Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
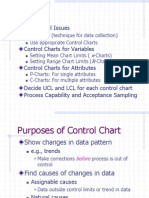
Control Charts For A-Ributes: Hometown Bank
Hochgeladen von
Aanchal ChadhaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Control Charts For A-Ributes: Hometown Bank
Hochgeladen von
Aanchal ChadhaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
9/21/16
Hometown Bank
Control Charts
for A-ributes
Example
p-chart: A chart used for controlling the
propor7on of defec7ve services or
products generated by the process.
p =
The operations manager of the booking services department of Hometown Bank
is concerned about the number of wrong customer account numbers recorded by
Hometown personnel.
Each week a random sample of 2,500 deposits is taken, and the number of
incorrect account numbers is recorded. The results for the past 12 weeks are
shown in the following table.
p(1 p)/n
Where
n = sample size
p = central line on the chart, which can be either the historical
average population proportion defective or a target value.
Control limits are: UCLp = p+zp and LCLp = pzp
z = normal deviate (number of standard deviations from the average)
Is the booking process out of statistical control? Use three-sigma control limits.
Hometown Bank
Hometown Bank
Using a p-Chart to monitor a process
Using a p-Chart to monitor a process
n = 2500
p=
p =
p =
147
= 0.0049
12(2500)
p(1 p)/n
0.0049(1 0.0049)/2500
p = 0.0014
UCLp = 0.0049 + 3(0.0014)
= 0.0091
LCLp = 0.0049 3(0.0014)
= 0.0007
Sample
Number
Wrong
Account #
Proportion
Defective
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
15
12
19
2
19
4
24
7
10
17
15
3
0.006
0.0048
0.0076
0.0008
0.0076
0.0016
0.0096
0.0028
0.004
0.0068
0.006
0.0012
Total
147
In class Problem
Example
Control Charts
Two types of error are possible with control
charts
A type I error occurs when a process is
thought to be out of control when in fact
it is not
A type II error occurs when a process is
thought to be in control when it is
actually out of sta7s7cal control
These errors can be controlled by the
choice of control limits
9/21/16
Process Capability
Process Capability
Process capability is the ability of the
process to meet the design specica7ons
for a service or product.
Nominal value is a target for design
specica7ons.
Tolerance is an allowance above or below
the nominal value.
Nominal
value
Process distribution
Lower
specification
20
Upper
specification
25
30
Process is capable
Process Capability
Process Capability Ra7o, Cp
Process capability ra7o, Cp, is the tolerance width divided by 6 standard
devia7ons (process variability).
Nominal
value
Process distribution
Lower
specification
20
Upper
specification
25
Cp =
Upper specification - Lower specification
6
30
Process is not capable
Intensive Care Lab
Process Capability Index, Cpk
Example
Process Capability Index, Cpk, is an index that measures the poten7al
for a process to generate defec7ve outputs rela7ve to either upper
or lower specica7ons.
Cpk = Minimum of
=
x Lower specica7on
3
Upper specica7on x=
3
We take the minimum of the two ra7os because it gives the worstcase situa7on.
The intensive care unit lab process has an average turnaround 7me
of 26.2 minutes and a standard devia7on of 1.35 minutes.
The nominal value for this service is 25 minutes with an upper
specica7on limit of 30 minutes and a lower specica7on limit of 20
minutes.
The administrator of the lab wants to have three-sigma performance
for her lab. Is the lab process capable of this level of performance?
