Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Probability Permutations and Combinations
Hochgeladen von
Lester LazoCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Probability Permutations and Combinations
Hochgeladen von
Lester LazoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PERMUTATIONS and COMBINATIONS
Achievement Standard 90643 (3.3) (part)
Key Words: factorial, fundamental theorem of counting, permutations combinations.
1. FACTORIALS.
Sigma 150, Ex 8.01
For a positive integer n, n ! = n(n-1)(n-2).3.2.1
Nulake p134
n ! is called n factorial,
0! = 1
Example: 6! = 6.5.4.3.2.1
= 720 (there is a button on your calculator that finds factorials)
2. THE FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF COUNTING.
Example 1: If a menu offers 2 different entrees, 4 different mains and 3 different
desserts then the total number of possible meals is 2 4 3 = 24
In general if a task can be performed in n1 ways, a second task in n2 ways and a third
task in n3 ways .., then the total number of distinct ways of performing all tasks
together is n1 n2 n3
Example 2: How many 4 or 5 digit telephone numbers are possible, assuming the first
is not zero?
ans 9 10 10 10 + 9 10 10 10 10 = 99 000
3. PERMUTATIONS.
A permutation is an arrangement of objects order is important
Sigma p154, Ex 8.02
Nulake p136
Example1: If I have 3 books (a, b, c) then there are 6
permutations of 2 of them.
ab, ba, ac, ca, bc, cb.
There are 6 possible ways that I could arrange 2 of them on a shelf.
The number of distinct permutations of n objects taking r at a time is : nPr =
n!
(n r)!
Example 2: A club has 12 members. How many ways could a president, vice-president
and treasurer be appointed.
12
P3 =
12!
(12 3)!
= 1 320
The number of permutations of n objects using all of them is n!
Example 3: In how many ways can 5 people line up in a queue?
ans 5! = 120
Sigma p159, Ex 8.03
Nulake p141
4. COMBINATIONS.
A combination is a selection of objects order is not important
Example 1: If I have 3 books (a, b, c) then there are 3 combinations of 2 of them.
ab, ac, bc.
There are 3 possible ways that I could select 2 of them.
The number of different combinations of n objects taking r at a time is :
n
r
Cr =
n!
(n r)!r!
Example 2: From a club of 12 members, how many ways are there of selecting a
committee of three?
12
C3 =
12!
(12 3)!3!
= 220
Example 3: A group consists of 8 boys and 5 girls:
(a) How many ways can you select 2 boys and 2 girls?
(b) How many ways can you select a committee of 4 containing at least
2 boys?
ans
(a) 8C2
(b)
C2 = 28 10
= 280
At least 2 boys = 2 boys and 2 girls + 3 boys and 1 girl + 4 boys
= 8C2 5C2 + 8C3 5C1 +8C4 5C0
= 280 + 280 + 70
= 630
5. PROBABILITY CALCULATIONS USING COMBINATIONS / PERMUTATIONS
Sigma p161, Ex 8.04, 8.05
Nulake p141
Example 1: 4 chocolates are chosen at random from a box containing 6 with hard
centres, and 8 with soft centres.
(a) Calculate the probability that 3 of the chocolates have soft centres.
(b) Calculate the probability that at least 3 of the chocolates have soft
centres.
(a) Total number of ways of selecting 4 chocolates = 14C4
= 1 001
Number of ways of selecting 3 soft centres (and 1 hard) = 8C3
= 336
P( 3 soft) = 333
1001
C1
or 0.3357
(b) Numbers of ways of selecting at least 3 soft = 8C3 6C1 + 8C4
= 336 + 70
= 406
P( at least 3 soft) = 406
1001
C0
or 0.4056
Example 2: A 4 digit security number is made using the digits 0, 1, ..9.
If a number is made up at random, what is the probability that it contains
the same digit repeated 3 times in a row.
(a) Total number of security codes = 104 = 10 000.
