Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
7.5 Absorption
Hochgeladen von
gesCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
7.5 Absorption
Hochgeladen von
gesCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
7.
5 Absorption
1. Identify the small intestine as the region for the absorption of digested
food
2. Explain the significance of villi and microvilli in increasing the internal
surface area of the small intestine
a. Describe the structure of a villus
b. Describe the roles of capillaries and lacteals in villi
3. State that water is absorbed in both the small intestine and the colon, but
that most absorption of water happens in the small intestine
Digested food absorbed in Ileum into blood or lymph
Adaptation for Efficient Absorption
a) very long enough time for absorption to occur
b) highly folded with villi large surface area for absorption
Villi = thousands of finger-like projections in the ileum wall
Label the structure of a villus & epithelial cells with microvilli
The continuous flow of blood ensures concentration gradient of nutrient molecules is
maintained.
Fat-soluble food molecules = enters lacteal
Eg: fatty acid, glycerol, Vitamin A, D, E & K
Water-soluble food molecules = enters
capillaries
Eg: glucose, amino acid, minerals, Vitamin C & B
The hepatic portal vein then delivers them to the
liver.
Liver: determines what and how much nutrients
enter the blood stream based on bodys need.
FUNCTIONS OF LIVER
1) Manufacture bile
2) Store excess glucose as glycogen (excess glycogen is turned into fats)
3) Interconversion of glucose and glycogen to keep glucose level in blood constant
4) Transamination = Interconversion of different amino acids
5) Deamination = excretion of excess amino acid in the form of urea (excreted in
urine)
6) Removal of old red blood cells
7) Detoxification = Breakdown of alcohol and other toxin
ASSIMILATION = process of moving food molecules into the
cells to be used
Each type of cells uses food molecules for different purposes.
Muscle cells take certain proteins to make muscle
Bone cells take calcium and phosphate
All cells take glucose to produce energy via respiration
EGESTION: removes
undigested food
Dietary Fibre: Includes cellulose of cell wall &
lignin in plants
Leftover water is reabsorbed in the gut
When rectum is full reflex action of muscle
contracts to squeeze faeces out of anus
Sphincter at anus prevents defaecation at an
inconvenient time
Xtra Info:
*DIGESTIVE JUICES
contains mucus that helps protect the gut from being digested by its own
enzymes
are largely made up of water that:
o acts as a solvent
o medium for biochemical reaction of digestion
o used in the hydrolysis reactions that split up food molecules
7.5 Absorption
1. Identify the small intestine as the region for the absorption of digested
food
2. Explain the significance of villi and microvilli in increasing the internal
surface area of the small intestine
a. Describe the structure of a villus
b. Describe the roles of capillaries and lacteals in villi
3. State that water is absorbed in both the small intestine and the colon, but
that most absorption of water happens in the small intestine
Digested food absorbed in Ileum into blood or lymph
Adaptation for Efficient Absorption
a) _______________________ enough time for absorption to occur
b) _______________________ with villi large surface area for absorption
Villi = thousands of finger-like projections in the ileum wall
Label the structure of a villus & epithelial cells with microvilli
The continuous flow of blood ensures concentration gradient of nutrient molecules is
maintained.
Fat-soluble food molecules = enters
________________
Eg: _____________________________________________
Water-soluble food molecules = enters
capillaries
Eg: _____________________________________________
The _______________________then delivers them to
the liver.
Liver: determines what and how much nutrients
enter the blood stream based on bodys need.
FUNCTIONS OF LIVER
1) Manufacture ________________
2) Store excess glucose as ________________ (excess glycogen is turned into fats)
3) Interconversion of glucose and glycogen to keep glucose level in blood
constant
4) ________________________ = Interconversion of different amino acids
5) _____________________ = excretion of excess amino acid in the form of urea
(excreted in urine)
6) Removal of haemoglobin & store iron
7) _____________________ = Breakdown of alcohol and other
toxin
_____________ = process of moving food molecules into the
cells to be used
Each type of cells uses food molecules for different purposes.
