Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
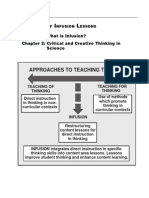
General Capabilities - CCT - Learning Continuum
Hochgeladen von
api-340721646Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
General Capabilities - CCT - Learning Continuum
Hochgeladen von
api-340721646Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Critical and Creative Thinking learning continuum
Sub-element
Level 1
Level 2
Level 3
Level 4
Level 5
Level 6
Typically, by the end of
Foundation Year, students:
Typically, by the end of
Year 2, students:
Typically, by the end of
Year 4, students:
Typically, by the end of
Year 6, students:
Typically, by the end of
Year 8, students:
Typically, by the end of
Year 10, students:
Inquiring identifying, exploring and organising information and ideas element
Pose questions
pose factual and
exploratory questions
based on personal
interests and experiences
pose questions to identify
and clarify issues, and
compare information in
their world
pose questions to expand pose questions to clarify
their knowledge about
and interpret information
the world
and probe for causes and
consequences
Identify
and clarify
information and
ideas
identify and describe
familiar information and
ideas during a discussion
or investigation
identify and explore
information and ideas
from source materials
identify main ideas
and select and clarify
information from a range
of sources
Organise
and process
information
gather similar information
or depictions from given
sources
organise information
based on similar or
relevant ideas from
several sources
collect, compare and
categorise facts and
opinions found in a
widening range of
sources
pose questions to
probe assumptions and
investigate complex
issues
pose questions to
critically analyse complex
issues and abstract ideas
identify and clarify
relevant information and
prioritise ideas
clarify information and
ideas from texts or
images when exploring
challenging issues
clarify complex
information and ideas
drawn from a range of
sources
analyse, condense
and combine relevant
information from multiple
sources
critically analyse
information and evidence
according to criteria such
as validity and relevance
critically analyse
independently sourced
information to determine
bias and reliability
Generating ideas, possibilities and actions element
Imagine
possibilities and
connect ideas
Consider
alternatives
Seek solutions
and put ideas
into action
use imagination to view
or create things in new
ways and connect two
things that seem different
build on what they know
to create ideas and
possibilities in ways that
are new to them
expand on known ideas
to create new and
imaginative combinations
combine ideas in a variety
of ways and from a range
of sources to create new
possibilities
draw parallels between
known and new ideas
to create new ways of
achieving goals
create and connect
complex ideas using
imagery, analogies and
symbolism
suggest alternative
and creative ways
to approach a given
situation or task
identify and compare
creative ideas to think
broadly about a given
situation or problem
explore situations
using creative thinking
strategies to propose a
range of alternatives
identify situations where
current approaches do
not work, challenge
existing ideas and
generate alternative
solutions
generate alternatives and
innovative solutions, and
adapt ideas, including
when information is
limited or conflicting
speculate on creative
options to modify ideas
when circumstances
change
predict what might
happen in a given
situation and when
putting ideas into action
investigate options
and predict possible
outcomes when putting
ideas into action
experiment with a range
of options when seeking
solutions and putting
ideas into action
assess and test options
to identify the most
effective solution and to
put ideas into action
predict possibilities,
and identify and test
consequences when
seeking solutions and
putting ideas into action
assess risks and explain
contingencies, taking
account of a range of
perspectives, when
seeking solutions and
putting complex ideas
into action
Critical and Creative Thinking learning continuum
Sub-element
Level 1
Level 2
Level 3
Level 4
Level 5
Level 6
Typically, by the end of
Foundation Year, students:
Typically, by the end of
Year 2, students:
Typically, by the end of
Year 4, students:
Typically, by the end of
Year 6, students:
Typically, by the end of
Year 8, students:
Typically, by the end of
Year 10, students:
