Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
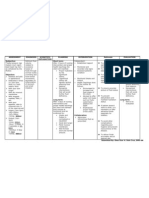
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Hochgeladen von
Chucky VergaraOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Hochgeladen von
Chucky VergaraCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Assessment
Problem: Difficulty
breathing
Nursing Diagnosis
Impaired gas
exchange related to
alveolar capillary
membrane changes
as evidenced by
Subjective:
difficulty of
Nahihirapan po
akong huminga., as breathing,
respiratory rate of
verbalized by the
38 cycles per
client.
minute, pulse rate of
102 beats per
minute, positive
Objectives:
crackles at right
RR: 38
lower thorax, harsh
cycles/minute
breath sounds at the
right chest area, use
PR:102
of accessory
beats/minute
muscles and pale in
with positive
appearance.
wheezes at right
lower thorax.
use of accessory
muscles in
breathing
pale in appearance
Planning
Intervention
Rationale
Goal:
Independent:
After 8 hours of
intervention, the client
will be able to
demonstrate improved
ventilation and
oxygenation of tissues
within clients normal
limits.
1. Evaluate the clients
vital capacity
1. To assess respiratory
insufficiency
2. Assist the client in a
semi-fowlers position
2. Facilitate easier
breathing
3. Emphasize adequate
rest
3. Promotes comfort
Outcomes:
After the interventions,
the client will be able to
show:
clear breath sounds
eliminate dyspnea
prevent the used of
accessory muscles
respiratory rate of <25
cycles per minute
relaxation to condition
Evaluation
The goal was met.
After 8 hours of
intervention, the
client was able to
show adequate gas
exchange such as:
clear breath sounds
4.Encourage adequate
oral fluid intake of 2000
ml per day
4. Helps liquefy
secretions
no dyspneic
episodes
5.Have standby oxygen
5.For emergency use
free breathing
without use of
accessory muscles
Dependent:
6. Administer
mucolytics as
prescribed.
7. Administer
antibiotics, as ordered
and monitor for side
effects
8. Administer
bronchodilator as
recommended.
6. Decreases mnusus
viscosity
7. Avoids further
multiplication of
microorganisms.
8. Helps enhance
passage of air to the
airway
respiratory rate of
19 cycles per
minute.
relaxed and lighten
face
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Respiratory Therapy: 66 Test Questions Student Respiratory Therapists Get Wrong Every Time: (Volume 1 of 2): Now You Don't Have Too!: Respiratory Therapy Board Exam Preparation, #1Von EverandRespiratory Therapy: 66 Test Questions Student Respiratory Therapists Get Wrong Every Time: (Volume 1 of 2): Now You Don't Have Too!: Respiratory Therapy Board Exam Preparation, #1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7 NCPDokument7 Seiten7 NCPVina EmpialesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viii NCPDokument6 SeitenViii NCPAdrian MangahasNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP PTBDokument6 SeitenNCP PTBJay Dela VegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP CopdDokument6 SeitenNCP Copdjoelette100% (1)
- Breathing Pattern Issues, Dyspnea, Tachypnea, O2 TherapyDokument2 SeitenBreathing Pattern Issues, Dyspnea, Tachypnea, O2 TherapySatra SabbuhNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument11 SeitenNCPRyan Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Interaction Immediate Cause Goal: Effectivenes SDokument6 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Interaction Immediate Cause Goal: Effectivenes SCatherine Kaye Marquez RoxasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan FinalDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan FinalSheana TmplNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaDokument2 SeitenImpaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaAngel Cabatingan100% (4)
- Pleural Effusion NCPsDokument7 SeitenPleural Effusion NCPsJaja Nagallo100% (2)
- Chest PhysiotherapyDokument79 SeitenChest PhysiotherapyRabab Ahmed100% (2)
- Improve Activity Tolerance Through Rest and RelaxationDokument7 SeitenImprove Activity Tolerance Through Rest and RelaxationKrisJane Ratilla Abiva100% (2)
- Group5 NCPDokument24 SeitenGroup5 NCPAkira AtomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For PneumoniaDokument3 SeitenNCP For PneumoniaKahMallari100% (10)
- 2 NCPDokument2 Seiten2 NCPJohn CenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDokument3 SeitenIneffective Breathing PatternTrixie Anne Gamotin100% (3)
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPEugine Elizabeth Pilarca PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Dokument6 SeitenWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decrease Cardiac Output Related To Altered Stroke VolumeDokument3 SeitenDecrease Cardiac Output Related To Altered Stroke VolumeRalph PelegrinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanDokument2 SeitenIneffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanJose Mari F. Esguerra0% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDokument10 SeitenNursing Care PlanElijah S GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measure Respiratory SystemDokument48 SeitenMeasure Respiratory SystemNoor Ahmed100% (1)
- Lecure-10 Measurements of The Respiratory SystemDokument48 SeitenLecure-10 Measurements of The Respiratory SystemNoor AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument10 SeitenNursing Care PlanmariasomorayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing DiagnosisDokument16 SeitenNursing DiagnosisSi Bunga JonquilleNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPMarius Clifford BilledoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Ineffective Breathing Pattern TalaDokument1 SeiteNCP Ineffective Breathing Pattern TalaJhen Bitco Fidel70% (10)
- Nursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingIvan Louise Fajardo ManiquizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care for Bronchial Asthma PatientDokument7 SeitenNursing Care for Bronchial Asthma PatientMardhiah WaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP - NCPDokument15 SeitenCP - NCPjezreel terreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asthma Nanda Diagnoses Goals InterventionsDokument4 SeitenAsthma Nanda Diagnoses Goals InterventionsZinya RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP JulieDokument14 SeitenNCP JulieJulie Mae RubioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Ventilator CareDokument9 SeitenMechanical Ventilator CareAnusha Verghese100% (2)
- Mechanical Ventilation Modes and Settings ExplainedDokument84 SeitenMechanical Ventilation Modes and Settings Explainedأبوأحمد الحكيم100% (1)
- Oxygen Therapy - Facemask, Nasal ProngDokument47 SeitenOxygen Therapy - Facemask, Nasal ProngLimYiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care of Pt.Dokument6 SeitenCare of Pt.hobradorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Ventilation Indications and TypesDokument55 SeitenMechanical Ventilation Indications and TypesElaine IsalosNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Micu Hascvd Cad - RioDokument5 SeitenNCP Micu Hascvd Cad - RioRio BonifacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument5 SeitenNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmm Estipona HaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDokument8 Seiten1 Ineffective Breathing PatternNoel MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Copd NCPDokument16 SeitenCopd NCPSuperMaye100% (1)
- Section IIDokument32 SeitenSection IImm3370350Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bautista - 3 Way Bottle SystemDokument4 SeitenBautista - 3 Way Bottle SystemKatherine BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssessmentDokument2 SeitenAssessmentEjoy Rayos AdawagNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument8 SeitenNCPFaustino LicudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Ventilation Knowledge-Feedback: Case1 QuestionsDokument19 SeitenMechanical Ventilation Knowledge-Feedback: Case1 QuestionsArtem 521Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nelec2 Week 10Dokument8 SeitenNelec2 Week 10Michelle MallareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation GuideDokument61 SeitenPulmonary Rehabilitation GuideNur akilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cap NCPDokument6 SeitenCap NCPMarlo Parayno100% (2)
- BronchoPulmonary Hygiene TechniquesDokument88 SeitenBronchoPulmonary Hygiene Techniques私 シャーロットNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument10 SeitenIneffective Airway ClearanceHannah VueltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech. Ventilation in New BornsDokument124 SeitenMech. Ventilation in New BornsRduuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Mechanical Ventilation (SIPHW)Dokument68 SeitenBasics of Mechanical Ventilation (SIPHW)Sudip beraNoch keine Bewertungen
- TÉCNICAS DEL AUXILIAR DE ENFERMERÍA EN EL ÁREA DE QUIRÓFANOVon EverandTÉCNICAS DEL AUXILIAR DE ENFERMERÍA EN EL ÁREA DE QUIRÓFANONoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Therapy: 66 Test Questions Student Respiratory Therapists Get Wrong Every Time: (Volume 2 of 2): Now You Don't Have Too!: Respiratory Therapy Board Exam Preparation, #2Von EverandRespiratory Therapy: 66 Test Questions Student Respiratory Therapists Get Wrong Every Time: (Volume 2 of 2): Now You Don't Have Too!: Respiratory Therapy Board Exam Preparation, #2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Monitoring Mechanical Ventilation Using Ventilator WaveformsVon EverandMonitoring Mechanical Ventilation Using Ventilator WaveformsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review On Normal ObstetricsDokument39 SeitenReview On Normal ObstetricsChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11effect of Visual Health Advisors On TheDokument14 Seiten11effect of Visual Health Advisors On TheChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- COPARchuckyDokument2 SeitenCOPARchuckyChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypertensionDokument14 SeitenHypertensionChucky Vergara100% (2)
- Case Presentation in MsDokument19 SeitenCase Presentation in MsChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- INTRODUCTIONDokument4 SeitenINTRODUCTIONChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Burn Pain ManagementDokument1 SeiteChemical Burn Pain ManagementChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- INTRODUCTIONDokument4 SeitenINTRODUCTIONChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complaint Letter To Our Beloved President Rodrigo Roa Duterte On Squatting and Urban Development Annex ADokument2 SeitenComplaint Letter To Our Beloved President Rodrigo Roa Duterte On Squatting and Urban Development Annex AChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 stages of human sexual responseDokument3 Seiten4 stages of human sexual responseChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing and Planning Nursing Interventions for Stroke PatientDokument1 SeiteAssessing and Planning Nursing Interventions for Stroke PatientChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- INTRODUCTIONDokument4 SeitenINTRODUCTIONChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CKD Chf. DM2Dokument24 SeitenCKD Chf. DM2Chucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review On Normal ObstetricsDokument39 SeitenReview On Normal ObstetricsChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gordons 11 Functional Patterns..QuestionsDokument1 SeiteGordons 11 Functional Patterns..Questionsmiss RN81% (32)
