Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cloud Experiments
Hochgeladen von
junkforme999Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cloud Experiments
Hochgeladen von
junkforme999Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
A Cloud Computing Solution in Universities
developerWorks
Technical topics
SOA and web services
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/webservices/...
Technical library
A Cloud Computing Solution in Universities
Virtual computing lab
This article details the concept of cloud computing using a Virtual Computing Lab (VCL). We specifically focus on a
cloud computing implementation methods through the VCL, how it helps within a research-oriented educational
institution of higher learning, and finally, we discuss some of the important factors that demonstrate how a VCL
provides a scalable, sustainable, economically valuable and viable contribution to the campus layer IT cyberinfrastructure.
Jithesh Moothoor is a Software Engineer in TXSeries, at IBM. He has successfully deployed Virtual Computing Lab at different universities in
India, as part of the IBM University Relation program. His areas of interest include high-performance computing, cloud computing, and UNIX
systems.
Vasvi A Bhatt is a Software Engineer in TXSeries, at IBM. Her areas of interest include cloud computing, and UNIX systems.
05 January 2010
Also available in Chinese Russian Spanish
Introduction
Over the past few years, the concept of cloud computing and virtualization has
gained much momentum and has become a more popular phrase in
information technology. Many organizations have started implementing these
new technologies to further reduce costs through improved machine
utilization, reduced administration time and infrastructure costs. Cloud
computing is the environment that enables customers to use applications on
the Internet such as storing and protecting data while providing a service.
VCL is a cloud computing idea developed at the North Carolina State University (NCSU) through a
collaboration of its College of Engineering and IBM Virtual Computing Initiative to address a growing set
of computational needs and user requirements for the university. This system can deliver user required
solutions for variety of service environments anytime and anyplace on demand/reservation.
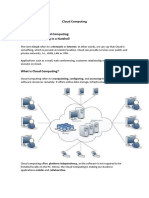
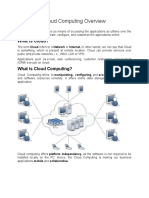
Architectural layers of cloud computing
A cloud computing platform dynamically provisions, configures, reconfigures, the servers as needed.
Servers in the cloud can be physical machines or virtual machines. Advanced clouds typically include
other computing resources such as storage area networks (SANs), network equipment, firewall and other
security devices. In general, cloud service providers tend to offer services that can be grouped mostly
into three categories:
1. Infrastructure as a service
2. Platform as a service
1 of 11
Saturday 30 November 2013 07:45 AM
A Cloud Computing Solution in Universities
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/webservices/...
3. Software as a service
These categories grouped together and explained with the help of VCL in Figure 1. Read more details
about cloud concepts in Resource section.
Figure 1. VCL Cloud Services
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS is the delivery of computer infrastructure as a service. Infrastructure as a service offers computing
capabilities and basic storage as standardized services over the network. Servers, storage systems,
switches, routers, and other systems are reserved and made available to handle workloads. IaaS clouds
make it very affordable way to provision resources such as servers, connections, storage, and related
tools necessary to build an application environment from scratch on-demand.
The benefits of IaaS include rapid provisioning, ability to scale and pay only for what you use. For a
startup or small business, one of the most difficult things is to keep capital expenditures under control. By
moving your infrastructure to the cloud, you have the provision to scale as if you owned your own
hardware and data center (which is not realistic with a traditional hosting provider) but you keep the
upfront costs to a minimum.
VCL delivers different infrastructure at one place. It provides a platform (internally no physical
infrastructure) virtualization environment in the Universities. Using this, student need not to set up any
specific physical infrastructure for their project assignment. VCL provides following services for
infrastructure.
Compute
Physical Machines
Virtual Machines
OS-level virtualization
Network
Storage
VCL manager provides appropriate virtualization (aggregation, dis-aggregation) of the available hardware
2 of 11
Saturday 30 November 2013 07:45 AM
A Cloud Computing Solution in Universities
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/webservices/...
resources before mapping the requested image onto that hardware. VCL services focus on controlling the
resource at the platform level.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a service is a virtualized platform that comprises one or more servers (virtualized over the set
of physical servers), operating systems, and specific applications (such as Apache and MySQL for
Web-based applications). In some cases, you can provide a VM image that contains all the necessary
user-specific applications. Platform as a service comprise a layer of software and provides it as a service
that can be used to build higher-level services. There are at least two perspectives on PaaS depending
on the perspective of the producer or consumer of the services:
The person producing (Here VCL) PaaS might produce a platform by integrating an OS, middleware,
application software, and even a development environment that is then provided to a customer as a
service.
