Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
SBI Specialist Officers - Operating Systems
Hochgeladen von
Aditya TomarCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SBI Specialist Officers - Operating Systems
Hochgeladen von
Aditya TomarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
State Bank of India
Specialist Officers Preparation Materials
Operating Systems Basics
Powered by
www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
For More Materials and Model Papers visit www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
1. What is an operating system?
co
An operating system is a program that acts as an intermediary between the user and the
computer hardware. The purpose of an OS is to provide a convenient environment in
which user can execute programs in a convenient and efficient manner. It is a resource
allocator responsible for allocating system resources and a control program which
controls the operation of the computer hardware.
on
Z.
2. Why paging is used?
Paging is solution to external fragmentation problem which is to permit the logical
address space of a process to be noncontiguous, thus allowing a process to be allocating
physical memory wherever the latter is available.
3. Explain the concept of the batched operating systems?
mb
iti
In batched operating system the users gives their jobs to the operator who sorts the
programs according to their requirements and executes them. This is time consuming but
makes the CPU busy all the time.
4. What is purpose of different operating systems?
8A
The machine purpose workstation individual usability &resources utilization mainframe
optimize utilization of hardware PC support complex games, business application Hand
held PCs Easy interface & min. power consumption.
5. What is virtual memory?
Gr
Virtual memory is hardware technique where the system appears to have more memory
that it actually does. This is done by time-sharing, the physical memory and storage parts
of the memory one disk when they are not actively being used.
6. What is Throughput, Turnaround time, waiting time and Response time?
w.
Throughput : number of processes that complete their execution per time unit.
Turnaround time : amount of time to execute a particular process.
Waiting time : amount of time a process has been waiting in the ready queue.
Response time : amount of time it takes from when a request was submitted until
the firstresponse is produced, not output (for time-sharing environment).
ww
7.What are the various components of a computer system?
LIKE our Facebook Page http://www.facebook.com/Gr8AmbitionZ
For More Materials and Model Papers visit www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
The hardware
The operating system
The application programs
The users.
co
8. What is a Real-Time System?
9.Explain the concept of the Distributed systems?
They
can
share
the
network
iti
Distributed systems work in a network.
resources,communicate with each other.
on
Z.
A real time process is a process that must respond to the eventswithin a certain time
period. A real time operating system is an operating system that can run realtime
processes successfully.
10. What is SCSI?
mb
SCSI - Small computer systems interface is a type of interface used for computer
components such as hard drives, optical drives, scanners and tape drives. It is a
competing technology to standard IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics).
11.What is a sector?
8A
Smallest addressable portion of a disk.
12.What are the different operating systems?
Gr
Batched operating systems
Multi-programmed operating systems
Timesharing operating systems
Distributed operating systems
Real-time operating systems.
w.
13.What is busy waiting?
ww
The repeated execution of a loop of code while waiting for an event to occur is called
busy waiting.
14.What are system calls?
LIKE our Facebook Page http://www.facebook.com/Gr8AmbitionZ
For More Materials and Model Papers visit www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
System calls provide the interface between a process and the operating system. System
calls for modern Microsoft windows platforms are part of the win32 API, which is
available for all the compilers written for Microsoft windows.
on
Z.
co
15.What are various scheduling queues?
Job queue
Ready queue
Device queue
16.What are java threads?
iti
Java is one of the small number of languages that support at the language level for the
creation and management of threads. However, because threads are managed by the java
virtual machine (JVM), not by a user-level library or kernel, it is difficult to classify Java
threads as either user- or kernel-level.
User thread
Kernel thread
18.What is a semaphore?
mb
17.What are types of threads?
Gr
8A
It is a synchronization tool used to solve complex critical section problems. A semaphore
is an integer variable that, apart from initialization, is accessed only through two standard
atomic operations: Wait and Signal.
19.What is a deadlock?
w.
Deadlock is a situation where a group of processes are all blocked and none of them can
become unblocked until one of the other becomes unblocked. The simplest deadlock is
two processes each of which is waiting for a message from the other.
20.What is cache memory?
ww
Cache memory is random access memory (RAM) that a computer microprocessor can
access more quickly than it can access regular RAM. As the microprocessor processes
data, it looks first in the cache memory and if it finds the data there (from a previous
reading of data), it does not have to do the more time-consuming reading of data.