(b) Total number of ways of getting 3 of the same in a row:
10
(c)
(1
9+9
P(3 in a row) =
180
10000
1) = 180
= 0018
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cenizas de Izalco - Capitulos 1 Al 15Dokument26 SeitenCenizas de Izalco - Capitulos 1 Al 15Gafriel100% (3)
- Trigonometry: Sides AnglesDokument28 SeitenTrigonometry: Sides AnglesOO O OONoch keine Bewertungen
- Kcpe Maths Made Familiar QNSDokument96 SeitenKcpe Maths Made Familiar QNSGodwin Ayieko100% (1)
- Finding Herself. KelloggDokument12 SeitenFinding Herself. KelloggMinerva MinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maclaurin 14Dokument3 SeitenMaclaurin 14ichkhuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chrome OS Recovery - Does Not Detect Image - Foros de Productos de GoogleDokument6 SeitenChrome OS Recovery - Does Not Detect Image - Foros de Productos de GoogleIsrael MarinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic:: Permutation and CombinationDokument27 SeitenTopic:: Permutation and Combinationshiven27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Study Package: MA MA MA MA Mathema Thema Thema Thema Thematics Tics Tics Tics TicsDokument21 SeitenStudy Package: MA MA MA MA Mathema Thema Thema Thema Thematics Tics Tics Tics TicsSandeep KunalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface Area and VolumeDokument49 SeitenSurface Area and VolumeKabeer GolechhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrigonometryDokument18 SeitenTrigonometrykhushivanshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 8: Chapter 5 Matrix: DR Chan Shiau Wei Email: Phone No: 011-33798215Dokument26 SeitenWeek 8: Chapter 5 Matrix: DR Chan Shiau Wei Email: Phone No: 011-33798215QayyumNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 Complex Numbers ExtraDokument60 Seiten3.1 Complex Numbers ExtraShalin RamliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics TDokument62 SeitenMathematics TRosdy Dyingdemon100% (1)
- Exercise 11.1: Solutions of Questions On Page Number: 171Dokument25 SeitenExercise 11.1: Solutions of Questions On Page Number: 171Jaya ChitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- BAHAN MATRIKULASI RevisiDokument8 SeitenBAHAN MATRIKULASI RevisiIsolihatun NurciptoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RD Sharma Jan2021 Class 8 Maths Solutions Chapter 20Dokument30 SeitenRD Sharma Jan2021 Class 8 Maths Solutions Chapter 20atharv jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 4 .7 Polynomials: Section 1Dokument11 SeitenWorksheet 4 .7 Polynomials: Section 1atiggy05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Partial FractionsDokument6 SeitenPartial FractionsEmmanuel MartinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Indices & Logarithms: 1.1 Exponent 1.2 Logarithms 1.3 Exponent & Logarithms EquationDokument22 SeitenChapter 1: Indices & Logarithms: 1.1 Exponent 1.2 Logarithms 1.3 Exponent & Logarithms EquationNur Suraya Shaarin100% (1)
- Chapter 20Dokument45 SeitenChapter 20RangerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polynomials: Nur Liyana BT Za'Im Siti Izzati Dyanah BT Zainal Wan Izzah KamilahDokument39 SeitenPolynomials: Nur Liyana BT Za'Im Siti Izzati Dyanah BT Zainal Wan Izzah KamilahLiyana Za'imNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEC 210 Complex NumberDokument37 SeitenGEC 210 Complex NumberMakinde FavourNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 MensurationDokument44 Seiten10 MensurationSridevi KamapantulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polynomial FunctionsDokument40 SeitenPolynomial Functionsnur hashimahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 - MatricesDokument39 SeitenChapter 11 - MatricesJhagantini Palanivelu0% (1)
- Chapter 05Dokument54 SeitenChapter 0510026722Noch keine Bewertungen
- Partial FractionDokument5 SeitenPartial FractionWada DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperbolic Functions (Sect. 7.7) : RemarkDokument8 SeitenHyperbolic Functions (Sect. 7.7) : RemarkCole Wong Kai KitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method of Partial FractionsDokument4 SeitenMethod of Partial Fractionsdjahangir07Noch keine Bewertungen
- MATH1251 Mathematics For Actuarial Studies and Finance Complex NumbersDokument35 SeitenMATH1251 Mathematics For Actuarial Studies and Finance Complex NumbersY ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric and Hyperbolic FunctionsDokument8 SeitenTrigonometric and Hyperbolic FunctionsJpricarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factor by GroupingDokument11 SeitenFactor by Groupingapi-276566085Noch keine Bewertungen
