Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Understanding Network Devices and Wireless Lab
Hochgeladen von
ramanshankarOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Understanding Network Devices and Wireless Lab
Hochgeladen von
ramanshankarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Georg Brown College
Fall 2016
Course: COMP1154
LAB 2
Date: Tuesday, Sep 20
Lab 2.1 Understanding Various Device Functions
Objectives
It is important to understand how all devices operate on a network. These
devices include repeaters, hubs, bridges, switches, brouters, routers, and
gateways. The purpose of this lab is to make sure you understand the
characteristics of all network devices.
After completing this lab, you will be able to:
Identify characteristics of repeaters, hubs, bridges, switches, brouters,
routers, and gateways
Activity
Fill in the Device(s) column of Table 2-1 with the device being described. You
can fill in the table with repeater, hub, bridge, switch, brouter, router, or
gateway. Note that more than one device might match a specific
characteristic
Characteristics
Device(s)
1. Operates at upper layers to translate
between different protocol suites
2. Filters traffic based on MAC address
3. Introduces the most latency on a network
4. Boosts the signal but does not segment the
network
5. Operates differently depending on whether
non-routable or routable protocols are in use
6. Creates broadcast domains
Georg Brown College
Fall 2016
Course: COMP1154
LAB 2
Date: Tuesday, Sep 20
7. Creates a virtual circuit between sender and
receiver
8. Forwards broadcast traffic
9. Filters traffic based on logical address
10.
Associated with the term micro-
segmentation
11.
Creates subnetworks
12.
Connects computers in a physical star and
uses shared bandwidth
13.
Creates collision domains
14.
Operates at layer 1 of the OSI model
15.
Operates at layer 2 of the OSI model
16.
Operates at layer 3 of the OSI model
Table 2-1 Network device characteristics
Lab 2.2 Understanding Wireless Parameters and Terminology
Objectives
Wireless is the fastest growing area of networking. You need to understand
how wireless devices operate, the associated standards and organizations,
wireless security measures, and wireless troubleshooting tips. In this lab, you
will match the correct wireless term with a definition.
After completing this lab, you will be able to:
Georg Brown College
Fall 2016
Course: COMP1154
LAB 2
Date: Tuesday, Sep 20
Describe how wireless works
Explain the various 802.11 standards and the associated organizations
Understand wireless security and troubleshooting methods
Activity
Match each term in the following bulleted list with a definition in the
numbered list. Each bulleted term is used only once. Use the Internet and
Web sites such as www.whatis.com and www.webopedia.com if you
need to search for a definition.
Wi-Fi Alliance
IEEE
802.11a
802.11b
802.11g
802.11n
802.11i
802.1x
Ad hoc mode
Infrastructure mode
CSMA/CA
BSS
ESS
SSID
WEP
WPA
Definition
Term
1. Organization that developed the 802.11 specifications
2. Wireless security standard that replaced WEP and uses the TKIP algorithm
3. The latest and fastest 802.11 standard
4. This mode specifies that the client device associates with an access point
5. The wireless network name that is often broadcast so that clients can
associate using it
6. The IEEE port-blocking specification
7. The network access method used by 802.11 devices
8. The IEEE security standard based on WPA2
9. The IEEE standard that specifies 54 Mbps in the 5 GHz range
10. This mode specifies that the client device communicate directly with other
Georg Brown College
Fall 2016
Course: COMP1154
LAB 2
Date: Tuesday, Sep 20
client devices and that no access point is used
11. A single access point in infrastructure mode
12. The original security standard for 802.11
13. The IEEE standard that specifies 11 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz range
14. Multiple access points connected in infrastructure mode
15. The IEEE standard that specifies 54 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz range
16. Organization developed to promote 802.11 usage
Lab 2.3: Performing Switch Startup and Initial Configuration
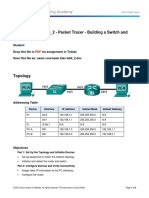
Topology
PC1
PC2
Addressing Table
Device
Interface
IPaddress
SubnetMask
PC1
NIC
192.168.5.10
255.255.255.0
PC2
NIC
192.168.5.20
255.255.255.0
Objectives
Task 1: Establishing a console session with Tera Term
Task 2: Initializing and Reloading a Switch
Task 3: Verify the default switch setting
Task 4: Manage the MAC address table
Task 5: Configure an IP address on PC1 and PC2
Scenario
Georg Brown College
Fall 2016
Course: COMP1154
LAB 2
Date: Tuesday, Sep 20
In this lab, you will examine and configure a standalone LAN switch
connected with two PCs. Although a switch performs basic functions in its
default out-of-the-box condition, there are a number of parameters that a
network administrator should modify to ensure a secure and optimized LAN.