21. What is thrashing?
LIKE our Facebook Page http://www.facebook.com/Gr8AmbitionZ
For More Materials and Model Papers visit www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
It is a phenomenon in virtual memory schemes when the processor spends most of its
time swapping pages, rather than executing instructions. This is due to an inordinate
number of page faults.
co
22. What are the states of a process?
New
Running
Waiting
Ready
Terminated
on
Z.
23.What is a binary semaphore?
iti
A binary semaphore is one, which takes only 0 and 1 as values. They are used to
implement mutual exclusion and synchronize concurrent processes.
24.What is a job queue?
mb
When a process enters the system it is placed in the job queue.
25.What is a ready queue?
8A
The processes that are residing in the main memory and are ready and waiting to execute
are kept on a list called the ready queue.
26.What are turnaround time and response time?
Turnaround time is the interval between the submission of a job and its completion.
Gr
Response time is the interval between submission of a request, and the first response to
that request.
w.
27.What are the operating system components?
Process management
Main memory management
File management
I/O system management
Secondary storage management
Networking
Protection system
ww
LIKE our Facebook Page http://www.facebook.com/Gr8AmbitionZ
For More Materials and Model Papers visit www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
Command interpreter system
28.What is mutex?
on
Z.
co
Mutex is a program object that allows multiple program threads to share the same
resource, such as file access, but not simultaneously. When a program is started a mutex
is created woth a unique name. After this stage, any thread that needs the resource must
lock the mutex from other threads while it is using the resource. the mutex is set to
unlock when the data is no longer needed or the routine is finished.
29.What is Marshalling?
The process of packaging and sending interface method parameters across thread or
process boundaries.
iti
30.What are residence monitors?
Early operating systems were called residence monitors.
mb
31.Why thread is called as a lightweight process?
It is called light weight process to emphasize the fact that a thread is like a process but is
more efficient and uses fewer resources( n hence lighter)and they also share the address
space.
Gr
Program execution
I/O operations
File system manipulation
Communication
Error detection
Resource allocation
Accounting
Protection
w.
8A
32.What are operating system services?
ww
33.What is a process?
A program in execution is called a process. Or it may also be called a unit of work. A
process needs some system resources as CPU time, memory, files, and i/o devices to
accomplish the task. Each process is represented in the operating system by a process
control block or task control block (PCB).Processes are of two types
LIKE our Facebook Page http://www.facebook.com/Gr8AmbitionZ
For More Materials and Model Papers visit www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
Operating system processes
User processes
co
34.What are the different job scheduling in operating systems?
Scheduling is the activity of the deciding when process will receive the resources they
request.
mb
iti
on
Z.
FCFS FCSFS stands for First Come First Served. In FCFS the job that has been
waiting the longest is served next.
Round Robin Scheduling Round Robin scheduling is a scheduling method where
each process gets a small quantity of time to run and then it is preempted and the
next process gets to run. This is called time-sharing and gives the effect of all the
processes running at the same time
Shortest Job First
The Shortest job First scheduling algorithm is a
nonpreemptive scheduling algorithm that chooses the job that will execute the
shortest amount of time.
Priority Scheduling Priority scheduling is a scheduling method where at all times
the highest priority process is assigned the resource.
35.What is dual-mode operation?
8A
In order to protect the operating systems and the system programs from the
malfunctioning programs the two mode operations were evolved
System mode
User mode.
Gr
36.What is a device queue?
A list of processes waiting for a particular I/O device is called device queue.
w.
37.What are the different types of Real-Time Scheduling?
Hard real-time systems required to complete a critical task within a guaranteed amount of
time.
ww
Soft real-time computing requires that critical processes receive priority over less
fortunate ones.
38.What is starvation ?
LIKE our Facebook Page http://www.facebook.com/Gr8AmbitionZ
For More Materials and Model Papers visit www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
Starvation is a resourcemanagement problem where a process does not get the resources
it needs for a long time because the resources are being allocated to other processes.
co
39.What is a long term scheduler & short term schedulers?
Long term schedulers are the job schedulers that select processes from the job queue and
load them into memory for execution.
on
Z.
