Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Auditing1 Odt
Hochgeladen von
Beviiee BisnarOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Auditing1 Odt
Hochgeladen von
Beviiee BisnarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
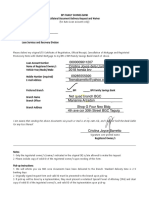
an official examination and verification of accounts and records,especially of financial accounts.
2.
a report or statement reflecting an audit; a final statement of account.
3.
the inspection or examination of a building or other facility to evaluateor improve its appropriateness
, safety, efficiency, or the like:
Auditing
Formal Definition: A systematic process of (1) objectively obtaining and evaluating evidence regarding assertions
about economic actions and events to ascertain the degree of correspondence between those assertions and
established criteria and (2) communicating the results to interested users.
Informal Definition: An auditor's job is to ensure the integrity of financial data. When performing an audit, an
auditor will request access to the business' financial records. This includes the ledgers, lists of receipts and
expenditures, bank balances, records of physical assets owned or leased and many other records. The auditor
will also interview personnel and review the business' accounting system and its internal controls. In essence,
the auditor will review any activity that affects the business' finances.
Audits exist because they add value through easing the cost of information asymmetry, not just because they are
required by law. For example, a privately-held company that does not issue securities on a public exchange
might engage a firm to audit its financial statements in order to obtain more desirable loan terms from a financial
institution. Without the audit, the lending party would not have assurance as to whether or not the company's
financial position is accurate. In turn, the lender could price protect (raise their price) against this information
asymmetry.
An auditor working for a private business may review a client's banking and other financial statements, to verify
that they have been correctly prepared and appropriately reported as required by the law. Auditors must keep
themselves educated of any changes in law that will affect how their clients must report financial information. It is
important that the auditor be able to give an unbiased evaluation of a client's records.
Auditors are not expected to guarantee that 100 percent of the transactions are recorded correctly. They are only
required to express an opinion as to whether the financial statements, taken as a whole, give a fair
representation of the organization's financial picture. In addition, audits are not intended to discover
embezzlements or other illegal acts. Therefore, a "clean" or unqualified opinion should not be interpreted as an
assurance that such problems do not exist.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Ba6 QuestionnareDokument1 SeiteBa6 QuestionnareBeviiee BisnarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhilippinesDokument9 SeitenPhilippinesBeviiee BisnarNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Philippine ConstitutionsDokument7 SeitenHistory of Philippine Constitutionsjackieferdie89% (47)
- The Attention-Deficit Disordder (Inattentive Type) ChecklistDokument7 SeitenThe Attention-Deficit Disordder (Inattentive Type) ChecklistBeviiee BisnarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPED 9 ReportDokument51 SeitenSPED 9 ReportBeviiee BisnarNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Acctg Equity Practice QuizDokument16 SeitenAcctg Equity Practice QuizJyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Member Statement: Questions?Dokument8 SeitenMember Statement: Questions?Michael CarsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- MACROECONOMIC AGGREGATES (At Constant Prices) : Base Year:2011-12Dokument3 SeitenMACROECONOMIC AGGREGATES (At Constant Prices) : Base Year:2011-12Vishnu KanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hanlon Heitzman 2010Dokument53 SeitenHanlon Heitzman 2010vita cahyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 7 CmaDokument16 SeitenPaper 7 CmaRama KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epc and Ppa ContractsDokument12 SeitenEpc and Ppa ContractsCOT Management Training InsituteNoch keine Bewertungen
- BA 421-Feasibility StudyDokument14 SeitenBA 421-Feasibility StudyMary Ann Jacolbe BaguioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac3059 ch1-3 PDFDokument60 SeitenAc3059 ch1-3 PDFTomson KosasihNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Insu-Wps OfficeDokument2 SeitenHistory of Insu-Wps OfficeSIDHARTH TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Defense ScriptDokument4 SeitenFinal Defense Scriptandeng100% (1)
- Audit of Wasting Assets Learning ObjectivesDokument3 SeitenAudit of Wasting Assets Learning ObjectivesTrisha Mae RodillasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moto BillDokument1 SeiteMoto Billmyyes3994Noch keine Bewertungen
- ATC List 2017 Updated 5517Dokument47 SeitenATC List 2017 Updated 5517Varinder AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collateral Document Delivery Request Form v2Dokument1 SeiteCollateral Document Delivery Request Form v2Teena BarrettoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overhead Costing - NotesDokument6 SeitenOverhead Costing - NotesMohamed MuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- TATA MOTORS Atif PDFDokument9 SeitenTATA MOTORS Atif PDFAtif Raza AkbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Copy - Mphasis &finsource PDFDokument2 SeitenSample Copy - Mphasis &finsource PDFSameer ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doing Business in BrazilDokument164 SeitenDoing Business in BrazilVarupNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAFE National Test OutlineDokument17 SeitenSAFE National Test Outlinejshen5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fed Foreclosure PetitionDokument80 SeitenFed Foreclosure PetitionudhayaisroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Red Cross (Non-Government Organization) : University of Perpetual Help System DALTADokument15 SeitenPhilippine Red Cross (Non-Government Organization) : University of Perpetual Help System DALTAFroilan Arlando BandulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bank of Maharashtra History INFORMATIONDokument3 SeitenBank of Maharashtra History INFORMATIONbharatNoch keine Bewertungen
- M & A Regulations Takeover Code: Amity Global Business SchoolDokument56 SeitenM & A Regulations Takeover Code: Amity Global Business SchoolAnkita DhimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annexure-B: Format - Daily Margin Statement To Be Issued To Clients Client Code: Clientname: ExchangeDokument1 SeiteAnnexure-B: Format - Daily Margin Statement To Be Issued To Clients Client Code: Clientname: ExchangeenamsribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- R1508D933901 - PS4S26-V1 Assessment PointDokument31 SeitenR1508D933901 - PS4S26-V1 Assessment PointRue Spargo Chikwakwata100% (3)
- Unclaimed Balances Law: (Republic Act 3936 As Amended by Presidential Decree No. 679)Dokument2 SeitenUnclaimed Balances Law: (Republic Act 3936 As Amended by Presidential Decree No. 679)Jornel MandiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02012020fin RT4 PDFDokument1 Seite02012020fin RT4 PDFPAO TPT PAO TPTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Competency IndicatorsDokument23 SeitenEngineering Competency IndicatorsSyed Muhammad JahangeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- SRM Sem1 Exam Fee ReceiptDokument2 SeitenSRM Sem1 Exam Fee Receiptdeeksha6548gkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost of Capital ChapterDokument26 SeitenCost of Capital Chapteremon hossainNoch keine Bewertungen