This lab introduces you to the basics of switch configuration.
Required Resources
1 Cisco Catalyst Switch 2960
2 PCs (Windows 7, Vista, or XP with terminal emulation program, such as
Tera Term)
Console cable to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
Ethernet cables to connect the PCs to the switch
Task 1: Establishing a Console Session with Tera Term
Step 1: Cable a network
Cable a network that is similar to the one in the topology diagram. You can use
any current switch in your lab as long as it has the required interfaces shown in
the topology.
Step 2: Create a console connection to the switch by Connecting a Cisco switch
and computer using a rollover console cable.
a. Connect the rollover console cable to the RJ-45 console port of the switch.
b. Connect the other cable end to the serial COM port on the computer.
Note: Serial COM ports are no longer available on most computers today. A
USB-to-DB9 adapter can be used with the rollover console cable for console
connection between the computer and a Cisco device.
Note: If using a USB-to-DB9 adapter to connect to the COM port, you may be
required to install a driver for the adapter provided by the manufacturer on your
computer. The correct COM port number is required to connect to the Cisco IOS
device using a terminal emulator.
To determine the COM port used by the adapter. If you are using a Microsoft
Windows 7 PC, you may need to perform the following steps to enable the COM
port:
1. Click the Windows Start icon to access the Control Panel.
2. Open the Device Manager.
3. Click the Ports (COM & LPT) tree link to expand it. The Cisco Virtual Comm
Port00 icon displays with a yellow exclamation point attached.
Georg Brown College
Fall 2016
Course: COMP1154
LAB 2
Date: Tuesday, Sep 20
c. Power up the Cisco switch and computer if these devices are not already on.
Step 3: Configure Tera Term to establish a console session with the switch.
Tera Term is a terminal emulation program. This program allows you to access the
terminal output of the switch. It also allows you to configure the switch.
a. Start Tera Term by clicking the Windows Start button located in the task bar.
Locate Tera Term under All Programs.
Note: If the program is not installed on the system, Tera Term can be
downloaded from the following link by selecting Tera Term:
http://logmett.com/index.php?/download/free-downloads.html
Georg Brown College
Fall 2016
Course: COMP1154
LAB 2
Date: Tuesday, Sep 20
b. In the New Connection dialog box, click the Serial radio button. Verify that the
correct COM port is selected and click OK to continue.
c. From the Tera Term Setup menu, choose the Serial port to verify the serial
settings. The default parameters for the console port are 9600 bauds, 8 data bits,
no parity, 1 stop bit, and no flow control. The Tera Term default settings match the
console port settings for communications with the Cisco IOS switch.
Georg Brown College
Fall 2016
Course: COMP1154
LAB 2
Date: Tuesday, Sep 20
d. When you can see the terminal output, you are ready to configure a Cisco switch.
The following console example displays the terminal output of the switch while it
is loading.
Task 2: Initializing and Reloading a Switch
In this task, you will use the erase startup-config command to ensure that the switch
has no prior configuration in the startup-config file. You will then reload the switch
software and observe the output that is generated during the reload. Finally, you will
investigate the properties of the switch.
Step 1: Enter privileged mode
Console into the switch and enter privileged EXEC mode The privileged EXEC
command set includes those commands contained in user EXEC mode, as well as the
configure command through which access to the remaining command modes are
gained. Enter privileged EXEC mode by entering the enable command.
Switch>enable
Switch#
Notice that the prompt changed in the configuration to reflect privileged
EXEC mode.
Step 2: Determine if there have been any virtual local-area networks (VLANs)
created. Use the show flash or dir flash: command to determine if any VLANs have
been created on the switch.
Switch#show flash
See if the vlan.dat file was found in flash
Which files or directories are found? ------------------------------------Step 3: Delete the VLAN file.
