Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Moment Curvature Analysis of Concrete Beam
Hochgeladen von
Rishabh LalaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Moment Curvature Analysis of Concrete Beam
Hochgeladen von
Rishabh LalaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
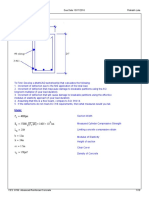
M-Phi Singly Reinforced Rectangular Concrete Section
Given: Signly Reinforced Rectangular Concrete Section
Task I
Section Geometry and Reinforced Concrete Properties:
Section Height
h := 34in
Section Width
b := 18in
Depth of centroid of reinforcement or Effective Depth
d := 31in
Measured Cylinder Compressive Strength
fcc := 5800psi
Yield Strength of Steel
fy := 67ksi
2
As := 6As9 = 6 in
Area of Steel in the section
cu := 0.0038
Limiting concrete compressive strain
Ec := 57000
o :=
1.8 fcc
Ec
(fcc psi) = 4.341 10 ksi
= 2.405 10
-3
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
Modulus of Elasticity
Concrete Strain Associated with Peak Stress
1/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
c
fc( c) := fcc 2
o
c
-
o
Rishabh Lala
Hognested Stress Function
if c o
0 if c > cu
(
(
)
)
c - o
fcc 1 - 0.15
cu - o
otherwise
Stress Strain Model
3
Stress (ksi)
610
( )
fc c
Stress Block of Hognested Model
410
psi
210
0
-3
2 10
-3
410
( c)
in/in
Youngs modulus of Mild Steel
Es := 29000ksi
fcr := 7.5 fcc psi
fcr = 571.183 psi
( )
( Es s)
fs s :=
fy
if s <
Es
fy
fy if s
Es
80
60
( ) 40
fs s
ksi
20
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
2/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
Solution
To Find: Key Points on Moment Curvature Diagram
1. Determine the curvature before cracking. This can be done using the modulus of elasticity and tensile strength of
concrete, using Igross (i.e. ignoring steel) for calculating section modulus.
Sg :=
b h
Section Modulus
6
Cracking Moment
M cr := fcr Sg
cr :=
ccr :=
fcr
Extreme tension fiber strain at cracking
Ec
h
Neutral Axis
gross :=
cr
Curvature
ccr
-6 1
gross = 7.74 10
M cr = 165.072 kip ft
in
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
3/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
2. Determinination of moment and curvature immediately after cracking. The moment remains the same. The
curvature, however goes from that associated with gross section to cracked section.
cmax := 0.00017844
Maximum strain. Adjusting this member until output
moment is equal to the cracking moment
y
C cc ( c , cmax) := fc cmax dy b
c
d - c
T( c , cmax) := As fs cmax
Tension Force in Reinforcement as a function of maximum
Strain and depth of neutral Axis
y
f
y dy
c
cmax
yc c , cmax :=
Location of Centroid of compressive stress block
y
f
dy
c
cmax
Zero c , cmax := C cc c , cmax - T c , cmax
c := root Zero c , cmax , c , 0.001 h , h
Sum of resultant forces should be equal to zero
Root function to determine the depth of neutral axis based
on shaded (assumed) strain
c = 9.418 in
C cc c , cmax = 71.149 kip
Checking of Equilibruim. OK
)(
T c , cmax = 71.149 kip
)) = 165.07 kip ft
T c , cmax d - c + yc c , cmax
M cr = 165.072 kip ft
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
Cracking Moment = Output Moment
4/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
Plotting Information
stressplot y , c , cmax :=
fc cmax
y + c - h
if y h - c
yplot := 0 ,
h
100
.. h
0 otherwise
fcstresslimit := 7000
fs cmax
fcstrainlimit := 0.008
d - c
Stress in Concrete after Cracking
= 11.858 ksi
Stress v/s Strain
80
30
60
Stress
Section Height (in)
Concrete Stress Block After Cracking
20
40
20
10
0.02
0
0
2 10
4 10
0.04
0.06
0.08
Strain
610
Concrete Stress (psi)
cr :=
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
cmax
c
= 1.895 10
-5 1
in
5/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
3) Moment Curvature for Yield Strain:
Maximum strain. Adjust this value till steel strain is
exactly equal to yield.
cmax := 0.001095
c := root Zero c , cmax , c , 0.001 h , h = 9.969 in
C cc c , cmax = 401.948 kip
T c , cmax = 401.948 kip
)(
)) = 922.081 kip ft
M y := T c , cmax d - c + yc c , cmax
Using root function to determine depth of neutral axis
based on the assumed maximum strain (shaded in gray
above).