Reflecting on thinking and processes element
Think about
thinking
(metacognition)
describe what they are
thinking and give reasons
why
describe the thinking
strategies used in given
situations and tasks
reflect on, explain and
check the processes
used to come to
conclusions
reflect on assumptions
made, consider
reasonable criticism and
adjust their thinking if
necessary
assess assumptions in
their thinking and invite
alternative opinions
give reasons to support
their thinking, and
address opposing
viewpoints and possible
weaknesses in their own
positions
Reflect on
processes
identify the main
elements of the steps in a
thinking process
outline the details and
sequence in a whole
task and separate it into
workable parts
identify pertinent
information in an
investigation and
separate into smaller
parts or ideas
identify and justify the
thinking behind choices
they have made
evaluate and justify the
reasons behind choosing
a particular problemsolving strategy
balance rational and
irrational components of
a complex or ambiguous
problem to evaluate
evidence
Transfer
knowledge into
new contexts
connect information from
one setting to another
use information from a
previous experience to
inform a new idea
transfer and apply
information in one setting
to enrich another
apply knowledge gained
from one context to
another unrelated context
and identify new meaning
justify reasons for
decisions when
transferring information
to similar and different
contexts
identify, plan and
justify transference
of knowledge to new
contexts
Analysing, synthesising and evaluating reasoning and procedures element
Apply logic and
reasoning
identify the thinking used
to solve problems in
given situations
identify reasoning used
in choices or actions in
specific situations
identify and apply
appropriate reasoning
and thinking strategies for
particular outcomes
assess whether there
is adequate reasoning
and evidence to justify
a claim, conclusion or
outcome
identify gaps in reasoning
and missing elements in
information
analyse reasoning used
in finding and applying
solutions, and in choice
of resources
share their thinking about
Draw
conclusions and possible courses of
design a course action
of action
identify alternative
courses of action or
possible conclusions
when presented with new
information
draw on prior knowledge
and use evidence when
choosing a course of
action or drawing a
conclusion
scrutinise ideas
or concepts, test
conclusions and modify
actions when designing a
course of action
differentiate the
components of a
designed course of
action and tolerate
ambiguities when drawing
conclusions
use logical and abstract
thinking to analyse and
synthesise complex
information to inform a
course of action
Evaluate
procedures and
outcomes
evaluate whether they
have accomplished what
they set out to achieve
explain and justify ideas
and outcomes
evaluate the effectiveness
of ideas, products,
performances, methods
and courses of action
against given criteria
explain intentions and
justify ideas, methods
and courses of action,
and account for expected
and unexpected
outcomes against criteria
they have identified
evaluate the effectiveness
of ideas, products and
performances and
implement courses of
action to achieve desired
outcomes against criteria
they have identified
check whether they
are satisfied with the
outcome of tasks or
actions
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Text InSPECtion on the Core: Close Reading Strategies for Uncovering Informational TextVon EverandText InSPECtion on the Core: Close Reading Strategies for Uncovering Informational TextNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structuring Learning Environments in Teacher Education to Elicit Dispositions as Habits of Mind: Strategies and Approaches Used and Lessons LearnedVon EverandStructuring Learning Environments in Teacher Education to Elicit Dispositions as Habits of Mind: Strategies and Approaches Used and Lessons LearnedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 MarzanoDokument2 SeitenChapter 4 MarzanoJocelyn Alejandra Moreno GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Thinker NaureenDokument20 SeitenCritical Thinker NaureenYasmeen JafferNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDP Teacher Template 1Dokument4 SeitenPDP Teacher Template 1api-236065109100% (1)