8
Georg Brown College
Fall 2016
Course: COMP1154
LAB 2
Date: Tuesday, Sep 20
a) If the vlan.dat file was found in flash, then delete this file.
Switch# delete flash:vlan.dat
Delete filename [vlan.dat]?
You will be prompted to verify the file name. At this point, you can change the file
name or just press Enter if you have entered the name correctly.
b) When you are prompted to delete this file, press Enter to confirm the deletion.
(Pressing any other key will abort the deletion.)
Delete flash:/vlan.dat? [confirm]
Switch#
Step 4: Erase the startup configuration file.
Use the erase startupconfig command to erase the startup configuration file from
NVRAM. When you are prompted to remove the configuration file, press Enter to
confirm the erase. (Pressing any other key will abort the operation.)
Switch#erasestartupconfig
Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all configuration files!
Continue? [confirm] [OK]Erase of nvram: complete
Switch#
Step 5: Reload the switch.
Reload the switch to remove any old configuration information from memory. When you
are prompted to reload the switch, press Enter to proceed with the reload. (Pressing any
other key will abort the reload.)
Switch# reloadProceed with reload? [confirm]
Note: You may receive a prompt to save the running configuration prior to reloading the
switch. Type no and press Enter.
System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: no
After the switch reloads, you should see a prompt to enter the initial configuration
dialog. Type no at the prompt and press Enter to bypass the initial configuration dialog.
Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog?
[yes/no]: no
How do you know that the startup configuration has been erased? --------------
Georg Brown College
Fall 2016
Course: COMP1154
LAB 2
Date: Tuesday, Sep 20
Task 3: Verify the default switch setting
Examine the current contents of NVRAM:
Switch>enable
Switch# show startup-config
startup-config is not present
Why does this message appear? _______________________
Examine the current running configuration file.
Switch#show running-config
How many Fast Ethernet interfaces does the switch have? _______________________
How many Gigabit Ethernet interfaces does the switch have? _____________________
What is the range of values shown for the vty lines? ____________________________
Examine the Fast Ethernet interfaces. Examine the default properties of the Fast
Ethernet interface used by PC1 & PC2
Switch#show interface fastethernet 0/1
Switch#show interface fastethernet 0/4
Are the interfaces up or down? ______________________________________
What event would make an interfaces go up? _________________________
What is the MAC address of the interfaces? __________________________
What is the speed and duplex setting of the interfaces? _________________
Examine the following version information that the switch reports. Using the appropriate
show command, investigate the switch model number, software version, and amount of
RAM and flash memory.
Switch# show version
What is the Cisco IOS version that the switch is running? ________________________
What is the system image filename?_________________________________________
What is the base MAC address of this switch? _________________________________
What is the amount of RAM and flash memory?________________________________
What is the switch model?_________________________________________________
10
Georg Brown College
Fall 2016
Course: COMP1154
LAB 2
Date: Tuesday, Sep 20
Task 4: Managing the MAC Address Table
Step 1: Record the MAC addresses of the hosts.
Determine and record the Layer 2 (physical) addresses of the PC network interface
cards using the following commands:
Start > Run > cmd > ipconfig /all
PC1: _______________________________________
PC2: _______________________________________
Step 2: Determine the MAC addresses that the switch has learned.
Display the MAC addresses using the show mac-address-table command in privileged
EXEC mode.
S1#show mac-address-table
How many dynamic addresses are there? _______________________________
How many MAC addresses are there in total? ____________________________
Do the dynamic MAC addresses match the host MAC addresses? ____________
Step 3: List the show mac-address-table options.
S1#show mac-address-table?
How many options are available for the show mac-address-table command?
________
Show only the MAC addresses from the table that were learned dynamically.
S1#show mac-address-table address dynamic
How many dynamic addresses are there? _________________
Step 4: Clear the MAC address table.
To remove the existing MAC addresses, use the clear mac-address-table command
from privileged EXEC mode.
S1#clear mac-address-table dynamic
Step 5: Verify the results.
Verify that the MAC address table was cleared.
S1#show mac-address-table
How many static MAC addresses are there? ________________________
How many dynamic addresses are there? __________________________
11
Georg Brown College
Fall 2016
Course: COMP1154
LAB 2
Date: Tuesday, Sep 20
Step 6: Examine the MAC table again.