This moment is much larger than the cracking moment.
M cr = 165.072 kip ft
stressplot y , c , cmax :=
fc cmax
y + c - h
if y h - c
yplot := 0 ,
h
100
.. h
0 otherwise
fs cmax
d - c
cmax
( d - c)
c
= 66.991 ksi
= 0.0023100
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
Adjust maximum strain until steel strain is equal to the
yield strain i.e. 0.00231 for GR67.
6/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
Concrete Stress Block at Yield
Steel Stress Strain Diagram
30
60
Stress
Section Height (in)
80
20
40
20
10
0
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0
0
2 10
4 10
610
Strain
Concrete Stress (psi)
y :=
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
cmax
c
= 1.098 10
-4 1
in
7/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
4 Select Arbitrary curvature to continue plot:
Maximum Concrete compressive Strain
cmax := 0.002
c := root Zero c , cmax , c , 0.001 h , h = 6.406 in
Use root function to determine depth of neutral axis based
on the assumed maximum strain
C cc c , cmax = 402 kip
)(
) ) = 960.107 kip ft
This moment is not much larger than the yield moment.
M 1 := T c , cmax d - c + yc c , cmax
Concrete Stress Block At 0.002
Steel Stress Strain Diagram
60
Stress
Section Height (in)
80
30
20
40
20
10
0
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0
0
2 10
4 10
Strain
6 10
Concrete Stress (psi)
1 :=
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
cmax
c
-4 1
= 3.122 10
in
8/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
5 Select arbitrary curvature to continue plot
cmax := 0.003
c := root Zero c , cmax , c , 0.001 h , h = 5.301 in
C cc c , cmax = 402 kip
)(
) ) = 968.61 kip ft
M 2 := T c , cmax d - c + yc c , cmax
Steel Stress Strain Diagram
80
30
60
Stress
Section Height
Stress Strain Diagram for 0.003
20
10
0
40
20
2000
4000
6000
0.02
0.06
0.08
Strain
Concrete Stress
2 :=
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
0.04
cmax
c
-4 1
= 5.66 10
in
9/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
6) Select Arbitrary Curvature to Continue Plot:
cmax := 0.004
c := root Zero c , cmax , c , 0.001 h , h = 5.323 in
C cc c , cmax = 402 kip
)(
) ) = 958.615 kip ft
M 3 := T c , cmax d - c + yc c , cmax
Steel Stress Strain Diagram
80
30
60
Stress
Section Height
Stress Block for 0.004
20
10
0
40
20
2000
4000
6000
0.02
0.06
0.08
Strain
Stress
3 :=
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
0.04
cmax
c
-4 1
= 7.515 10
in
10/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
7 Arbitrary curvature to continue moment curvature plot:
cmax := 0.005
c := root Zero c , cmax , c , 0.001 h , h = 6.653 in
C cc c , cmax = 402 kip
)(
) ) = 914.034 kip ft
M 4 := T c , cmax d - c + yc c , cmax
4 :=
cmax
c
-4 1
= 7.515 10
in
Steel Stress Strain Diagram
80
30
60
Stress
Section Height
Stress Block for 0.005
20
10
0
40
20
2000
4000
Stress
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
6000
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
Strain
11/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
0
M
cr
Mcr
My
M h :=
M
1
M2
M3
M4
Rishabh Lala
gross
cr
y
h :=
1
2
Moment Curvature Graph: Hognested Stress - Strain Model
3
110
Curvature
800
Mh
kip ft
600
400
200
0
0
2 10
-4
-4
410
6 10
-4
-4
8 10
h in
Moment
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
12/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
Todishini Model
Section Geometry and Reinforced Concrete Properties:
h := 34in
Section Height
b := 18in
Section Width
d := 31in
Depth of centroid of reinforcement or Effective Depth
fcc := 5800psi
Measured Cylinder Compressive Strength
Yield Strength of Steel
fy := 67ksi
2
As := 6As9 = 6 in
Area of Steel in the section
cu := 0.0038
Limiting concrete compressive strain
3
(fcc psi) = 4.341 10 ksi