The Short term schedulers are the CPU schedulers that select a process form the ready
queue and allocate the CPU to one of them.
40.What is fragmentation?
Fragmentation occurs in a dynamic memory allocation system when many of the free
blocks are too small to satisfy any request.
iti
41.What is context switching?
mb
Transferring the control from one process to other process requires saving the state of the
old process and loading the saved state for new process. This task is known as context
switching.
42.What is relative path and absolute path?
8A
Absolute path - Exact path from root directory.
Relative path - Relative to the current path.
43.What are the disadvantages of context switching?
Gr
Time taken for switching from one process to other is pure over head. Because the
system does no useful work while switching. So one of the solutions is to go for
threading when ever possible.
w.
44.What is the state of the processor, when a process is waiting for some event to occur?
Waiting state
45.What is the difference between Primary storage and secondary storage?
ww
Main memory - only large storage media that the CPU can access directly.
Secondary storage - extension of main memory that provides large nonvolatile
storage capacity.
46.What is process synchronization?
LIKE our Facebook Page http://www.facebook.com/Gr8AmbitionZ
For More Materials and Model Papers visit www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
co
A situation, where several processes access and manipulate the same data concurrently
and the outcome of the execution depends on the particular order in which the access
takes place, is called race condition. To guard against the race condition we need to
ensure that only one process at a time can be manipulating the same data. The technique
we use for this is called process synchronization.
47.What is a data register and address register?
Mutual exclusion
Hold and wait
No preemption
Circular wait
mb
iti
48.What are deadlock prevention techniques?
on
Z.
Data registers - can be assigned to a variety of functions by the programmer.
They can be used with any machine instruction that performs operations on data.
Address registers - contain main memory addresses of data and instructions or
they contain a portion of the address that is used in the calculation of the complete
addresses.
49.What is the difference between Complier and Interpreter?
8A
An interpreter reads one instruction at a time and carries out the actions implied by that
instruction. It does not perform any translation. But a compiler translates the entire
instructions.
Gr
50.What is a Safe State and what is its use in deadlock avoidance?
w.
When a process requests an available resource, system must decide if immediate
allocation leaves the system in a safe state. System is in safe state if there exists a safe
sequence of all processes. Deadlock Avoidance : ensure that a system will never enter an
unsafe state.
51.What is the difference between microkernel and macro kernel?
ww
Micro-Kernel : A micro-kernel is a minimal operating system that performs only
the essential functions of an operating system. All other operating system
functions are performed by system processes.
LIKE our Facebook Page http://www.facebook.com/Gr8AmbitionZ
For More Materials and Model Papers visit www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
Monolithic : A monolithic operating system is one where all operating system
code is in a single executable image and all operating system code runs in system
mode.
co
52.What is DRAM?
53.What are the different functions of Scheduler?
on
Z.
Dynamic Ram stores the data in the form of Capacitance, and Static RAM stores the data
in Voltages.
Scheduler deals with the problem of deciding which of the process in the ready queue is
to be allocated the CPU. Short Term Schedulers, Long Term Schedulers
54.What is a trap and trapdoor?
mb
iti
Trapdoor is a secret undocumented entry point into a program used to grant access
without normal methods of access authentication. A trap is a software interrupt, usually
the result of an error condition.
55.What are local and global page replacements?
8A
Local replacement means that an incoming page is brought in only to the relevant
process' address space. Global replacement policy allows any page frame from any
process to be replaced. The latter is applicable to variable partitions model only.
56.What is cache-coherency?
Gr
In a multiprocessor system there exist several caches each may containing a copy of
same variable A. Then a change in one cache should immediately be reflected in all other
caches this process of maintaining the same value of a data in all the caches s called
cache-coherency.
w.
57.What are the benefits of multithreaded programming?
Responsiveness
Resources sharing
Economy
Utilization of multiprocessor architectures.
ww
58. While running DOS on a PC, which command would be used to duplicate the entire
diskette? diskcopy.
