cost of
producing corn than does China. Similarly, China has a lower opportunity cost of
producing electronics than does the United States. So, a mutually beneficial trade
will involve the United States specializing in the good in which they have a
comparative advantage, which is corn. Likewise, China will specialize in the good in
which they have a comparative advantage, electronics. Then the two countries will
trade.
For example, suppose the U.S. produces at the point 22, 2 , and China produces at
the point 3,17 . Then the following trade is suggested. The U.S. will give China
eight units of corn in exchange for seven units of electronics. Then the U.S. will be
able to consume at the point 14,9 , and China will be able to consume at the point
11,10 .
Both these points are outside the respective countrys ppf, so this trade is
mutually beneficial.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Essentials of Development Economics, Third EditionVon EverandEssentials of Development Economics, Third EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- CHPT 2 EconDokument8 SeitenCHPT 2 EconJindessaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Econ 351 Midterm 1 Questions and AnswersDokument11 SeitenEcon 351 Midterm 1 Questions and Answerstony4dongNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 101 Midterm 1 PracticeDokument4 SeitenECON 101 Midterm 1 PracticeexamkillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Managers and EconomicsDokument13 SeitenChapter 1 Managers and EconomicsForappForapp100% (1)
- EC102 - Problem Set 1 - Answer KeyDokument19 SeitenEC102 - Problem Set 1 - Answer KeyEd ZNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC101 Revision Questions - Graphical Analysis - SolutionsDokument10 SeitenEC101 Revision Questions - Graphical Analysis - SolutionsZaffia AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eco McqsDokument13 SeitenEco McqsUn Konown Do'erNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2 - Demand and SupplyDokument8 SeitenTopic 2 - Demand and SupplydbodzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Labor Productivity and Comparative Advantage: The Ricardian ModelDokument15 SeitenChapter 3 Labor Productivity and Comparative Advantage: The Ricardian Modeljing chenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision QuestionDokument19 SeitenRevision QuestionSharina DailamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 17 MankiwDokument9 SeitenChapter 17 Mankiwcik siti100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Tutorial: Demand, Supply and MarketsDokument62 SeitenMultiple Choice Tutorial: Demand, Supply and Marketssorrylex100% (1)
- Mock Exam 2Dokument6 SeitenMock Exam 2Anne Raquel MadambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADL 04 Managerial Economics V3Dokument6 SeitenADL 04 Managerial Economics V3solvedcare100% (1)
- Elasticity Graphs Use The Graph Below To Answer Questions 1 &2Dokument6 SeitenElasticity Graphs Use The Graph Below To Answer Questions 1 &2SaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8/competitive Firms and MarketsDokument19 SeitenChapter 8/competitive Firms and Marketsi.abdellah100% (1)
- Macro 95 Ex 2Dokument17 SeitenMacro 95 Ex 2Engr Fizza AkbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 102 Homework 1 (Due Tuesday, September 27, 2012) (Answer Key Is at The Bottom of This Document)Dokument16 SeitenECON 102 Homework 1 (Due Tuesday, September 27, 2012) (Answer Key Is at The Bottom of This Document)Marc Aderades LaureanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elasticity - Utility ExplainedDokument16 SeitenElasticity - Utility ExplainedreemmajzoubNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPSC Eco McqsDokument61 SeitenPPSC Eco Mcqsamna yousafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manegerial EconomicsDokument97 SeitenManegerial EconomicsSanjay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- More Multiple Choice Questions With AnswersDokument14 SeitenMore Multiple Choice Questions With AnswersJudz Sawadjaan100% (2)
- Tut 2 TwoDokument56 SeitenTut 2 TwoBraceley & CoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Econ201 Quiz 4Dokument10 SeitenEcon201 Quiz 4arichard88215Noch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet - 2 Demand & SupplyDokument2 SeitenWorksheet - 2 Demand & SupplyPrince SingalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Questions 1Dokument4 SeitenMultiple Choice Questions 1Ankit Dubey100% (1)
- Microeconomics - ECO402 Final Term QuizDokument28 SeitenMicroeconomics - ECO402 Final Term QuizSuleyman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DocxDokument16 SeitenDocxaksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demand Curve ExercisesDokument19 SeitenDemand Curve ExercisesHussein DarwishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 Micro-Economics ReviewDokument55 SeitenChapter 9 Micro-Economics ReviewMeg GregoireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microeconomics Problems SetDokument33 SeitenMicroeconomics Problems SetBeri Z HunterNoch keine Bewertungen
- MicroeconomicsDokument10 SeitenMicroeconomicsCarlos Funs0% (1)
- Market Forces and Demand & Supply AnalysisDokument13 SeitenMarket Forces and Demand & Supply AnalysisDiem Suong100% (1)
- Economics Practice ExamDokument33 SeitenEconomics Practice ExamMelissa Douglas100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Economics For Managers (Question Bank & Answers)Dokument13 SeitenChapter 1: Economics For Managers (Question Bank & Answers)tk_atiqah100% (1)
- Chap010 Labor EconomicsDokument12 SeitenChap010 Labor EconomicsKoki MostafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Questions for Exam 1 Chapter 1-2Dokument33 SeitenStudy Questions for Exam 1 Chapter 1-2Ahmed MahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- D AND S MCQDokument14 SeitenD AND S MCQSarmela DamotheranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perfect Competition MC Practice With AnswersDokument8 SeitenPerfect Competition MC Practice With AnswersMaría José AmezquitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Exam 3Dokument8 SeitenSample Exam 3Luu Nguyen Quyet ThangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONSDokument6 SeitenChapter 6 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONSHabiba MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eco201 Exam1Dokument8 SeitenEco201 Exam1sonhai0901100% (1)