Ec := 57000
o :=
1.71 fcc
Ec 0.9
Modulus of Elasticity
-3
Concrete Strain Associated with Peak Stress
= 2.539 10
c
2
cc
o if
fc( c) :=
c
cu
2
c
1+
0 otherwise
Todishini Stress Function
Stress Block for Todeschini Model
3
8 10
6 10
( )
fc c
Stress Block of Todishini Model
3
4 10
psi
3
2 10
0
0
-3
1 10
2 10
-3
-3
3 10
-3
4 10
( c)
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
13/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
Youngs modulus of Mild Steel
Es := 29000ksi
fcr := 7.5 fcc psi
fcr = 571.183 psi
( )
fs s :=
( Es s)
fy
if s <
Es
fy
fy if s
Es
80
60
( ) 40
fs s
ksi
20
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
14/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
Solution (Todishini)
To Find: Key Points on Moment Curvature Diagram
1. Determine the curvature before cracking. This can be done using the modulus of elasticity and tensile strength of
concrete, using Igross (i.e. ignoring steel) for calculating section modulus.
Sg :=
b h
Section Modulus
6
Cracking Moment
M cr_t := fcr Sg
cr_t :=
ccr :=
fcr
Extreme tension fiber strain- at cracking
Ec
Neutral Axis
gross_t :=
cr
Curvature
ccr
gross_t = 7.74 10
-6 1
M cr_t = 165.072 kip ft
in
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
15/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
2. Determinination of moment and curvature immediately after cracking. The moment remains the same. The
curvature, however goes from that associated with gross section to cracked section.
cmax := 0.000181950
Maximum strain. Adjusting this member until output
moment is equal to the cracking moment
C cc ( c , cmax) :=
fc cmax dy b
c
d
c
T( c , cmax) := As fs cmax
Tension Force in Reinforcement as a function of maximum
Strain and depth of neutral Axis
y
f
y dy
c
cmax
yc c , cmax :=
Location of Centroid of compressive stress block
y
f
dy
c
cmax
Zero c , cmax := C cc c , cmax - T c , cmax
c := root Zero c , cmax , c , 0.001 h , h
Sum of resultant forces should be equal to zero
Root function to determine the depth of neutral axis based
on shaded (assumed) strain
c = 9.541 in
C cc c , cmax = 71.208 kip
Checking of Equilibruim. OK
)(
T c , cmax = 71.208 kip
)) = 165.064 kip ft
T c , cmax d - c + yc c , cmax
M cr_t = 165.072 kip ft
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
Cracking Moment = Output Moment
16/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
Plotting Information
stressplot y , c , cmax :=
fc cmax
y + c - h
if y h - c
yplot := 0 ,
h
100
.. h
0 otherwise
fcstresslimit := 7000
fs cmax
fcstrainlimit := 0.008
d - c
Stress in Concrete after Cracking
= 11.868 ksi
Steel Stress Strain Diagram
80
30
60
Stress
Section Height (in)
Concrete Stress Block After Cracking
20
40
20
10
0
0
0
2 10
4 10
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
610
Strain
Concrete Stress (psi)
cr_t :=
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
cmax
c
-5 1
= 1.907 10
in
17/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
3) Moment Curvature for Yield Strain:
Maximum strain. Adjust this value till steel strain is
exactly equal to yield.
cmax := 0.00107784
c := root Zero c , cmax , c , 0.001 h , h = 9.863 in
C cc c , cmax = 401.943 kip
T c , cmax = 401.943 kip
)(
)) = 924.559 kip ft
M y_t := T c , cmax d - c + yc c , cmax
Using root function to determine depth of neutral axis
based on the assumed maximum strain (shaded in gray
above).
This moment is much larger than the cracking moment.
M cr = 165.072 kip ft
stressplot y , c , cmax :=
fc cmax
y + c - h
if y h - c
yplot := 0 ,
h
100
.. h
0 otherwise
d - c
fs cmax
= 66.991 ksi
c
cmax
( d - c)
c
= 0.0023100
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
Adjust maximum strain until steel strain is equal to the
yield strain i.e. 0.00231 for GR67.