The person using (users in Universities) PaaS would see an encapsulated service that is presented to
them through an interface. The customer interacts only with the platform through the interface, and the
platform does what is necessary to manage and scale it to provide a given level of service. The Virtual
appliances can be classified as instances of PaaS.
Using VCL, Students need not to physically install any specific services, solution stacks or databases on
their machine. It provides the images to students where they can simply select these images and use
them on a machine provided in a cloud.
Services
Solution Stacks
Java
PHP
.NET
Storage
Databases
File Storage
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is the ability to access software over the Internet as a service. Software as a service has a
complete application to offer as a service on demand. A single instance of the software runs on the cloud
and services multiple end users or client organizations. Here the best example remote application service
is Google Apps, which provides several enterprise applications through a standard Web browser.
VCL allows any of the software as a service solutions, virtualization solutions, and terminal services
solutions available today. VMWare, XEN, MS Virtual Server, Virtuoso, and Citrix are typical examples.
VCL also as allows any of the access/service delivery options those are suitable from RDP or VNC
desktop access, to X-Windows, to a Web service or similar.
3 of 11
Saturday 30 November 2013 07:45 AM
A Cloud Computing Solution in Universities
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/webservices/...
Cloud computing infrastructure models
Cloud computing architects need to make some considerations about infrastructure models when moving
from a standard enterprise application deployment model to one based on cloud computing. There are
three basic service models to consider in a university based cloud computing, such as Public, Private and
Hybrid clouds.
1. Public clouds
Public computing clouds are open to anyone who wants to sign up and use them. Public clouds are run
by vendors, and applications from different customers are likely to be mixed together on the clouds
servers, storage systems, and networks. One of the benefits of public clouds is that they can be much
larger than a companys private cloud and can offer the ability to scale up and down on demand, shifting
infrastructure risks from the enterprise to the cloud provider.
IBM operates a cloud data center for its customers. Multiple customers share the same infrastructure, but
each others cloud is secure and separated as though behind its own firewall.
2. Private clouds
The intention of designing the private cloud is basically an organization that needs more control over their
data than they can get by using a vendor hosted service. Private clouds are built for the exclusive use of
one organization, providing the utmost control over data, security, and quality of service. Private clouds
typically sit behind the firewall of an organization (enterprise or university), and only people within that
organization have permission to access the cloud and its resources.
3. Hybrid clouds
Hybrid clouds combine both public and private cloud models. This model introduces the complexity of
determining how to distribute applications across both a public and private cloud. If the data is small, or
the application is stateless, a hybrid cloud can be much more successful than if large amounts of data
must be transferred into a public cloud for a small amount of processing.
VCL can work on Hybrid cloud model. It can provide services and infrastructure to the students and
faculties of single university acting as a private cloud. It can also extend this services for inter university
using public cloud. This requires more secure network.
Heterogeneous resource clouds
The main intention of designing heterogeneous cloud in universities is to significantly decrease the
configuration scale of the cluster system through consolidating heterogeneous workloads, while
increasing the number of requests for parallel workload by provisioning enough resources (e.g., based on
Globus, Hadoop, or Condor). For large organization, different utilities often maintain dedicated cluster
systems for different workloads. Thus the main challenge is to consolidate heterogeneous workloads of
the same organization on the cloud computing platform through VCL.
From the perspective of a VCL, it can transform and support any type of environment (as heterogeneous)
as long as an image with the appropriate environment manager is available.
High-level architecture of VCL
This VCL architecture mainly is intended for designing and configuring a cloud computing system that
4 of 11
Saturday 30 November 2013 07:45 AM
A Cloud Computing Solution in Universities
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/webservices/...
serve both the educational and research missions of the university in a very economical and cost efficient
manner. VCL delivers a range of functionalities and services that map well onto the cloud computing
requirements and its expectations. There are few principal components in the VCL architecture as shown
in Figure 2.For more information about VCL and its working model, see the Resource section.