Muscle cells take certain proteins to make muscle
Bone cells take calcium and phosphate
All cells take glucose to produce energy via respiration
EGESTION: removes undigested food
Dietary Fibre: Includes _________ of cell wall &
lignin in plants
Leftover water is _______________in the gut
When rectum is full reflex action of muscle
contracts to
squeeze
faeces out of anus
Sphincter at anus prevents defaecation at an
inconvenient time
Xtra Info:
*DIGESTIVE JUICES
- contains mucus that helps __________________________ from being digested by its
own enzymes
- are largely made up of water that:
o acts as a ___________________
o __________________________________________ of digestion
o used in the ____________________ reactions that split up food molecules
Add on: Food test
+ visking tube experiment
Describe the use of:
iodine solution to test for starch
Benedicts solution to test for reducing sugars
biuret test for proteins
ethanol emulsion test for fats and oils
DCPIP test for vitamin C
Explain that different sequences of amino acids give different shapes to protein
molecules
Relate the shape and structure of protein molecules to their function, limited to the
active site of enzymes and the binding site of antibodies
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Step 1 UworldDokument25 SeitenStep 1 UworldKarl Abiaad100% (23)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Effect of Enzymes On Digestion: RationaleDokument2 SeitenThe Effect of Enzymes On Digestion: RationaleMelchie Iligan TomanggongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organically Induced Trance StatesDokument19 SeitenOrganically Induced Trance StatesmarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Acting On Digestive System of AnimalsDokument11 SeitenDrugs Acting On Digestive System of AnimalsSunil100% (3)
- 0417 s14 QP 32Dokument2 Seiten0417 s14 QP 32gesNoch keine Bewertungen
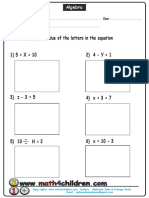
- Algebra Find X PDFDokument2 SeitenAlgebra Find X PDFgesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 Specimen Paper 2Dokument8 Seiten2020 Specimen Paper 2gesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0417 s14 QP 32Dokument8 Seiten0417 s14 QP 32Aya IhabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information and Communication Technology: Paper 0417/11 Written PaperDokument29 SeitenInformation and Communication Technology: Paper 0417/11 Written PapergesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information and Communication Technology: Paper 0417/11 Written PaperDokument29 SeitenInformation and Communication Technology: Paper 0417/11 Written PapergesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch1 MathsDokument3 Seitench1 MathsgesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Practice Test 2 Levels 3-5 - With CalculatorDokument28 Seiten1st Practice Test 2 Levels 3-5 - With CalculatorgesNoch keine Bewertungen
- HindiDokument228 SeitenHindiTarun Dutt Devrani54% (13)
- 8 Math Paper 1Dokument10 Seiten8 Math Paper 1gesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Element Symbols Part 1 and 2Dokument3 SeitenElement Symbols Part 1 and 2gesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Static ElectricityDokument24 SeitenStatic ElectricitygesNoch keine Bewertungen
- KS3 Summary Revision Worksheets-2jnbiuu PDFDokument104 SeitenKS3 Summary Revision Worksheets-2jnbiuu PDFTrúc HồNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3 - Sound WavesDokument2 SeitenTopic 3 - Sound WavesgesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Find The Unknown Value Given in Each ShapeDokument2 SeitenFind The Unknown Value Given in Each ShapegesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Check KrishaDokument11 SeitenMaths Check KrishagesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Static Electricity AssignmentDokument4 SeitenStatic Electricity AssignmentgesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Sheet - 1 Name of The Student: - Class:-10 Sec - Academic YearDokument4 SeitenWork Sheet - 1 Name of The Student: - Class:-10 Sec - Academic YeargesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Displacement, Average Speed, Average Velocity, Acceleration: Ph150 - Exercise #6Dokument2 SeitenDisplacement, Average Speed, Average Velocity, Acceleration: Ph150 - Exercise #6gesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy AssignmentDokument5 SeitenEnergy AssignmentgesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACFrOgAO2L 2xe8B7718oECzneMqcI2HFMd2y3CLjH3JPGnQWD e8F30Pd NzUHQC4XdLaKTuL oHq-HE8IRnhsJrqTZ1yZGmLa4JL8HOcFhBggFAx4AeLyE0o5al0wDokument162 SeitenACFrOgAO2L 2xe8B7718oECzneMqcI2HFMd2y3CLjH3JPGnQWD e8F30Pd NzUHQC4XdLaKTuL oHq-HE8IRnhsJrqTZ1yZGmLa4JL8HOcFhBggFAx4AeLyE0o5al0wgesNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLASS 9 CBSE TEST PAPER & SfgfgvOLUTION PDFDokument56 SeitenCLASS 9 CBSE TEST PAPER & SfgfgvOLUTION PDFjamemag50% (2)
