Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Stefan's Constant
Hochgeladen von
Physics InstrumentsCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Stefan's Constant
Hochgeladen von
Physics InstrumentsCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Trisha Banerjee @ 2010
Incandescent lamp
Photovoltaic
cell
Power
supply
Trisha Banerjee @ 2010
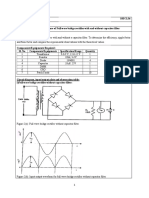
Object:- To determine the Stefan's constant by using an incandescent
lamp and the photovoltaic cell.
Apparatus:-
1) A regulated supply 0- 15 V and 0- 5 amp.
2) An incandescent lamp 6 V , 12 W with lamp house .
3) A photovoltaic cell mounted in a house.
4) optical bench with two strands , one for lamp to use the other for
photovoltaic cell.
5) A unit is operative on 230 V = 10% at 50 Hz AC mains.
Trisha Banerjee @ 2010
Both are hidden
by a dark cover.
Trisha Banerjee @ 2010
Power supply:-
Vg Ig
Trisha Banerjee @ 2010
Incandescent light:-
Trisha Banerjee @ 2010
incandescent lamp :-
The incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is a
source of
electric light that works by incandescence (a general term for heat-driven light
emissions,
which includes the simple case of black body radiation). An electric current passes
through a thin filament, heating it to a temperature that produces light. The enclosing
glass bulb
contains either a vacuum or an inert gas to prevent oxidation of the hot filament.
Incandescent bulbs are also sometimes called electric lamps, a term also applied to the
original arc lamps.
Incandescent bulbs are made in a wide range of sizes and voltages, from 1.5 volts to
about 300 volts. They require no external regulating equipment and have a low
manufacturing cost, and work well on either alternating current or direct current. As a
result the incandescent lamp is widely used in household and commercial lighting, for
portable lighting such as table lamps, car headlamps, and flashlights, and for
decorative and advertising lighting.
Trisha Banerjee @ 2010
Photo voltaic cell:-
Photovoltaics is the direct conversion of light into electricity at the atomic level.
Some
materials exhibit a property known as the photoelectric effect that causes them to
absorb photons of light and release electrons. When these free electrons are
captured, an electric current results that can be used as electricity.
The photoelectric effect was first noted by a French physicist, Edmund Bequerel, in
1839, who found that certain materials would produce small amounts of electric
current when exposed to light. In 1905, Albert Einstein described the nature of light
and the photoelectric effect on which photovoltaic technology is based, for which he
later won a Nobel prize in physics. The first photovoltaic module was built by Bell
Laboratories in 1954. It was billed as a solar battery and was mostly just a curiosity as
it was too expensive to gain widespread use. In the 1960s, the space industry began
to make the first serious use of the technology to provide power aboard spacecraft.
Through the space programs, the technology advanced, its reliability was
established, and the cost began to decline. During the energy crisis in the 1970s,
photovoltaic technology gained recognition as a source of power for non-space
applications.
Trisha Banerjee @ 2010
The diagram above illustrates the operation of a basic photovoltaic cell, also called a
solar cell. Solar cells are made of the same kinds of semiconductor materials, such
as silicon, used in the microelectronics industry. For solar cells, a thin
semiconductor wafer is specially treated to form an electric field, positive on one
side and negative on the other. When light energy strikes the solar cell, electrons
are knocked loose from the atoms in the semiconductor material. If electrical
conductors are attached to the positive and negative sides, forming an electrical
circuit, the electrons can be captured in the form of an electric current -- that is,
electricity. This electricity can then be used to power a load, such as a light or a tool.
Trisha Banerjee @ 2010
Principle in brief:-
here we are using the relation
Stefan's cont = 2.43 X 10 (-4) { Vs/ T}
result in joule per sqr meter per sec per quad Kelvin.
Where Vs = Vo +Vs in volts with Vo volts corresponding to work function of photo
cathode and Vs volt corresponding to maximum kinetic energy of photo electrons which
in turn correspond to photons of maximum energy emitted by a black body at
temperature T Kelvin ( temperature of the incandescent filament which acts as a black
body radiator.
Vo= minimum work function , i.e. obtain from the intercept on the Y axis obtain from
the graph of Vs( mV) and T ( in Kelvin)
Vs = voltage of the photovoltaic cell obtain from multimeter.