An end-user access interface (web-based)
A resource-manager (or VCL manager) which includes a scheduler, security, performance monitoring,
virtual network management, etc
An image repository (or image)
Computational, storage and networking hardware
Security
Figure 2. VCL physical architecture
User
Initially user accesses VCL through a Web interface to select desired combination of application from a
menu. See Figure 3. If a user specific image combination is not already available as an image, an
authorized user can have the flexibility to construct their own image from the VCL library components.
The VCL manager software then maps that user request to available software application images and
(possibly heterogeneous) hardware resources, and schedules it for either immediate use (on demand) or
for later use.
Figure 3. New reservation of resource with desired image
The mode of access to resources will depend on the service offering. See Figure 4. It may range from
RDP or VNC type of access to a remote desktop, to an ssh-based or an X-Win access to a Linux service,
5 of 11
Saturday 30 November 2013 07:45 AM
A Cloud Computing Solution in Universities
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/webservices/...
to Web-based access, and as a proxy access to a computational cluster.
Figure 4. Current reservation and ssh-based connection
VCL manager
The typical job of VCL manager includes checking the environments, managing computers and managing
images. The VCL manager software comprising the following products:
1. IBM xCAT and VM loader
The Extreme Cluster Administration Toolkit (xCAT) is a collection of mostly script based tools to build,
configure, administer, and maintain Linux clusters. The VCL used xCAT to load the requested bare-metal
image to a blade server.
While the original VCL was bare-metal oriented, today it loads either a VMware-based image or a
bare-metal image. The VCL system processes the request. If it does not find an available real or virtual
server with the desired image already loaded, it selects any available server meeting the specifications
required for that image, xCAT, or the appropriate VM loader, dynamically loading the desired image.
Here, the physical machine provisioning happened through xCAT and the virtual machine provisioning
happened through VMware ESXi, VMware ESX Standard server, VMware free server.
If all servers are busy, the Web interface informs the student on the available times using a grid.
2. VCL middle layer demon service (vcld)
The core part of VCL manager is a perl based VCL demon service (vcld) used to perform the actual
provisioning and deployment. Based on the type of environment requested - whether it is a bare-metal
image, a lab machine, or a virtual machine image, vcld ensures the image is loaded and makes it
available for the requests. Common utilities of a vcld service are:
Communicate between Web interface and database to get the installation details and process
reservation/job assigned by the VCL Web portal
Initiating xCAT or VMware commands to perform requested operation
Monitor the image installation procedure and installing requested postscript installation tools
Maintaining the machine provisioning and deployment procedure
Configuring and administrating the installed image for the requested use
Maintaining the installation and configuration time
3. An open source web server (Apache)
The PHP based Web application (deployed in Apache Web server) is the heart of VCL and provides tools
to request, manage, and govern all VCL resources. The Web interface allows authenticated users,
6 of 11
Saturday 30 November 2013 07:45 AM
A Cloud Computing Solution in Universities
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/webservices/...
displays a list of applications they are authorized to use, and allows them to reserve the use of an
application either immediately or sometime in the future for a specified length of time. The range of future
time and the length of reservation are customizable and can differ based on the user. The major utilities
provided by Web interface includes:
Image creation This interface allow users to create customized environments.
Image revision control This interface provide privileged users to create multiple revisions of same
image.
Manage users This provides user privilege control, it grants varying levels of control to users through
Web interface.
Manage resource This interface provides a method to schedule the resources in the pool.
4. An open source data base (MySQL)
The MySQL database to track each servers state, maintains information about each image, and
implements a privilege tree.
Image
In VCL, the term image is a software stack that incorporates the following utilities:
Base-line operating system, and if virtualization is needed for scalability, this will allow on hypervisor
layer
Desired middleware or application that runs on the selected operating system
End-user access solution that is appropriate for the selected operating system
Images can be loaded on bare-metal, or to an operating system/application virtual environment of choice.
If the user's desired combination of images is not available, the user has the privilege to construct the
images in their own choice from the VCL component library. When a user has the right to create an
image, that user usually starts with a NoApp or base-line image (Windows XP or Linux) and extends it to
the applications.