Upper specification = 30 minutes
Lower specification = 20 minutes
Average service = 26.2 minutes
= 1.35 minutes
9/21/16
Intensive Care Lab
Intensive Care Lab
Assessing Process Capability
Example
Example
Upper specica7on = 30 minutes
Lower specica7on = 20 minutes
Average service = 26.2 minutes
= 1.35 minutes
=
x Lower specica7on
Cpk = Minimum of
Assessing Process Capability
Cpk =
Minimum of
Cpk =
Minimum of
26.2 20.0
3(1.35)
1.53, 0.94
Cp =
Upper specica7on x
Cp =
30.0 26.2
3(1.35)
= 0.94
Process
Capability
Index
In Class Problem
What it means to operate at 6-sigma
Nominal value
Six sigma
Four sigma
Two sigma
Lower
specification
Upper
specification
= 1.23 Process Capability Ra7o
Before Process Modification
Upper specification = 30.0 minutes Lower specification = 20.0 minutes
Average service = 26.2 minutes
= 1.35 minutes Cpk = 0.94 Cp = 1.23
In Class Problem
Eects of Reducing
Variability on Process Capability
30 - 20
6(1.35)
Does not meet 3 (1.00 Cpk) target due to a shift in mean
(Note variability is ok since Cp is over 1.0)
Upper specica7on - Lower specica7on
6
Range
Popula7on in range
Expected frequency outside
range
Approx. frequency for daily
event
0.682689492137
1 in 3
Twice a week
0.954499736104
1 in 22
Every three weeks
0.997300203937
1 in 370
Yearly
0.999936657516
1 in 15,787
Every 43 years (twice in a
life7me)
0.999999426697
1 in 1,744,278
Every 5,000 years (once in
history)
0.999999998027
1 in 506,842,372
Every 1.5 million years
Mean
9/21/16
Six Sigma
3.4 defects per million
Cpk = 2
Impact of number of parts or produc7on steps
on yield:
6 sigma
1 100%
5 100%
10 100%
100 99.97%
4 sigma
3 sigma
99%
97%
94%
54%
99%
71%
50%
0%
Designing in 6-sigma
Reduce the number of parts in a product
Reduce the number of steps in a process
Six Sigma
Improvement Model
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a comprehensive and exible system for
achieving, sustaining, and maximizing business success
by minimizing defects and variability in processes.
It relies heavily on the principles and tools of TQM.
It is driven by a close understanding of customer needs;
the disciplined use of facts, data, and sta7s7cal analysis;
and diligent a-en7on to managing, improving, and
reinven7ng business processes.
1. Dene Determine the current process
characteris7cs cri7cal to customer sa7sfac7on
and iden7fy any gaps.
2. Measure Quan7fy the work the process does
that aects the gap.
3. Analyze Use data on measures to perform
process analysis.
4. Improve Modify or redesign exis7ng methods to
meet the new performance objec7ves.
5. Control Monitor the process to make sure high
performance levels are maintained.
Six Sigma
Implementa7on
Top Down Commitment from corporate leaders.
Measurement Systems to Track Progress
Tough Goal Sejng through benchmarking bestin-class companies.
Educa7on: Employees must be trained in the
whys and how-tos of quality.
Communica7on: Successes are as important to
understanding as failures.
Customer Priori7es: Never lose sight of the
customers priori7es.
Six Sigma Educa7on
Green Belt: An employee who achieved the rst level of
training in a Six Sigma program and spends part of his
or her 7me teaching and helping teams with their
projects.
Black Belt: An employee who reached the highest level
of training in a Six Sigma program and spends all of his
or her 7me teaching and leading teams involved in Six
Sigma projects.
Master Black Belt: Full-7me teachers and mentors to
several black belts.
9/21/16
International Quality
Documentation Standards
ISO
9000
ISO
14000
Malcolm Baldrige Na7onal Quality
Award
Named ater the late secretary of commerce, a strong proponent of
enhancing quality as a means of reducing the trade decit. The
award promotes, recognizes, and publicizes quality strategies and
achievements.
A set of standards governing documenta7on
of a quality program.
1.
2.
3.
4.
Documenta7on standards that require par7cipa7ng
companies to keep track of their raw materials use
and their genera7on, treatment, and disposal of
hazardous wastes.