18/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Steel Stress Strain Diagram
Concrete Stress Block at Yield
80
30
60
Stress
Section Height (in)
Rishabh Lala
20
40
20
10
0
0.02
0
0
2 10
4 10
610
0.04
0.06
0.08
Strain
Concrete Stress (psi)
y_t :=
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
cmax
c
-4 1
= 1.093 10
in
19/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
4 Select Arbitrary curvature to continue plot:
Maximum Concrete compressive Strain
cmax := 0.002
c := root Zero c , cmax , c , 0.001 h , h = 6.283 in
Use root function to determine depth of neutral axis based
on the assumed maximum strain
C cc c , cmax = 402 kip
)(
)) = 961.431 kip ft
M 1_t := T c , cmax d - c + yc c , cmax
This moment is not much larger than the yield moment.
Steel Stress Strain Diagram
80
30
60
20
Stress
Section Height (in)
Concrete Stress Block At 0.002
10
40
20
0
0
0
2 10
4 10
0.02
0.06
0.08
Strain
Concrete Stress (psi)
1_t :=
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
0.04
6 10
cmax
c
-4 1
= 3.183 10
in
20/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
5 Select arbitrary curvature to continue plot
cmax := 0.003
c := root Zero c , cmax , c , 0.001 h , h = 5.206 in
C cc c , cmax = 402 kip
)(
)) = 969.876 kip ft
M 2_t := T c , cmax d - c + yc c , cmax
Steel Stress Strain Diagram
80
30
60
Stress
Section Height
Stress Block Diagram at 0.002
20
10
0
40
20
2000
4000
6000
0.02
0.06
0.08
Strain
Concrete Stress
2_t :=
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
0.04
cmax
c
-4 1
= 5.762 10
in
21/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
6) Arbitrary curvature to continue moment curvature plot:
cmax := 0.004
c := root Zero c , cmax , c , 0.001 h , h = 5.16 in
C cc c , cmax = 402 kip
)(
)) = 961.753 kip ft
M 3_t := T c , cmax d - c + yc c , cmax
Steel Stress Strain Diagram
80
30
60
Stress
Section Height
Stress Model for 0.004
20
10
0
40
20
2000
4000
6000
0.02
0.06
0.08
Strain
Stress
3_t :=
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
0.04
cmax
c
-4 1
= 7.752 10
in
22/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
7 Arbitrary curvature to continue moment curvature plot:
cmax := 0.005
c := root Zero c , cmax , c , 0.001 h , h = 6.45 in
C cc c , cmax = 402 kip
)(
)) = 918.538 kip ft
M 4_t := T c , cmax d - c + yc c , cmax
Steel Stress Strain Diagram
80
30
60
Stress
Section Height
Stress Diagram for 0.005
20
10
0
40
20
2000
4000
6000
0.02
0.06
0.08
Strain
Stress
4_t :=
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
0.04
cmax
c
-4 1
= 7.752 10
in
23/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
0
M
cr_t
Mcr_t
My_t
M T :=
M
1_t
M2_t
M3_t
M
4_t
Rishabh Lala
gross_t
cr_t
y_t
T :=
1_t
2_t
3_t
4_t
Moment Curvature Graph: Hognested Stress - Strain Model
3
110
Curvature
800
MT
kip ft
600
400
200
0
0
2 10
-4
-4
410
6 10
-4
-4
8 10
T in
Moment
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
24/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
Task II
ACI Moment Strength and Corresponding Curvature
f'c := fcc
a :=
As fy
0.85 f'c b
1 :=
0.85 if f'c < 4000psi
= 0.76
0.65 if f'c > 8000psi
f'c - 4000psi
0.85 - 0.05
otherwise
1000psi
y :=
fy
-3
y = 2.31 10
Es
cu := 0.003
c :=
a
1
c = 5.961 in
t :=
d-c
c
cu
t = 0.013
Tension := fy As
arm := d -
a
2
M n := Tension arm = 962.621 kip ft
is moment Reduction Factor
:=
return 0.9 if t > 0.005
return 0.65 if t y
(t - y) otherwise
return
0.65
+
0.25
(0.005 - y)
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
25/34
Homework #7
Due Date 10/07/2016
Rishabh Lala
= 0.9
M n := M n
ACI :=
M n = 866.359 kip ft
cu
c
= 5.033 10
-4 1
in
Moment Curvature Graph: Hognested, Todeschini and ACI Model
110
800
Mh
Curvature
kip ft
600
MT
kip ft
Mn
400
kip ft
200
0
-4
2 10
4 10
-4
610
-4
-4
810
h in , T in , ACI in
Moment
Hognested Model
Todeschini Model
ACI Model
Discussion:
The key observations from the moment curvature of the three models are:
1. Moment-Curvature for both Hognested and Todeschini's models are almost the same.
2. The curvature seizes to increase after 0.004 strain is reached for both the models.
3. Before and after cracking, almost similar curvature change is observed.
4. Yield point given by both the models are almost the same with percentage change of 0.45 x 10-4%., and
Hognested's being on the higher side.
5. Comparitively, more ductility is observed in the moment curvature by Todesc hini's Model by 3.1 x 10-4% (comparing
0.004 curvature of both models).
6. ACI assumes conservative moment allowed for design as compared to aformentioned Moment Curvature Models.
CES: 6706: Advanced Reinforced Concrete
26/34
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- تصميم الكمرات بطريقة ultimate PDFDokument42 Seitenتصميم الكمرات بطريقة ultimate PDFqaisalkurdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Am Exams Paper 2014Dokument12 SeitenAm Exams Paper 2014akanagesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 - Bending Members: A Beginner's Guide To The Steel Construction Manual, 14 EdDokument5 SeitenChapter 8 - Bending Members: A Beginner's Guide To The Steel Construction Manual, 14 Edv pavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- WIND02 v2-21: Detailed Wind Load Analysis Per ASCE 7-10Dokument3 SeitenWIND02 v2-21: Detailed Wind Load Analysis Per ASCE 7-10gmontesroy100% (1)
- AM Exam July 2016Dokument12 SeitenAM Exam July 2016Altin CeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rolled - MomentDokument5 SeitenRolled - MomentAdekimi EmmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05.06 Duct Supports DS-06 Base PlateDokument2 Seiten05.06 Duct Supports DS-06 Base Platehighway20049922Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chartered Membership Examination: Thursday, 5 July 2018Dokument18 SeitenChartered Membership Examination: Thursday, 5 July 2018Nitin shepurNoch keine Bewertungen
- CXXC XCFXCXCV DfethDokument16 SeitenCXXC XCFXCXCV Dfethprompt consortiumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wood Shearwall & Connection: 'File:///var/www/apps/conversion/tmp/scratch - 7/347313706.xls'#$woodwallDokument3 SeitenWood Shearwall & Connection: 'File:///var/www/apps/conversion/tmp/scratch - 7/347313706.xls'#$woodwallChoky NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- RaftDokument48 SeitenRaftHariom KhungarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthquake Design of RectangularDokument6 SeitenEarthquake Design of RectangularFerry R. A. PratomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Preparation Associate Member Past Paper 20150710Dokument16 SeitenExam Preparation Associate Member Past Paper 20150710Sanjay ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- UB UC Steel SectionsDokument10 SeitenUB UC Steel SectionsMuhammad HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project: Steel Building Design Case Study Subject: Project Plan SHEET 1 of 131Dokument5 SeitenProject: Steel Building Design Case Study Subject: Project Plan SHEET 1 of 131clam2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shear Hinge For Coupling BeamDokument7 SeitenShear Hinge For Coupling BeamLavender HoneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bridge Design: Saif HaroonDokument30 SeitenBridge Design: Saif HaroonphiliSCDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deck Girder - BracingDokument3 SeitenDeck Girder - BracingvibishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installation - Typical 3.3m.precast Concrete Beam Design (EN1992)Dokument5 SeitenInstallation - Typical 3.3m.precast Concrete Beam Design (EN1992)zms msswiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pinned Connection Precast ConcreteDokument3 SeitenPinned Connection Precast ConcreteFandy SipataNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Section 2 Example Bridge (E)Dokument11 Seiten03 Section 2 Example Bridge (E)Diego Benavides KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design - Calculation - For - Bracing - Connection 1 PDFDokument10 SeitenDesign - Calculation - For - Bracing - Connection 1 PDFLian Jia JieNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0 - BASE SHEAR REDISTRIBUTION BETWEEN THE RC DUAL SYSTEM STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS - V.Sigmund Itd. - 2008 - 8158 PDFDokument8 Seiten0 - BASE SHEAR REDISTRIBUTION BETWEEN THE RC DUAL SYSTEM STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS - V.Sigmund Itd. - 2008 - 8158 PDFnebojsadj6411Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pages From Hilti BE 500Dokument1 SeitePages From Hilti BE 500Anonymous S7Cq7ZDgPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development Length Calculation For 20Mm Dia Bar: B y C DC RDokument2 SeitenDevelopment Length Calculation For 20Mm Dia Bar: B y C DC RkarthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arch ActionDokument14 SeitenArch ActionvempadareddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Calculation of Rss Building 3VIN 9 554 D1 S1 202 R0 Design of Foundations DataDokument56 SeitenDesign Calculation of Rss Building 3VIN 9 554 D1 S1 202 R0 Design of Foundations DataARUNKUMAR KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hot Finished Square Hollow Sections in Accordance With EN 10210Dokument5 SeitenHot Finished Square Hollow Sections in Accordance With EN 10210bggariyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Strength of Concrete Vu Area Required For Baseplate AreaDokument5 SeitenBearing Strength of Concrete Vu Area Required For Baseplate AreaSunidhi ItagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is 13920Dokument183 SeitenIs 13920p_ignatiusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial ExcelDokument15 SeitenTrial ExcelCyndrille John BragatNoch keine Bewertungen
- LiquidRet IndianDokument13 SeitenLiquidRet Indianchandra BandaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beams On Elastic FoundationDokument5 SeitenBeams On Elastic FoundationKazi Shahazada Shahanewaz HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- XyzDokument64 SeitenXyzP S HARSHITANoch keine Bewertungen
- DE010 of-053123-1.0-P-Vulcraft Joist and Deck Plans - Datum ReviewedDokument9 SeitenDE010 of-053123-1.0-P-Vulcraft Joist and Deck Plans - Datum ReviewedAzeemuddin Gulam MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sesmic Load at Floor LevelDokument14 SeitenSesmic Load at Floor LevelJennifer PearsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Given Data: Given Data:: Design of Raft Foundation Design of Raft FoundationDokument8 SeitenGiven Data: Given Data:: Design of Raft Foundation Design of Raft FoundationBikram BhusalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bi Material BeamDokument22 SeitenBi Material BeamPraveen KumaarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Design Method BDokument3 SeitenBearing Design Method BDhurai KesavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress Check For E.J PierDokument29 SeitenStress Check For E.J PierVasu Deva Rao ChilukuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welding Connection 2Dokument55 SeitenWelding Connection 2dinu69inNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Design Parameters:: Loads: 1Dokument5 SeitenBasic Design Parameters:: Loads: 1Timo SchenkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bridge Rating Flowchart SDDokument5 SeitenBridge Rating Flowchart SDSuvash DhakalNoch keine Bewertungen
- P-M Curve - 15-4-2015 - FinalDokument41 SeitenP-M Curve - 15-4-2015 - FinalVishal PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of ColumnDokument8 SeitenDesign of ColumnAfsar MansuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Rectangular Water TankDokument308 SeitenDesign of Rectangular Water Tankලහිරු විතානාච්චි100% (1)
- SBC of Soil at 2.5m DEPTH 25 T/M: (A) Check For One Way ShearDokument36 SeitenSBC of Soil at 2.5m DEPTH 25 T/M: (A) Check For One Way ShearAnonymous mcHqIfbnV1Noch keine Bewertungen
- RCC Beam With Different Choice of Design WSD For Singly & Doubly ReinforcementDokument5 SeitenRCC Beam With Different Choice of Design WSD For Singly & Doubly ReinforcementdsanandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Racking Analysis of Underground Structures: Date: Note No. By: Sheet NoDokument4 SeitenRacking Analysis of Underground Structures: Date: Note No. By: Sheet NoStructural SpreadsheetsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of RCC Post-Tensioned Flat SlabsDokument6 SeitenDesign of RCC Post-Tensioned Flat SlabsjayadushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aizawal-Tuipang (NH-54) - PKG 6: Design Notes-Retaining WallDokument114 SeitenAizawal-Tuipang (NH-54) - PKG 6: Design Notes-Retaining Wallnikhilnagpal2121994Noch keine Bewertungen