Computational hardware/network storage
Virtualization completely abstracts the hardware to the point where software stacks can be deployed and
redeployed without being tied to a specific physical server. VCL servers provide a pool of resources that
are exploited for the users needs. The resources are allocated depending on the particular applications
that are to be computed. The storage and network resource are dynamic, meeting both the workload and
user demands.
The term compute clouds are usually complimented by storage clouds that provide virtualized storage
through VCL facilitating the storage of virtual machine images. In VCL, computational hardware and
storage can be anything from a blade center, to a collection of diverse desktop units or workstations, to
an enterprise server or to a high-performance computing engine.
A typical VCL installation will have one or more blade chassis, usually one of the blades being designated
as the management node. Each blade has at least two networking interfaces one for the public
7 of 11
Saturday 30 November 2013 07:45 AM
A Cloud Computing Solution in Universities
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/webservices/...
network, and the other for a private network that is used to manage the blades and load images. Storage
is attached either directly through fiber or through a network. See Figure 5, below.
Figure 5. VCL Application Storage
Security in VCL
It is difficult to justify, what security means in the context of cloud. The ultimate level of security measures
needed for any distributed system comes from both authentication and authorization of services. VCL
implemented the following level of securities in their system:
LDAP based authentication
VCL authentication is an affiliation based LDAP service. Based on the user affiliation, VCL supports
different LDAP services for separate user access.
Environment level authentication
This mode of authentication will vary depending on the environment. It is usually determined by the
image creation time. In Windows, it will create a single one-time account that gets created at reservation
time and will expire after use. In a Linux environment, it can make use of either existing authentication
infrastructure or can also use standalone account mechanism.
Apart from these, if a user is authorized and allowed to make a VCL reservation, VCL IP-locks the
provisioned environment to end-user IP address using OS level firewall.
High Performance Computing and VCL
There are mainly two implications for the High Performance Computing (HPC) level of machine utilization
in universities. First, the need for HPC machines in universities - it is mainly to solve/compute demanding
problems. Second, it is very hard to accommodate the hardware resources for increasing requests from
VCL. The basic working model of VCL on HPC services is fairly simple. See Figure 6, below. To know
more about VCL HPC and its usage, see Resource section.
Figure 6. Basic model of HPC in VCL
8 of 11
Saturday 30 November 2013 07:45 AM
A Cloud Computing Solution in Universities
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/webservices/...
Prerequisite for HPC
Network switch A new private network for message traffic using NIC that would be used for public
network user access.
You need to configure Virtual Local Area Networks (VLAN) on one chassis switch module. One for
public internet access and one for private message passing interface.
VCL management node configured blade VLAN based on image metadata.
Working method
The basic working model of HPC in a VCL is as shown in Figure 7. Under VCL control, xCAT loads HPC
computational images to idle blade nodes, and the VCL control software adjusts VLAN settings on the
chassis Ethernet switches, to connect the servers to private HPC networks. In an HPC environment, VCL
provides public access only through login nodes. The master HPC login node image includes
components of the HPC scheduler. Currently, Load Sharing Facility (LSF) is used in VCL (like platform
computing). Each HPC client image has access to a large amount of storage (in terabytes), as well as
user home directories and HPC backup storage. When an HPC image is loaded, the VCL manager
scheduler recognizes it and begins to assign it work.
Figure 7. Basic layout of Blade Server in VCL HPC
9 of 11
Saturday 30 November 2013 07:45 AM
A Cloud Computing Solution in Universities
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/webservices/...
The integration of HPC in VCL significantly increases resource utilization by the reuse of blade servers.
This method allows the infrastructure to be shared among user requests, which leads to a greater
availability of resources.
Benefits of using VCL in labs a cloud solution
We have identified some major capabilities of VCL cloud computing with help of the VCL lab performance
through diagrams to explain major benefits. In universities, users are typically students and faculties.
Cloud computing systems serving these users within a university environment must at least provide the
following capabilities:
Services and support to a wide range of users.
A wide-range of course materials and academic support tools to instructors, teachers, professors, and
other educators and university staff.
Research level computational systems and services in support of the research mission of the university.