More than likely, an application running on your PC1 has already sent a frame out the
NIC to S1. Look at the MAC address table again in privileged EXEC mode to see if S1
has relearned the MAC address for PC1
S1#show mac-address-table
How many dynamic addresses are there? ________________________________
Why did this change from the last display?____________________________________
If S1 has not yet relearned the MAC address for PC1, ping the PC2 from PC1 and then
repeat Step 6.
Task 5: Configure an IP address on PC1 and PC2
Step 1: Configure the IP addresses and default gateway for PC1 and PC2 as
shown in table.
On a PC, click Start and choose Control Panel. Click Change Adapter Settings and
then right-click Local Area Network. Choose Properties. When you are presented with
the Local Area Connection Properties dialog, click Internet Protocol version 4
(TCP/IPv4) and then click Properties. In the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)
Properties window, click the Use the Following IP Address radio button and enter the
appropriate IP address, subnet mask.
Step 2: Verify connectivity.
To verify the hosts and switch are correctly configured, ping the IP address of PC2 and
switch from PC1.
PC1>ping 192.168.5.20
PC1>ping 192.168.5.100
Was the ping successful? ________________________
If not, troubleshoot the switch and host configuration. Note that this may
take a couple of tries for the pings to succeed.
12
Georg Brown College
Fall 2016
Course: COMP1154
LAB 2
13
Date: Tuesday, Sep 20
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Von EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- PLC Programming from Novice to Professional: Learn PLC Programming with Training VideosVon EverandPLC Programming from Novice to Professional: Learn PLC Programming with Training VideosBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Serial Port Complete: COM Ports, USB Virtual COM Ports, and Ports for Embedded SystemsVon EverandSerial Port Complete: COM Ports, USB Virtual COM Ports, and Ports for Embedded SystemsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (9)
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionVon EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- Apollo Configuration Management ManualDokument308 SeitenApollo Configuration Management ManualBob Andrepont100% (1)
- Basic PLC TrainingDokument114 SeitenBasic PLC TrainingAffan Pringgo100% (12)
- 2.3.3.4 Lab - Building A Simple NetworkDokument14 Seiten2.3.3.4 Lab - Building A Simple NetworkMaria Tudosa50% (2)
- Some Tutorials in Computer Networking HackingVon EverandSome Tutorials in Computer Networking HackingNoch keine Bewertungen
- SplunkFundamentals1 Module3Dokument9 SeitenSplunkFundamentals1 Module3ealfora100% (1)
- CCNA 3 Case Study (1sem SY14-15)Dokument6 SeitenCCNA 3 Case Study (1sem SY14-15)Juan Carlos DeLeon Gomez100% (2)
- CCNA 3 Student Lab ManualDokument192 SeitenCCNA 3 Student Lab ManualNazmul HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedVon EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.5.1.2 Lab - Building A Switch and Router NetworkDokument8 Seiten6.5.1.2 Lab - Building A Switch and Router NetworkParthPatel100% (8)
- POST 1663671206 07795894dcDokument55 SeitenPOST 1663671206 07795894dcMarta IndrianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Packet Tracer 1.3.1Dokument11 SeitenPacket Tracer 1.3.13qtrtymNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Rise of The Platform A Seismic Shift in Business ModelsDokument6 SeitenThe Rise of The Platform A Seismic Shift in Business ModelsCharmaine LiewNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 2013 PDFDokument924 Seiten9 2013 PDFbarretimufuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex SQL Queries ExamplesDokument6 SeitenComplex SQL Queries ExamplesqwertyvibesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna Icnd1 Labs PDFDokument99 SeitenCcna Icnd1 Labs PDFEbenezer KobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barracuda Web App Firewall Administrator Guide PDFDokument258 SeitenBarracuda Web App Firewall Administrator Guide PDFbas6677Noch keine Bewertungen
- Open-Source Robotics and Process Control Cookbook: Designing and Building Robust, Dependable Real-time SystemsVon EverandOpen-Source Robotics and Process Control Cookbook: Designing and Building Robust, Dependable Real-time SystemsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- PLC Programming Using SIMATIC MANAGER for Beginners: With Basic Concepts of Ladder Logic ProgrammingVon EverandPLC Programming Using SIMATIC MANAGER for Beginners: With Basic Concepts of Ladder Logic ProgrammingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- 2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple NetworkDokument13 Seiten2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple NetworkDaisy Galvan33% (3)