Here Ro should be calculated properly i.e. (Rg X 3.9 ) ohm , and Rg= Vg/Ig .
And Ig and Vg are obtained carefully which is obtained by just illumination or glow of
the lamp in dark.
Initially we have to measure Rg . So for this power supply should be at minimum , i.e.
fully anticlock.
Trisha Banerjee @ 2010
Precaution:-
1) carefully find out the glow resistance Rg of filament by taking Vg voltage drop
across the filament when Ig is ampere current passes through it and just makes it to
glow.
2) carefully take the readings of Vs through multimeter of photovoltaic cell.
Trisha Banerjee @ 2010
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Planks ConstantDokument5 SeitenPlanks Constantprateekjain01100% (4)
- Experiment 11: NPN BJT Common Emitter CharacteristicsDokument7 SeitenExperiment 11: NPN BJT Common Emitter CharacteristicsMalikAlrahabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6Dokument13 SeitenChapter 6aregawi weleabezgiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viva Questions PDFDokument4 SeitenViva Questions PDFRiya SalujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiments For B. Tech. 1 Year Physics LaboratoryDokument6 SeitenExperiments For B. Tech. 1 Year Physics LaboratoryDipti GahlotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expt. 3 Planck's ConstantDokument10 SeitenExpt. 3 Planck's ConstantSandeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical FiberDokument6 SeitenOptical FiberSarveenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IodineDokument2 SeitenIodineShihabudheen100% (3)
- Babinet Compensator BirefringenceDokument8 SeitenBabinet Compensator BirefringenceReddyvari Venugopal100% (2)
- Experiment No. 3: ISC (Class - 12)Dokument3 SeitenExperiment No. 3: ISC (Class - 12)Bindeswar Saha0% (2)
- IV (M) QM Gamma Ray MicroscopeDokument2 SeitenIV (M) QM Gamma Ray MicroscopeAbhigyan HazarikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Four Probe MethodDokument20 SeitenFour Probe MethodSuresh Senanayake43% (7)
- Carrier Generation and RecombinationDokument9 SeitenCarrier Generation and RecombinationwaveletNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave Optics (Xiii) Teaching NotesDokument16 SeitenWave Optics (Xiii) Teaching NotesSankar KumarasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of Planck Constant Using Photocell: Name: Shivam Roll No.: 20313127Dokument13 SeitenCalculation of Planck Constant Using Photocell: Name: Shivam Roll No.: 20313127shivamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interference and DiffractionDokument27 SeitenInterference and DiffractionphydotsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conductor, Semiconductor, InsulatorDokument22 SeitenConductor, Semiconductor, InsulatorNishit ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variation of Magnetic FieldDokument2 SeitenVariation of Magnetic FieldVinit Kumar50% (2)
- Lab 5th Assignment About GM CounterDokument9 SeitenLab 5th Assignment About GM CounterJamil100% (1)
- Viva Questions .. (12th) Term 2Dokument7 SeitenViva Questions .. (12th) Term 2Sandeep kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Activity 4Dokument4 SeitenPhysics Activity 4Ankit PanigrahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fresnel's BiprismDokument6 SeitenFresnel's Biprismprateekjain010% (1)
- BH Curve PDFDokument7 SeitenBH Curve PDFAviteshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Particle in A 1d Box Quantum MechanicsDokument22 SeitenParticle in A 1d Box Quantum Mechanicsvivek patel0% (1)
- Lecture 03 - Diode Applications (Rectification)Dokument16 SeitenLecture 03 - Diode Applications (Rectification)Joseph NgowiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectrostaticsDokument39 SeitenElectrostaticsshreyas bulbule100% (1)
- To Verify The Richardson-Dushman Equation and To Find Out The Work Function of The Electron Emitting Material.Dokument20 SeitenTo Verify The Richardson-Dushman Equation and To Find Out The Work Function of The Electron Emitting Material.Mohit ManaktalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE LAB - Experiment No.2-1Dokument4 SeitenAE LAB - Experiment No.2-1Prajwal PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viva QuestionsDokument1 SeiteViva QuestionshithesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Rydberg ConstantDokument8 SeitenDetermination of Rydberg ConstantReddyvari Venugopal100% (1)