With these requirements, the major challenges of planning a cloud computing solution in a higher
educational, research-oriented institute involves following factors:
Excellent resource utilization depending on different user demands
Variety of diverse service environments
Operating cloud infrastructure as an economically viable model
In universities the usage of resources will vary depending on the academic calendar. Demand for
resources will be more during assignments and year-end time. The research projects and other research
oriented activities are active throughout the year. So for a university based cloud computing system to be
economically viable, it requires a proper scheduling mechanism to monitor demand and allocate the
system resources. VCL provides good scheduling mechanism to identify the ebbs and flows of campus
activities.
Here, by the observations and insights from the VCL environment at Universities, the important inference
that we can identify in VCL is that, with the help of desktop and HPC utilization, VCL provides efficient
utilization of the computational infrastructure in Universities labs. Also, using the VCL blades for both
HPC and VCL desktops provides economical services with optimum use of resources.
We can thus conclude that a VCL is an open-source Web based system used to dynamically provision
and broker remote access to a dedicated computer environment for a user. VCL cloud provides
exceptional computing power through a unique Open Software and Hardware Solution to run and host all
university projects and learning programs.
Acknowledgements
The VCL Paper provides information on the use of VCL in universities. I wish to thank Mr. Aaron Peeler,
Program Manager and core member of VCL development team, for providing us with support to write this
article and offer suggestion/comments about VCL and its working model.
10 of 11
Saturday 30 November 2013 07:45 AM
A Cloud Computing Solution in Universities
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/webservices/...
Resources
Learn
For information on concepts of VCL, installation details and the mailing list,
see Open source VCL APACHE incubator.
Dig deeper into SOA and web
services on developerWorks
Overview
New to SOA and web services
Technical library (articles and more)
The Cost Effective VCL will provide information on the performance of VCL in
universities.
Downloads and products
The Hadoop core Web site is the best resource for learning about Hadoop.
Standards
Here you will get the concepts of VCL and its detailed working model.
Wikipedia explains the topic of cloud computing and its related technologies.
Browse the technology bookstore for books on these and other technical
topics.
Get products and technologies
JBoss Application Server, Geronimo, and WebSphere Application Server are
some of the most popular application servers providing a local and Web
services model for SaaS.
Download IBM product evaluation versions or explore the online trials in the
IBM SOA Sandbox and get your hands on application development tools and
middleware products from DB2, Lotus, Rational, Tivoli, and
WebSphere.
Open source projects
Events
developerWorks Labs
Experiment with new directions in
software development.
JazzHub
Software development in the
cloud. Register today and get free
private projects through 2014.
IBM evaluation software
Evaluate IBM software and
solutions, and transform
challenges into opportunities.
Discuss
Check out developerWorks blogs and get involved in the developerWorks
community.
11 of 11
Saturday 30 November 2013 07:45 AM
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionVon EverandCloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEH v12 Lesson 12 - Introduction To Cloud CompDokument23 SeitenCEH v12 Lesson 12 - Introduction To Cloud CompAbhay JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingVon EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud ComputingDokument14 SeitenCloud ComputingNabeela Khaled100% (1)
- LECTDokument17 SeitenLECTSruthi RNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT2-Introduction To Cloud Computing4 PDFDokument95 SeitenUNIT2-Introduction To Cloud Computing4 PDFjanuaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xperiment: Loud OmputingDokument7 SeitenXperiment: Loud OmputingTejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC Evolution Od CloudDokument51 SeitenCC Evolution Od CloudTushar MircheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing TutorialDokument36 SeitenCloud Computing TutorialTAMIRE SANTOSH MOHAN100% (1)