LIKE our Facebook Page http://www.facebook.com/Gr8AmbitionZ
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Operating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesVon EverandOperating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- OS CN DS DBMS SE Interview QuestionsDokument38 SeitenOS CN DS DBMS SE Interview QuestionsSeshu Gagan60% (5)
- Operating System Interview Questions & AnswersDokument17 SeitenOperating System Interview Questions & AnswersBharat AttriNoch keine Bewertungen
- OS Interview PDFDokument14 SeitenOS Interview PDFAntriksh TawraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating SystemDokument14 SeitenOperating SystemNishant MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wa0000.Dokument18 SeitenWa0000.h.hyadav8881Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Are A Process and Process Table?Dokument10 SeitenWhat Are A Process and Process Table?JackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating System Interview QuestionsDokument22 SeitenOperating System Interview QuestionsKasab Hu maiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 159 - CS8493, CS6401 Operating Systems - Important QuestionsDokument16 Seiten159 - CS8493, CS6401 Operating Systems - Important Questionsmargaretwambui294Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aos VivaDokument14 SeitenAos VivaChaithanya DamerlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VivaDokument40 SeitenVivaShruthi JalalpuramNoch keine Bewertungen
- OS 2marks With Answers For All UnitsDokument19 SeitenOS 2marks With Answers For All UnitsPraveen MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mca 105 Assignment No 1Dokument8 SeitenMca 105 Assignment No 1Rajesh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OS Questions and AnswerDokument185 SeitenOS Questions and AnswerG/herNoch keine Bewertungen
- Windows Operating SystemDokument9 SeitenWindows Operating Systemthesingh_0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems: 1. Explain The Concept of ReentrancyDokument8 SeitenOperating Systems: 1. Explain The Concept of Reentrancyapi-3804388100% (1)
- Operating System Questions: by Admin - January 17, 2005Dokument12 SeitenOperating System Questions: by Admin - January 17, 2005Lieu Ranjan GogoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- OS Short QuestionDokument26 SeitenOS Short QuestionWaseem AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating SystemDokument25 SeitenOperating SystemprudhviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating System QuestionsDokument3 SeitenOperating System QuestionsPraveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems: Vartika DhagatDokument8 SeitenOperating Systems: Vartika Dhagatsandeep18100@yahoo.inNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems: 1. Explain The Concept of ReentrancyDokument7 SeitenOperating Systems: 1. Explain The Concept of ReentrancyRahul PariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sri Manakula Vinayagar Engineering CollegeDokument21 SeitenSri Manakula Vinayagar Engineering Collegenaveenraj_mtechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating System Interview QuestionsDokument16 SeitenOperating System Interview QuestionsSIVA RAMA PRASAD KANAKAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explain The Concept of ReentrancyDokument3 SeitenExplain The Concept of ReentrancymaniarunaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems: Thanks For Downloading. Enjoy The ReadingDokument9 SeitenOperating Systems: Thanks For Downloading. Enjoy The ReadingMrunal RuikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- OS Interview QuestionsDokument42 SeitenOS Interview QuestionsKvijay VinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Os 2 MarksDokument4 SeitenOs 2 MarksOmar MuhammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osy ADokument24 SeitenOsy Aaeromatic234Noch keine Bewertungen
- C Y Yyy Yyyyyyy Y Y Yyyy Yyyy Yy Y Yyy Y Yyy YDokument56 SeitenC Y Yyy Yyyyyyy Y Y Yyyy Yyyy Yy Y Yyy Y Yyy YnavsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Paging? Why Paging Is Used?: Resource Allocator and ManagerDokument8 SeitenWhat Is Paging? Why Paging Is Used?: Resource Allocator and ManagerAbhijeet MaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating System NOTESDokument15 SeitenOperating System NOTESmgs181101Noch keine Bewertungen
- Os FaqDokument14 SeitenOs Faqd_dharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating SystemDokument9 SeitenOperating SystemTarun GautamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating System Subject Code:16Scccs8 Class:Iii B.SC (CS) : Unit-IDokument19 SeitenOperating System Subject Code:16Scccs8 Class:Iii B.SC (CS) : Unit-IHenrikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OS - Q-Bank Unit - 01-02 - EngineerHubDokument22 SeitenOS - Q-Bank Unit - 01-02 - EngineerHubStuti PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Os Interview QuestionsDokument9 SeitenOs Interview Questionsamandeep651Noch keine Bewertungen