Category 1 Leadership
120 points
Category 2 Strategic Planning
85 points
Category 3 Customer and Market Focus
85 points
Category 4 Measurement, Analysis, and
Knowledge Management
90 points
5. Category 5 Human Resource Focus
6. Category 6 Process Management
7. Category 7 Business Results
85 points
85 points
450 points
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Sources of Information PDFDokument91 SeitenSources of Information PDFworseukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Card Types, Benefits & RisksDokument14 SeitenCredit Card Types, Benefits & RisksAsef KhademiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Citibank Performance EvaluationDokument9 SeitenCitibank Performance EvaluationMohit Sharma67% (6)
- Recruitment AgreementDokument5 SeitenRecruitment AgreementTricia GrafiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acctg 16 - Midterm Exam PDFDokument4 SeitenAcctg 16 - Midterm Exam PDFjoan miral0% (1)
- Wiley CMAexcel Learning System Exam Review 2017: Part 1, Financial Reporting, Planning, Performance, and Control (1-year access)Von EverandWiley CMAexcel Learning System Exam Review 2017: Part 1, Financial Reporting, Planning, Performance, and Control (1-year access)Noch keine Bewertungen
- SPC: Statistical Process ControlDokument53 SeitenSPC: Statistical Process ControlSaoloan NaiborhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Process ControlDokument66 SeitenStatistical Process Controlanshuldce50% (2)
- Statistical Process ControlDokument43 SeitenStatistical Process ControlninaswayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Quality ControlDokument38 SeitenStatistical Quality ControlAlpesh SantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality ControlDokument13 SeitenQuality ControlEuniceChungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Marketing Proposal for Udzungwa Falls LodgeDokument25 SeitenDigital Marketing Proposal for Udzungwa Falls LodgeLouis Fanuel100% (1)
- Statistical Quality Control (SQC) FinalDokument47 SeitenStatistical Quality Control (SQC) FinalSagar DhageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics For Business and Economics: Bab 20Dokument43 SeitenStatistics For Business and Economics: Bab 20balo100% (1)
- Statistical Process ControlDokument42 SeitenStatistical Process ControlErick Bok Cang YeongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Process Control (SPC)Dokument36 SeitenStatistical Process Control (SPC)SYEDOUNMUHAMMAD ZAIDI100% (1)
- Process Capability and SPC : Operations ManagementDokument43 SeitenProcess Capability and SPC : Operations ManagementRahul KhannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Charts GuideDokument36 SeitenControl Charts GuideGulshan KandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Project Report On Market Strategey of Tommy HilfigerDokument49 SeitenA Project Report On Market Strategey of Tommy HilfigerKamal King54% (13)
- Final Notes On SQCDokument12 SeitenFinal Notes On SQCShashank Srivastava100% (1)
- SPCDokument59 SeitenSPCadibhai06100% (2)
- Unit 6 Control Charts For Attribute Data: STAT8010 Applied Statistical TechniquesDokument29 SeitenUnit 6 Control Charts For Attribute Data: STAT8010 Applied Statistical TechniquesIsha BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Which Control Charts To Use WhereDokument115 SeitenWhich Control Charts To Use Whereanbarasuar1964Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10 ExternalitiesDokument28 Seiten10 ExternalitiesShantyruckmalla Ciie PiscesgirlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistic ProcessDokument39 SeitenStatistic ProcessxredjokerxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Charts NotesDokument39 SeitenControl Charts NotesFred Muthoka100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Solutions PDFDokument50 SeitenChapter 3 Solutions PDFHayu AriantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch.4 - Control Charts For AttributesDokument34 SeitenCh.4 - Control Charts For AttributesAbdullah Hazeem100% (3)
- Generic Pharmaceutical Industry Yearbook Torreya Feb2016 GphaDokument72 SeitenGeneric Pharmaceutical Industry Yearbook Torreya Feb2016 GphaSheltie ForeverNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch07 PDFDokument85 Seitench07 PDFNadya Azzan100% (2)