- Cloud ComputingDokument15 SeitenCloud ComputingHala GharibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Based E-Voting ReportDokument23 SeitenCloud Based E-Voting ReportVinu DavisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution of Cloud ComputingDokument8 SeitenEvolution of Cloud Computinghiteshsharma01abuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrastructure As A Service (Iaas) : Cloud Computing Is Computing in Which Large Groups of Remote Servers AreDokument4 SeitenInfrastructure As A Service (Iaas) : Cloud Computing Is Computing in Which Large Groups of Remote Servers Arebhariprasad_mscNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing All Units PDFDokument110 SeitenCloud Computing All Units PDFRahul Gudla100% (1)
- Cloud ComputingDokument20 SeitenCloud ComputingxyzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Various Approaches For Cloud ComputingDokument8 SeitenVarious Approaches For Cloud ComputingAvneesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Challenges WithDokument10 SeitenCloud Computing Challenges WithAIRCC - IJCNCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud ComputingDokument26 SeitenCloud ComputingGagandeep Kaur100% (1)
- Virtualizing The Private Cloud For Maximum Resource UtilizationDokument5 SeitenVirtualizing The Private Cloud For Maximum Resource UtilizationIjarcet JournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 What Is Cloud Computing:: 1.1.1 Infrastructure As A Service (IAAS)Dokument78 Seiten1.1 What Is Cloud Computing:: 1.1.1 Infrastructure As A Service (IAAS)Luckinsi SamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing: Mini Project Work Entiled OnDokument24 SeitenCloud Computing: Mini Project Work Entiled OnZeanav KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing TDokument6 SeitenCloud Computing TROW OF 2 GONoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Infrastructure and Services PDFDokument29 SeitenCloud Infrastructure and Services PDFbuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis On Cloud ComputingDokument71 SeitenThesis On Cloud Computingashutoshsnp96Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit III VirtualizationDokument31 SeitenUnit III Virtualizationsri nidhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing GuideDokument39 SeitenCloud Computing GuideCalin SeitanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing in Higher Education Oppo PDFDokument10 SeitenCloud Computing in Higher Education Oppo PDFGabrielGarciaOrjuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing EssayDokument14 SeitenCloud Computing EssayDeepak100% (2)
- Cloud 3Dokument16 SeitenCloud 3vikram kumar jonnalagaddaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5Dokument44 SeitenUnit 5kaustubhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osamah Shihab Al-NuaimiDokument7 SeitenOsamah Shihab Al-NuaimiOmar AbooshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing: Issues and ChallengesDokument7 SeitenCloud Computing: Issues and ChallengesadamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing: A Security Concern: MBA (Marketing) SEM II IMS, Lucknow UniversityDokument12 SeitenCloud Computing: A Security Concern: MBA (Marketing) SEM II IMS, Lucknow UniversityShadaab AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud FinalDokument6 SeitenCloud FinalDivyasriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment: Q1. What Is Cloud Computing? AnsDokument8 SeitenAssignment: Q1. What Is Cloud Computing? Ansvashishttyagi91Noch keine Bewertungen
- Iaas Implementation of A Private Cloud Using Open Source TechnologyDokument7 SeitenIaas Implementation of A Private Cloud Using Open Source TechnologyTú NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arya College of Engineering and Research Centre: Industrial TrainingDokument28 SeitenArya College of Engineering and Research Centre: Industrial Trainingriya ahujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 1-Cloud ComputingDokument34 SeitenUNIT 1-Cloud ComputingMalathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nisha Report3.....Dokument19 SeitenNisha Report3.....abdulqaiyum710636Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Overview of Cloud ComputingDokument7 Seiten2-Overview of Cloud ComputinginderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Architectures in Cloud ComputingDokument35 SeitenArchitectures in Cloud Computingsuga1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud ComputingDokument6 SeitenCloud Computingshariful islamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Platform Architecture Over Virtualized DataDokument10 SeitenCloud Platform Architecture Over Virtualized DataIbrahim AlJarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud ComputingDokument25 SeitenCloud Computingmukulsharma3779Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Landscape-The Importance of StandardsDokument4 SeitenCloud Computing Landscape-The Importance of StandardsChanchal JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing: (A Computing Platform For Next-Generation Internet)Dokument7 SeitenCloud Computing: (A Computing Platform For Next-Generation