- Truss AnalysisDokument35 SeitenTruss AnalysisSandip BudhathokiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pile Design SpreadsheetDokument180 SeitenPile Design SpreadsheetsubamanivelNoch keine Bewertungen
- v375 Ebook Ebook Download Reinforced Concrete Structures Analysis and Design by David FanellaDokument7 Seitenv375 Ebook Ebook Download Reinforced Concrete Structures Analysis and Design by David FanellaGandhi HammoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepared by Date PRA 28-Jan-17 Checked by Revision Dr. Yeri R0 MegaDokument1 SeitePrepared by Date PRA 28-Jan-17 Checked by Revision Dr. Yeri R0 MegapravinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix - Ii: Principles of Construction, Material and Design of Ferrocement TankDokument5 SeitenAppendix - Ii: Principles of Construction, Material and Design of Ferrocement TankbenzzenhdNoch keine Bewertungen
- R.C.C DesignDokument14 SeitenR.C.C DesignVinayan PuthukadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cross Section Properties (All Dimensions Are in CMS)Dokument2 SeitenCross Section Properties (All Dimensions Are in CMS)Hanamantrao KhasnisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torsion Tension and Column (11-16)Dokument33 SeitenTorsion Tension and Column (11-16)2011kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- My UNIX CommandsDokument2 SeitenMy UNIX CommandsRishabh Lala100% (1)
- Python and PerlDokument21 SeitenPython and PerlRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deflections Due To Loading As Per ACIDokument8 SeitenDeflections Due To Loading As Per ACIRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansys CommandsDokument1 SeiteAnsys CommandsRishabh Lala100% (1)
- Whats Research and How Do We Do ResearchDokument2 SeitenWhats Research and How Do We Do ResearchRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lala 2 PDFDokument13 SeitenLala 2 PDFRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My UNIX CommandsDokument2 SeitenMy UNIX CommandsRishabh Lala100% (1)
- Resume Rishabh Lala PDFDokument1 SeiteResume Rishabh Lala PDFRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matrix Structural AnalysisDokument2 SeitenMatrix Structural AnalysisRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- McuserDokument253 SeitenMcuserIoan LeonteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume Rishabh LalaDokument1 SeiteResume Rishabh LalaRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research, Building Codes, and Engineering PracticeDokument1 SeiteResearch, Building Codes, and Engineering PracticeRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- One Who Tries Never FailsDokument1 SeiteOne Who Tries Never FailsRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- State of Art PapersDokument1 SeiteState of Art PapersRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major ProjectDokument59 SeitenMajor ProjectRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument11 SeitenAssignment 1Rishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResearchDokument2 SeitenResearchRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Column ShorteningDokument10 SeitenColumn ShorteningRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Requirements RishabhDokument1 SeiteDesign Requirements RishabhRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Railway Engineering NotesDokument1 SeiteRailway Engineering NotesRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Analysis ConceptsDokument21 SeitenSoftware Analysis ConceptsRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concentration Part IIIDokument2 SeitenConcentration Part IIIRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Burj KhalifaDokument18 SeitenReport On Burj KhalifaRishabh Lala85% (13)
- Structural Engineering NotesDokument5 SeitenStructural Engineering NotesRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout Notes1Dokument6 SeitenHandout Notes1Rishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Engineering NotesDokument5 SeitenStructural Engineering NotesRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Design NotesDokument3 SeitenSteel Design NotesRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Put Your Shoulders To WheelDokument1 SeitePut Your Shoulders To WheelRishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covers According To Exposure Class 4.1 (BS 8500-1:2006)Dokument3 SeitenCovers According To Exposure Class 4.1 (BS 8500-1:2006)Rishabh LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPWH - Guard HouseDokument180 SeitenDPWH - Guard HouseErnest BelmesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cantilever Calculation ToolDokument10 SeitenCantilever Calculation ToolEnoch Twumasi50% (2)