- Classroom TalkDokument8 SeitenClassroom Talkapi-340721646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson PresentationDokument27 SeitenLesson Presentationsadaf hashmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bachelor of Arts in English Studies: Course Specification Critical ThinkingDokument17 SeitenBachelor of Arts in English Studies: Course Specification Critical ThinkingNancy Tran NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 MarzanoDokument3 SeitenChapter 7 MarzanoJocelyn Alejandra Moreno GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edtpa Lesson PlansDokument11 SeitenEdtpa Lesson Plansapi-338231791Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rational and Irrational Numbers r1Dokument27 SeitenRational and Irrational Numbers r1Phani Kumar100% (1)
- Critical Thinking - The Disposition Toward Critical ThinkingDokument38 SeitenCritical Thinking - The Disposition Toward Critical ThinkingScott CarlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test-Taking Strategies For The Staar Eoc TestDokument30 SeitenTest-Taking Strategies For The Staar Eoc Testapi-2555419470% (1)
- Assure ModelDokument2 SeitenAssure Modelapi-317151826Noch keine Bewertungen
- Marzano's Levels of Thinking Question StemsDokument1 SeiteMarzano's Levels of Thinking Question StemsNathan LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assess Higher Order Thinking With Test QuestionsDokument45 SeitenAssess Higher Order Thinking With Test Questionsjoanna_gladysNoch keine Bewertungen
- InfusionDokument9 SeitenInfusionSheikhLanMapeala100% (1)
- Assessment: Formative & Summative: Practices For The ClassroomDokument23 SeitenAssessment: Formative & Summative: Practices For The ClassroomNiaEka1331Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3 Summarising PDFDokument10 SeitenTopic 3 Summarising PDFTan Lee FenNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTE Early (Reading Comprehension)Dokument2 SeitenLTE Early (Reading Comprehension)Early Dwinata AprilyanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emotional DisturbanceDokument2 SeitenEmotional Disturbanceapi-341965740Noch keine Bewertungen
- ThemeDokument24 SeitenThemedarth vadarNoch keine Bewertungen
- LDC Text Structure Guide PDFDokument2 SeitenLDC Text Structure Guide PDFintiw_23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Learning StylesDokument64 SeitenLearning Styleskamesh_p20013342Noch keine Bewertungen
- Today A Reader Tomorrow A Leader Project-FinalDokument19 SeitenToday A Reader Tomorrow A Leader Project-Finalapi-300622282Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Good Read Literacy Strategies With NewspapersDokument55 SeitenA Good Read Literacy Strategies With Newspapersapi-302151325Noch keine Bewertungen
- Learner Agency Teacher Activity SheetDokument4 SeitenLearner Agency Teacher Activity SheetfriboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Matters Assignment Week 5Dokument6 SeitenAssessment Matters Assignment Week 5api-266497495Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science Differentiation BriefDokument5 SeitenScience Differentiation BriefToh YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH03 Concise Fralick 5eDokument30 SeitenCH03 Concise Fralick 5eDenysse Solano CcantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Ged Rla 31 AugustDokument12 SeitenPre Ged Rla 31 Augustapi-686738446Noch keine Bewertungen
- Top Five Qualities of Effective Teachers, According To StudentsDokument3 SeitenTop Five Qualities of Effective Teachers, According To StudentsJaypee AdorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comprehension ArticleDokument6 SeitenComprehension Articleapi-287028643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jena Parsons ResumeDokument3 SeitenJena Parsons Resumeapi-218642075Noch keine Bewertungen
- Table Talk StrategyDokument3 SeitenTable Talk Strategyapi-248208787Noch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Styles and Multiple IntelligencesDokument12 SeitenLearning Styles and Multiple IntelligencesLaura CoravuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curry/Samara Model for Differentiating InstructionDokument24 SeitenCurry/Samara Model for Differentiating InstructionMansi NarangNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSOE Lesson Plan Template: Grade SubjectDokument8 SeitenHSOE Lesson Plan Template: Grade Subjectapi-307146309Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eng 101 - English Composition (Syllabus)Dokument6 SeitenEng 101 - English Composition (Syllabus)Arslan BaigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flipped Lesson Plan Template: Worksheet For Preparing What Students Will Do Before, During, and After The LessonDokument3 SeitenFlipped Lesson Plan Template: Worksheet For Preparing What Students Will Do Before, During, and After The LessonJANoch keine Bewertungen