- 6.4.3.5 Lab - Building A Switch and Router NetworkDokument11 Seiten6.4.3.5 Lab - Building A Switch and Router NetworkfutjulyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccnpv6 Tshoot Sba Stud ExamDokument9 SeitenCcnpv6 Tshoot Sba Stud ExamAtilio Alexander100% (1)
- CCNPv7 - TSHOOT - Lab4 2 - Mixed Layer 2 3 Connectivity - StudentDokument13 SeitenCCNPv7 - TSHOOT - Lab4 2 - Mixed Layer 2 3 Connectivity - StudentfranzeskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Create Excel Files CDokument29 SeitenCreate Excel Files CSaka Kely100% (1)
- 2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple NetworkDokument11 Seiten2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple Networkrafid80% (5)
- Exploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxVon EverandExploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Mikrobasic ManualDokument207 SeitenMikrobasic Manualfkimya100% (1)
- Documento Clientes FerDokument23 SeitenDocumento Clientes FercrespofernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sem1 Batch1 PDFDokument73 SeitenSem1 Batch1 PDFMustapha OulcaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab6 - 2 CiscoDokument8 SeitenLab6 - 2 CiscoMoussa MarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab1: Learning About Switches: 1 ObjectivesDokument4 SeitenLab1: Learning About Switches: 1 ObjectivesPrinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1 - Part A (2.3.8) - Navigate The IOS by Using Tera Term For Console Connectivity-UpdatedDokument6 SeitenLab 1 - Part A (2.3.8) - Navigate The IOS by Using Tera Term For Console Connectivity-Updatedkhalifaalmuhairi20Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3.3.5 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management Address NewportDokument4 Seiten2.3.3.5 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management Address Newportgerardo1028Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1 - The Basics: ObjectivesDokument7 SeitenLab 1 - The Basics: Objectivesjramisch44Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1.4.7 Lab - Establishing A Console Session With Tera TermDokument11 Seiten2.1.4.7 Lab - Establishing A Console Session With Tera Term12niverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switch Installation StepsDokument14 SeitenSwitch Installation StepsRudra TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFO8490-Lab 6 Packet Filtering Firewall-1.7Dokument4 SeitenINFO8490-Lab 6 Packet Filtering Firewall-1.7Surjeet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erras LindiardaMahentar - LAM+4Dokument10 SeitenErras LindiardaMahentar - LAM+4Erras LmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1.3.1Dokument12 SeitenLab 1.3.1Alondra CarmonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - 1 - Basic Switch LABDokument14 Seiten2 - 1 - Basic Switch LABVanesaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network DeviDokument11 Seiten11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network DeviRichardWhitley20% (5)
- Configuring NAT Pool Overload and PATDokument6 SeitenConfiguring NAT Pool Overload and PATahaj94Noch keine Bewertungen
- ESwitching Lab 1 3 1Dokument12 SeitenESwitching Lab 1 3 1Derek Ang Yew PinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple Network - ILMDokument18 Seiten2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple Network - ILMshm2hotmail.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network Device InformationDokument11 Seiten11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network Device InformationRazvan Buicliu0% (4)
- 2.3.3.4 Lab - Building A Simple NetworkDokument14 Seiten2.3.3.4 Lab - Building A Simple Networkroberto002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Lab :building A Simple Network With AnswersDokument14 SeitenCisco Lab :building A Simple Network With AnswersEmzy Soriano50% (2)
- LABSEC-2020 ASA 8.3 (Or Higher) Lab Guide PDFDokument11 SeitenLABSEC-2020 ASA 8.3 (Or Higher) Lab Guide PDFRiadh MadhourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab - Activity CCNA Exploration 1 Chapt: 11.5.5Dokument12 SeitenLab - Activity CCNA Exploration 1 Chapt: 11.5.5Rico Agung FirmansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab - Establishing A Console Session With Tera TermDokument5 SeitenLab - Establishing A Console Session With Tera TermKevin KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 5 1Dokument56 Seiten11 5 1Mario Alejandro Godoy PatiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple Network PDFDokument13 Seiten2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple Network PDFPetra Miyag-aw100% (1)