- CS1252 - Operating Sysytem - (Unit-I)Dokument5 SeitenCS1252 - Operating Sysytem - (Unit-I)Bavya Mohan100% (1)
- Operating Systems Interview QuestionsDokument15 SeitenOperating Systems Interview QuestionsSachin NayeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating System Viva QuestionsDokument7 SeitenOperating System Viva QuestionsSyed Ansar100% (1)
- Short Type S and Answers On: Operating SystemDokument31 SeitenShort Type S and Answers On: Operating SystemRAJESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems: 1. Explain The Concept of ReentrancyDokument7 SeitenOperating Systems: 1. Explain The Concept of Reentrancyapi-3736604Noch keine Bewertungen
- 003 Operating System VerifiedDokument51 Seiten003 Operating System VerifiedKurumeti Naga Surya Lakshmana KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final QBDokument28 SeitenFinal QBKavi PriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short Notes On OSDokument26 SeitenShort Notes On OSakttripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abrar Ali Os 2Dokument11 SeitenAbrar Ali Os 2abrar aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating System 2 Marks and 16 Marks - AnswersDokument45 SeitenOperating System 2 Marks and 16 Marks - AnswersDiana Arun75% (4)
- Operating Systems: 1. Explain The Concept of Reentrancy?Dokument8 SeitenOperating Systems: 1. Explain The Concept of Reentrancy?ram91221Noch keine Bewertungen
- Operating SystemDokument15 SeitenOperating SystemBonventure KipkiruiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating System 2Dokument29 SeitenOperating System 2nazim khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems FAQ's Explain The Concept of ReentrancyDokument14 SeitenOperating Systems FAQ's Explain The Concept of ReentrancyFakrullah ImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- OS Project 1Dokument16 SeitenOS Project 1NarayanaMunnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Os-2 Marks-Q& ADokument21 SeitenOs-2 Marks-Q& ARaja MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Os (2marks Only)Dokument20 SeitenOs (2marks Only)John mugiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Operating System Notes in 2022 - Last Minute Notes - Operating System Overview - Techno-RJDokument15 SeitenBest Operating System Notes in 2022 - Last Minute Notes - Operating System Overview - Techno-RJyetsedawNoch keine Bewertungen
- THREADSDokument3 SeitenTHREADSJames Joshua Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Platform Technologies ReviewerDokument9 SeitenPlatform Technologies ReviewerRaissa GonzagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Os Interview NotesDokument4 SeitenOs Interview NotesAmisha SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ict Workshop For TeachersDokument4 SeitenIct Workshop For TeachersAditya TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Science Notes CH01 Overview of CPPDokument10 SeitenComputer Science Notes CH01 Overview of CPPAditya TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ut No IDokument1 SeiteUt No IAditya TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data File HandlingDokument8 SeitenData File HandlingAditya TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Word Shortcut KeysDokument1 SeiteMicrosoft Word Shortcut KeysAditya TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Science - Class 12 Notes PDFDokument133 SeitenComputer Science - Class 12 Notes PDFAditya Tomar88% (8)
- PointerDokument9 SeitenPointerAditya TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- OracleDokument57 SeitenOracleStoriesofsuperheroesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java Short NotesDokument16 SeitenJava Short NotesAditya TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- OracleDokument57 SeitenOracleStoriesofsuperheroesNoch keine Bewertungen
- OracleDokument57 SeitenOracleStoriesofsuperheroesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java Short NotesDokument16 SeitenJava Short NotesAditya TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Abriviations PDFDokument4 SeitenMarketing Abriviations PDFAditya TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Library Management System SynopsisDokument3 SeitenLibrary Management System SynopsisAnju RathorNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Efficient Signcryption Scheme With Key Privacy IVDokument29 SeitenAn Efficient Signcryption Scheme With Key Privacy IVAditya TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attention Seeking: A Perspective From Chaos Theory: Introduction and OverviewDokument13 SeitenAttention Seeking: A Perspective From Chaos Theory: Introduction and OverviewAditya TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- M.tech. CSE Seminar DatesheetDokument1 SeiteM.tech. CSE Seminar DatesheetAditya TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Library Management System SynopsisDokument3 SeitenLibrary Management System SynopsisAnju RathorNoch keine Bewertungen