- A1 c9 Study Guide and Review Worked Out Solution KeyDokument31 SeitenA1 c9 Study Guide and Review Worked Out Solution KeyLiezl CanlasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject: Mathematics Unit: Measurement Topic: Area of Regular PolygonDokument7 SeitenSubject: Mathematics Unit: Measurement Topic: Area of Regular PolygonAtasha LewisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Hyperbolic Functions - 08032016Dokument6 Seiten3 Hyperbolic Functions - 08032016muhammad ruzaini bin omarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperbolic FunctionsDokument9 SeitenHyperbolic Functionstresa mariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 6 Division of PolynomialsDokument33 SeitenWeek 6 Division of PolynomialsyvonnemarisseadornaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Number PDFDokument22 SeitenComplex Number PDFSanjanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation Trigonometry (Wecompress - Com) 1535913988 354634Dokument49 SeitenPresentation Trigonometry (Wecompress - Com) 1535913988 354634monikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For Trigonometry 3rd Edition by YoungDokument90 SeitenSolution Manual For Trigonometry 3rd Edition by Younga731759159Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2: Limit of A Function and Limit Laws: Learning ObjectivesDokument16 Seiten2.2: Limit of A Function and Limit Laws: Learning ObjectiveskofinyameNoch keine Bewertungen
- L17 Hyperbolic Functions PDFDokument14 SeitenL17 Hyperbolic Functions PDFHey ShinnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5-5 Solving Polynomial EquationsDokument7 Seiten5-5 Solving Polynomial Equationsapi-281499569Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cramers Rule 3 by 3 PracticeDokument5 SeitenCramers Rule 3 by 3 PracticeSaherNoch keine Bewertungen
- R (X) P (X) Q (X) .: 1.7. Partial Fractions 32Dokument7 SeitenR (X) P (X) Q (X) .: 1.7. Partial Fractions 32RonelAballaSauzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.3 (A) - Inverse MatricesDokument23 Seiten4.3 (A) - Inverse MatricessureintharaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cramers Rule 2 by 2 PracticeDokument5 SeitenCramers Rule 2 by 2 PracticeSaherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Half PDFDokument183 SeitenHalf PDFTanveer Ali100% (2)
- Trigonometry PresentationDokument55 SeitenTrigonometry PresentationNazir PriceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polynomial FunctionsDokument81 SeitenPolynomial FunctionsJessica CagbabanuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex NumbersDokument24 SeitenComplex Numbersmatthew chombaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Equations (Finals)Dokument2 SeitenDifferential Equations (Finals)Frederick BuizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Number Sheet SolutionsDokument143 SeitenComplex Number Sheet Solutionsayush.aher06Noch keine Bewertungen
- AlgebraDokument9 SeitenAlgebrayididiyayibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partial Fractions: Syllabus RequirementsDokument9 SeitenPartial Fractions: Syllabus RequirementsChandini ManoharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2-01 Probability STATDokument13 SeitenLesson 2-01 Probability STATallan.manaloto23100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Analytic TrigonometryDokument20 SeitenChapter 1 - Analytic Trigonometrysimsonisna100% (1)
- 11 - Mensuration PDFDokument23 Seiten11 - Mensuration PDFNEON GAMINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- ComplexDokument33 SeitenComplexDipin Preet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consider The Quadratic Equation X + 1 0. Solving For X, Gives X - 1Dokument30 SeitenConsider The Quadratic Equation X + 1 0. Solving For X, Gives X - 1Akshita SoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cat CombinationDokument14 SeitenCat CombinationpreethishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permutations and CombinationsDokument46 SeitenPermutations and Combinationsapi-285179261Noch keine Bewertungen
- English Class X Maths Chapter02Dokument18 SeitenEnglish Class X Maths Chapter02Deblina DeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument33 SeitenChapter 5g77116370% (1)
- 2012 Multi V AirconditioningDokument82 Seiten2012 Multi V AirconditioningLester LazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce Project Narrative FinalDokument6 SeitenCe Project Narrative FinalLester LazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Analysis of AlternativesDokument2 SeitenList of Analysis of AlternativesLester LazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce Project Narrative FinalDokument6 SeitenCe Project Narrative FinalLester LazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Groups, Organizations and Institutions Activities or Tasks Interests or Expectations and The Project Potentials (Resources, SkillsDokument2 SeitenGroups, Organizations and Institutions Activities or Tasks Interests or Expectations and The Project Potentials (Resources, SkillsLester LazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative AnalysisDokument2 SeitenNarrative AnalysisLester LazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Alternatives: Difficult Condition On TransportationDokument2 SeitenAnalysis of Alternatives: Difficult Condition On TransportationLester LazoNoch keine Bewertungen
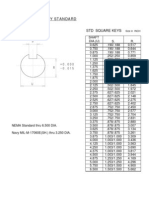
- Dimensiones de Cuñas y CuñerosDokument1 SeiteDimensiones de Cuñas y CuñerosPedro VelazquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dimensiones de Cuñas y CuñerosDokument1 SeiteDimensiones de Cuñas y CuñerosPedro VelazquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Engineering TermsDokument23 SeitenCommon Engineering TermsAitazaz Ahsan0% (1)