Internet)Srini VasuluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assg 7Dokument8 SeitenAssg 7bhalaninaman7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report Cloud ComputingDokument15 SeitenReport Cloud ComputingsaneshsivanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Deployment ModelsDokument5 SeitenCloud Computing Deployment ModelsShreyas GokhaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing OverviewDokument6 SeitenCloud Computing OverviewsasikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON in ELECTIVE 4Dokument7 SeitenLESSON in ELECTIVE 4GENED Bernadine GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shri Ramswaroop Memorial University: Submitted To Mr. Anand RaiDokument19 SeitenShri Ramswaroop Memorial University: Submitted To Mr. Anand RaiAaqib KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Microsoft Azure FundamentalsDokument8 SeitenIntroduction To Microsoft Azure FundamentalsFAseeh MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part A Unit 3Dokument8 SeitenPart A Unit 3vijayccnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 1 - Describe Cloud ConceptsDokument12 SeitenPart 1 - Describe Cloud ConceptsCarlo SeixasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Overview of Cloud ComputingDokument18 SeitenDetailed Overview of Cloud ComputingAravind Kumar CSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing - Quick GuideDokument25 SeitenCloud Computing - Quick GuideMadhav ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing2Dokument14 SeitenCloud Computing2MeganadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review Cloud Computing SecuriDokument5 SeitenLiterature Review Cloud Computing SecuriSathishkumar ThirumoorthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Md. Moniruzzaman - CC - Assign-1Dokument4 SeitenMd. Moniruzzaman - CC - Assign-1MD Monowar Ul IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Face Consultants Limited: Concrete Society'S Technical Report: 4 EditionDokument14 SeitenFace Consultants Limited: Concrete Society'S Technical Report: 4 EditionVincent_rko1Noch keine Bewertungen
- How To Measure MTFDokument64 SeitenHow To Measure MTFamtcorporationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creating REST API Using NodeJS and Consuming in AngularJSDokument8 SeitenCreating REST API Using NodeJS and Consuming in AngularJSserignemodouNoch keine Bewertungen
- GWSSB Vendor List 19.11.2013Dokument18 SeitenGWSSB Vendor List 19.11.2013sivesh_rathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Softening N Penetration Test BitumenDokument11 SeitenSoftening N Penetration Test BitumenEdwin LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- S09 Power TrainDokument90 SeitenS09 Power TrainPLANEAMIENTO MDRILLNoch keine Bewertungen
- RequirementsDokument18 SeitenRequirementsmpedraza-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Assurance Plan (1) ..Dokument5 SeitenQuality Assurance Plan (1) ..ARUNKUMARANNANBHEDANoch keine Bewertungen
- Mauser 98K - Model 48 Rifle ManualDokument20 SeitenMauser 98K - Model 48 Rifle ManualMeor Amri96% (28)
- Advance Logic Activity On CountersDokument31 SeitenAdvance Logic Activity On CountersKrinx BuliganNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENOVIA V6 Product PortfolioDokument32 SeitenENOVIA V6 Product PortfolioARUN PATILNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prospects For Alkaline Zero Gap Water Electrolysers For Hydrogen ProductionDokument16 SeitenProspects For Alkaline Zero Gap Water Electrolysers For Hydrogen Productionkhan47pkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Woson 23 Litre B Class Touch AutoclaveDokument2 SeitenWoson 23 Litre B Class Touch AutoclaveBashar MohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- AB-522 Standard Pneumatic Test Procedure RequirementsDokument16 SeitenAB-522 Standard Pneumatic Test Procedure RequirementsShank HackerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultrasonic Mixer: Project 99.11Dokument11 SeitenUltrasonic Mixer: Project 99.11Febri SandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement Advisory Committee Summary - Attachment 3Dokument70 SeitenMeasurement Advisory Committee Summary - Attachment 3MauricioICQNoch keine Bewertungen
- BKLT DeaeratorDokument24 SeitenBKLT Deaeratormalikgaurav01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Portal Info StubDokument11 SeitenPortal Info Stubzamanqomaru8Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Sample of Wet Soil Has A Volume of 0Dokument8 SeitenA Sample of Wet Soil Has A Volume of 0eph0% (1)
- Acceleration GrpahDokument14 SeitenAcceleration GrpahRAFAEL TORRESNoch keine Bewertungen
- GM Passlock II SystemDokument14 SeitenGM Passlock II Systemalmia tronicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20 Site SummaryDokument2 Seiten20 Site SummaryMuzammil WepukuluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Flashcards: by Jonathan DonadoDokument520 SeitenExam Flashcards: by Jonathan Donadosolarstuff100% (1)