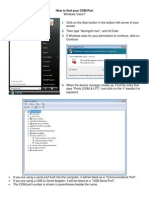
- Communication Port in Vista/ Win 7Dokument1 SeiteCommunication Port in Vista/ Win 7Aditya TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Previous Year Question Paper SolvedDokument9 SeitenIB Previous Year Question Paper SolvedAditya TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22 ERDiagDokument18 Seiten22 ERDiagAditya TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Previous Year Question Paper SolvedDokument9 SeitenIB Previous Year Question Paper SolvedAditya TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Courier ServicesDokument27 SeitenE Courier ServicesAditya TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- UHP Water Jetting Unit: Ultrabar 10 ECDokument1 SeiteUHP Water Jetting Unit: Ultrabar 10 ECFrederik CañabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASHRAE - HVAC Noise and Vibration ControlDokument93 SeitenASHRAE - HVAC Noise and Vibration Controlmnt6176100% (3)
- Perdele Economic B 2VVDokument4 SeitenPerdele Economic B 2VVakitainupufNoch keine Bewertungen
- GeothermalenergyDokument2 SeitenGeothermalenergyapi-238213314Noch keine Bewertungen
- Appexchange Publishing GuideDokument29 SeitenAppexchange Publishing GuideHeatherNoch keine Bewertungen
- MXRoad Student Software ManualDokument89 SeitenMXRoad Student Software ManualBabulalSahu100% (10)
- Dispersant Manual WebDokument108 SeitenDispersant Manual Webcamilinrodriguezzzz100% (1)
- ComE 223-Computer Fundamentals & Programming IIDokument2 SeitenComE 223-Computer Fundamentals & Programming IIDinah Fe Tabaranza-OlitanNoch keine Bewertungen
- How McAfee Took First Step To Master Data Management SuccessDokument3 SeitenHow McAfee Took First Step To Master Data Management SuccessFirst San Francisco PartnersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fab - Y-Strainers - 2nd EditionDokument15 SeitenFab - Y-Strainers - 2nd EditionRichard V. Quispe CastillonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creating Your Online CSSD Student Profile - MA Acting ProgrammesDokument7 SeitenCreating Your Online CSSD Student Profile - MA Acting ProgrammesEleanor ShawNoch keine Bewertungen
- L11 ImageplacementDokument2 SeitenL11 ImageplacementJayram JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ann (02) 23 08 2018Dokument73 SeitenAnn (02) 23 08 2018Paul RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pli New 22012006Dokument119 SeitenPli New 22012006Sai PraneethNoch keine Bewertungen
- HT P1200Dokument16 SeitenHT P1200vantuyetphamNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Choose Circuit Breakers For Electric MotorsDokument2 SeitenHow To Choose Circuit Breakers For Electric Motorsحسن التميميNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ficha Tecnica Talesun 410WDokument2 SeitenFicha Tecnica Talesun 410WIes IngenieriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Validation Protocol For Efficacy of Chemical DisinfectantsDokument8 SeitenValidation Protocol For Efficacy of Chemical DisinfectantsMohamed KamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ryan Donnelly - Artificial Intelligence in GamingDokument12 SeitenRyan Donnelly - Artificial Intelligence in GamingJavier Pardo MuñozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Códigos de Fallas de Problemas Específicos de PEUGEOTDokument8 SeitenCódigos de Fallas de Problemas Específicos de PEUGEOTJesus GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gambar SuspensiDokument1 SeiteGambar SuspensiMashiro HikariNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTE931 Integrated Circuit 3-Terminal Positive Voltage Regulator 5V, 3ADokument2 SeitenNTE931 Integrated Circuit 3-Terminal Positive Voltage Regulator 5V, 3AWilfredo MolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wallenius Wilhelmsen HistoryDokument28 SeitenWallenius Wilhelmsen Historymanayani52100% (1)
- Nift Panchkula Thesis Gaurav Bajaj 2009 Uar 646Dokument10 SeitenNift Panchkula Thesis Gaurav Bajaj 2009 Uar 646vedahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment (Module 1) IntroductionDokument3 SeitenAssignment (Module 1) Introductionkunal kumar100% (1)
- Bohol HRMD Plan 2011-2015Dokument233 SeitenBohol HRMD Plan 2011-2015Don Vincent Bautista Busto100% (1)