- Socratic Seminar Explanation and Assignment SheetDokument3 SeitenSocratic Seminar Explanation and Assignment Sheetapi-285996086100% (1)
- Active Reading TechniquesDokument9 SeitenActive Reading TechniquesSudi Hope StodolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scaffolding Instruction For Ells-Resource Guide For Mathem PDFDokument83 SeitenScaffolding Instruction For Ells-Resource Guide For Mathem PDFjenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Unit Plan 1Dokument15 SeitenIntegrated Unit Plan 1api-242356907Noch keine Bewertungen
- School-Based Restorative Justice As An Alternative To Zero-Tolerance Policies, Berkeley, Nov 2010.Dokument40 SeitenSchool-Based Restorative Justice As An Alternative To Zero-Tolerance Policies, Berkeley, Nov 2010.Rick ThomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Analytical Thinking - A ChecklistDokument1 SeiteCritical Analytical Thinking - A Checklistronnie_ramsamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constructivist TeacherDokument19 SeitenConstructivist TeacherHectorDiaz100% (1)
- Nina M. Kurfman: 927 Village Park Way Savoy, IL 61874 (309) 531-3669Dokument3 SeitenNina M. Kurfman: 927 Village Park Way Savoy, IL 61874 (309) 531-3669njohnso8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Writing The Literature ReviewDokument23 SeitenWriting The Literature ReviewHarry FerdinandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Six Areas of The PLTS Framework: Independent Enquirers Team WorkersDokument2 SeitenThe Six Areas of The PLTS Framework: Independent Enquirers Team WorkersrafaelmariasanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Developing The Four Essential SkillsDokument2 SeitenDeveloping The Four Essential SkillsdavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ainsworth Rigourous Curric Diagram PDFDokument1 SeiteAinsworth Rigourous Curric Diagram PDFChrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ppat Cooperating Teachers HandbookDokument29 SeitenPpat Cooperating Teachers HandbookLorraine PorrasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lacks Essential Features of Effective PBL Needs Further Development Incorporates Best PBL PracticesDokument3 SeitenLacks Essential Features of Effective PBL Needs Further Development Incorporates Best PBL PracticeswendistraubNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCH 76220 wk6 LPDokument7 SeitenTCH 76220 wk6 LPapi-307146309Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2. Critical Thinking ReadingDokument12 SeitenChapter 2. Critical Thinking ReadingnolanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teachers’ Perceptions of Their Literacy Professional DevelopmentVon EverandTeachers’ Perceptions of Their Literacy Professional DevelopmentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delivering Inclusive and Impactful Instruction: Universal Design for Learning in Higher EducationVon EverandDelivering Inclusive and Impactful Instruction: Universal Design for Learning in Higher EducationNoch keine Bewertungen
- RubricDokument7 SeitenRubricapi-266405967Noch keine Bewertungen
- IrcriticalthinkingDokument19 SeitenIrcriticalthinkingapi-340721646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths 6 CharacteristicsDokument9 SeitenMaths 6 Characteristicsapi-340721646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reading ComprehensionDokument45 SeitenReading Comprehensionapi-340721646100% (1)
- Resilience SummaryDokument9 SeitenResilience Summaryapi-340721646Noch keine Bewertungen
- RubricDokument7 SeitenRubricapi-266405967Noch keine Bewertungen
- ComprehensionresearchDokument13 SeitenComprehensionresearchapi-340721646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Four Key Questions and Why They MatterDokument12 SeitenFour Key Questions and Why They Matterapi-340721646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ecological Modernization Theory: Taking Stock, Moving ForwardDokument19 SeitenEcological Modernization Theory: Taking Stock, Moving ForwardFritzner PIERRENoch keine Bewertungen