- Unit-I - Topic-PolarizationDokument12 SeitenUnit-I - Topic-PolarizationMUSICAL MASTI RINGTONENoch keine Bewertungen
- 29777-10546-LAB VIVA Part-1Dokument3 Seiten29777-10546-LAB VIVA Part-1Reddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- WWW - Thinkiit.in: Important DefinitionsDokument37 SeitenWWW - Thinkiit.in: Important Definitionsthinkiit100% (2)
- Newton's Ring ExperimentDokument3 SeitenNewton's Ring ExperimentRoshnee BoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moving Coil GalvanometerDokument2 SeitenMoving Coil GalvanometerKashish PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective MassDokument4 SeitenEffective Massagnirailways100% (4)
- A Project On Radioactive ElementsDokument23 SeitenA Project On Radioactive ElementsMK Jas75% (4)
- GM CounterDokument29 SeitenGM CounterDhanapal PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moving Coil GalvanometerDokument3 SeitenMoving Coil GalvanometerdayabaddageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Semiconductor Physics-Edited PDFDokument57 SeitenUnit 4 Semiconductor Physics-Edited PDFMUSICAL MASTI RINGTONENoch keine Bewertungen
- Photoelectric EffectDokument7 SeitenPhotoelectric EffectAnushka Jaiswal100% (1)
- Notes and Experiment To Verify Malus Law FinalDokument7 SeitenNotes and Experiment To Verify Malus Law FinalVivek SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-1 Structure and Bonding ModelsDokument18 SeitenUnit-1 Structure and Bonding ModelsAbhi PathaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extrinsic SemiconductorsDokument28 SeitenExtrinsic SemiconductorsSahil AhujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charging & Discharging of CapacitorDokument25 SeitenCharging & Discharging of CapacitorrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electron Diffraction Tube PDFDokument7 SeitenElectron Diffraction Tube PDFRangga TaufiqurahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of CRODokument7 SeitenStudy of CROGarima Saraf100% (1)
- Operating Characteristics of GM CounterDokument7 SeitenOperating Characteristics of GM Counterrishi4charmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment of Ohm's LawDokument8 SeitenExperiment of Ohm's LawIstiak AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE 1109 - Electrical Properties of SolidDokument35 SeitenECE 1109 - Electrical Properties of SolidIván RañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSCIS PROJECT On Moving Coil GalvanomeDokument12 SeitenPHYSCIS PROJECT On Moving Coil Galvanomesantosh kumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Ballastic GalvanometerDokument4 SeitenTheory of Ballastic GalvanometerAniket Patel (Annu)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Charge To Mass Ratio ReportDokument8 SeitenCharge To Mass Ratio Reportlucy lucyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Helium Neon LaserDokument10 SeitenHelium Neon LaserSai SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wavelength of Mercury Spectrum - SpectrometerDokument3 SeitenWavelength of Mercury Spectrum - SpectrometerHarshit Kothala100% (1)
- Determining Lande G-Factor Using EsrDokument9 SeitenDetermining Lande G-Factor Using EsrKuljot Shah Singh100% (1)
- ISET ERenouvelable 3Dokument23 SeitenISET ERenouvelable 3Saleh LaifiNoch keine Bewertungen
- G2 - Residential Lighting LaboratoryDokument13 SeitenG2 - Residential Lighting LaboratoryMahmoud A. AboulhasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Various Illumination Methods: Notes byDokument40 SeitenVarious Illumination Methods: Notes bylucky asifNoch keine Bewertungen
- RW 0004PhotovoltaicsRev5Dokument4 SeitenRW 0004PhotovoltaicsRev5Olawale John AdeotiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ballistic GalvanometerDokument14 SeitenBallistic GalvanometerPhysics Instruments100% (1)
- Prism Angle and Minimum DeviationDokument8 SeitenPrism Angle and Minimum DeviationPhysics InstrumentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Helmholtz GalvanometerDokument11 SeitenHelmholtz GalvanometerPhysics Instruments100% (5)
- Experiment of Finding The Resolving Power of TheDokument10 SeitenExperiment of Finding The Resolving Power of ThePhysics Instruments100% (1)