- Why FCU 2011 - 04 - 11Dokument5 SeitenWhy FCU 2011 - 04 - 11Mohammed MohieNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Rice Milling SystemDokument27 Seiten6 Rice Milling SystemYohanes ArifiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permutations and CombinationsDokument2 SeitenPermutations and CombinationsLester LazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistic FormulasDokument3 SeitenStatistic FormulasKiran PoudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Gas Turbine WorkDokument172 SeitenHow Gas Turbine WorkLester LazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easy Permutations and CombinationsDokument3 SeitenEasy Permutations and CombinationsChat Peng TangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Construction Manual - BTC - Nov - 2013 - EN - 0 PDFDokument48 SeitenBuilding Construction Manual - BTC - Nov - 2013 - EN - 0 PDFAndreaRebecaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Estimates (2016)Dokument6 SeitenConstruction Estimates (2016)Lester LazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Practice Scales: Keep in Mind..Dokument6 SeitenHow To Practice Scales: Keep in Mind..Amilcar Robles SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical TablesDokument10 SeitenStatistical TablesramanatenaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit AnalysisDokument9 SeitenCircuit AnalysisLester LazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equipment Production RateDokument5 SeitenEquipment Production RateLester Lazo100% (3)
- Deadliest Earthquakes On RecordDokument8 SeitenDeadliest Earthquakes On RecordLester LazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schnugh V The State (Bail Appeal) Case No 92-09 (Van Niekerk & Parker, JJ) 31jan'11 PDFDokument25 SeitenSchnugh V The State (Bail Appeal) Case No 92-09 (Van Niekerk & Parker, JJ) 31jan'11 PDFAndré Le RouxNoch keine Bewertungen
- EN GB SPIKE Prime Python ProgramsDokument31 SeitenEN GB SPIKE Prime Python ProgramsAMINE BOURASSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prizm Programming GuideDokument168 SeitenPrizm Programming GuideBucur MateiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Note 5 - Acoustics Impedance TransmissionDokument16 SeitenNote 5 - Acoustics Impedance TransmissionABB TRX IJMNoch keine Bewertungen
- WHITECROFT Energy Directive BrochureDokument32 SeitenWHITECROFT Energy Directive BrochureAriel TambisNoch keine Bewertungen
- NIOS Configuration Class: Course SummaryDokument2 SeitenNIOS Configuration Class: Course SummaryforeverbikasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar TimeDokument3 SeitenSolar TimeAkshay Deshpande0% (1)
- Psychology From Inquiry To Understanding Canadian 3rd Edition Lynn Test BankDokument38 SeitenPsychology From Inquiry To Understanding Canadian 3rd Edition Lynn Test Bankvoormalizth9100% (12)
- Environment OotDokument19 SeitenEnvironment OotMonojoy BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 12Dokument76 SeitenCH 12Christian JeremiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are You Going To Do Today?: Learning ObjectivesDokument10 SeitenWhat Are You Going To Do Today?: Learning ObjectivesMaryantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core CompetenciesDokument3 SeitenCore CompetenciesS on the GoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Point Exercise IDokument6 SeitenPower Point Exercise IAze FerriolsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Outline in Grade 1 MathematicsDokument3 SeitenCourse Outline in Grade 1 MathematicsRoselyn GutasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Textual Equivalence: Thematic and Information Structures: Because and Moreover, Which Are Called ConjunctionsDokument7 SeitenTextual Equivalence: Thematic and Information Structures: Because and Moreover, Which Are Called ConjunctionsDaniEllaNetNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Ebook PDF) - Statistics. .Spss - TutorialDokument15 Seiten(Ebook PDF) - Statistics. .Spss - TutorialMASAIER4394% (17)
- TEACHeXCELS Required ReadingsDokument69 SeitenTEACHeXCELS Required ReadingsJessica MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRM ThreeshortcasesDokument4 SeitenHRM ThreeshortcaseskhanmohsinjamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths InterviewDokument6 SeitenMaths InterviewKeamogetse BoitshwareloNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOUNTAINDokument8 SeitenMOUNTAINlara_sin_crof6873Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adu-Yeboah Emmanuel. Mphil in Leadership, UpsaDokument146 SeitenAdu-Yeboah Emmanuel. Mphil in Leadership, UpsaEmmanuel Adu-YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 802.11n: Next-Generation Wireless LAN Technology: White PaperDokument13 Seiten802.11n: Next-Generation Wireless LAN Technology: White PaperALEXANDRE JOSE FIGUEIREDO LOUREIRONoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimization Module For Abaqus/CAE Based On Genetic AlgorithmDokument1 SeiteOptimization Module For Abaqus/CAE Based On Genetic AlgorithmSIMULIACorpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabulation of Data and Parts of A Table - Presentation of Data - Everonn - Class-11th CommerceDokument2 SeitenTabulation of Data and Parts of A Table - Presentation of Data - Everonn - Class-11th CommerceMd Shawfiqul IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leopold, L. T. 1968 Hydrology For Urban Planning - A Guide Book On TheDokument26 SeitenLeopold, L. T. 1968 Hydrology For Urban Planning - A Guide Book On TheFiguraDesfiguraNoch keine Bewertungen