- Quality Control Project: DataDokument13 SeitenQuality Control Project: DataWaqar DarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Charts - MBADokument30 SeitenControl Charts - MBAShivangi Dhamija100% (1)
- Control Charts for Attributes Monitoring with p-Chart ExampleDokument26 SeitenControl Charts for Attributes Monitoring with p-Chart ExampleBurcu Gözde Bilol100% (1)
- Control ChartsDokument38 SeitenControl ChartsHassan MirzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Note 8: Process Capability and Statistical Quality ControlDokument46 SeitenTechnical Note 8: Process Capability and Statistical Quality ControlVipin NairNoch keine Bewertungen
- SQC MATH. (Vikas, Vaibhav, Swanand, ShreeDokument39 SeitenSQC MATH. (Vikas, Vaibhav, Swanand, ShreeVikasPatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Quality ControlDokument3 SeitenStatistical Quality ControlHunson Abadeer100% (1)
- Quality ManagementDokument10 SeitenQuality ManagementTifarie Luesas33% (3)
- Statistical Quality Control: by 4Th Edition © Wiley 2010 Powerpoint Presentation by R.B. Clough - Unh M. E. Henrie - UaaDokument40 SeitenStatistical Quality Control: by 4Th Edition © Wiley 2010 Powerpoint Presentation by R.B. Clough - Unh M. E. Henrie - UaaInderpreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- MGT 6421 Quality Control ChartsDokument12 SeitenMGT 6421 Quality Control ChartsRoque EstradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control ChartsDokument36 SeitenControl ChartsArpit AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control ChartsDokument36 SeitenControl ChartsEr Vaibhav NyatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation ManagementDokument66 SeitenOperation ManagementsemerederibeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Quality ControlDokument13 SeitenStatistical Quality ControlsekelanilunguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch03 SPC and Process CapabilityDokument55 SeitenCh03 SPC and Process CapabilityRaj Kumar100% (1)
- Chap 04Dokument9 SeitenChap 04gttomcatNoch keine Bewertungen
- As 6 Control Charts For AttributesDokument32 SeitenAs 6 Control Charts For AttributesRoque Estrada100% (1)
- SPCDokument62 SeitenSPCSagar KansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CONTROL CHARTS GUIDEDokument26 SeitenCONTROL CHARTS GUIDEAnurag KushwahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Statistical Quality ControlDokument24 SeitenOverview of Statistical Quality ControlJayalal WettasingheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control ChartsDokument36 SeitenControl ChartsYusranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q8 IM13EFinalDokument44 SeitenQ8 IM13EFinalJb Macaroco100% (1)
- Statistical Quality Control (S.Q.C.) Presented By-: Nikhil Garg ROLL NO-0129626Dokument38 SeitenStatistical Quality Control (S.Q.C.) Presented By-: Nikhil Garg ROLL NO-0129626jolaakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Charts For Attributes 2Dokument42 SeitenControl Charts For Attributes 2وسام توفيقNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Quality ControlDokument82 SeitenStatistical Quality ControlShahmirBalochNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Quality Control PDFDokument82 SeitenStatistical Quality Control PDFInshal KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Control Charts For AttributesDokument48 SeitenChapter 5 Control Charts For Attributesgeletaw mitawNoch keine Bewertungen
- IENG 486 Lecture 17Dokument38 SeitenIENG 486 Lecture 17Matías IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Total Quality Management, Statistical Process ControlDokument11 SeitenTotal Quality Management, Statistical Process ControlElmer GatchalianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Chart BasicsDokument36 SeitenControl Chart Basicstikar69314Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Business Statistics: Statistical Applications in Quality and Productivity ManagementDokument67 SeitenBasic Business Statistics: Statistical Applications in Quality and Productivity ManagementToufiq Khan MajlisNoch keine Bewertungen
- P ChartDokument21 SeitenP ChartSumit Patil100% (1)
- Control Chart BasicsDokument35 SeitenControl Chart BasicsPamela MorcillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Quality Control 7Th Edition Montgomery Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDokument67 SeitenStatistical Quality Control 7Th Edition Montgomery Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFMrsSydneyBennettMDjnkc100% (7)