- GOST R 52029-2003 Water. Unit of HardnessDokument4 SeitenGOST R 52029-2003 Water. Unit of HardnessOMER EKERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dream Residences - Water Supply & Fire Protection BOMDokument1 SeiteDream Residences - Water Supply & Fire Protection BOMPatrick LlenaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capital CostDokument2 SeitenCapital CostRajibDebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Safety and Health Narrative MethodsDokument46 SeitenConstruction Safety and Health Narrative MethodsEldreen Ann Jebulan Vargas100% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingDokument5 SeitenSafety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakinghafizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar On Steam EngineDokument26 SeitenSeminar On Steam EngineEr Akhilesh Singh100% (1)
- Hd26000 Casing TongDokument121 SeitenHd26000 Casing TongTerry Smith100% (1)
- Lesson 6-GlassDokument32 SeitenLesson 6-Glasslewis imaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 CACCDHDokument60 SeitenChapter 11 CACCDHmeda012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Amercoat 37-B-1 / 37-G-1: Product Data/ Application InstructionsDokument4 SeitenAmercoat 37-B-1 / 37-G-1: Product Data/ Application InstructionsTony KhouryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ieema Member's Directory Listing FormDokument12 SeitenIeema Member's Directory Listing Formsudhakarrrrrr0% (1)
- Superwool Plus BlanketDokument2 SeitenSuperwool Plus Blanketdnageshm4n244Noch keine Bewertungen
- ME 231 Montazami Whharris 9-10-18 SOLUTIONDokument4 SeitenME 231 Montazami Whharris 9-10-18 SOLUTIONEduardo Perez UriegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristics of NanomaterialsDokument9 SeitenCharacteristics of Nanomaterialssandhiya padmanabanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PowerTech 4.5L &6.8L Diesel Engines - Level 12 Electronic Fuel System-Stanadyne DE10 Pump-CTM331Dokument550 SeitenPowerTech 4.5L &6.8L Diesel Engines - Level 12 Electronic Fuel System-Stanadyne DE10 Pump-CTM331grand fir100% (39)
- Uses of The Elements and Compounds in Our Daily LifeDokument4 SeitenUses of The Elements and Compounds in Our Daily LifeTaibah Nurwahidah Mohamad89% (9)
- NCSE 2006 Integrated ScienceDokument19 SeitenNCSE 2006 Integrated ScienceChristian PatriceNoch keine Bewertungen
- EVERBUILD® EVERFLEX® 565 Clean Room Silicone: Product Data SheetDokument3 SeitenEVERBUILD® EVERFLEX® 565 Clean Room Silicone: Product Data Sheetsamira bashirvandNoch keine Bewertungen
- CatalogDokument482 SeitenCatalogAnonymous 6EW2MsFbkNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIL-F-5509D - Fittings, Flared Tube, Fluid ConnectionDokument18 SeitenMIL-F-5509D - Fittings, Flared Tube, Fluid ConnectionthomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commissioning ProceduresDokument152 SeitenCommissioning Proceduresmabrarahmed100% (1)
- Arch. DictionaryDokument68 SeitenArch. DictionaryVinay GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2D Numerical Analysis of Hydraulic Fracturing in Heterogeneous Geo-Materials - 2009 - c49 PDFDokument11 Seiten2D Numerical Analysis of Hydraulic Fracturing in Heterogeneous Geo-Materials - 2009 - c49 PDFMoataz Hesham SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visit ReportDokument13 SeitenVisit ReportAlankrutha DevuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thin Cylinders: Presented By: Balvinder Budania Asstt - ProfDokument44 SeitenThin Cylinders: Presented By: Balvinder Budania Asstt - ProfBalvinderNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12d20105a Experimental Stress AnalysisDokument1 Seite12d20105a Experimental Stress AnalysissubbuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ryobi ELS52G Manual 1 Log SplitterDokument14 SeitenRyobi ELS52G Manual 1 Log SplitterFrank MatzkaNoch keine Bewertungen