- Aditya Birla - FATCA and CRS - UBO - NON INDIVIDUALS PDFDokument2 SeitenAditya Birla - FATCA and CRS - UBO - NON INDIVIDUALS PDFHoaccounts AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo 4life en InglesDokument40 SeitenCatalogo 4life en InglesJordanramirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polystylism in The Context of Postmodern Music. Alfred Schnittke's Concerti GrossiDokument17 SeitenPolystylism in The Context of Postmodern Music. Alfred Schnittke's Concerti Grossiwei wuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guest Speaker SpeechDokument12 SeitenGuest Speaker SpeechNorhana Manas83% (82)
- Destiny by T.D. JakesDokument17 SeitenDestiny by T.D. JakesHBG Nashville89% (9)
- 19-Year-Old Female With Hypokalemia EvaluatedDokument5 Seiten19-Year-Old Female With Hypokalemia EvaluatedMohammed AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grimoire of Baphomet A-Z EditionDokument18 SeitenGrimoire of Baphomet A-Z EditionTheK1nGp1N100% (1)
- New Member OrientationDokument41 SeitenNew Member OrientationM.NASIRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Storm and Sewer Drains For Rajarhat (Ward No 4) in West Bengal Using Sewergems SoftwareDokument47 SeitenStudy of Storm and Sewer Drains For Rajarhat (Ward No 4) in West Bengal Using Sewergems SoftwareRuben Dario Posada BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intern - Annapolis PharmaceuticalsDokument34 SeitenIntern - Annapolis Pharmaceuticalsjoycecruz095Noch keine Bewertungen
- How Should Management Be Structured British English StudentDokument7 SeitenHow Should Management Be Structured British English Studentr i s uNoch keine Bewertungen
- Susan Oyama The Ontogeny of Information Developmental Systems and Evolution Science and Cultural Theory 2000Dokument297 SeitenSusan Oyama The Ontogeny of Information Developmental Systems and Evolution Science and Cultural Theory 2000Marelin Hernández SaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Apostolic Church, Ghana English Assembly - Koforidua District Topic: Equipping The Saints For The MinistryDokument2 SeitenThe Apostolic Church, Ghana English Assembly - Koforidua District Topic: Equipping The Saints For The MinistryOfosu AnimNoch keine Bewertungen
- AefiDokument38 SeitenAefizedregga2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Compiled May 5, 2017 Case DigestDokument16 SeitenCompiled May 5, 2017 Case DigestGrace CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- SalutogenicshandbookDokument16 SeitenSalutogenicshandbookAna EclipseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21st CenturyDokument22 SeitenTrends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21st CenturyGabrelle Ogayon100% (1)
- The Sweetheart Doctrine and Its InapplicabilityDokument4 SeitenThe Sweetheart Doctrine and Its InapplicabilityJosiah BalgosNoch keine Bewertungen
- M04 - Conditional Obligations and Reciprocal Obligations PDFDokument12 SeitenM04 - Conditional Obligations and Reciprocal Obligations PDFTam GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology of GingerDokument24 SeitenPharmacology of GingerArkene LevyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Man of Sorrows Wednesday of Holy Week Divine IntimacyDokument5 SeitenThe Man of Sorrows Wednesday of Holy Week Divine IntimacyTerri ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lumafusion Shortcuts LandscapeDokument2 SeitenLumafusion Shortcuts Landscapepocho clashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community ResourcesDokument30 SeitenCommunity Resourcesapi-242881060Noch keine Bewertungen
- CLNC 2040 Reflection of Assistant ExperiencesDokument4 SeitenCLNC 2040 Reflection of Assistant Experiencesapi-442131145Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vmware Vsphere Professional 8 Exam Dumps PDF (VCP DCV)Dokument158 SeitenVmware Vsphere Professional 8 Exam Dumps PDF (VCP DCV)romal ghulamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fitting A Logistic Curve To DataDokument12 SeitenFitting A Logistic Curve To DataXiaoyan ZouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salzer Panel Accessories Price List - 01st January 2019Dokument40 SeitenSalzer Panel Accessories Price List - 01st January 2019Chandra SekaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deforestation Contributes To Global Warming: Bruno GERVETDokument11 SeitenDeforestation Contributes To Global Warming: Bruno GERVETMajid JatoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Exam ADM3350 Summer 2022 PDFDokument7 SeitenMidterm Exam ADM3350 Summer 2022 PDFHan ZhongNoch keine Bewertungen