- 11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network Device InformationDokument8 Seiten11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network Device InformationSuen Clarke0% (1)
- Migrating To H3C Lab Guide Lab01 Basic Config v2.8Dokument32 SeitenMigrating To H3C Lab Guide Lab01 Basic Config v2.8Vargas AlvaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 1 Chapter 2 Exam Answer v5 & v5.02 2015 (100%) : March 21, 2015 byDokument14 SeitenCCNA 1 Chapter 2 Exam Answer v5 & v5.02 2015 (100%) : March 21, 2015 byAmine MaacheNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA ICND1 (100-105) - Part8 EditedDokument92 SeitenCCNA ICND1 (100-105) - Part8 EditedVesela SveskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNPv6 TSHOOT Lab10-1-Comp-Env Student PDFDokument17 SeitenCCNPv6 TSHOOT Lab10-1-Comp-Env Student PDFidonotexist100Noch keine Bewertungen
- How to Get Started with Cisco Router Configuration BasicsDokument8 SeitenHow to Get Started with Cisco Router Configuration Basicshaha2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7.2.7 Computer NetwoksDokument5 Seiten7.2.7 Computer NetwoksNurali D.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratorio de Enseñaza 2: TopologyDokument7 SeitenLaboratorio de Enseñaza 2: TopologyVICUÑA HUAYLINOS CESAR AUGUSTONoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA3 ProjectDokument9 SeitenCCNA3 ProjectMalik HaroonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network Device InformationDokument8 Seiten11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network Device InformationSachinNoch keine Bewertungen
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksVon EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNoch keine Bewertungen
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkVon EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB ICSTT-SDS-8402 - en Plantguard Dual 24 VDC Digital Input Module P8402Dokument2 SeitenABB ICSTT-SDS-8402 - en Plantguard Dual 24 VDC Digital Input Module P8402salic2013Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On The Impact of Instruction Set Architectures On ProcessDokument81 SeitenA Study On The Impact of Instruction Set Architectures On Process吕治宽Noch keine Bewertungen
- Downgrade Instruction 2019.10Dokument4 SeitenDowngrade Instruction 2019.10János SchmidtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java Language Fundamental by Druga SirDokument48 SeitenJava Language Fundamental by Druga SirSheikhShoaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employee Onboarding Process at OlaDokument9 SeitenEmployee Onboarding Process at OlaAyush JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux-5-SystemTap Beginners Guide-En-USDokument76 SeitenRed Hat Enterprise Linux-5-SystemTap Beginners Guide-En-USBuland Kumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- SafeQ4 - Quick Start GuideDokument21 SeitenSafeQ4 - Quick Start GuideLuki LeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Language Extensions For CBEA 2.6Dokument168 SeitenLanguage Extensions For CBEA 2.6Ruben PalmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zetcode Com Tkinter DrawingDokument9 SeitenZetcode Com Tkinter DrawingjhdmssNoch keine Bewertungen
- FORE0714ra Davao071114Dokument17 SeitenFORE0714ra Davao071114angelomercedeblogNoch keine Bewertungen
- AI Writer AssistantsohqncDokument2 SeitenAI Writer Assistantsohqncthreadcinema8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Guid - Volume Atenuator and Source SelectionDokument23 SeitenGuid - Volume Atenuator and Source SelectionDementia AlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cfe 011Dokument174 SeitenCfe 011MUHAMMAD TAUFIQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Back-Ups Rs 1000Dokument115 SeitenManual Back-Ups Rs 1000geniusppangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hype Cycle For Application Architecture and Integration, 2021Dokument82 SeitenHype Cycle For Application Architecture and Integration, 2021dennyliaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Hadoop - Introduction, Architecture, Ecosystem, ComponentsDokument8 SeitenWhat Is Hadoop - Introduction, Architecture, Ecosystem, ComponentsAhmed MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Winfiol CMDDokument46 SeitenWinfiol CMDAmber FrancisNoch keine Bewertungen
- SliceViewer and VoxelViewer - enDokument55 SeitenSliceViewer and VoxelViewer - enemadhsobhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cakephp TestDokument22 SeitenCakephp Testhathanh13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final PDFDokument71 SeitenFinal PDFEric Gabrielson100% (1)