- 9 3 21 Compair Atvt enDokument4 Seiten9 3 21 Compair Atvt enAcika PeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Electronics 1968 10 S OCRDokument84 SeitenPractical Electronics 1968 10 S OCRCarlos SoaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- FL Studio TutorialsDokument8 SeitenFL Studio TutorialsRoberto DFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test AND Measurement: Eagle PhotonicsDokument90 SeitenTest AND Measurement: Eagle PhotonicsPankaj SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kali Linux - An Ethical Hacker's Cookbook - Second Edition: Practical recipes that combine strategies, attacks, and tools for advanced penetration testing, 2nd EditionVon EverandKali Linux - An Ethical Hacker's Cookbook - Second Edition: Practical recipes that combine strategies, attacks, and tools for advanced penetration testing, 2nd EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- RHCSA Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9: Training and Exam Preparation Guide (EX200), Third EditionVon EverandRHCSA Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9: Training and Exam Preparation Guide (EX200), Third EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Azure DevOps Engineer: Exam AZ-400: Azure DevOps Engineer: Exam AZ-400 Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps SolutionsVon EverandAzure DevOps Engineer: Exam AZ-400: Azure DevOps Engineer: Exam AZ-400 Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps SolutionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linux For Beginners: The Comprehensive Guide To Learning Linux Operating System And Mastering Linux Command Line Like A ProVon EverandLinux For Beginners: The Comprehensive Guide To Learning Linux Operating System And Mastering Linux Command Line Like A ProNoch keine Bewertungen
- iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]Von EverandiPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- iPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsVon EverandiPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Excel : The Ultimate Comprehensive Step-By-Step Guide to the Basics of Excel Programming: 1Von EverandExcel : The Ultimate Comprehensive Step-By-Step Guide to the Basics of Excel Programming: 1Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Windows Server 2019 Administration Fundamentals - Second Edition: A beginner's guide to managing and administering Windows Server environments, 2nd EditionVon EverandWindows Server 2019 Administration Fundamentals - Second Edition: A beginner's guide to managing and administering Windows Server environments, 2nd EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Linux Shell Scripting Cookbook - Third EditionVon EverandLinux Shell Scripting Cookbook - Third EditionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Linux for Beginners: Linux Command Line, Linux Programming and Linux Operating SystemVon EverandLinux for Beginners: Linux Command Line, Linux Programming and Linux Operating SystemBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Mastering Swift 5 - Fifth Edition: Deep dive into the latest edition of the Swift programming language, 5th EditionVon EverandMastering Swift 5 - Fifth Edition: Deep dive into the latest edition of the Swift programming language, 5th EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kali Linux Intrusion and Exploitation CookbookVon EverandKali Linux Intrusion and Exploitation CookbookBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Java Professional Interview Guide: Learn About Java Interview Questions and Practise Answering About Concurrency, JDBC, Exception Handling, Spring, and HibernateVon EverandJava Professional Interview Guide: Learn About Java Interview Questions and Practise Answering About Concurrency, JDBC, Exception Handling, Spring, and HibernateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionVon EverandMastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hello Swift!: iOS app programming for kids and other beginnersVon EverandHello Swift!: iOS app programming for kids and other beginnersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linux: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Learn Linux Operating System, Command Line and Linux Programming Step by StepVon EverandLinux: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Learn Linux Operating System, Command Line and Linux Programming Step by StepBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (9)
- Ubuntu 23.04 Essentials: A Guide to Ubuntu 23.04 Desktop and Server EditionsVon EverandUbuntu 23.04 Essentials: A Guide to Ubuntu 23.04 Desktop and Server EditionsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
















































































































![iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/728318688/198x198/f3385cbfef/1714829744?v=1)






