- Trisha Banerjee at 2010Dokument7 SeitenTrisha Banerjee at 2010Physics InstrumentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment If Planck's ConstantDokument12 SeitenExperiment If Planck's ConstantPhysics InstrumentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fan Systems: Fan and System MatchingDokument28 SeitenFan Systems: Fan and System Matchingvalerio.garibayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energetica ExaminationDokument11 SeitenEnergetica ExaminationDwi NicHeNoch keine Bewertungen
- QI 003 Dial GaugeDokument13 SeitenQI 003 Dial Gaugeipkm123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Protect 8.inv: Industrial InvertersDokument4 SeitenProtect 8.inv: Industrial InvertersMossin SimonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 11 - Paper 1 and 2 HLDokument13 SeitenUnit 11 - Paper 1 and 2 HLUncharted FireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coal Analysis For vtps-500MWDokument90 SeitenCoal Analysis For vtps-500MWJagadeesh NetiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat NotesDokument216 SeitenHeat NotesSaswata Pradhan100% (1)
- Mass Moment of Inertia of FlywheelDokument8 SeitenMass Moment of Inertia of Flywheelabdulaziz67% (3)
- AE 2012 Fuid Mechanics SyllabusDokument4 SeitenAE 2012 Fuid Mechanics SyllabusamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRKTCT - 19. A Capacitor With Capacitance 0.1F in An RC Circuit Is Initially Charged Up ToDokument5 SeitenCRKTCT - 19. A Capacitor With Capacitance 0.1F in An RC Circuit Is Initially Charged Up ToWilburNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Thermodynamics: BSEE 2019-2023 3 Semester Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences, IslamabadDokument26 SeitenApplied Thermodynamics: BSEE 2019-2023 3 Semester Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences, IslamabadAliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hall Effect and Hall VoltageDokument2 SeitenHall Effect and Hall VoltageHimanshu TyagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hall Effect-1Dokument4 SeitenThe Hall Effect-1lewyn.socialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Building Load Calculation StudyDokument40 SeitenElectrical Building Load Calculation StudyMuraryspotty100% (14)
- Time Dependent Schrodinger EquationDokument26 SeitenTime Dependent Schrodinger EquationLearning Scholar100% (1)
- Energy Transfer in TurbomachinesDokument60 SeitenEnergy Transfer in TurbomachinesBasavaraja K M Kotyal83% (6)
- Experiment 01Dokument15 SeitenExperiment 01frank samndomiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Studies On The Effect of Using Phase Change Material in Salinity-Gradient Solar PondDokument11 SeitenExperimental Studies On The Effect of Using Phase Change Material in Salinity-Gradient Solar PondVIJAY DHARANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac Drive: User ManualDokument53 SeitenAc Drive: User ManualJOHNATAN MARINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Description Mechanical Dimensions: 6.8V To 400V GPP Transient Voltage SuppressorsDokument4 SeitenDescription Mechanical Dimensions: 6.8V To 400V GPP Transient Voltage SuppressorsRabshaqaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kicks and Gas MigrationDokument42 SeitenKicks and Gas MigrationJohnny Sanchez100% (1)
- HoneyWell 69-1815EFSDokument96 SeitenHoneyWell 69-1815EFSRemiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE - Physics - MCQ 2 - Forces and ShapeDokument7 SeitenIGCSE - Physics - MCQ 2 - Forces and ShapeKyi Nue KhinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systemair MUB - F 042 400D4Dokument2 SeitenSystemair MUB - F 042 400D4diziodavide21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unified Power Flow ControllerDokument17 SeitenUnified Power Flow ControllerAdeniji Olusegun50% (2)
- Electrical System A40F Copy Prosis - 3.4.0.12Dokument857 SeitenElectrical System A40F Copy Prosis - 3.4.0.12Bontor Tua100% (3)
- Bahagian A: Kertas 2Dokument17 SeitenBahagian A: Kertas 2wahidms84Noch keine Bewertungen
- E2488 092014 Standard Guide ForDokument8 SeitenE2488 092014 Standard Guide ForBAN ZANGHANANoch keine Bewertungen
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan (Speed and Velocity)Dokument5 SeitenSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan (Speed and Velocity)Rey Mark Buena Mercado100% (2)
- Heat Balance in Fusion WeldingDokument4 SeitenHeat Balance in Fusion WeldingjohanNoch keine Bewertungen