- AHRLACDokument18 SeitenAHRLACVictor Pileggi100% (1)
- Cif Purge Plug Systems en 3Dokument3 SeitenCif Purge Plug Systems en 3abdeljalil elbadrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychrometric Chart - Us and Si UnitsDokument1 SeitePsychrometric Chart - Us and Si UnitsRaden_Rici_Abi_1914Noch keine Bewertungen
- Know PlywoodDokument3 SeitenKnow PlywoodNirvana NircisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piping Handbook - Hydrocarbon Processing - 1968Dokument140 SeitenPiping Handbook - Hydrocarbon Processing - 1968VS271294% (16)
- Cbse PMT 2012Dokument33 SeitenCbse PMT 2012Vishal RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Korantin PPDokument4 SeitenKorantin PPteddy garfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]Von EverandiPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Linux For Beginners: The Comprehensive Guide To Learning Linux Operating System And Mastering Linux Command Line Like A ProVon EverandLinux For Beginners: The Comprehensive Guide To Learning Linux Operating System And Mastering Linux Command Line Like A ProNoch keine Bewertungen
- iPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsVon EverandiPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Linux Shell Scripting Cookbook - Third EditionVon EverandLinux Shell Scripting Cookbook - Third EditionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Excel : The Ultimate Comprehensive Step-By-Step Guide to the Basics of Excel Programming: 1Von EverandExcel : The Ultimate Comprehensive Step-By-Step Guide to the Basics of Excel Programming: 1Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Kali Linux - An Ethical Hacker's Cookbook - Second Edition: Practical recipes that combine strategies, attacks, and tools for advanced penetration testing, 2nd EditionVon EverandKali Linux - An Ethical Hacker's Cookbook - Second Edition: Practical recipes that combine strategies, attacks, and tools for advanced penetration testing, 2nd EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Mastering Windows PowerShell ScriptingVon EverandMastering Windows PowerShell ScriptingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Windows Server 2019 Administration Fundamentals - Second Edition: A beginner's guide to managing and administering Windows Server environments, 2nd EditionVon EverandWindows Server 2019 Administration Fundamentals - Second Edition: A beginner's guide to managing and administering Windows Server environments, 2nd EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- RHCSA Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9: Training and Exam Preparation Guide (EX200), Third EditionVon EverandRHCSA Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9: Training and Exam Preparation Guide (EX200), Third EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAC OS X UNIX Toolbox: 1000+ Commands for the Mac OS XVon EverandMAC OS X UNIX Toolbox: 1000+ Commands for the Mac OS XNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linux for Beginners: Linux Command Line, Linux Programming and Linux Operating SystemVon EverandLinux for Beginners: Linux Command Line, Linux Programming and Linux Operating SystemBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Linux: A Comprehensive Guide to Linux Operating System and Command LineVon EverandLinux: A Comprehensive Guide to Linux Operating System and Command LineNoch keine Bewertungen
- RHCSA Exam Pass: Red Hat Certified System Administrator Study GuideVon EverandRHCSA Exam Pass: Red Hat Certified System Administrator Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mastering Swift 5 - Fifth Edition: Deep dive into the latest edition of the Swift programming language, 5th EditionVon EverandMastering Swift 5 - Fifth Edition: Deep dive into the latest edition of the Swift programming language, 5th EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- React.js for A Beginners Guide : From Basics to Advanced - A Comprehensive Guide to Effortless Web Development for Beginners, Intermediates, and ExpertsVon EverandReact.js for A Beginners Guide : From Basics to Advanced - A Comprehensive Guide to Effortless Web Development for Beginners, Intermediates, and ExpertsNoch keine Bewertungen
- RedHat Enterprise Linux 9 for Beginners: A comprehensive guide for learning, administration, and deployment (English Edition)Von EverandRedHat Enterprise Linux 9 for Beginners: A comprehensive guide for learning, administration, and deployment (English Edition)Noch keine Bewertungen






















































































![iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/728318688/198x198/f3385cbfef/1715193157?v=1)




