- Control ChartDokument25 SeitenControl ChartSURYAPRAKASH GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Charts: Walter A. ShewhartDokument28 SeitenControl Charts: Walter A. Shewhartmimossmart26036Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6.FQA-QUALITY CONTROL-Presentation1Dokument23 Seiten6.FQA-QUALITY CONTROL-Presentation1grace mwenjeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cult Comm Event: Lohri Bonfire CelebrationDokument3 SeitenCult Comm Event: Lohri Bonfire CelebrationAanchal ChadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radhika's Menu '17Dokument1 SeiteRadhika's Menu '17Aanchal ChadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CF Session11 - 20170205233647Dokument6 SeitenCF Session11 - 20170205233647Aanchal ChadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analyzing Employee Performance Metrics to Improve Customer ServiceDokument4 SeitenAnalyzing Employee Performance Metrics to Improve Customer ServiceAanchal ChadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIMA-Quotation For Audio System (Sub Woofer)Dokument2 SeitenIIMA-Quotation For Audio System (Sub Woofer)Aanchal ChadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objective Function 0: Min MinDokument2 SeitenObjective Function 0: Min MinAanchal ChadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AanchalChadha WACII1ADokument3 SeitenAanchalChadha WACII1AAanchal ChadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Marketing of PEPSICODokument18 SeitenGlobal Marketing of PEPSICOashrafur_chowdhury100% (1)
- Market Retail Edelweiss 10.01.18 PDFDokument310 SeitenMarket Retail Edelweiss 10.01.18 PDFRohan ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 29 Managing and Running A Small Business: Student Name: Student IDDokument15 SeitenUnit 29 Managing and Running A Small Business: Student Name: Student IDFahmina AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customer & Product AuditDokument7 SeitenCustomer & Product AuditWhenas WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics For Engineers (HMTS 3201) : Time Allotted: 3 Hrs Full Marks: 70Dokument4 SeitenEconomics For Engineers (HMTS 3201) : Time Allotted: 3 Hrs Full Marks: 70gaurav kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSc Financial Markets, Financial Institutions and Banking - Lecture 1 IntroductionDokument26 SeitenMSc Financial Markets, Financial Institutions and Banking - Lecture 1 IntroductionLumumba KuyelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Replenishment Planning - Process StepsDokument1 SeiteReplenishment Planning - Process StepsNishu NishuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2 - Recruitment SourcesDokument47 SeitenWeek 2 - Recruitment Sourcesyousuf AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRM Retail Big Bazaar (India) Case StudyDokument42 SeitenCRM Retail Big Bazaar (India) Case StudyAbhijit Malankar100% (1)
- Hanson Aggregates Opinion 11-21-2022Dokument15 SeitenHanson Aggregates Opinion 11-21-2022E Frank CorneliusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting and Management Problems of SmallDokument128 SeitenAccounting and Management Problems of SmallelohoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LLPDokument15 SeitenLLPAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- D. None of These.: 1 - Page DR/ Magdy Kamel Tel/ 01273949660Dokument10 SeitenD. None of These.: 1 - Page DR/ Magdy Kamel Tel/ 01273949660magdy kamelNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB Ques (1) .Bank 1Dokument12 SeitenLAB Ques (1) .Bank 1kakka22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-3 Mari HandoutsDokument10 SeitenPre-3 Mari HandoutsEmerlyn Charlotte FonteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inymart AcademyDokument10 SeitenInymart AcademySmash HulkNoch keine Bewertungen
- EGMC002 Final Edition YJDokument17 SeitenEGMC002 Final Edition YJVikrant VatsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Rubrics EconomicsDokument2 SeitenProject Rubrics EconomicsYummy Chum23Noch keine Bewertungen
- OB Case Study - Lenovo IBMDokument16 SeitenOB Case Study - Lenovo IBMNithi HariNoch keine Bewertungen
- L'Oreal of Paris - Q1Dokument3 SeitenL'Oreal of Paris - Q1rahul_jain_76Noch keine Bewertungen