- Basic Economics Mcqs Paper with AnswersDokument27 SeitenBasic Economics Mcqs Paper with AnswersAmeer HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10e 12 Chap Student WorkbookDokument23 Seiten10e 12 Chap Student WorkbookkartikartikaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 - The Economic Impact of UnionsDokument8 SeitenChapter 11 - The Economic Impact of Unionshui200x100% (2)
- Homework 2 AKDokument10 SeitenHomework 2 AKTrang NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 BA520 Quantitative Analysis Assignment 7Dokument6 Seiten1 BA520 Quantitative Analysis Assignment 7Dinesh Boppana0% (1)
- Measuring A Nation'S Income: Questions For ReviewDokument4 SeitenMeasuring A Nation'S Income: Questions For ReviewNoman MustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC questions on economics conceptsDokument3 SeitenMC questions on economics conceptsMihaela Gavrilita50% (2)
- Lesson Plan TemplateDokument3 SeitenLesson Plan Templateapi-277618170Noch keine Bewertungen
- Monopolistic Competition MCQsDokument40 SeitenMonopolistic Competition MCQsAmanda D.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Public Goods, Externalities, and Information Asymmetries: Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument52 SeitenPublic Goods, Externalities, and Information Asymmetries: Multiple Choice QuestionsYannah HidalgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MR MOYO'S ECONOMICS REVISION NOTESDokument30 SeitenMR MOYO'S ECONOMICS REVISION NOTESFaryalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 - Market Structures WorksheetDokument2 SeitenChapter 9 - Market Structures WorksheetTerry CueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mankiw Chapter 7 Outline PDFDokument3 SeitenMankiw Chapter 7 Outline PDFspecinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm practiceDokument9 SeitenMidterm practiceIzza NaseerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 2010 QUIZ 5 Key ConceptsDokument12 SeitenECON 2010 QUIZ 5 Key ConceptsFallon FarmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- (ECON2103) (2016) (F) Midterm 0irzkjdi 91741Dokument11 Seiten(ECON2103) (2016) (F) Midterm 0irzkjdi 91741luther evanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam#1 (1) SolutionDokument6 SeitenExam#1 (1) SolutionaininhusninaNoch keine Bewertungen
- StMarks SeWa Neg Grapevine Classic Round 4Dokument94 SeitenStMarks SeWa Neg Grapevine Classic Round 4EmronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Chapter 28 Unemployment: Current Population SurveyDokument4 SeitenSummary Chapter 28 Unemployment: Current Population SurveyDini KusumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Econometric Chapter 10 Regression Panel DataDokument3 SeitenSolution Econometric Chapter 10 Regression Panel Datadumuk473Noch keine Bewertungen
- Issues in Malaysia and Impact to InflationDokument22 SeitenIssues in Malaysia and Impact to InflationAneesa RoslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TUTMACDokument63 SeitenTUTMACThùy Dương NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 8 - Lesson 4 - Business CycleDokument18 SeitenUnit 8 - Lesson 4 - Business Cycleapi-260512563Noch keine Bewertungen
- Take Off StageDokument8 SeitenTake Off StageRuben Jr. MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poverty AlliviationDokument19 SeitenPoverty Alliviation09itm6832mbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter One For Ijeoma IG CLASS-1Dokument77 SeitenChapter One For Ijeoma IG CLASS-1Onyebuchi ChiawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LayoffDokument30 SeitenLayoffsonuka83% (6)
- Netherlands PPDokument20 SeitenNetherlands PPtouyen12112003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee ActDokument21 SeitenMahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee ActKaranbir KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing Ielts Task 1 ExampleDokument5 SeitenWriting Ielts Task 1 Exampleappl3s100% (1)
- Active and Passive VoiceDokument5 SeitenActive and Passive Voicemerlyn m romerovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jan 2013 Ec1Dokument14 SeitenJan 2013 Ec1profoundlifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Income and Employment TheoryDokument4 SeitenIncome and Employment TheorysukhmanchawlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Grapes of Wrath!!!!Dokument10 SeitenThe Grapes of Wrath!!!!mattmcneill8Noch keine Bewertungen
- FloJoe CAE CollocationsDokument7 SeitenFloJoe CAE CollocationsRichard Holguín100% (11)
- Global Themes For World Studies EEDokument2 SeitenGlobal Themes For World Studies EEAnonymous J5sNuoIyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECO121 Questions C23-28ADokument5 SeitenECO121 Questions C23-28ATrần Quang NinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiscal Space: Special ReportDokument19 SeitenFiscal Space: Special ReportNgô Túc HòaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airport EIA Final ReportDokument20 SeitenAirport EIA Final ReportMcKenzie StaufferNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subscribe To Deepl Pro To Edit This DocumentDokument5 SeitenSubscribe To Deepl Pro To Edit This DocumentAbdulhakk AgaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Issues/Problems in The PhilippinesDokument8 SeitenSocial Issues/Problems in The PhilippinessoftenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final15 SolDokument7 SeitenFinal15 SolStowe EighmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- De 6Dokument2 SeitenDe 6ejao100% (8)
- Virgin Atlantic's shorter working year schemeDokument6 SeitenVirgin Atlantic's shorter working year schemeIulian ComanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 23 - Agg Expenditure - Equilibrium Output-TheKeynesianCrossDokument30 SeitenChapter 23 - Agg Expenditure - Equilibrium Output-TheKeynesianCrossSanjana JaggiNoch keine Bewertungen
- What's Available, How To Qualify, and Where To Apply: Government Assistance ProgramsDokument5 SeitenWhat's Available, How To Qualify, and Where To Apply: Government Assistance ProgramsJonhmark AniñonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 203 Sample Midterm2Dokument16 Seiten203 Sample Midterm2Annas GhafoorNoch keine Bewertungen