- C H N 2:levels of Clientele in CHN: IndividualDokument5 SeitenC H N 2:levels of Clientele in CHN: IndividualFlorence NightingaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutritional Management of StrokeDokument25 SeitenNutritional Management of StrokeChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of CancerDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of CancerChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- GordonsDokument4 SeitenGordonsChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Performance IndicatorDokument2 SeitenKey Performance IndicatorChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SuctioningDokument1 SeiteSuctioningChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Total Joint Replacement Patient GuideDokument33 SeitenTotal Joint Replacement Patient GuideChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caritas Fund Provider 2ndDokument1 SeiteCaritas Fund Provider 2ndChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revised Human Life Is Sacred Because We Are All Created in The Image and Likeness of GodDokument3 SeitenRevised Human Life Is Sacred Because We Are All Created in The Image and Likeness of GodChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verified AnswerDokument5 SeitenVerified AnswerChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- LoysDokument3 SeitenLoysChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Insert Date) : Request For Permission To Conduct Research in SchoolsDokument1 Seite(Insert Date) : Request For Permission To Conduct Research in SchoolsChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sen. Trillanes Vs BOC Comm FaeldonDokument2 SeitenSen. Trillanes Vs BOC Comm FaeldonChucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippinehistoryitsrootsanddevelopment 110709034735 Phpapp02Dokument47 SeitenPhilippinehistoryitsrootsanddevelopment 110709034735 Phpapp02Chucky VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jonsen SieglerDokument2 SeitenJonsen SieglerBramantyo NugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- D H ADokument250 SeitenD H AKath Cuevas0% (1)
- 21 Test BankDokument17 Seiten21 Test BankNaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osce 2023Dokument695 SeitenOsce 2023Debashish BiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dialysis BrochureDokument13 SeitenDialysis BrochureRaffy FlorentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decongestants & Anti-Histamine Jul 2009Dokument63 SeitenDecongestants & Anti-Histamine Jul 2009Anonymous JLfSQ29FZPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ent Secretory Otitis MediaDokument3 SeitenEnt Secretory Otitis MediaIrena DayehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippines Airlines Vs NLRCDokument3 SeitenPhilippines Airlines Vs NLRCHoreb FelixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saudi Internship GuideDokument47 SeitenSaudi Internship GuideRizky KykyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.Dokument1 SeiteNCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.dominoredwing2024100% (1)
- Reaction PaperDokument4 SeitenReaction PaperJam Knows RightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jwara Visheshank July 2011Dokument8 SeitenJwara Visheshank July 2011Ravi Sharma100% (1)
- DPH COVID Positive Result LetterDokument3 SeitenDPH COVID Positive Result LetterJoe Aronson100% (1)
- 2022 VijayDutta CVDokument8 Seiten2022 VijayDutta CVKartik DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study CaseDokument3 SeitenDrug Study CaseKatrina Ponce100% (1)
- Diabetes Foot Screen: - Can't Feel The 5.07 FilamentDokument4 SeitenDiabetes Foot Screen: - Can't Feel The 5.07 FilamentSteve ChipmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LECTURE 4 Introduction To MicrobiologyDokument36 SeitenLECTURE 4 Introduction To MicrobiologyArcee Feb Dela PazNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEP Practice QuestionsDokument8 SeitenPEP Practice QuestionsCynthia ObiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Study On Anemia of Chronic DiseaseDokument44 SeitenA Case Study On Anemia of Chronic DiseaseKeThSantiban100% (3)
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionsDokument20 SeitenUpper Respiratory Tract Infectionsshamma shahulhameedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ashun Davis Roughdraft ResumeDokument3 SeitenAshun Davis Roughdraft Resumeapi-360486400Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carotid Sinus Massage Procedure DetailsDokument3 SeitenCarotid Sinus Massage Procedure DetailsSandeep m rNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cdi Reviewer MidtermDokument8 SeitenCdi Reviewer MidtermKIMBERLY MARGARETTE REDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific evidence for clinical use of horsetailDokument23 SeitenScientific evidence for clinical use of horsetailDanilo Maciel Carneiro100% (1)
- RCT Appraisal Sheets 2005 EnglishDokument4 SeitenRCT Appraisal Sheets 2005 EnglishAmanda SoebadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Responding To The Epidemic: Strengthening Youth Sector InvolvementDokument26 SeitenResponding To The Epidemic: Strengthening Youth Sector InvolvementBeverly DatuNoch keine Bewertungen
- NU 120 Skin Integrity - Care - PlanDokument4 SeitenNU 120 Skin Integrity - Care - Planmrsfelic08100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan (Post Op Exlap)Dokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan (Post Op Exlap)Kay D. BeredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency Medicine Guide to Shock and GI BleedingDokument90 SeitenEmergency Medicine Guide to Shock and GI BleedingAstri GunardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFPC 99 Topics Starter Study DocumentDokument372 SeitenCFPC 99 Topics Starter Study DocumentaayceeNoch keine Bewertungen