- Fresh COIDokument1 SeiteFresh COIgesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.4 Chemical DigestionDokument4 Seiten7.4 Chemical DigestiongesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 6 Magnetism Electromagnetism - UnlockedDokument43 SeitenSection 6 Magnetism Electromagnetism - UnlockedgesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.1 7.2 Animal Nutrition Alimentary CanalDokument6 Seiten7.1 7.2 Animal Nutrition Alimentary CanalgesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.4 Chemical DigestionDokument4 Seiten7.4 Chemical DigestiongesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.3 Mechanical DigestionDokument5 Seiten7.3 Mechanical Digestionges100% (1)
- CHALLENGE: Can You and Your: Partner Write Down An Animal/plant Species For Every Letter of The Alphabet Eg. NtelopeDokument18 SeitenCHALLENGE: Can You and Your: Partner Write Down An Animal/plant Species For Every Letter of The Alphabet Eg. NtelopegesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diarrhea NCPsDokument10 SeitenDiarrhea NCPsJoia De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Module 4 Layers Bio-Security, Vaccination and Cleaning Poultry HousesDokument30 SeitenLearning Module 4 Layers Bio-Security, Vaccination and Cleaning Poultry HousesTshegofatsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sci7 q2 Mod3 LevelsofbiologicalorganizationDokument27 SeitenSci7 q2 Mod3 LevelsofbiologicalorganizationShenzhen Henry-PachecoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BrochureDokument26 SeitenBrochureapi-466148385Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Presentation TofDokument33 SeitenCase Presentation TofISLAMIC KNOWLEDGE BASED ON TRULY HADIS100% (1)
- Barium StudiesDokument16 SeitenBarium StudiesRuby Dela RamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vipaka CharakaDokument33 SeitenVipaka CharakaPreetiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Foods: DigestibilityDokument17 SeitenEvaluation of Foods: DigestibilityMudasirNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 7-11 Notes PrefiDokument7 SeitenMODULE 7-11 Notes PrefiPASCUAL, ALJON R.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mouth, Esophagus, Stomach, Small Intestine, Large Intestine, Rectum, AnusDokument2 SeitenMouth, Esophagus, Stomach, Small Intestine, Large Intestine, Rectum, AnusFia Ramadhania ZahroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fecal Fat Test-2020Dokument4 SeitenFecal Fat Test-2020Djdjjd SiisusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q2 Science Week3 Digestive SystemDokument55 SeitenQ2 Science Week3 Digestive Systemuni dearestNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of Inflammation and Genetics in Periodontal DiseaseDokument14 SeitenThe Role of Inflammation and Genetics in Periodontal DiseaseNishtha KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioavailability o Fdisperse Dosage FormDokument94 SeitenBioavailability o Fdisperse Dosage Formpharmashri5399Noch keine Bewertungen
- GIT QuizDokument2 SeitenGIT QuizHiro TakanoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Chemistry of DigestionDokument18 SeitenThe Chemistry of DigestionHarsh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community Guide To Good Practice For Hygiene and The Application of The HACCP Principles in The Production of Natural Sausage CasingsDokument53 SeitenCommunity Guide To Good Practice For Hygiene and The Application of The HACCP Principles in The Production of Natural Sausage CasingsEmanuele BelleiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GIT DrugsDokument180 SeitenGIT DrugsMaria Linevel Balderamos Dalida100% (1)
- BW Science 4Dokument5 SeitenBW Science 4Sarah Visperas RogasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document 1Dokument127 SeitenDocument 1Samsam AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supergut Sample ReportDokument29 SeitenSupergut Sample ReportshanmugapriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Human Digestive SystemDokument25 SeitenThe Human Digestive SystemKrizza Kyle Sarmon MancaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Humans Like Junk Food Steven WitherlyDokument208 SeitenWhy Humans Like Junk Food Steven WitherlyAndra GanaiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Heat Stress On Lactational Performance of Dairy Cows PDFDokument8 SeitenImpact of Heat Stress On Lactational Performance of Dairy Cows PDFIngridAlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy Statement - Jenna KnoxDokument1 SeitePhilosophy Statement - Jenna Knoxapi-533712019Noch keine Bewertungen