Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: January 2015 Semester End Make Up Examinations
Hochgeladen von
Abhyudaya SinghOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: January 2015 Semester End Make Up Examinations
Hochgeladen von
Abhyudaya SinghCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
U.S.N.
BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019
(Autonomous Institute, Affiliated to VTU, Belgaum)
January 2015 Semester End Make Up Examinations
Course: Design of Machine Elements II
Course Code: 12 ME 5DCDM2
Instructions:
1.
2.
Duration 3hrs
Max Marks: 100
Date : 23.01.2015
1. Answer any five full questions
2. Missing Data, if any may be assumed suitably
3. Use of Design Data Hand book is permitted
UNIT 1
a) Derive expressions for stresses at the outer and inner fibers for the curved beam with
usual notations. State the assumptions.
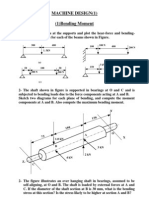
b) For the section A-B shown in Fig. 1b find bending moment, maximum tensile
stress, maximum compressive stress and their locations.
Fig 1.b
OR
a) Obtain expressions for stresses in full length and graduated length leaves of leaf
springs.
b) Design a spring for an elevator shaft at the bottom of which 4 identical springs are
set in parallel to absorb a shock of the elevator in case of failure. The weight of the
elevator is 50kN and the counter weight is 15kN. The elevator has a free fall of
1200mm from rest. Select suitable spring material with a spring index of 8.
08
12
10
10
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
UNIT 2
a) In a multiple disc clutch the radial width of the friction material is to be 0.25 of
maximum radius. The coefficient of friction is 0.2. The clutch is to transmit 50 kW
at 3000 rpm. Its maximum diameter is 250 mm and the axial force is limited to
600N. Determine:
a) Number of driving and driven discs
b) Mean unit pressure on each contact surface assuming uniform wear.
b) A simple band brake of drum diameter 600 mm has a band passing over it with an
angle of contact of 2100 while one end is connected to the fulcrum other end is
connected to the brake lever at a distance of 400 mm from the fulcrum. The brake
lever is 1 m long. The brake is to absorb 15 kW at 720 rpm. Design the band and
brake lever of rectangular cross section assuming the depth to be twice the width.
Assume allowable stress as 80 MPa for lever and for steel band 50 MPa, = 0.3.
UNIT 3
a) What is pressure angle in gear teeth? Mention the different involute gear tooth
profile systems based on it.
b) A pair of carefully cut spur gears (200 Full Depth Involute) transmits 20 kW at 230
rpm of the gear. Reduction ratio is 5:1. The pinion is made of cast steel (heat
treated) with allowable stress of 197 MN/m2. Gear is made of Cast iron with
allowable stress of 56 MN/m2. Pitch line velocity of the pinion is not to exceed 7.5
m/sec. Determine the module, face width and number of teeth on pinion & gear.
OR
a) Define virtual number of teeth on a helical gear. Obtain an expression for the same.
b) Two steel bevel gears, both having a BHN of 250, connect shafts at 900. The teeth
are 200 full depth involute and the module is 6 mm. The number of teeth on pinion
and gear are 24 & 54. The face width is 60 mm. Determine the wear load.
UNIT 4
a) Derive the Petroff s equation used to determine the coefficient of friction in the
design
of Journal Bearings .
b) A Journal Bearing 80 mm dia. and length 120 mm has radial clearance of 0.075
mm. The load on the Journal is 2.5 kN.and it is rotating at 2500 rpm. The oil used is
SAE 10 and its operating temperature is 80 o C. Determine the power loss due to
friction in accordance with (i) Petroffs Equation (ii) Mc. Kees Equation
10
10
04
16
08
12
06
14
UNIT 5
a) A flat belt is required to transmit 10 kW from a pulley of 600 mm effective diameter 10
running at 300 rpm. The angle of contact is spread over 2.75 radians. Determine the
width of belt whose thickness is 10 mm. The allowable stress for the belt is 2.25
N/mm2.Assume = 0.3.
b) Select a standard V-Belt to transmit 30 kW power from an AC induction motor 10
rotating at 1500 rpm to a centrifugal pump rotating at 750 rpm. Drive operates
8 hrs/day. Calculate the number of belts.
*******
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 12ME5DCDM2Dokument3 Seiten12ME5DCDM2Abhyudaya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rr312404 Design of Machine ElementsDokument9 SeitenRr312404 Design of Machine ElementsSrinivasa Rao GNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Me 5dcdm2Dokument3 Seiten12 Me 5dcdm2Abhyudaya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- PMD ModelDokument8 SeitenPMD ModelDamodara SatyaDeva MadhukarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NR 320301 Machine DesignDokument8 SeitenNR 320301 Machine DesignSrinivasa Rao GNoch keine Bewertungen
- DME Model QuesDokument3 SeitenDME Model QuesSiva RamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 2303 - Design of Machine Elements December 2010Dokument3 SeitenMe 2303 - Design of Machine Elements December 2010Ilaya Perumal K0% (1)
- Dme Model Key 2019Dokument25 SeitenDme Model Key 2019Siva RamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Makalah GTWDokument8 SeitenMakalah GTWfaisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 331 - DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS EXAMDokument5 SeitenME 331 - DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS EXAMarumugam_rNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15ME641Dokument3 Seiten15ME641Anmol NairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Machine Members-II Feb 2022Dokument3 SeitenDesign of Machine Members-II Feb 2022Anand KedhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Machine ElementsDokument4 SeitenDesign of Machine ElementsChandani KannakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0326 Me 2303 Design of Machine ElementsDokument3 Seiten0326 Me 2303 Design of Machine ElementsSaravanan MathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Dokument3 SeitenQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.lavanya babuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Curved Beams and SpringsDokument11 SeitenDesign of Curved Beams and SpringsAnonymous utfuIcnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design ExercisesDokument13 SeitenDesign ExercisesBookieeNoch keine Bewertungen
- rr320305 Design of Machine Members IIDokument8 Seitenrr320305 Design of Machine Members IISrinivasa Rao GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design ProblemsDokument13 SeitenDesign ProblemsAristotle RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- DME 2 Test PaperDokument1 SeiteDME 2 Test PaperhemarajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument2 SeitenGujarat Technological UniversityHerat HirparaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12me52 MQP-1Dokument3 Seiten12me52 MQP-1SumitKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 April CE201-D - Ktu QbankDokument2 Seiten2018 April CE201-D - Ktu Qbanklakshmi dileepNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12ME5DCDM2Dokument3 Seiten12ME5DCDM2Abhyudaya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08 r05310305 Design of Machine Members IDokument9 Seiten08 r05310305 Design of Machine Members IKrupanandareddyYarragudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- QB Unit-3,4,5Dokument7 SeitenQB Unit-3,4,5Agranshu BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- r13 Mos Old Q PapersDokument21 Seitenr13 Mos Old Q PapersSrinu ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Machine Elements Exam QuestionsDokument8 SeitenDesign of Machine Elements Exam Questionsslv_prasaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Snist Dom Previous PaperDokument9 SeitenSnist Dom Previous PaperKapil Siddhant DevulapalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Machine Elements IDokument8 SeitenDesign of Machine Elements Imesab100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Design & Industrial Drafting SUBJECT CODE:-2141907 Tutorial - 01Dokument10 SeitenMachine Design & Industrial Drafting SUBJECT CODE:-2141907 Tutorial - 01The AIRS CreationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Common To ME, AME) : 2 2 Ut 2 Yt 2 2Dokument2 Seiten(Common To ME, AME) : 2 2 Ut 2 Yt 2 2Faisal PashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B. Tech. EXAMINATION, 2020: No. of Printed Pages: 05 Roll No. ......................Dokument5 SeitenB. Tech. EXAMINATION, 2020: No. of Printed Pages: 05 Roll No. ......................Gopu KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Btech Auto 5 Sem Design of Machine Components Pau5i101 2020Dokument2 SeitenBtech Auto 5 Sem Design of Machine Components Pau5i101 2020Pagal KutaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering College: Design of Machine Elements - IDokument1 SeiteSree Vidyanikethan Engineering College: Design of Machine Elements - Ibsoumya 123456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dme Home Assignment 2019-20Dokument4 SeitenDme Home Assignment 2019-20VenkateshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Previous Exam QuestionsDokument8 SeitenPrevious Exam QuestionssallyreffatNoch keine Bewertungen
- DME Chapter Three: or (Summer 15)Dokument7 SeitenDME Chapter Three: or (Summer 15)honeyfunnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Btech Auto 5 Sem Design of Machine Components Pau5i101 2018Dokument2 SeitenBtech Auto 5 Sem Design of Machine Components Pau5i101 2018Pagal KutaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TUK University Exams June 2016 Mechanical Engineering Technology Advanced Machine DesignDokument8 SeitenTUK University Exams June 2016 Mechanical Engineering Technology Advanced Machine DesignCharles OndiekiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gtustudies - FMD IMP Question BankDokument5 SeitenGtustudies - FMD IMP Question BankJaideep ZalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam MCT3214 Nov09Dokument6 SeitenFinal Exam MCT3214 Nov09Deerah Aziz100% (1)
- MODEL QUESTION PAPER Mechanical VibrationsDokument3 SeitenMODEL QUESTION PAPER Mechanical VibrationsDarani PriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- dmm1 PDFDokument9 Seitendmm1 PDFmohan_rapaka6095Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Machine Elements - IIDokument8 SeitenDesign of Machine Elements - IIprasaad26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Members Design AssignmentDokument13 SeitenMachine Members Design AssignmentHafiz Mahar28Noch keine Bewertungen
- ADGITM Machine Design Exam QuestionsDokument4 SeitenADGITM Machine Design Exam QuestionsVishal JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Design - II: (Also Old Sem-VI Equivalence) (126112)Dokument2 SeitenMachine Design - II: (Also Old Sem-VI Equivalence) (126112)Harshal DesaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- DMM-2 3 1 Q&aDokument6 SeitenDMM-2 3 1 Q&aAnand vinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument2 SeitenGujarat Technological UniversityDhruvNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12ME5DCDM2Dokument3 Seiten12ME5DCDM2Abhyudaya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design1 SheetsDokument9 SeitenDesign1 SheetsYou channelNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME6503 DME Question PapersDokument27 SeitenME6503 DME Question PapersSaravanan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4363 111 Machine Design IDokument6 Seiten4363 111 Machine Design Iyogesh_b_k100% (2)
- MECHANICS (ME10001) : AluminumDokument2 SeitenMECHANICS (ME10001) : AluminumRahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- MECH 2013 DT022 - 023 Ken Keating Sem 2 2010-1Dokument4 SeitenMECH 2013 DT022 - 023 Ken Keating Sem 2 2010-1Shiyas BasheerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsVon EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Public Sector Companies in IndiaDokument39 SeitenList of Public Sector Companies in IndiaAbhyudaya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- DVGDokument53 SeitenDVGbalajigandhirajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belt, Rope & Chain Drives - PDF PDFDokument36 SeitenBelt, Rope & Chain Drives - PDF PDFabhisar100% (3)
- Curved BeamDokument85 SeitenCurved Beampoojasmita14100% (3)
- ClutchDokument41 SeitenClutchJyoten Panditpautra100% (1)
- 12ME5DCDM2Dokument3 Seiten12ME5DCDM2Abhyudaya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- DESIGN OF SPRINGSDokument112 SeitenDESIGN OF SPRINGSchshbt80% (5)
- 12ME5DCDM2Dokument3 Seiten12ME5DCDM2Abhyudaya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: January 2015 Semester End Make Up ExaminationsDokument2 SeitenBMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: January 2015 Semester End Make Up ExaminationsAbhyudaya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: January 2015 Semester End Make Up ExaminationsDokument2 SeitenBMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: January 2015 Semester End Make Up ExaminationsAbhyudaya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12ME5DCDM2Dokument3 Seiten12ME5DCDM2Abhyudaya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11ME5DCDM2Dokument3 Seiten11ME5DCDM2Abhyudaya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12ME5DCDM2Dokument3 Seiten12ME5DCDM2Abhyudaya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12ME5DCDM2Dokument4 Seiten12ME5DCDM2Abhyudaya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12ME5DCDM2Dokument3 Seiten12ME5DCDM2Abhyudaya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11ME5DCDM2Dokument3 Seiten11ME5DCDM2Abhyudaya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11ME5DCDM2Dokument3 Seiten11ME5DCDM2Abhyudaya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen